OCR Business GCSE - Topic 1 Business Activity
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Business
An organisation which exists to sell goods or services to customers
Needs
Food, Water, Shelter, Clothes, Warmth
Wants
Goods and services, which we do not need, but are pleasant to have
The Economic problem
This results from unlimited wants, but limited resources to produce the goods and services to satisfy those wants. This creates scarcity
Scarcity
The lack of sufficient products to fulfill the wants of the population.
Factors of production
Land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship
Market
The aim of a market is to bring buyers and sellers together
Private sector
Businesses are owned by private companies or individuals. They run to make profit
Public sector
Organisations are owned by central government or regional authorities. They can be operated for the benefit of everyone, or for one particular group.
The Free Market System
This is also known as the capitalist system, or the Laissez-faire system. There is no interference from the government in the workings of the economy.
The Planned Economy
Where the governments controls everything in the market, like resources, prices and production.
The Mixed Economy
Where a market has some elements of the planned economy as well as the free market system. The government operates the public sector, mostly in defence and education, whilst the private sector isn't, but is restricted with laws.
Primary sector
Businesses that are involved in extracting raw materials
Secondary Sector
Businesses that are involved in manufacturing or constructing
Tertiary sector
Businesses that are involved in commercial services and activities that enables goods to get to the final customer or provide a direct service
Deindustrialisation and Industrialisation
The economy is getting to be more based in the tertiary sector in developed nations, while in less developed countries the economy is mainly primary and increasingly secondary sector
Reasons for primary sector decline in the UK
Raw materials used up
Greater demand for imports
Reasons for secondary sector decline in the UK
Manufacturing in the UK is too expensive
Machinery is replacing workers
Reasons for increase in tertiary sector in the UK
Increases in disposable (extra) income means more consumers spending on services and goods
Population increase increases demand for healthcare and education
Tertiary businesses sell abroad as well as the UK
Less scope for machinery as tertiary secotr worker can't be replaced by them.
Reasons for growth and decline in business activity
Consumer wants and needs changes (trends)
Number of people employed
Value of the goods and services provided
Technological development
The chain of production
The process of turning a raw material into a sellable product
Entrepreneur
someone who spots a business opportunity, takes advantage of it and takes the risk of running a business
Potential Rewards for risk taking
Financial gain
Independance
Self Satisfaction
Changing consumer habits : ethical brands e.g. increasing sustainability
Potential drawbacks for risk taking
Financial loss
Health : Insomnia, Headaches, Mental health, Fatigue
Grants
The government giving money to to help the development of enterprise/risk taking which does not have to be payed back
Reasons for why some businesses could fail
Poor management
Poor planning
No demand for good or service
Poor location
Poor cash flow
High costs
Too much competition
Poor quality of good or service
Insufficient profit
External factors e.g. unfavorable exchange rates
Business plan
A plan that sets out in detail what a business is going to do in a given time
Business plan: The business
Name and address
Idea
Business objective
Business plan: Management
Ownership (business type)
Firm's management structure
Experience of owners and managers
Business plan: Market
What market research has been done
Customers : location
The competition: how strong are they, where are they
How is product different from competition
Potential for growth and how it can be achieved
Business plan: Marketing
Analasys on on the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
How is the product going to be sold
Marketing mix (advertisement)
Cost of each part of marketing
Business plan: Resources
Size and kind of resources needed
Number of employees needed and the skills they need
Growth plans and resources needed in the future
Business plan: Financial plan
Startup and running costs
Sources of revenue
Amount of capital and who owns
Detail of existing loans and how they are going to be payed
Estimate of future revenues and cost
Business plan: Prospects
Firm's prospects over 3 to 5 years based on facts and evidence
Sole trader advantages
You own everything and control everything
Small capital needed to start
Finances private
Quick decisions
Sole trader disadvantages
Unlimited liability
Sole trader dies, business evaporates
Skill shortage
Always have to work - can't take days off
Partnership advantages
More capital
Shared costs
Shared workload
Wider range of skills
More ideas
Partnership disadvantages
Unlimited liability
Shared profits
Shared decision making - disagreements
Franchise organization
A contractual association between a franchisor and franchisees.Franchisees buy the right from the franchisor to trade under the business name
unlimited liability
The owner is personally and fully responsible for all losses and debts of the business
limited liability
A form of business ownership in which the owners are liable only up to the amount of their individual investments.
Uses of business plan
Investors can check it to have more confidence in their investment
Helps reduce risk
Banks insist on a business plan before lending
Shows realisticness of a business idea and its prospects
Private limited company
a company in which shareholders must be invited.
Owned by shareholders, managed and controlled by directors and employees
Limited liability
Public limited company
Shares are open to the general public, limited liability, AGM meetings, managed by board of directors
Public limited company advantages
Limited liability
Shareholders have little influence
banks more likely to lend more money
receive economies of scale
shareholders can trade easily
Public limited company disadvantages
vulnerable to takeovers
high setup costs
difficult to manage
less privacy
financial records public
Private limited company advantages
Limited liability
Cheap setup
Can raise capital more easily
control over share price
separate legal identity to owners
can sue and be sued in its own right
Private limited company disadvantages
difficult for investors to get back - would expect dividends
less privacy
potential shareholders may not want to buy shares
admin costs
Survival
(Business Objective)
ensuring the business's long term future in a market
profit maximisation
making the largest number of profits possible over a period of time to be distributed amongst some of the business's shareholders via a dividend
growth (business strategy)
increasing the business size e.g. new products or new places
providing a service
ensuring high levels of customer satisfaction (even if less profit is made)
market share
increasing the percentage of industry controlled by the business
Profit satisficing
Managers/Directors ensure a minimum profit level to please shareholders.
competitive (business aim)
maintaining a position in the market similar to rival businesses
start-up business aims and objectives
survival
efficient
reducing the average costs of production
customer loyalty
achieving a satisfied and larger consumer base
increase share price
achieving higher returns for shareholders
Return on Capital
ensuring a profit of finance invested into the business
employment
maintaining and improving staff working for the business
social/community
Improving links and funding initiatives with the local area
environmental protection
reducing the impact of the business on the natural world
ethical
ensuring the business operates in a fair way
not for profit
achieving a return for stakeholders other than shareholders(normally the aim of a charity)
established business aims and objectives
growth + profit maximisation
public sector business aims and objectives
providing a service
characteristics of aims and objectives
Specific, Measurable, Attainable/Achievable,Realistic, Time-related
A mission statement should be
-Neither too narrow nor too broad
-Fitting the market environment
-Based on distinctive competencies
-Motivating
Mission Statement
a statement of the organization's purpose - what it wants to accomplish in the larger environment
Aim of a business
The strategic goals of a business for the future; It's a statement of purpose e.g. we want to grow the business.
business objective
a target that must be achieved in order to realise the stated aim
Stakeholders
everyone within and outside an organisation that have an interest in the way that the organisation operates
Internal Stakeholders
employees, owners, board of directors, managers
External Stakeholders
bank, local commnunity, national government
Reasons for business growth
innovation, increase market share, spread risk, eliminate rivals, protection from competition
Constraints on business growth
-Diseconomies of scale
-barriers to entry
-regulation
-access to finance
-owner objectives
-occupational constraint
Organic growth
A business growth strategy that involves a business growing gradually using its own resources, such as gaining new customers, investing in factors of production, increasing market share and finding new products/markets
External growth
Business expansion achieved by means of merging with or taking over another business, from either the same or a different industry
Merging of Businesses
Merger - a combination of 2 or more businesses to make 1 larger business.(A + B = AB)
takeover
an act of taking control of a company by buying most of its shares(A + B = A/C)
Reasons why some businesses would like to remain small
niche market, market saturation, availability of finance/capital, less risk
economies of scale
factors that cause a producer's average cost per unit to fall as output rises
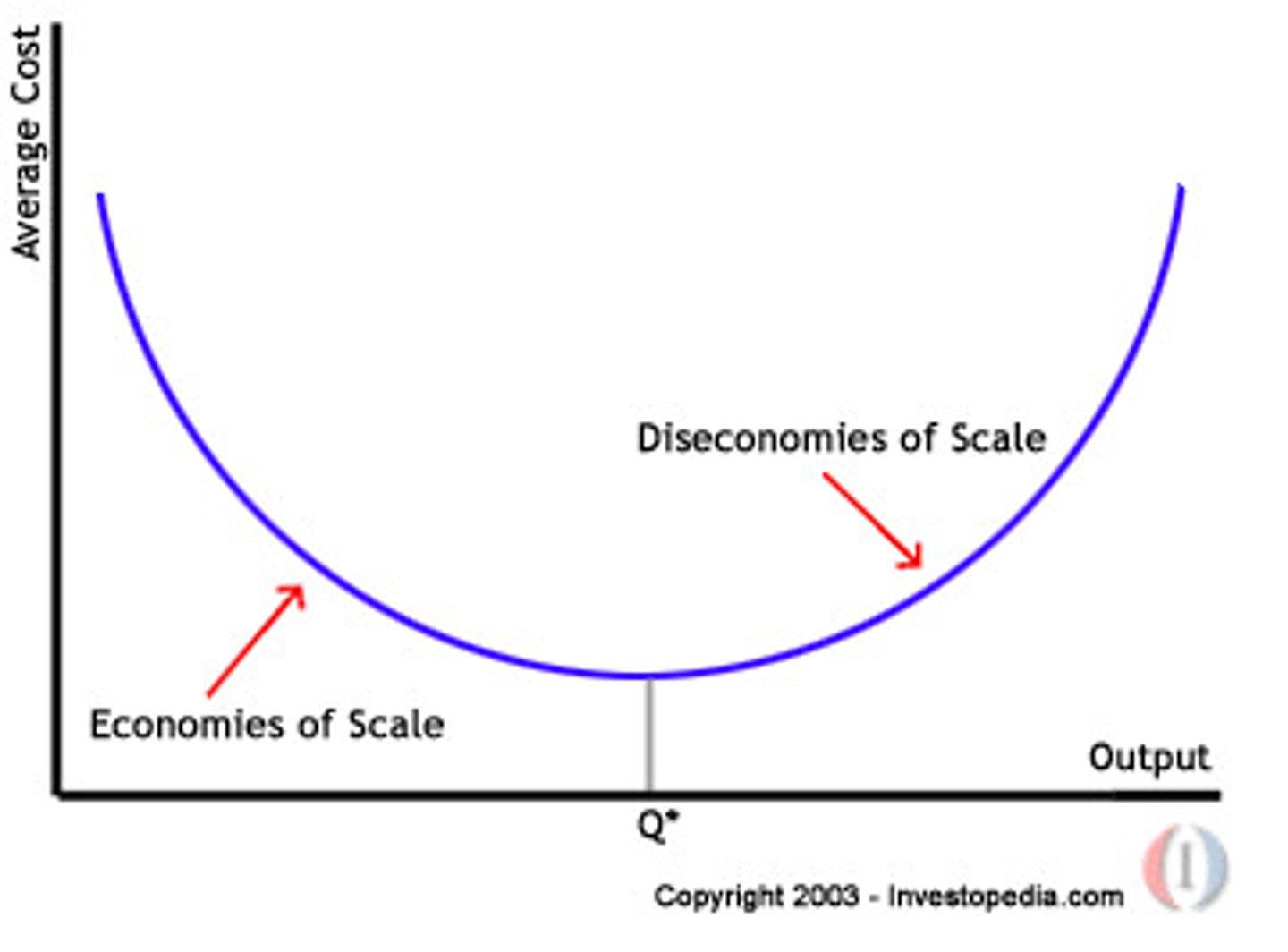
diseconomies of scale
increases in cost per unit when output increases
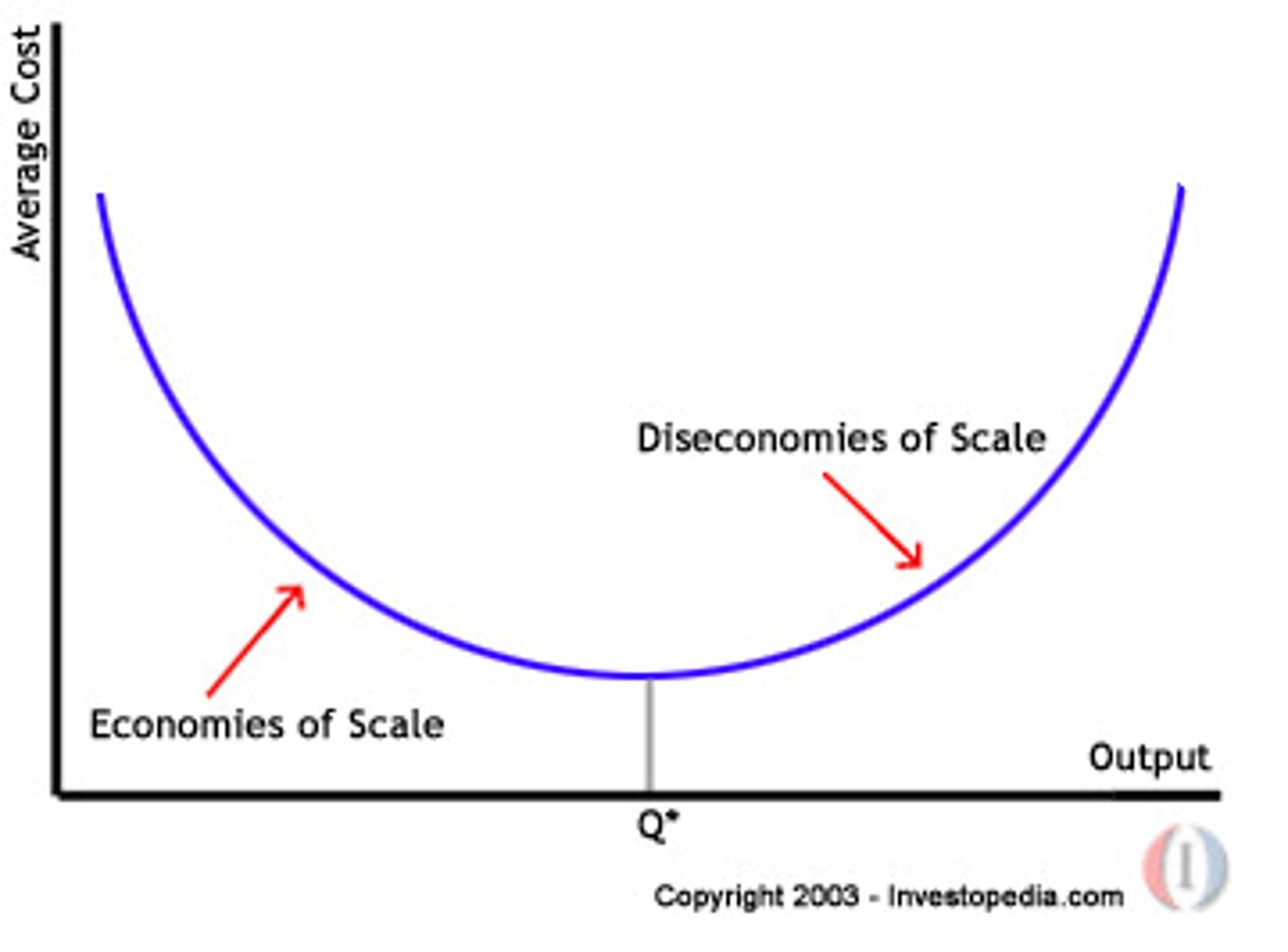
Internal economies of scale
- Technical economies - bigger and newer machines and equipment can be used
- Financial economies - large firms find is easier/less expensive to raise capital and borrow money
- Managerial economies large firms can use managers mreo effectively and can employ specialists
- Purchasing economies large firms can buy their supplies in bulk/large quanitities at a cheaper price
External economies of scale
The cost reductions available to all businesses as the industry grows
labour economies - firms will be able to draw on specialised workers trained by local gov.
infrastructure - localised industries create suitable transport networks etc.
specialist suppliers created e.g. ancillary industries - specialised companies set up to supply the industry
examples of diseconomies of scale
managerial diseconomies - too many layers of management are created
loss of flexibility - large firms unable to change production quickly
communication problems - chains of command longer than short firms
worker demotivation - workers may feel remote and alienated from the firm
types of integration
vertical - businesses at different stages of production e.g. forestry, furniture maker, furniture shop
horizontal - similar businesses at the same level of production e.g. baker + baker
lateral
conglomerate
Vertical Integration
businesses at different stages of production e.g. forestry furniture maker, furniture shop
forward vertical integration is integrating with the next stage of production, whilst backward vertical integration is integrating with the previous stage of production
Horizontal Integration
similar businesses involved in the same level of production and sharing resources at that level
Lateral integration
the merging of two firms that produce similar goods but are not in competition with each other e.g a brushmaker and a combmaker
Conglomerate integration
Merger with or takeover of a business in a different industry
Advantages of horizontal integration
allows economies of large scale production to be achieved
Disadvantages of horizontal integration
reduced choice, may lead to a monopoly
Advantages of conglomerate integration
- Can spread risk, as if one market fails, the losses can be compensated for by profits in another
- Can overcome seasonal fluctuations in their markets and have more consistent year-round sales (e.g. if a mince pie company took over a company that made chocolate bars)
- The business is larger and therefore more financially secure
- The buyer acquires the other company's assets and resources
- The business gains the customers and sales of the acquired business
disadvantages of conglomerate integration
no understanding of the new business activity, which may lead to diseconomies of scale.
Advantages of forward vertical integration
- The business can control supply of their products and could decide to not supply to competition
- Can increase profits by cutting out the middle man
- possibly improve job securitis for workers
disadvantages of forward vertical integration
may lead to higher prices and/or reduced choice
advantages and disadvantages of backwards vertical integration
adv:control over supply of components
dis:may lead to reduction in variety of available goods for consumers/other businesses