the nucleus
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
which organelle was the first to be discovered
the nucleus and is the defining characteristic of eukaryotic cells
2 hypothesises of where nuclei come from
membrane bound ribosomes encapsulated the region of DNA (invagination of membrane of DNA)
a cell surrounded another cell via endosymbiosis. An experiment using archaea in bacteria to show how many similarities in the yeast nuclear and mitochondrial genes and the archaea genes
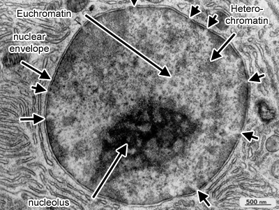
heterochromatin: dense staining of interphase DNA
euchromatin: less dense staining interphase DNA
nucleolus: high dense staining of RNA and ribosomes are synthesised
territories of a nucleus can be…
inherited but can change following differentiation or disease (the location of a gene changes depending on its transcriptional status)
the nucleolus
it is a collection of macromolecules including: rRNA genes, precursor rRNA, mature rRNA, rRNA processing enzymes, scoRNPs, ribosomal protein subunit, partly assembled ribosomes
also processes mRNA and tRNA
the nuclear envelope
a double unit membrane perforated with pores and supported by a fibrous meshwork called the lamina. The lamina is responsible for ensuring the asymmetric naturre of the double unit membrane
nuclear access is controlled by..
the pore in aa size dependent matter
particles with a molecular weight greater than 50,000 cannot enter the nucleus by simple diffusion but can enter by active signal- dependent transport