Ap Human Geography: Chapter 1 Vocabulary
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:28 PM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
Place
a specific point on Earth, distinguished by a particular characteristic.
2
New cards
Region
an area of Earth defined by one or more distinctive characteristics
3
New cards
scale
the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole.
4
New cards
space
the physical gap or interval between two objects.
5
New cards
connection
relationships among people and objects across the barrier of space.
6
New cards
map
a two-dimensional or flat-scale model of Earth’s surface, or a portion of it.
7
New cards
cartography
the science of mapmaking
8
New cards
Geographic Information System
A device that captures, stores, queries, and displays the geographic data
9
New cards
Global Positioning System
a system that determines the precise position of something on Earth.
10
New cards
map scale
the relationship of a feature’s size on a map to its actual size on Earth.
11
New cards
projection
The scientific method of transferring locations on Earth’s surface to a flat map
12
New cards
meridian
an arc connecting the North and South poles
13
New cards
longitude
The numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians drawn on a globe and measuring distance east and west of the prime meridian
14
New cards
parallel
a circle drawn around the globe parallel to the equator and at right angles to the meridians.
15
New cards
latitude
The numbering system to indicate the location of a parallel
16
New cards
prime meridian
The meridian that passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England, is 0° longitude,
17
New cards
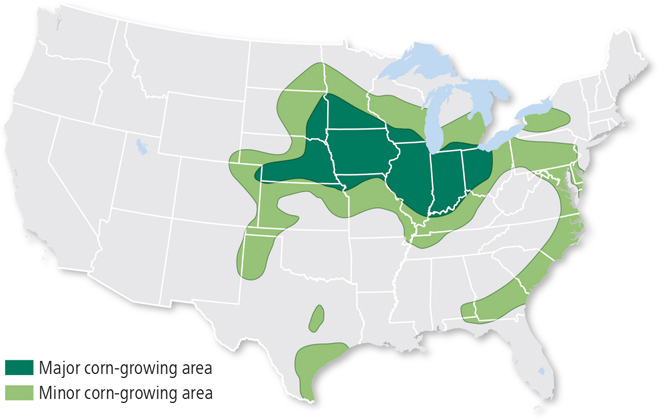
isoline map
connects with lines all the places that have particular values
18
New cards
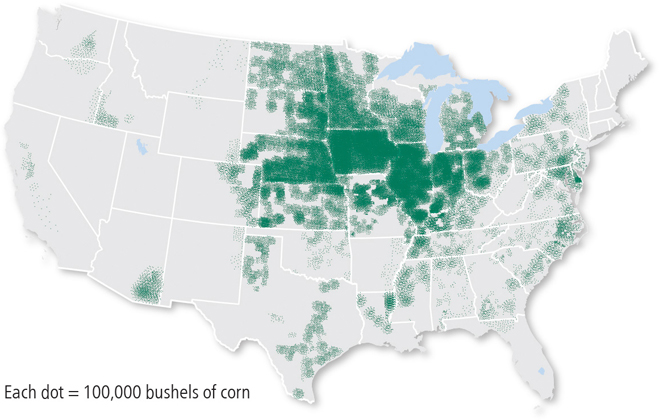
dot distribution map
depicts data as points and shows how those points are clustered together or spread out over an area. Each dot represents a predetermined number of observations, which could be one or many
19
New cards
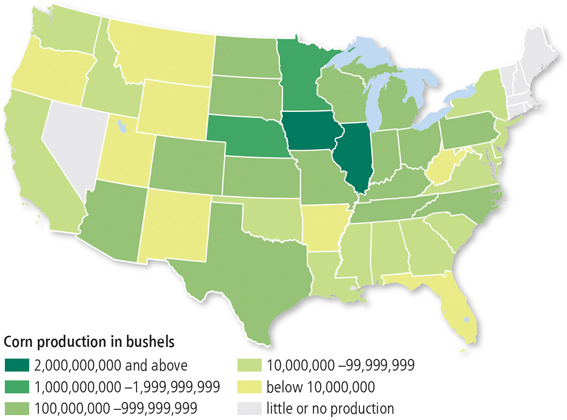
Choropleth Map
a map where recognizable areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the variable
20
New cards
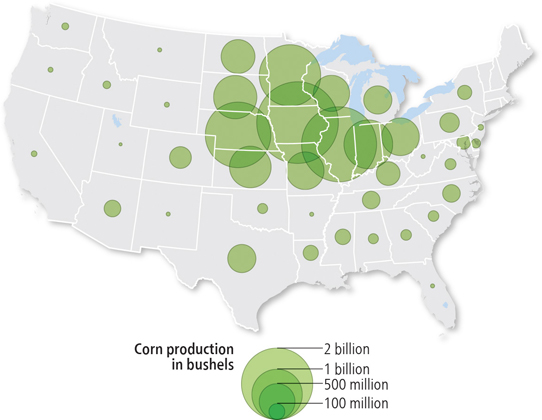
Graduated symbol map
displays symbols that change in size according to the value of the variable. A higher value is typically represented by a larger symbol
21
New cards
cartogram
is a map in which the size of a country or U.S. state is proportional to the value of a particular variable,
22
New cards
Location
the position that something occupies on Earth’s surface.
23
New cards
situation
also known as relative location, is the location of a place relative to other places.
24
New cards
absolute location
the position of a place in a way that never changes, such as geographic coordinates of latitude and longitude.
25
New cards
cultural landscape
a combination of cultural features such as language and religion, economic features such as agriculture and industry, and physical features such as climate and vegetation
26
New cards
formal region
also called a uniform region, is an area within which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics.
27
New cards
functional region
also called a nodal region, is an area organized around a node or focal point
28
New cards
Vernacular/perceptual region
an area that people believe exists as part of their cultural identity
29
New cards
culture
the body of customary beliefs, material traits, and social forms that together constitutes the distinct tradition of a group of people
30
New cards
spatial association
the relationship between the distribution of one feature and the distribution of another feature
31
New cards
globalization
a force or process that involves the entire world and results in making something worldwide in scope
32
New cards
distribution
he arrangement of a feature in space
33
New cards
density
the frequency with which something occurs in space
34
New cards
concentration
The extent of a feature’s spread over space
35
New cards
pattern
the geometric arrangement of objects in space
36
New cards
poststructuralist geography
examines how the powerful in a society dominate, or seek to control, less powerful groups, how the dominated groups occupy space, and confrontations that result from the domination.
37
New cards
humanistic geography
emphasizes the different ways that individuals form ideas about place and give those places symbolic meanings
38
New cards
behavioral geography
emphasizes the importance of understanding the psychological basis for individual human actions in space
39
New cards
diffusion
The process by which a feature spreads across space from one place to another over time
40
New cards
hearth
place from which an innovation originates
41
New cards
relocation diffusion
The spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another
42
New cards
expansion diffusion
The spread of a feature from one place to another in an additive process
43
New cards
hierarchical diffusion
the spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places
44
New cards
contagious diffusion
the rapid, widespread diffusion of a characteristic throughout the population
45
New cards
stimulus diffusion
the spread of an underlying principle even though a characteristic itself apparently fails to diffuse.
46
New cards
distance decay
The farther away someone is from another, the less likely the two are to interact. Contact diminishes with increasing distance and eventually disappears.
47
New cards
space-time compression
the reduction in the time it takes for something to reach another place
48
New cards
assimilation
the process by which a group’s cultural features are altered to resemble those of another group
49
New cards
acculturation
process of changes in culture that result from the meeting of two groups
50
New cards
sustainability
the use of Earth’s resources in ways that ensure their availability in the future.
51
New cards
conservation
The sustainable use and management of Earth’s natural resources to meet human needs such as food, medicine, and recreation
52
New cards
preservation
the maintenance of resources in their present condition with as little human impact as possible.
53
New cards
biotic
composed of living organisms.
54
New cards
abiotic
composed of nonliving organisms
55
New cards
ecosystem
A group of living organisms and the abiotic spheres with which they interact
56
New cards
ecology
The scientific study of ecosystems
57
New cards
cultural ecology
The geographic study of human–environment relationships
58
New cards
environmental determinism
the belief that human geographers should apply laws from the natural sciences to understanding relationships between the physical environment and human actions
59
New cards
possibilism
the physical environment may limit some human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to their environment
60
New cards
polder
a piece of land that is created by draining water from an area