organisation of the organism
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
what cell is this
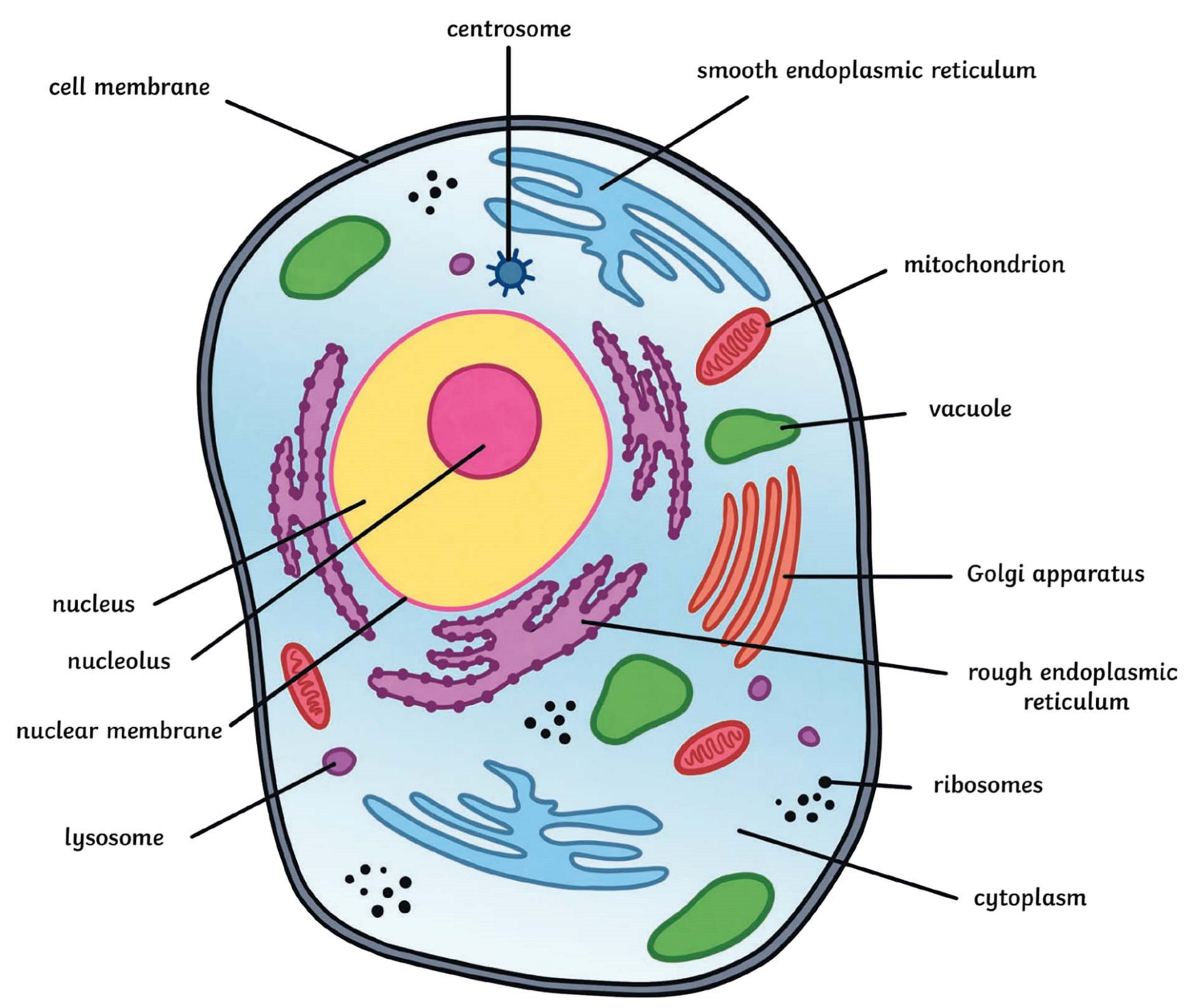
animal cell
what is the animal cell membrane made of
thin layer of protein and fat
features of an animal cell membrane
partially permeable, around the outside, separates inside from outside
what does partially permeable
only substances small enough can pass through
what is the cell membrane
a layer around the cell that controls what goes in and out the cell
what is the cytoplasm
clear jelly substance where metabolic reactions take place
What substances are dissolved in the cytoplasm
salts, amino acids, sugars, protein, fatty acids
what is the nucleus
where genetic information is store in
what is genetic information in the nucleus
chromosomes, made of DNA
what is a ribosome
place where protein synthesis takes place
what is protein synthesis
the making of proteins
where is the ribosomes
in the cytoplasm w
where is the nucleus
in the cytoplasm
are vesicles found in animal cells or plant cells
animal cells
what is a vesicle
organelle that transports recycled waste that the organism needs for survival
what is the rough endoplasmic reticulum
organelle that holds ribosomes on it to transport proteins
what does the endoplasmic reticulum do
stores lipids
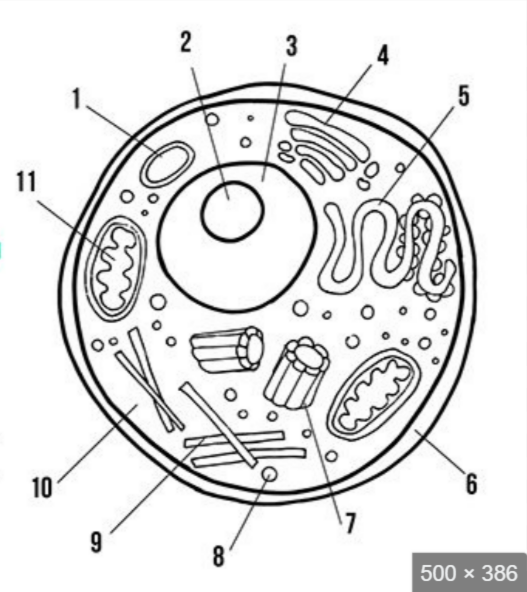
what is label 3
nucleus
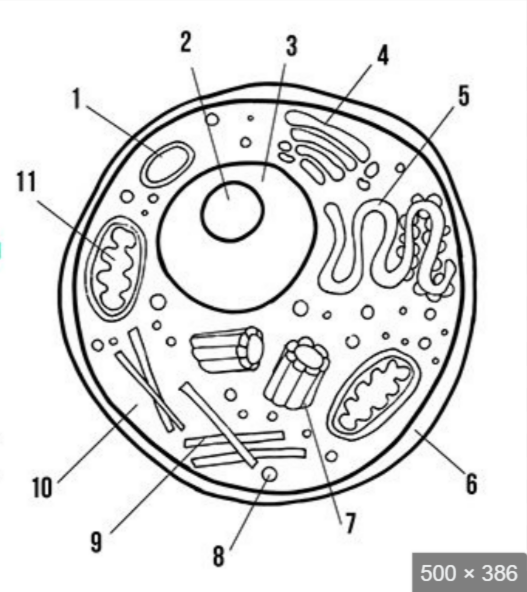
what is label 5
endoplasmic reticulum
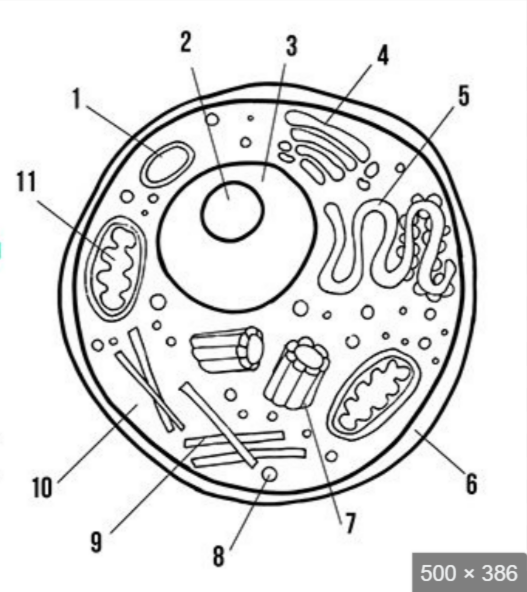
what is label 6
cell membrane
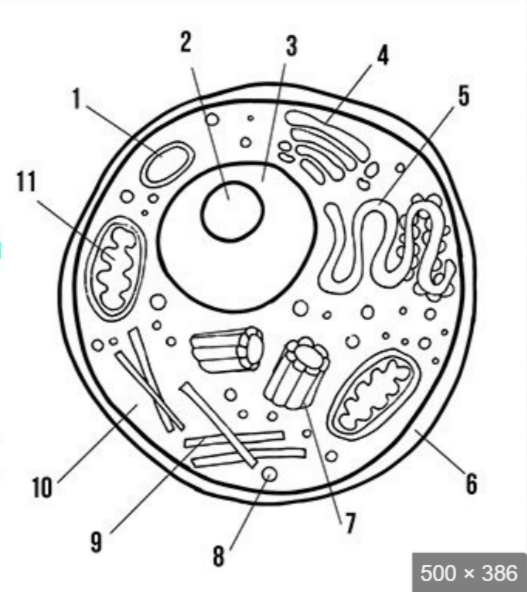
what is label 8
ribosomes
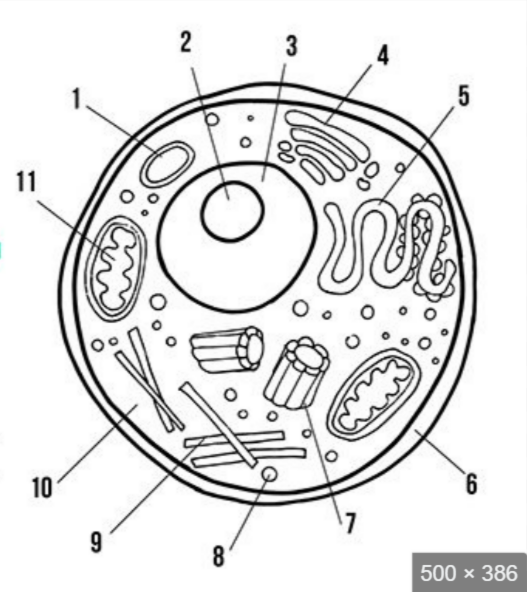
what is label 10
cytoplasm
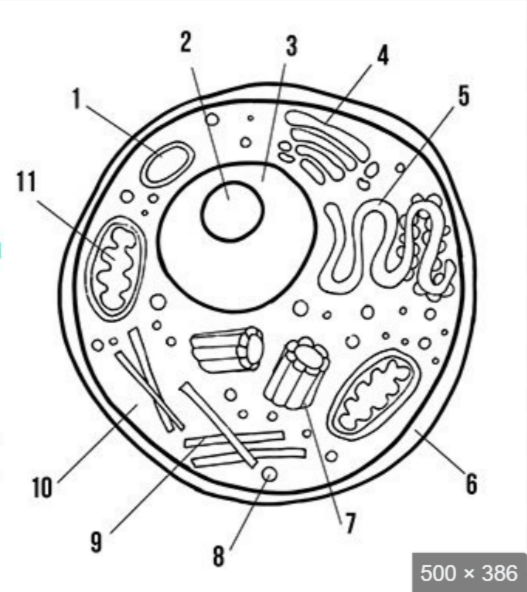
what is label 11
mitochondria
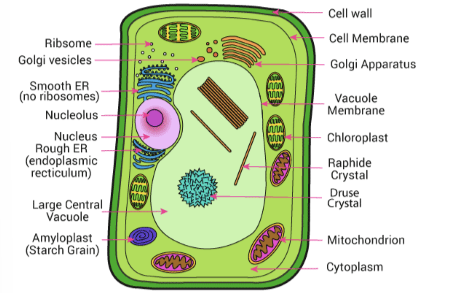
what cell is this
plant cell
what are two things a plant cell has that an animal cell does not have
cell wall, vacuole
what is the cell wall made of
cellulose
purpose of the cell wall
keep cell shape, stop cell from bursting, protects cell
what does fully permeable mean
all substances can get in
vacuole features
fluid-filled, large
what fluid is the vacuole full of
cell sap
what is cell sap made of
solution of mainly sugar and other substances w
what does the vacuole do
press outward on cell wall to keep the shape of the cell
what does the mitochondria do
aerobic respiration
what does a chloroplast do
absorbs energy from the sun and does photosynthesis
what gives a plant its green colour
chlorophyll
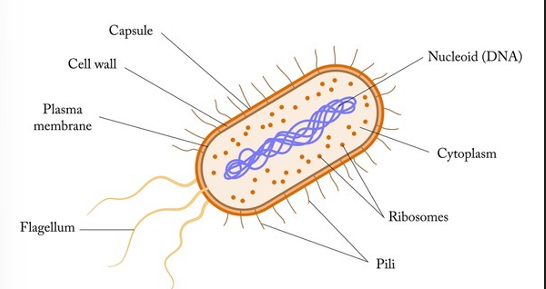
what cell is this
bacteria cell
what is the cell wall of bacteria made of
peptidoglycan
purpose of a cell wall in a bacteria cell
supports cell and stop it from bursting
what are two features an animal and plant cell have that the bacteria cell does not have
mitochondria, nucleus
what does prokaryote mean
before nucleus w
hat does eukaryote mean
after nucleus
what is the circular DNA in a bacteria cell
provides instructions for making proteins
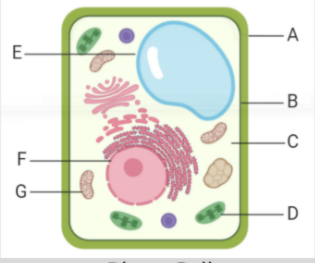
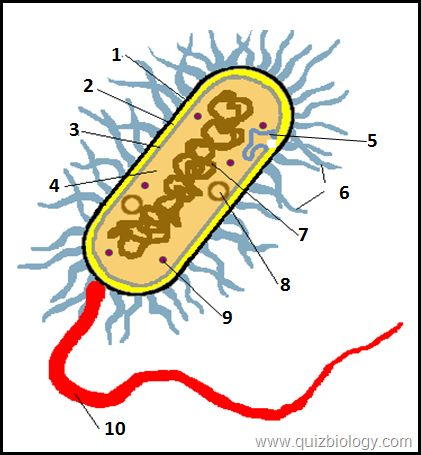
what is label A
cell wall w
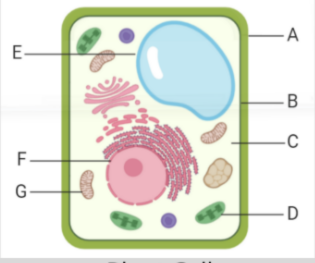
what is label B
cell membrane
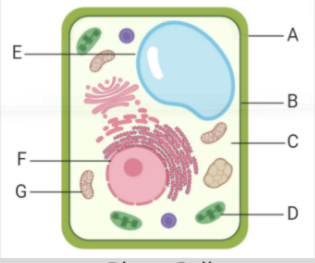
what is label D
mitochondria
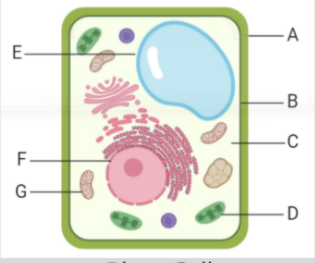
what is label 6
cytoplasm
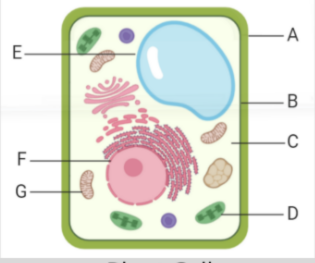
what is label E
vacuole
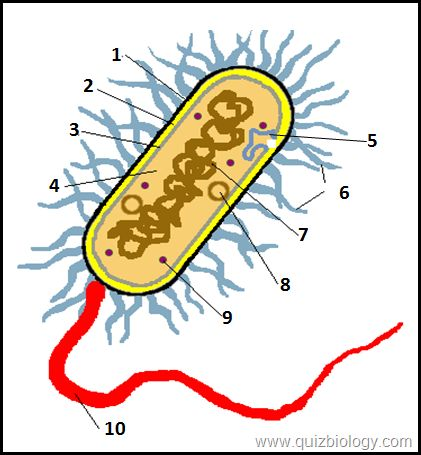
what is label 2
cell wall
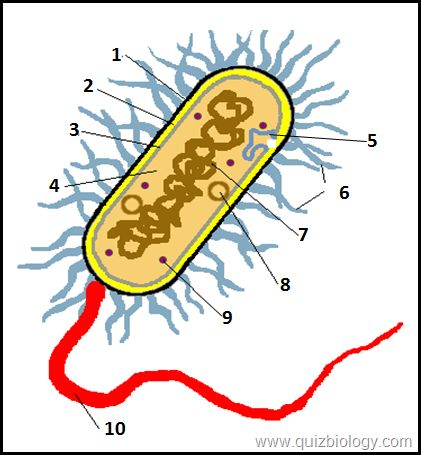
what is label 3
cell membrane
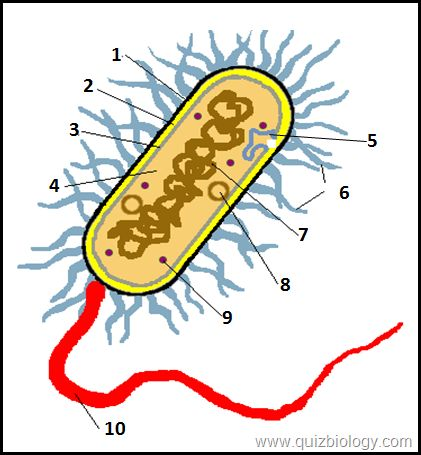
what is label 4
cytoplasm
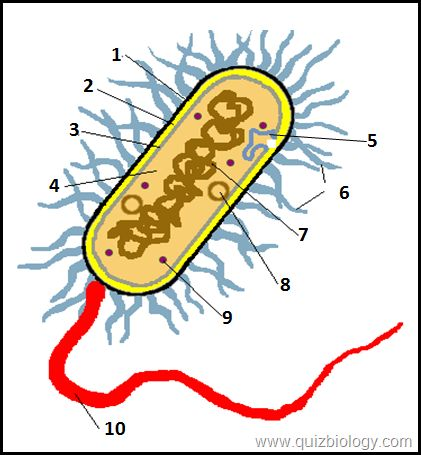
what is label 6
pili
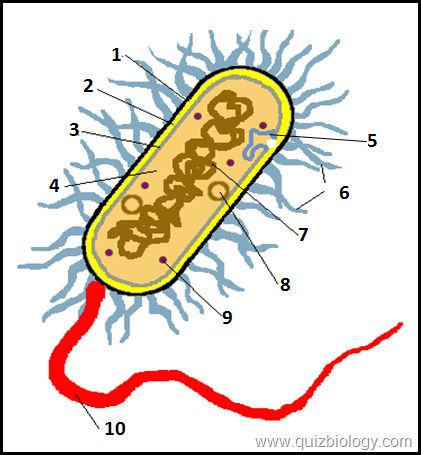
what is label 7
plasmid
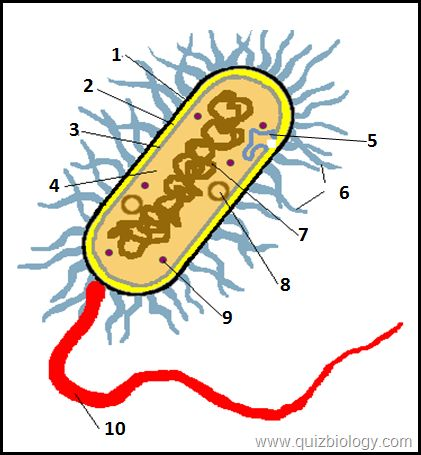
what is label 8
circular DNA
what is label 9
ribosomes
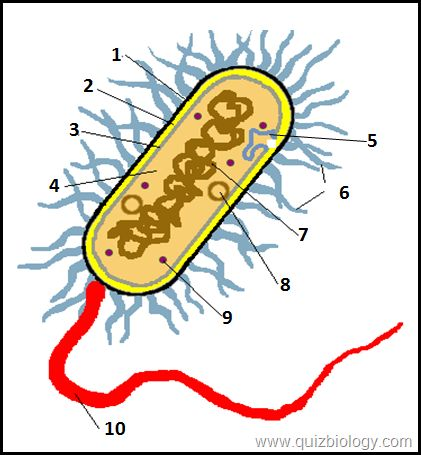
what is label 10
flagellum
what is a specialised cell
cell that performs function from the rest of the cells
where are ciliated cells found
lining the trachea and bronchi
where are neurone cells found
nervous system
where are red blood cells found
blood of animals
where are sperm cells found
testes of mammals
where are egg cells found
ovaries of mammal
where are root hair cells found
tips of the roots of flower plants
where are palisade mesophyll cells found
leaves of flowering plants
what is the function of ciliated cells
move mucus upwards
functions of neurone cells
conduct electrical impulses
function of red blood cells
transport oxygen
function of sperm cell
male gamete for sexual reproduction
function of egg cell
female gamete in reproduction
function of root hair cell
absorption of water and mineral ions
function of palisade mesophyll cells
photosynthesis
what is tissue
cells that do a similar task that are found together w
what is an organ
group of different tissue
what is the organ system
Several organs working together to perform a particular function
what is a microscope
glass lens or device that magnifies anything microscopic w
why do we use electric microscopes
see anything smaller than a normal microscope can’t show
how to calculate magnification
image size = actual size x magnification