How fabrics are made
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Last updated 7:11 AM on 11/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
What is the most common way of making fabric?
Weaving and kntting
2
New cards
How do you weave fibres?
Warp threads are placed on a loom. Weft threads go over and under the warp threads.
3
New cards
What is the difference between a fragile fabric and a sturdy fabric?
A sturdy fabric's threads are tightly woven together, whereas a fragile's fabrics' are loosely woven together
4
New cards
Where do woven fabrics have the most stretch?
The stretch on the bias and are not stretch lengthwise or crosswise
5
New cards
What is the selvage?
The uncut, unfinished edge of the fabric
6
New cards
What are filling threads
Crosswise grain threads
7
New cards
What are warp threads?
The lengthwise grain threads that run parallel to the selvage
8
New cards
What is the lengthwise grain?
The warp, the threads that run up and down parallel to the selvage
9
New cards
What is the crosswise grain?
The weft, the threads that is woven under and over the warp
10
New cards
What is the bias?
The stretchiest part of the fabric
11
New cards
What are the three kinds of basic weaves?
Plain, twill, and satin
12
New cards
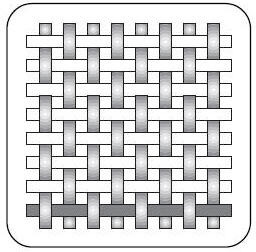
How do you identify a plain weave?
It looks like a grid. It is over one, under one (or the other way around)
13
New cards
What are some examples of plain weave fabrics?
Broadcloth, musin, and gingham
14
New cards
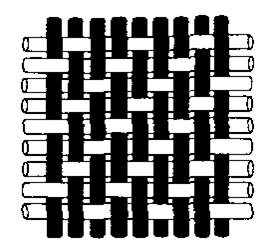
How do you identify a twill weave?
There is a diagonal line. It is over two, under one (or the other way around)
15
New cards
What are some examples of twill weave fabrics?
Denim, gabardine, and chino
16
New cards
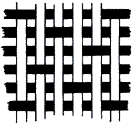
How do you identify a satin weave?
It is smooth and shiny. Over one, under three or more (or the other way around)
17
New cards
What are some examples of satin weave fabrics?
Charmeuse, peau de soie, and jacquard
18
New cards
How is knitted fabric made?
They are made by a series of interlocking loops connected by more loops to form fabric.
19
New cards
How are knits made?
Machines or by hand
20
New cards
What are the upsides to knit fabric?
The fabric is stretchy, wrinkle resistant and keeps you warm
21
New cards
Why does knit fabric keep you warm?
Because it traps air and absorbs perspiration
22
New cards
What are the two kinds of knits?
Single knit and double knit
23
New cards
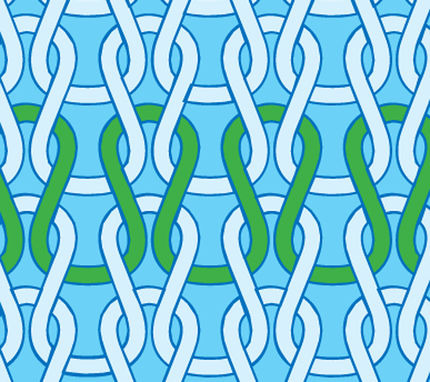
How do you identify a single knit?
Bumps (V shapes) on the right side, vertical lines on the wrong side
24
New cards
What are two examples of single knits?
Jersey knit and single knit
25
New cards
How do you identify a double knit?
V shaped stitched form lengthwise rows of loops or whales. There are vertical lines on both sides of the fabric

26
New cards
What are two examples of double knits?
Ribbing and double knit
27
New cards
Why are knits are popular in sports wear?
They are stretchy, breathable, and depending on what it's made of, they absorb or wick away water.
28
New cards
What are non-woven fabrics?
Fabrics that are not woven or knitted.
29
New cards
What are non-woven fabrics made of?
Fibres
30
New cards
What is an example of a non-woven fabric?
An inelastic fabric that does not fray.
31
New cards
What is true felt made of?
All wool or part wool fibres.
32
New cards
How is felt made?
By using moisture, heat, and pressure
33
New cards
What is felt used for?
Coats and crafts
34
New cards
What is a bonded fibre?
A mass of fibres held together using a bonding agent (ex. glue)
35
New cards
What is interfacing?
A fabric used to make certain parts of a garment more stable. Adds firmness, shape, structure and support to a garment