Scott's final study tip review + formula portion (5/55)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
CO
CO = HR * SV
normal 4-8L/min
SV normal and units
normal = 60-130mL/beat
HR
HR = QT/SV
CaO2, CvO2, C(a-v)O2 normal values
CaO2 = 20vol%
CvO2 = 15vol%
A-v = 3.5-5.0%
CcO2
(Hb x 1.34) + (PAO2 × 0.003)
YES its the Pb equation one.
PAO2
(Pb - 47)FiO2 - (PCO2 / R)
MAP normal + units
80-100mmHg, <60mmHg affects organs
MPA normal + units
10-20mmHg
SVR normal + units
900 - 1400dyne-sec/cm5
PVR normal + units
110 - 250dyne-sec/cm5
Qs/Qt normal value
2-5%
CI normal + units
2.5-4.0L/min/m²
P/F. what value = ARDS?
PaO2 / FiO2
>400 (lower is ARDS)
What does the dicrotic notch on an arterial or pulmonary artery waveform represent?
During systemic arterial pressure, it represents aortic valve closure.
Preload vs after load
The filling pressure of the ventricle at the end of ventricular diastole, with venous return being the most determining factor.
afterload = stretch!
what is SVR based off of?
LV after load (direct relationship, increased = increased), because the LV pumps into systemic circulation
Transducer
Main part of invasive hemodynamic monitoring system by converting fluid pressure to an electrical signal.
CVP
Estimates RV preload.
Pressures in the heart/vasculature system
RA: 0-8mmHg
RVP/CVP = 20-30 / 0-8
PAP = 20-30 / 8-15
PAWP = 8-12
Why is there a balloon on the end of a pulmonary artery catheter?
To float and wedge into the PA to create a closed system where pressure can be measured from the PA to the LA.
What are the different ports in a PA catheter used for?
Proximal (white/blue): @RA to measure CVP and CO. Can also inject drugs and get blood samples.
Distal (yellow): @PA to measure PAP, PCWP, and get SvO2 sample
Balloon inflation (red): near tip @PA, left deflated unless obtaining wedge.
During insp phase of spontaneous breathing
PA waveform decreases
Affected by right side of heart?
CVP, RVP, PAP
Central and pulmonary issues.
CVP assesses
circulation and venous return
RV fxn
What parameter is best used to assess left ventricular afterload?
SVR
What measured pressure filling pressure of the RH? of LH?
CVP, PCWP
Be able to identify the various waveforms associated with the insertion of a PA catheter.
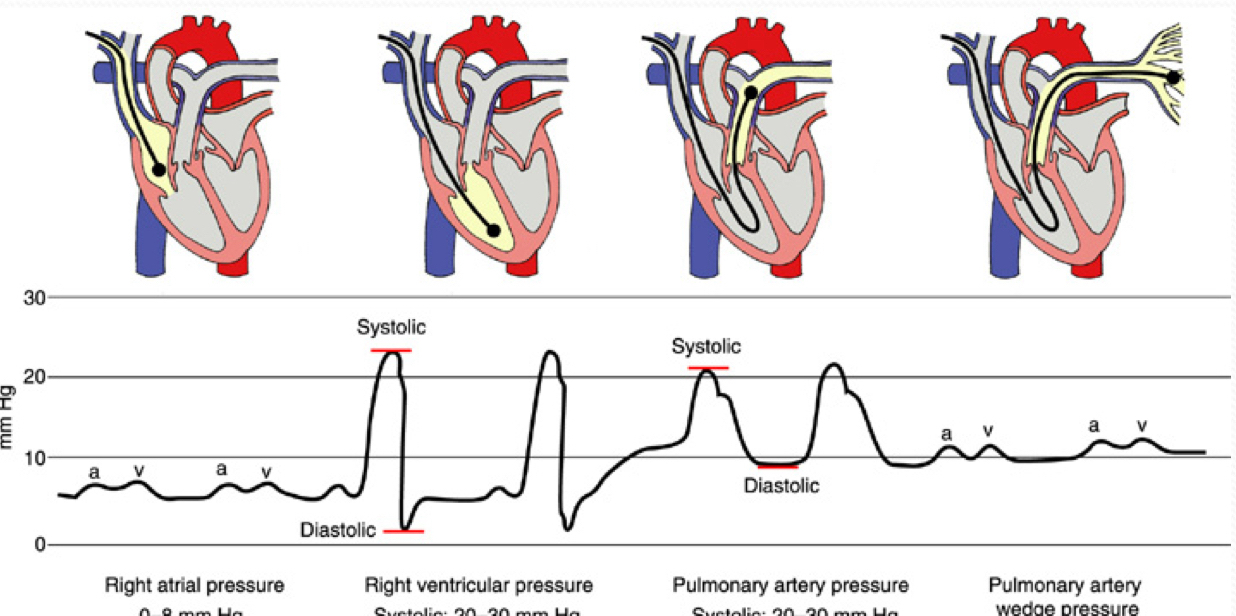
What happens if a transducer is above or below the phlebostatic axis?
Above = higher pressure as column of fluid is longer, inversely true.
What to shock? Cardiovert?
Pulseless V’s! Vtach and Vfib
CV the rest.
Epi and amiodarone in ACLS
1mg every 3-5min throughout ENTIRE code
1st dose = 300mg, 2nd = 150mg.
Lidocaine and magnesium sulfate
Lidocaine used if amiodarone is unavailable (max dose 3mg/Kg, give 1-1.5mg/Kg then repeat 0.75 until max)
Used in Torsades de Pointes or hypomagnesemia, 1-2g w/ 10mL sugar water slowly.
Drugs to give w/o IV
Lidocaine
Atropine
Narcan
Epinephrine
DOUBLE DOSES W/ 5-10 FLUSH.
SCREAM
Shock
CPR
Rhythm
Epi
Antiarrhythmic
Medications
What adjustments on PCV help increase patient’s Ve?
Increase PIP/PC settings
Decrease PEEP
Increase RR
In what scenario is pressure-controlled ventilation (PCV) most often used?
Limiting pplat
With which of the following modes would most frequently associated with "breath stacking" and patient dyssynchrony?
VC SIMV and PC SIMV
Compared to a pressure-controlled strategy, what is the primary advantage of volume-controlled ventilatory support?
Guarantees a stable Ve
Which of the following arteries should be palpated in pulseless adults and children older than 1 year of age?
carotid
What is the best way to increase CPR survival rates in the field?
CPR and early defibrillator
Briefly describe the 4 main categories of shock and give an example of each one.
Distributive (SANES)
hypovolemic (hem/nonhem)
cardiogenic (MI, arrhythmias, ❤ issues)
obstructive (vascular or mechanical)
Please describe the basic therapeutic approaches taken for the patient in shock.
O2 therapy (early intubation!)
PA catheter
Fluid
vasopressors (norepi, vasopressin)
antibiotics (if source of infection found)
Be able to describe the basics of ECMO.
Temporarily supports lungs and/or ❤ by circulating blood from pt outside the body, through a gas exchanger, then back to the pt in 2 different ways: VA or VV. SVR plays a huge role, as the longer/thinner the tubing, the more resistance there is to flow. Bigger hole = more flow
Blood is pulled OUT from (typically) the femoral VEIN, to an oxygenator (O2 in, CO2 out), then brought back to a cannulation port (neck, central or femoral (MC)) to then flow to the body. In shorter terms, it pulls O2 poor blood, mechanically does gas exchange, and then deposits rich/arterial blood back into the body to then circulate.
Two types of pumps
Centrifugal/vortex
Roller/occlusive
What is centrifugal pump based off of?
Preload (volume in R ❤ ), afterload (resistance against pump outlet from L ❤ ), and the set RPM (rate per minute).
Roller pump
Occludes part of circuit tubing, drained by gravity into a reservoir and pulled into a pump. So instead of moving it into a container that pumps, it stays in the pump tubing and little “things” push the tubing to push it forward with positive pressure.
Based off of diameter of tubing, roller occlusion and set RPM.
Oxygenator fxn. what does sweep flow do? RPM?
Contains hollow fibers for blood + gas to pass through called sweep flow. Sweep flow has no CO2, as the CO2 in the blood diffuses int the sweep fibers and is flushed out of the oxygenator. This is based off of a sweep flow setting, as the higher the setting the more CO2 removed. This then allows the desired amount of CO2 saturated blood to be sent back to the patient either through VA (artery) or VV (vein).
In other words, sweep flow is controlled to maintain desired CO2; RPM is set to adjust blood volume.
ACT
activated clotting time, being the MC test for anticoagulation at the bedside. Need to balance clotting factor + monitor it through a bedside Istat to increase or decrease heparin. KEY to maintain this while pt is on ECMO and during insertion.
VA ECMO support
Minimum of 2 circuits used (1 venous, 1 arterial) to give HEMODYNAMIC support (BOTH LUNGS AND HEART). Portion of venous volume is drained into gas exchanger and then puts back fully concentrated blood back into arterial circulation. This helps decrease preload and increase afterload
Indications: cariogenic shock and a bridge to ventricular assist device or heart transplant
Disadvantage: hole will remain open if not surgically closed.
Artery access points for VA
right carotid artery in newborn
L or R femoral artery (w/ reperfusion line to give supplemental BF to lower leg + decrease ischemia risk)
axillary artery
transthoracically into aorta
VV ECMO support
“replaces” LUNG’S JOB, as the blood is returned to VENOUS circulation, and letting the heart pump the blood to where it needs to go. Insert a cannula by cracking the chest and centrally putting it in.
Indications: bridge to lung transplant, lower risk of embolism and do not risk hurting an artery.
Be able to identify common cannulation sites for VV and VA ECMO.
VV (vein to vein) w/ dual-site cannulation: femoral vein and right internal jugular vein
VV (vein to vein) w/ single dual-lumen cannula: right internal jugular vein and sits in RA.
VA (vein to artery): femoral vein → artery, RA → ascending aorta.
Be able to describe the function of an intra-aortic balloon pump. Where is it inserted into? What happens during systole and diastole?
Stabilizes ❤ after MI. It’s inserted @ femoral artery → aortic arch just before L subclavian artery and ABOVE renal artery.
Systole: deflates to draw blood into aorta, decreasing LV workload, increased CO + flow to coronary arteries.
Diastole: inflated w/ He to cause + pressure towards ventricle allowing O2 rich blood to be pushed into the coronary arteries due to closed valve.
Describe how intra-aortic balloon pumps augment cardiac output and promote coronary blood flow
During inflation @ diastole, balloon inflates, increasing aortic pressure, pushing blood BACKWARDS into the coronary arteries which then goes to the capillaries of the myocardium.
During deflation @systole, balloon deflates creating a suction into the aorta which reduces afterload/LV workload and improving cardiac output. This allows blood to easily go from the LV → aorta → systemic arteries
General definition of VAD
Attached to one or both ventricles and the aorta to augment or replace its fxn to bridge to something. All VADs are preload-dependent, after load-sensitive, EKG-independent and anti coagulated.
Be able to compare and contrast pulsatile and non-pulsatile Ventricular Assist Devices.
Pulsatile ones resemble the heart (generate an artificial “pulse” to circulate blood, having a palpable pulse); whereas, nonpulasatile ones provide a laminar flow instead of pulses, not having strong palpable pulse, if any.
MAP is key to monitoring hemodynamics, with ideal range being 65-90mmHg.9
Suckdown from VADs?
LV collapses due to hypovolemia/tension or VAD overdrive due to nonpulsatile type. Treat by IV to increase preload and reduce speed.