Water + Electolytes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Water
essential for life in all organisms
efficient solvent meaning it can transport nutrients to cells, remove waste products and transport metabolites in cells
allows redistribution of heat around body and reduces temp through evaporation in sweat
medium essential for biochemical reaction of metabolism in and out of cells
water in body
50-70% of total body mass is water
depends on fat percentage
intracellular fluid
fluid inside cells
approx 2/3 of body fluid
extracellular fluid
fluid outside of cells
approx 1/3 of body fluid
interstitial fluid
80% of ECF which is found in spaces between cells of tissues
plasma is the final 20%
osmotic concentration
measure of solute concentration in a solution, also known as osmolarity
dehydration
dynamic process of losing water
Euhydration
normal body water content
absense of hyper or hypohydration
hyperhydration
state of excess body water content
hypohydration
state of insufficient/ suboptimal body water concentration
diuretic
substance that increases the rate of which urine is produced
water balance
day to day fluctuations are roughly 2.5 litres in healthy, non-exercising people
Water loss occurs through
evaporation from skin (sweat)
evaporation from respitory tract (breathing)
excretion from kidney (urine)
excretion from large intestine (feaces)
osmoregulation
a negative feedback loop that regulates water balance in body
osmoregulation step-by-step
1, hypothalamus detects changes in blood water levels
2, hypothalamus signals pituitary gland to release anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
3, ADH travels to kidneys and signals them to reabsorb more water from urine
4, Reduces concentration of solutes in the blood and restores water balance
temporary hypohydration/dehydration
1, hypothalamus detects drop in water level
2, activation of sensation of thirst and pituitary gland releases ADH
3, Kidneys reabsorb more water from urine
4, Body conserves fluids and restores water balance
Temporary hyperhydration
1, pituitary gland supresses ADH production
2, kidneys excrete more water in urine
3, body restores water balance by removing excess water
kidneys
control retention and loss of water
diagram - movement of fluid
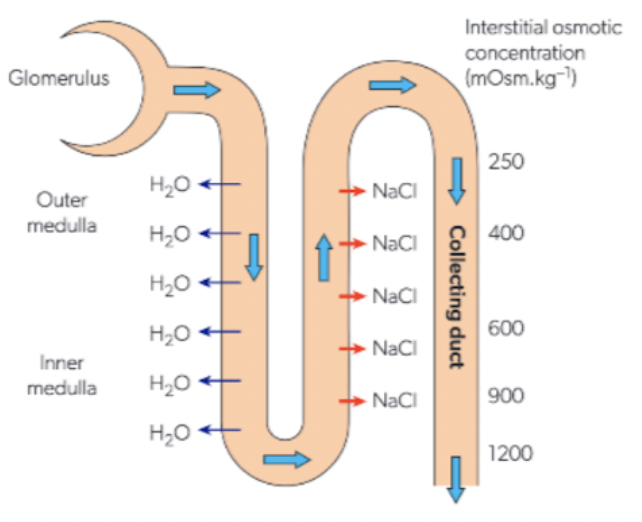
3 ways to monitor hydration status
measure body mass
urine color
urine testing with osmometer
hot conditions impact on hydration
water balance can be disrupted due to exercise or hot environments
metabolic heat is lost through sweat evaporation
sweat loss is greater in hot climates so more water is needed to avoid dehydration
dehydration increases health risk like heat stroke
athletes should avoid losing more then 2% body mass by fluid loss
Regulation of electrolytes during exercise
1, at start of exercise, water moves from plasma to interstitial and intracellular spaces
2, water movement is determined by amount of active muscles and exercise intensity
3, metabolic by products increase asmatic pressure
4, muscle activity raises blood pressure, forcing water out of blood and. reducing plasma volume
5, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and kidneys regulate water levels and electrolyte balance
hyponatremia
condition where concentration of sodium in body fluid is too low
occurs during endurance sports
symptoms include: bloating, nausea, vomiting, and heaaches
can cause brain swelling, seizuers, coma, and sometimes dealth
hypernatrimea
condition where concentration of sodium in body fluid is too high
result of dehydration or excess sodium
symptoms include: bloating, nausea, vomiting, and headaches
can cause brain swelling, seizures, coma, and sometimes dealth
occurs during or up to 24 hours after physical activity
cardiovascular drift
phenomenon characterised by rise in heart rate and fall in stroke volume over time, during prolonged aerobic exercise at a steady intensity