Plant Tissues
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L.S
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Meristematic Tissue
Cells that are not permanent. They go through cell division.
Apical Meristem
Located at the growing points of the tips of roots and shoots. (Lengthens the plant)
Lateral Meristem
This tissue is also called cambium. It makes the plant ‘‘wider’’
Epidermis
Waxy Cuticle prevents water loss.
Transparent to allow for photosynthesis.
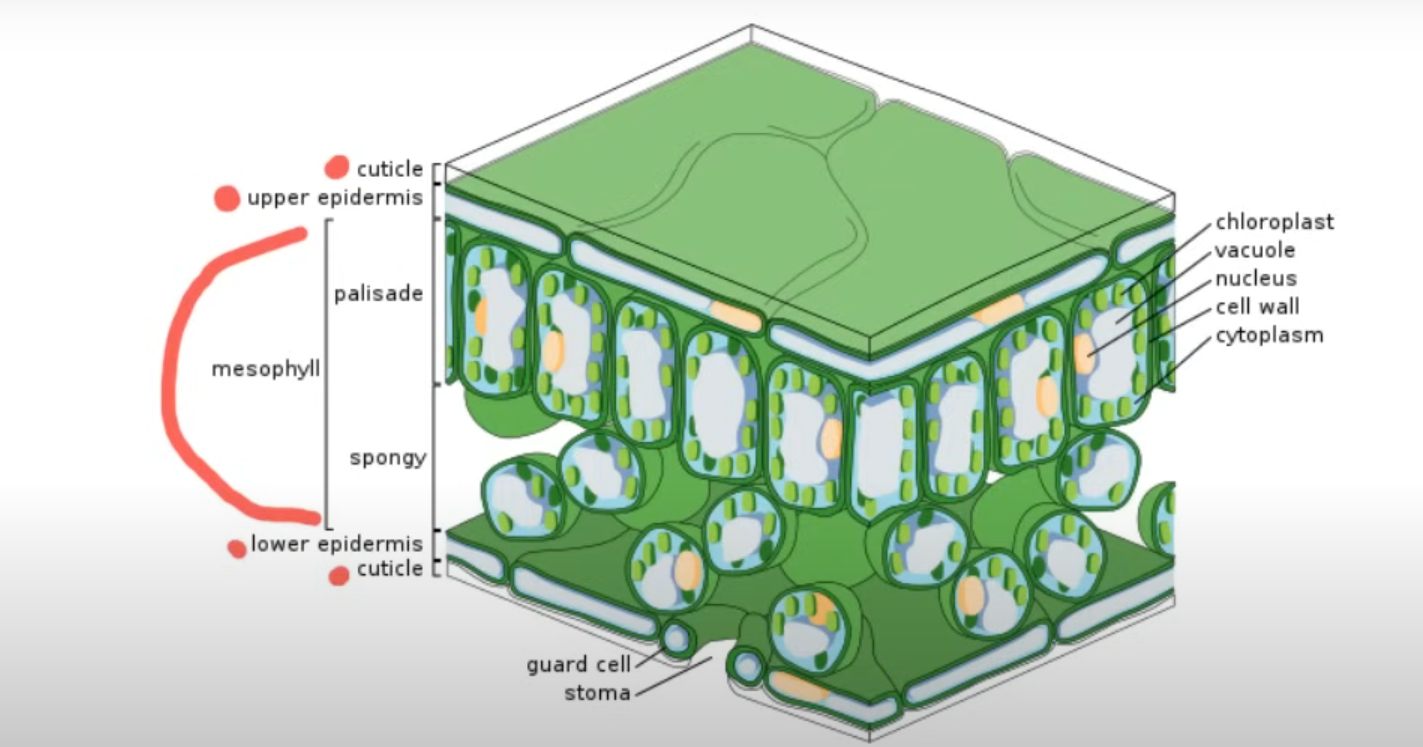
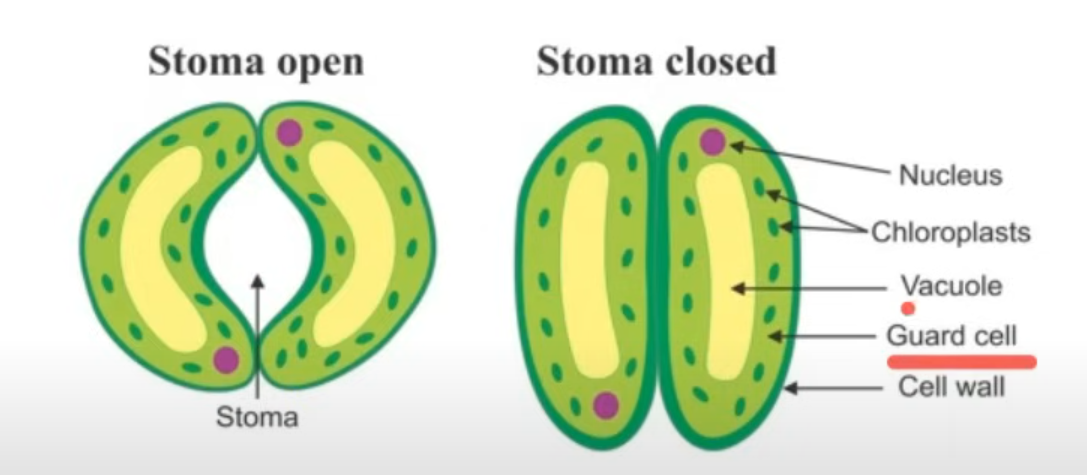
Specialised Epidermis: Stomata
Guard cells surround the stomata. It controls what enters and leaves the
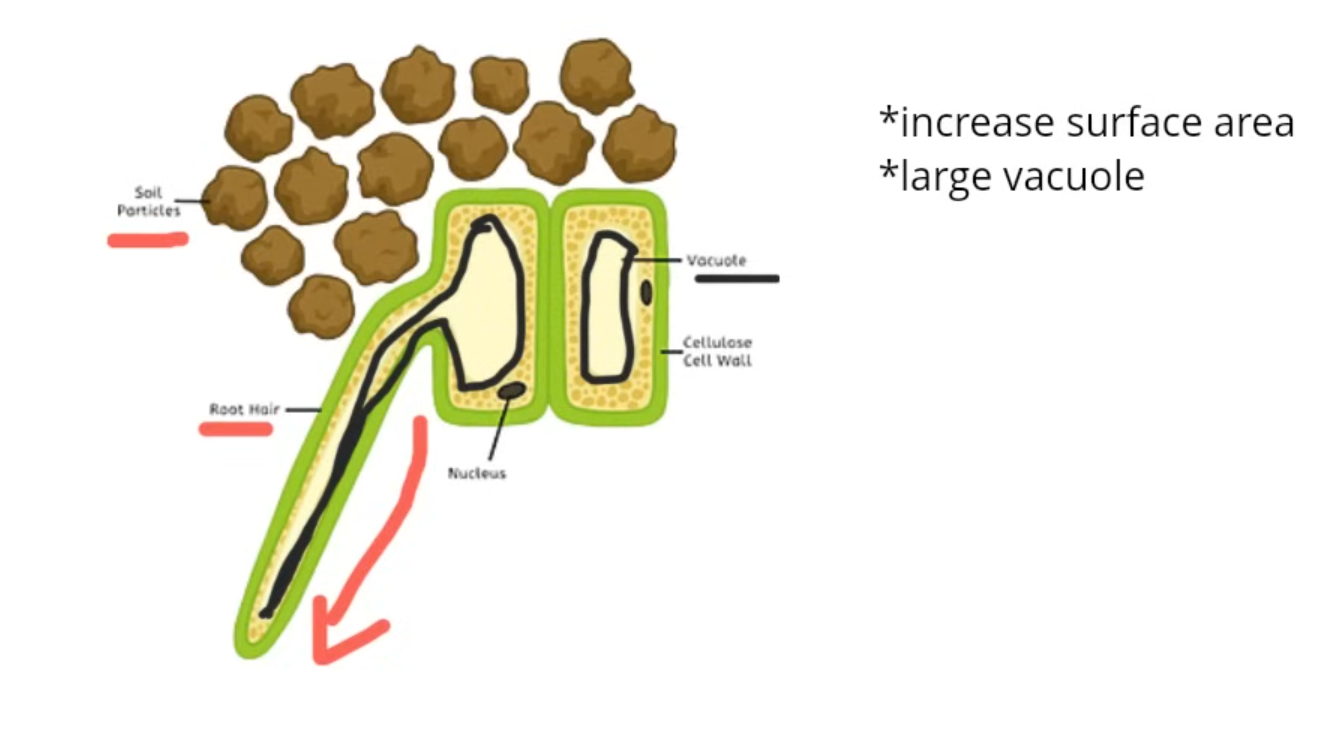
Specialised Epidermis: Root hair cell
No waxy cuticle.
Elongated to increase the total surface area for maximum Absorbtion.
Large Vacuole
Parenchyma
Thin Cell Walls
Intercellular air spaces
Functions:
Packaging tissue
Storage
Allows for gaseous exchange
Allows for osmosis
Chlorenchyma
Parenchyma with Chloroplasts.
Collenchyma
Thicken corners with cellulose
Unevenly thickened
Function
Support and strength
Allows the plant to be flexible
Sclerenchyma
Thickest of all tissues
Evenly thickened walls
Functions
Streangth and rigidity
Fibers are in wood and bark
Sclereids are found in nuts and stone fruits
Cells are dead
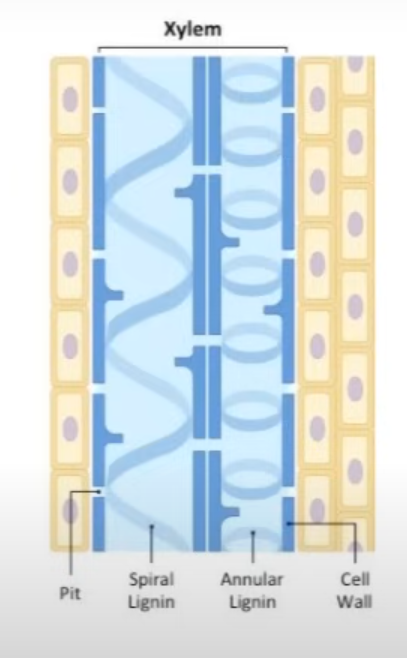
Xylem
Structure:
Elongated cells.
Large Lumen
Dead and Empty
Cell Wall thickened with Lignin
Pits for lateral water movement.
Vessels - Round and arranged end- to -end
Tracheids - Tapered ends and arranged in and overlaps
Phloem
Arranged end-to- end
Sieve plates
Companion cells