Articulation System
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Vocal Tract Cavities (3)
oral cavity
nasal cavity
pharyngeal cavity
Oral Cavity
lips anteriorly to palatoglossal arch (anterior faucial arch)
Nasal Cavity
extend horizontally from the nostrils anteriorly to the upper most portion of the pharynx posteriorly
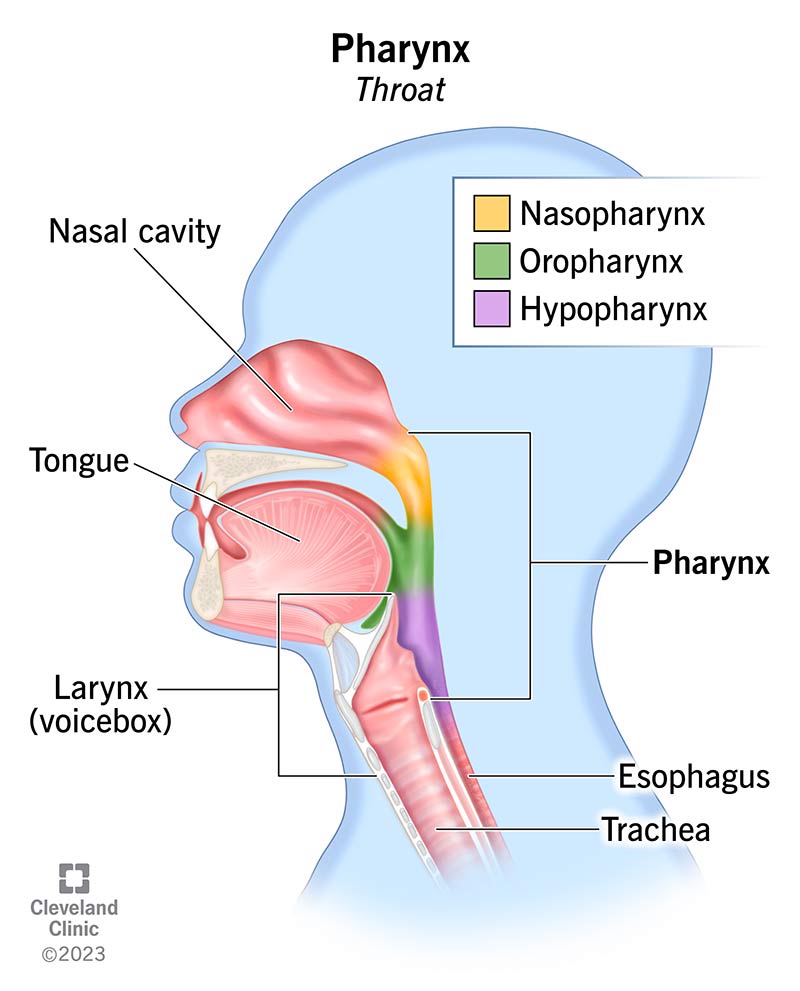
Pharyngeal Cavity
extends from the base of skull to 6th cervial vertebrae
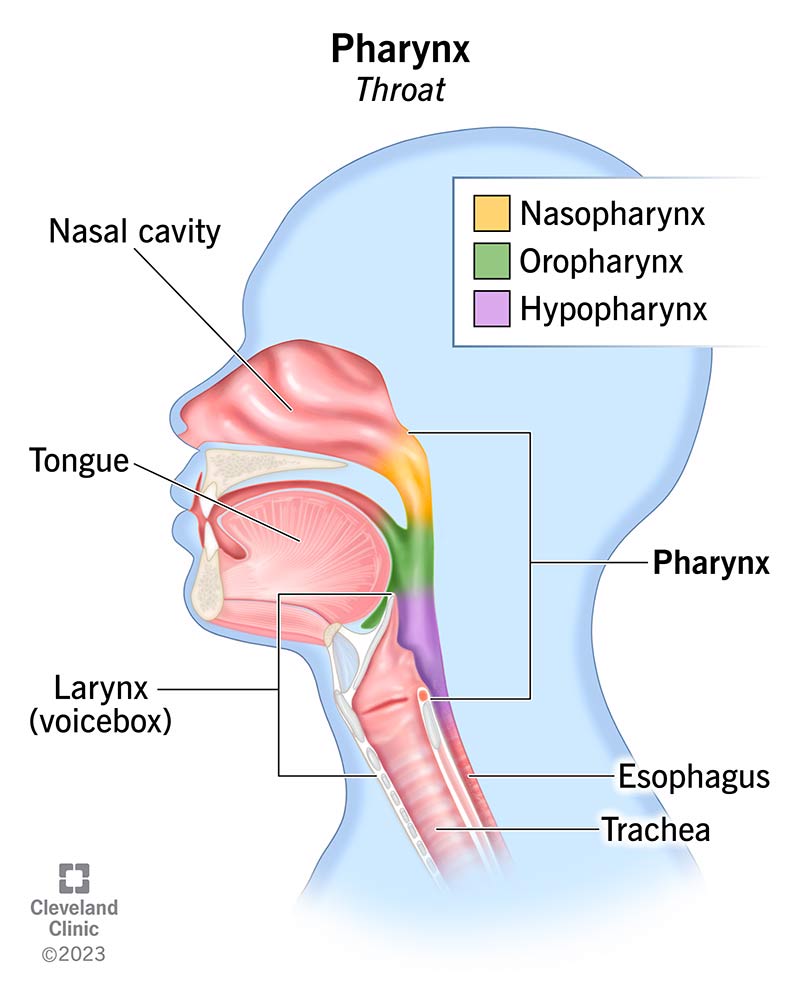
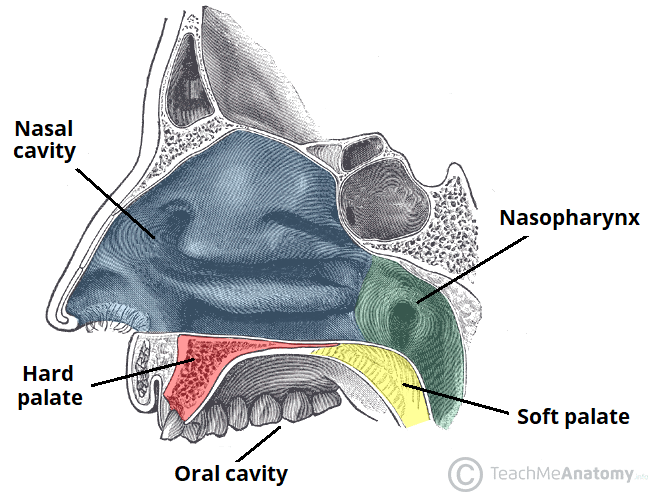
Pharyngeal Cavity: Nasopharynx
begins with attachment to the sphenoid and occipital bone and ends at the velum
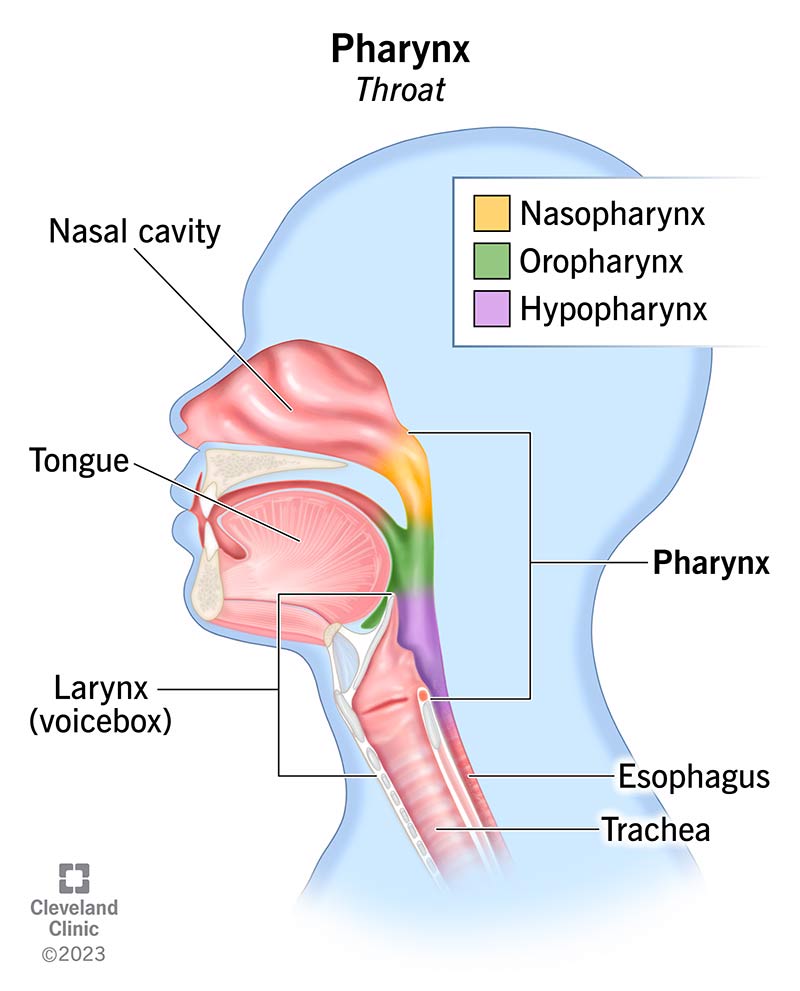
Pharyngeal Cavity: Oropharynx
Extends from the velum and epiglottis
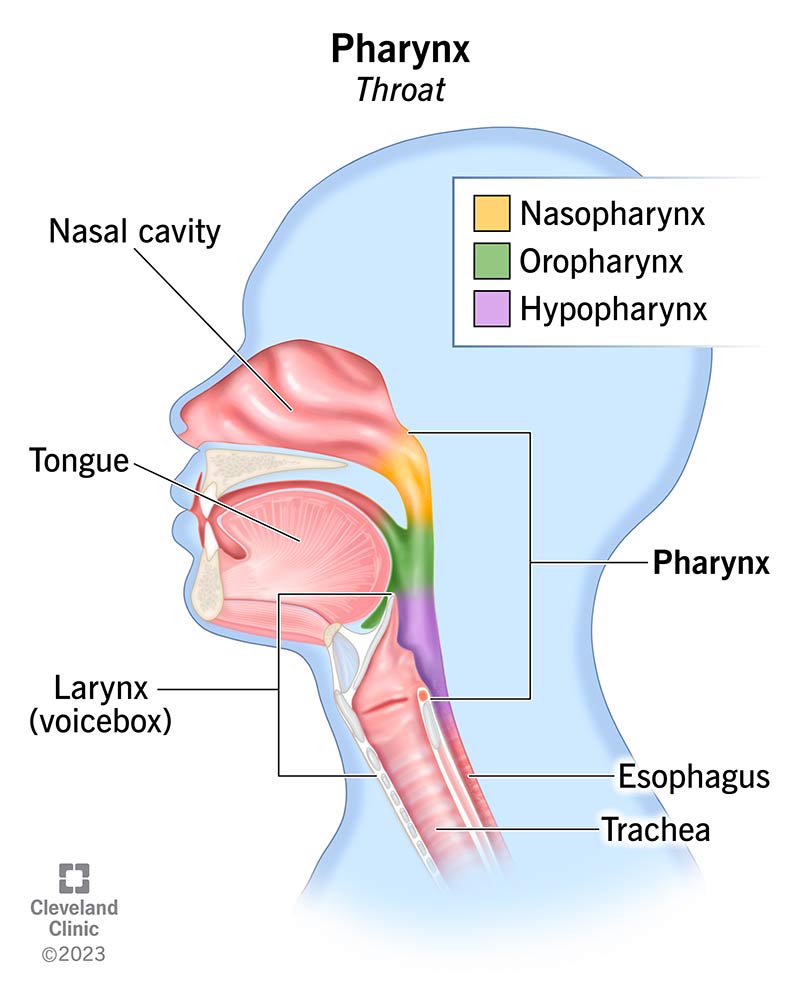
Pharyngeal Cavity: Laryngopharynx (Hypopharynx)
Extends from epiglottis to esophagus
posterior to the oral cavity to larynx
anterior to the cervical vertebrae
superior to the esophagus
Articulation
movement of structures to form speech sounds
(8) Articulators: Moveable
tongue
lips
velum
pharynx
mandible
(8) Articulators: Immoveable
teeth
hard palate
alveolar ridge
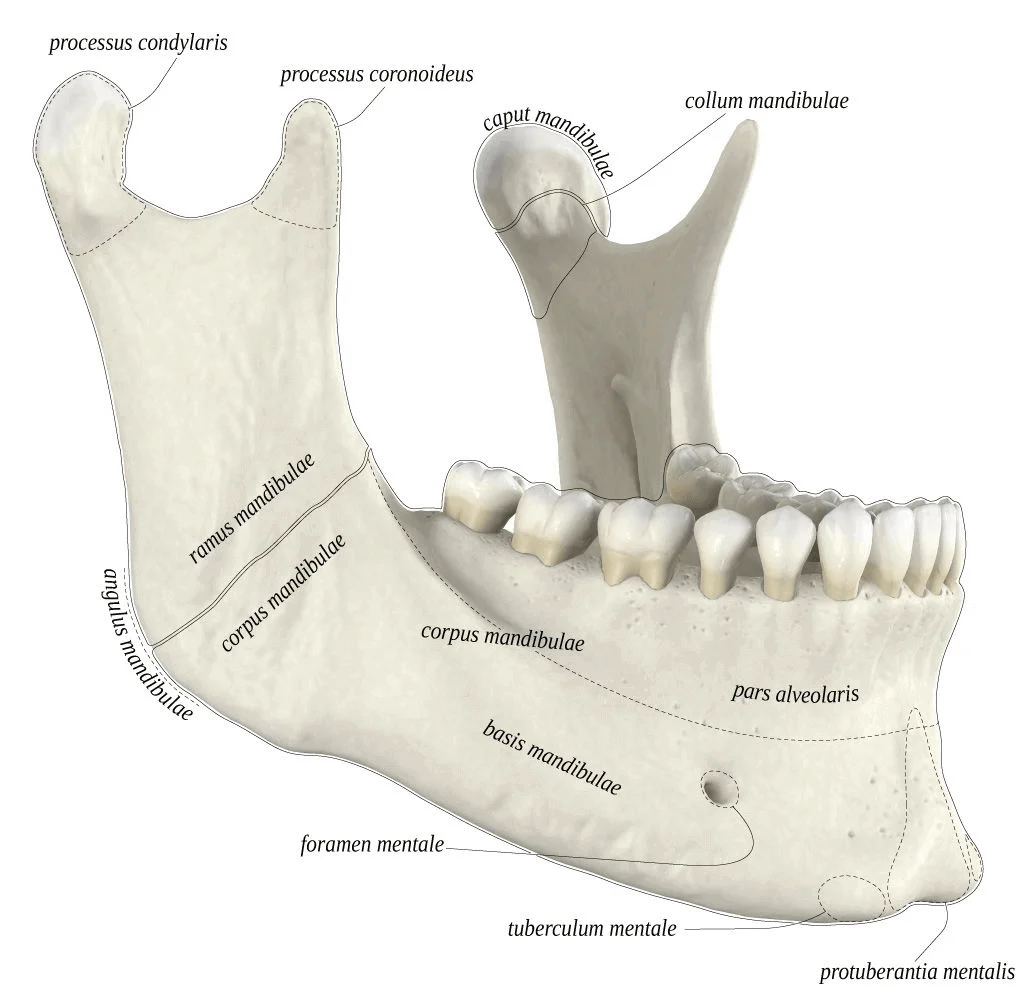
Facial Bone: Mandible
unpaired bone (fused during development)
mental symphasis: fusion point at the anterior midline
corpus/body: lateral mass containing the teeth
*ramus: superior extension
angle: bend between corpus and ramus (important for swallowing)
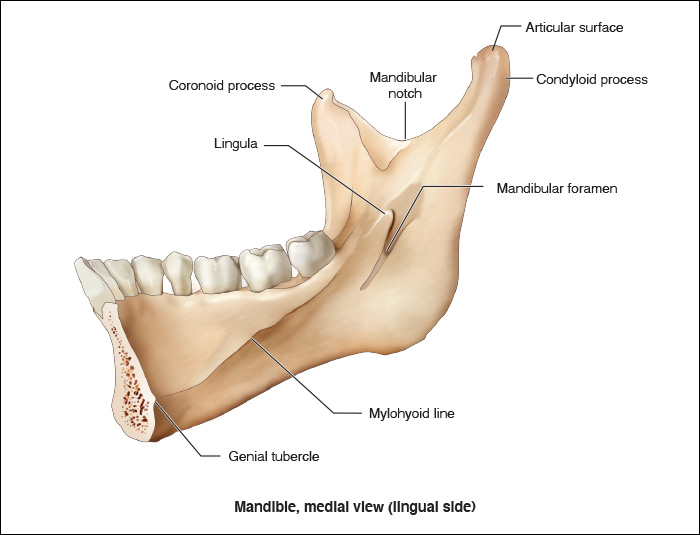
Ramus Anatomy
condylar process: posterior extension of ramus
articulates with temporal bone to form a temporomandibular joint (TMJ is a moveable joint in skull)
coronoid process: anterior extension of ramus
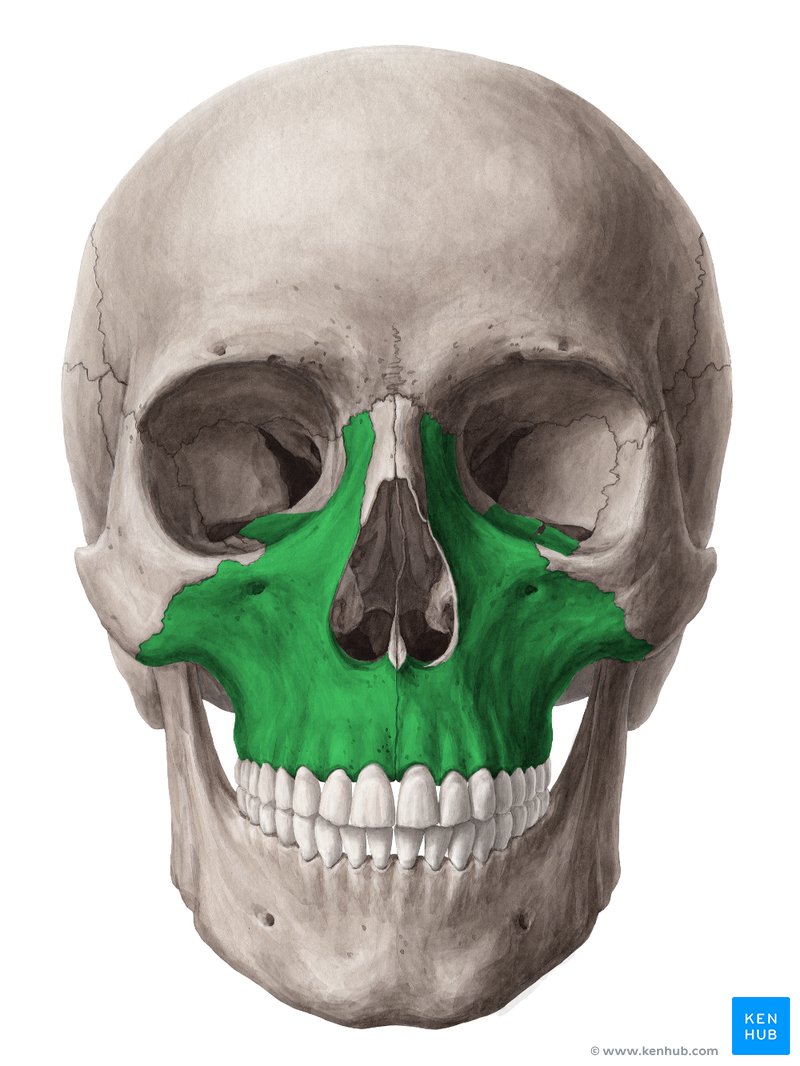
Facial Bones: Maxilla (upper jaw bone)
paired bone; fused at the midline
creates:
hard palate (bony roof of mouth)
lateral nose
upper dental ridge
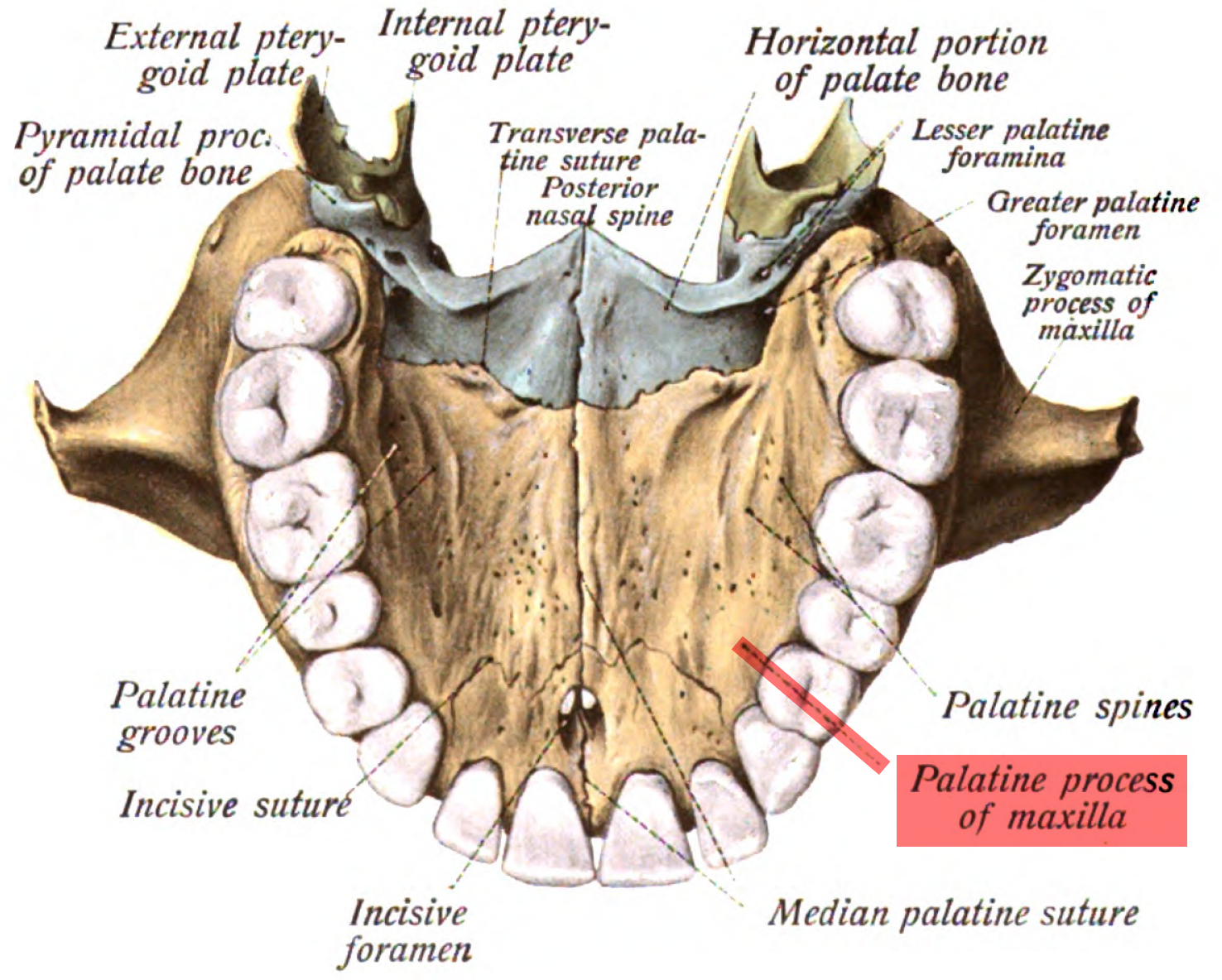
Palatine Process
horizontal extension creates ¾ of the hard palate
connects at the intermaxillary structure (fibrous joints, mobile)
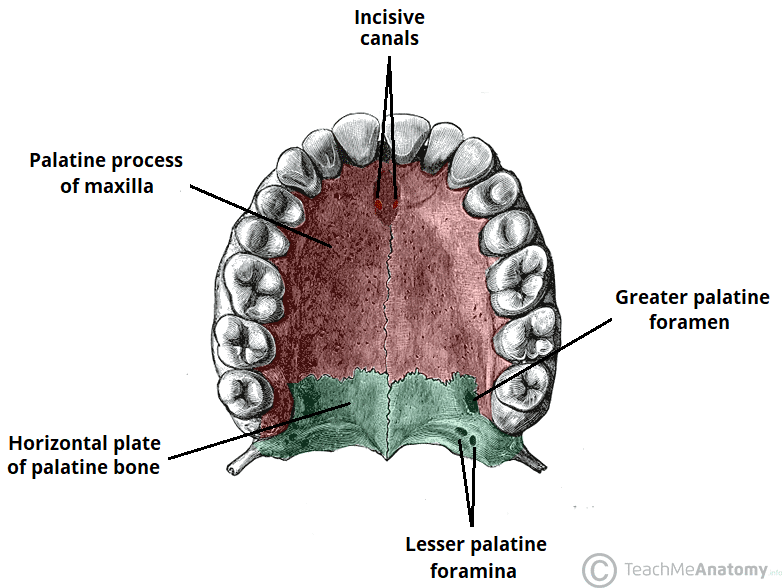
Cleft Palate
incomplete closure of palatine process during development
Facial Bone: Nasal bone
paired
create anterior bony structure of nose
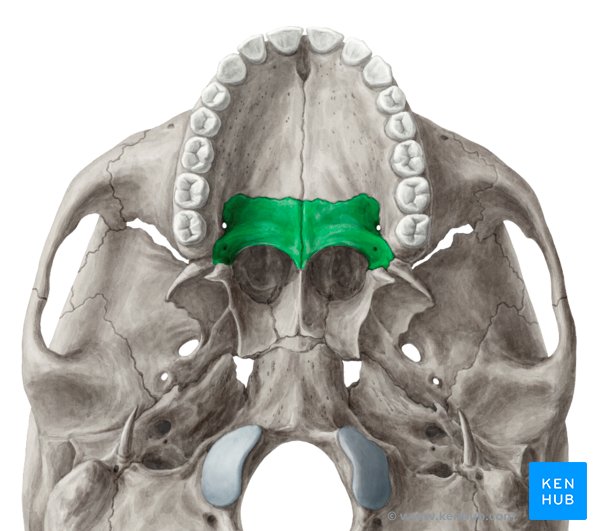
Facial Bone: Palatine Bone
paired
forms ¼ posteior of the hard palate
forms lateral wall of nasal cavity
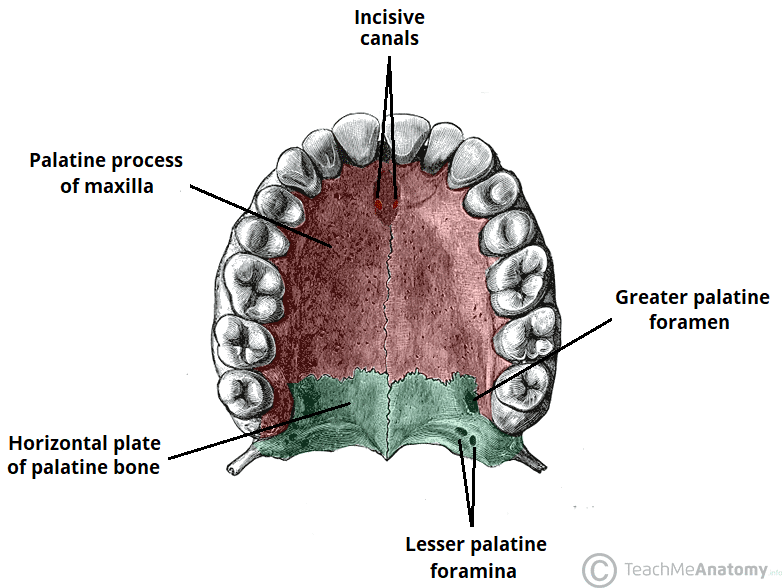
Facial Bone: Vomer
unpaired
*creates inferior/posterior nasal septum
connects with sphenoid, ethmoid, maxillae and palatine bone
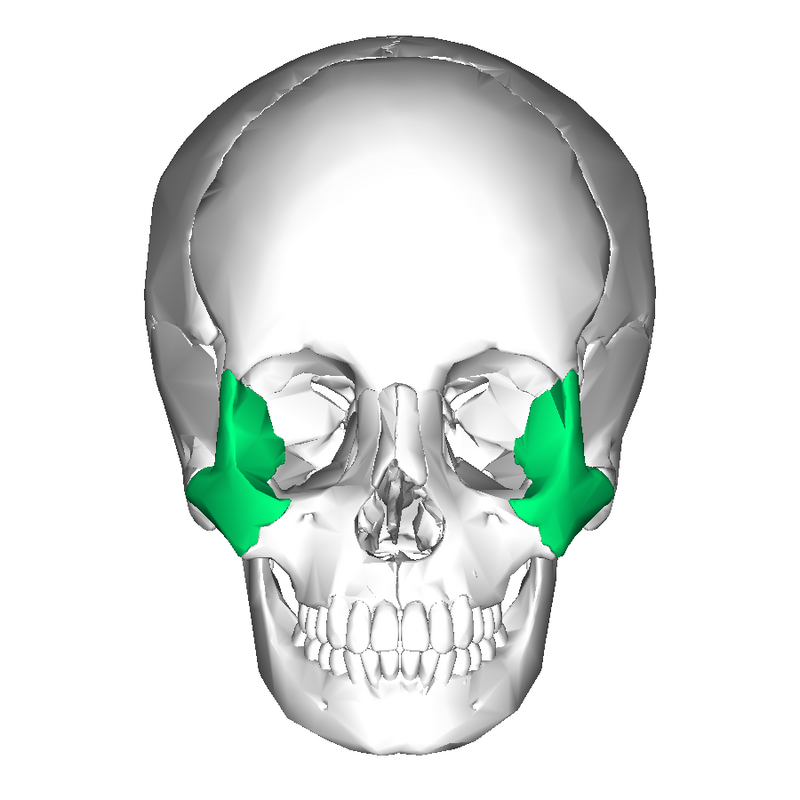
Facial Bone: Zygomatic Bone
paired
aka cheeks
numerous processes
Inferior Nasal Concha
scroll like paired bones
inferior part of nasal cavity
ethmoid bone creates superior and middle concha
super sensitive
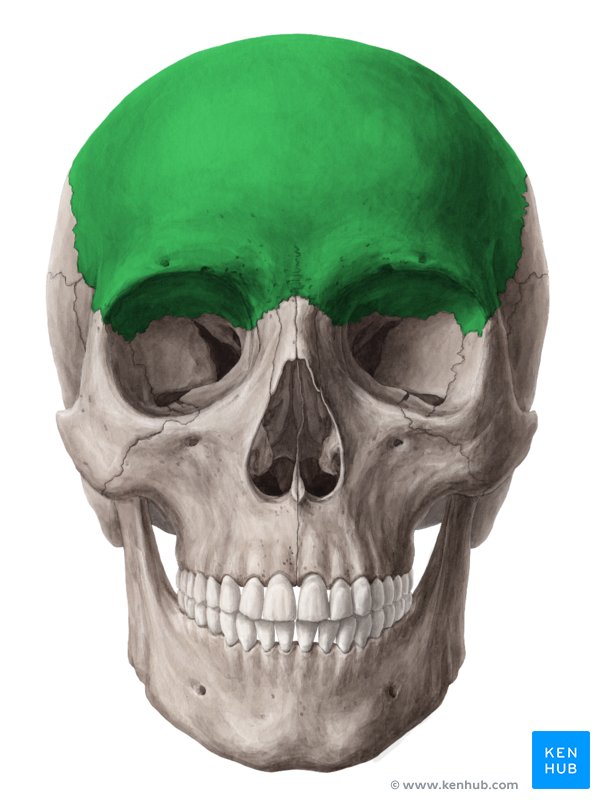
Cranial Bones: Frontal Bone
unpaired
creates forehead
superior, anterior cranium, supraorbital region
*articulates with the maxilla, nasal, and zygomatic facial bone
Suture
fibrous joint, immobile
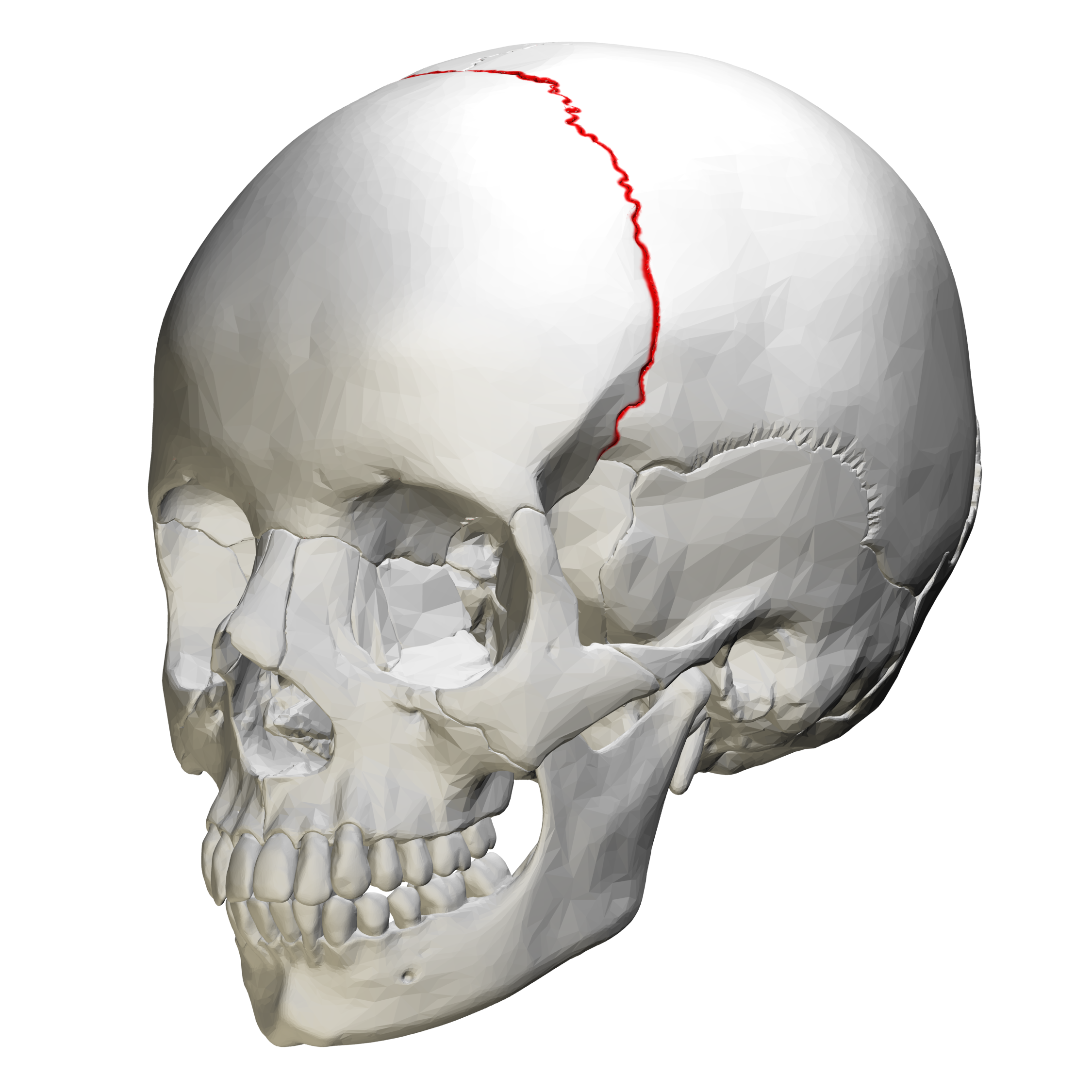
Coronal Suture
between frontal and parietal bones
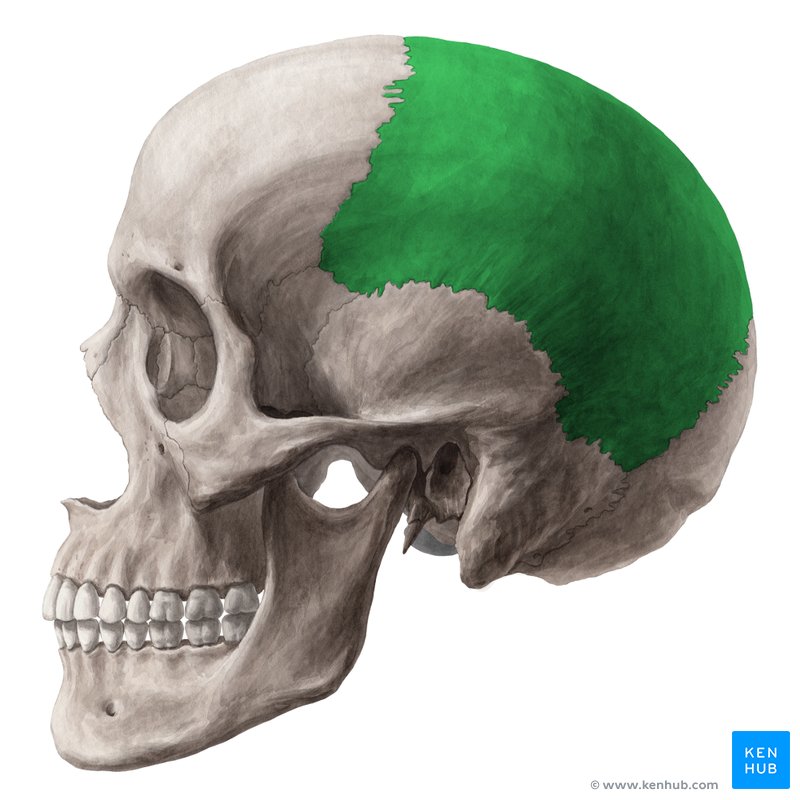
Cranial Bone: Parietal Bone
paired
superior, lateral portion of cranium
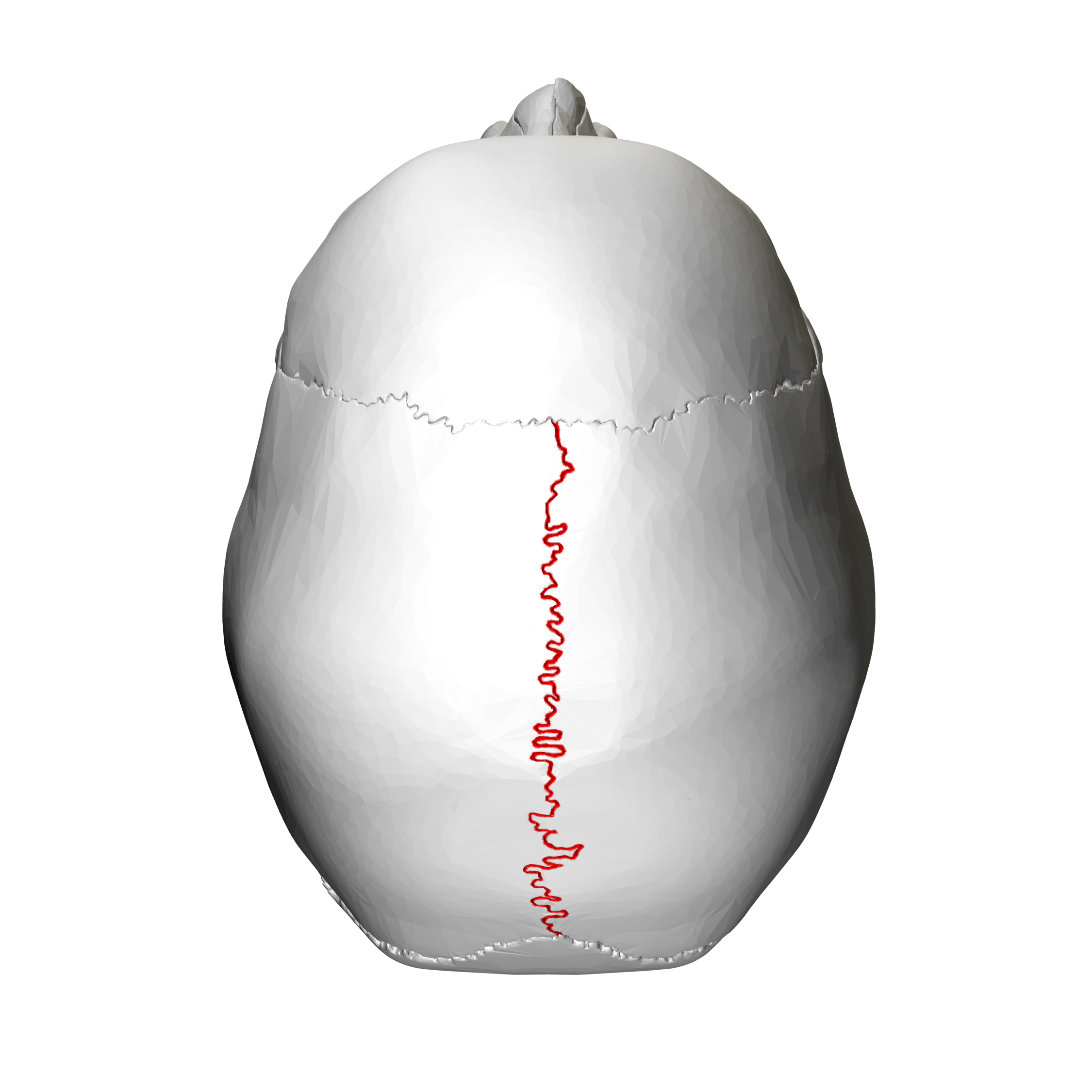
Pariteal Bone: Sagittal Suture
between R/L parietal bone
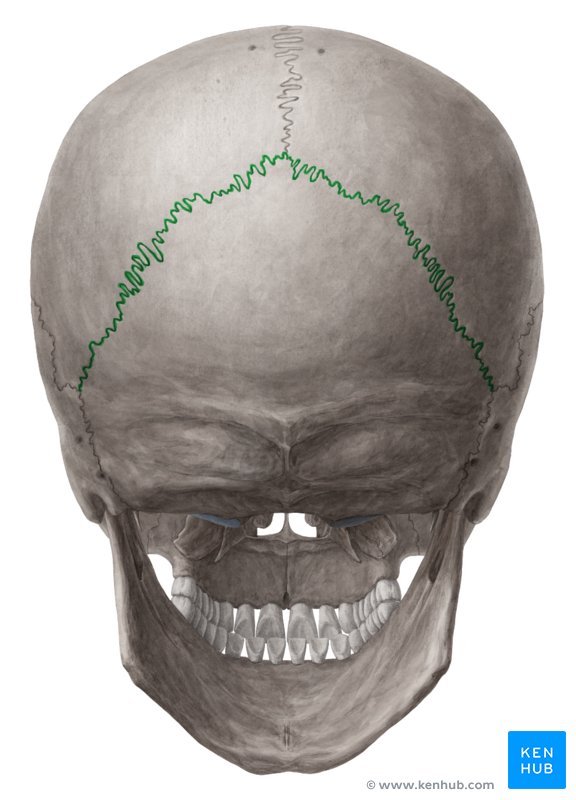
Pariteal Bone: Lambdoidal Suture
between parietal and occipital bone (base) posteriorly
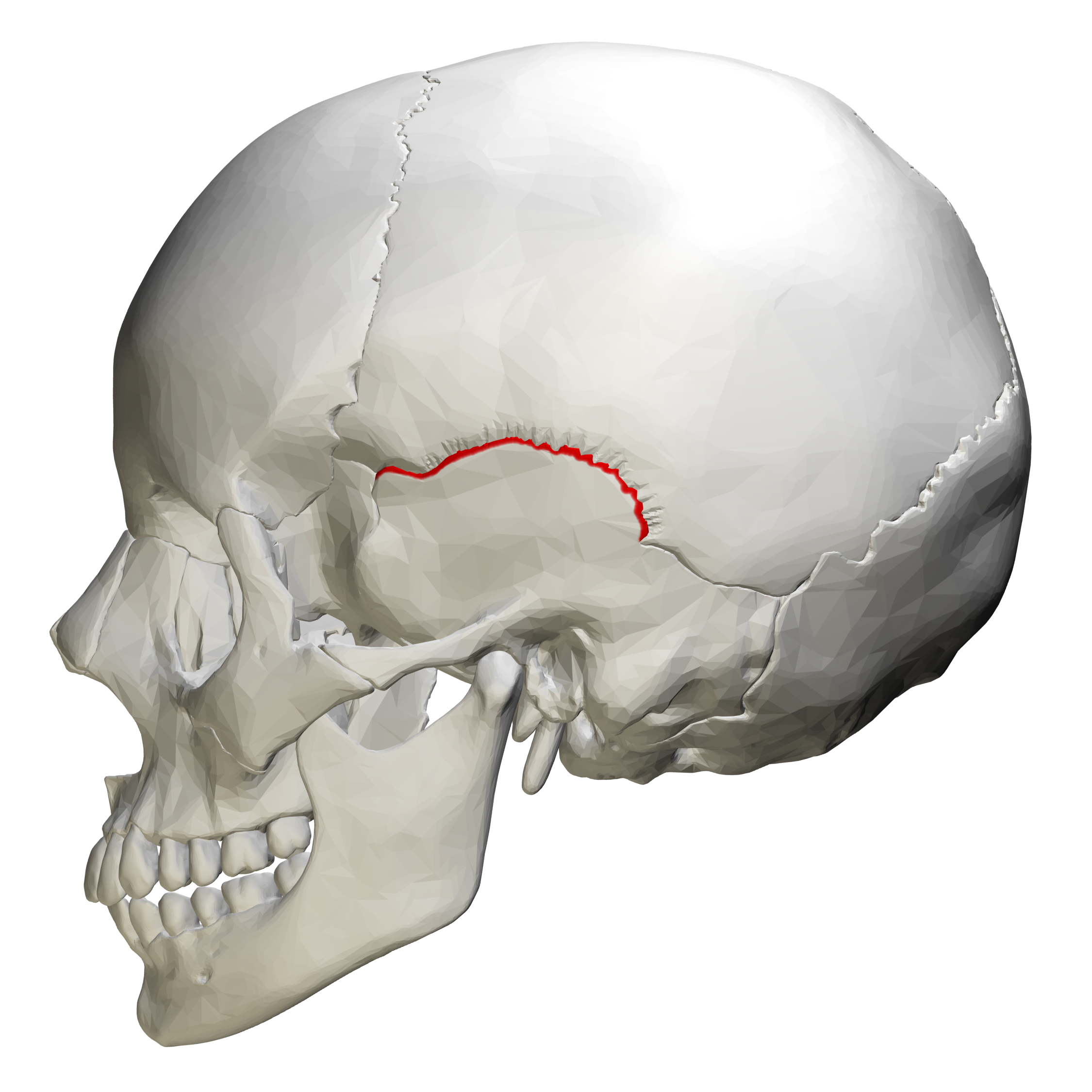
Pariteal Bone & Temporal Bone: Squamosal Suture
between temporal and parietal bone
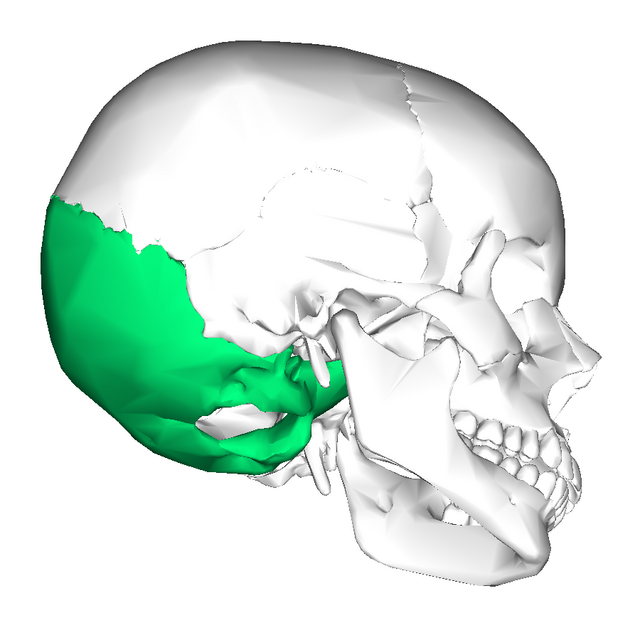
Occipital Bone
unpaired; posterior and inferior region of cranium
articulates with temporal, parietal and sphenoid bone
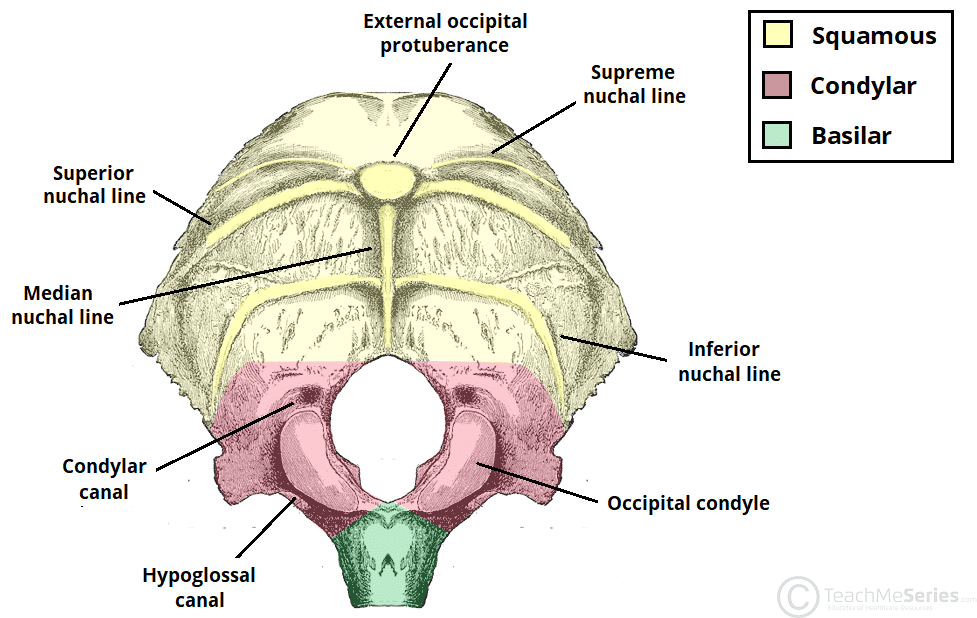
Occipital Bone: Landmarks
foramen magnum: large hole in base of skull (brainstem/spinal cord leaves skull
condoyles: bumps articulating with CV1 atlas
allows pivoting up and down
synovial joint
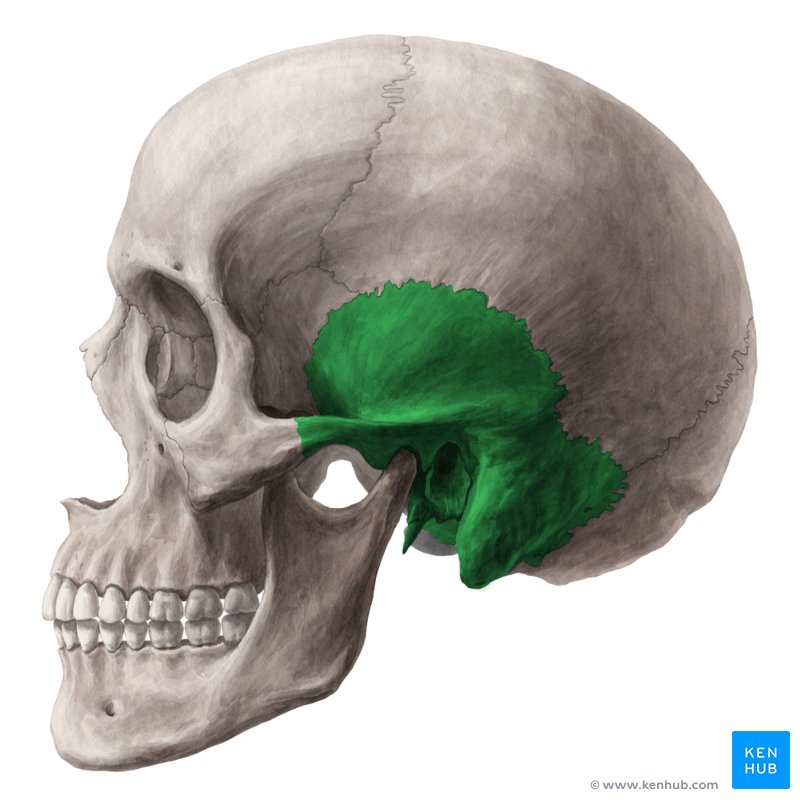
Temporal Bone
paired
2 main sections
*helps create the external auditory meatus (external ear canal)
*articulates with the mandible with the condylar process (synovial joint)
*The styloid process (stylohyoid ligament) is part of the temporal bone
houses the organs for hearing and balance
Temporal Fossa: created by temporal, parietal, frontal and sphenoid bones
attachment site for temporalis muscle
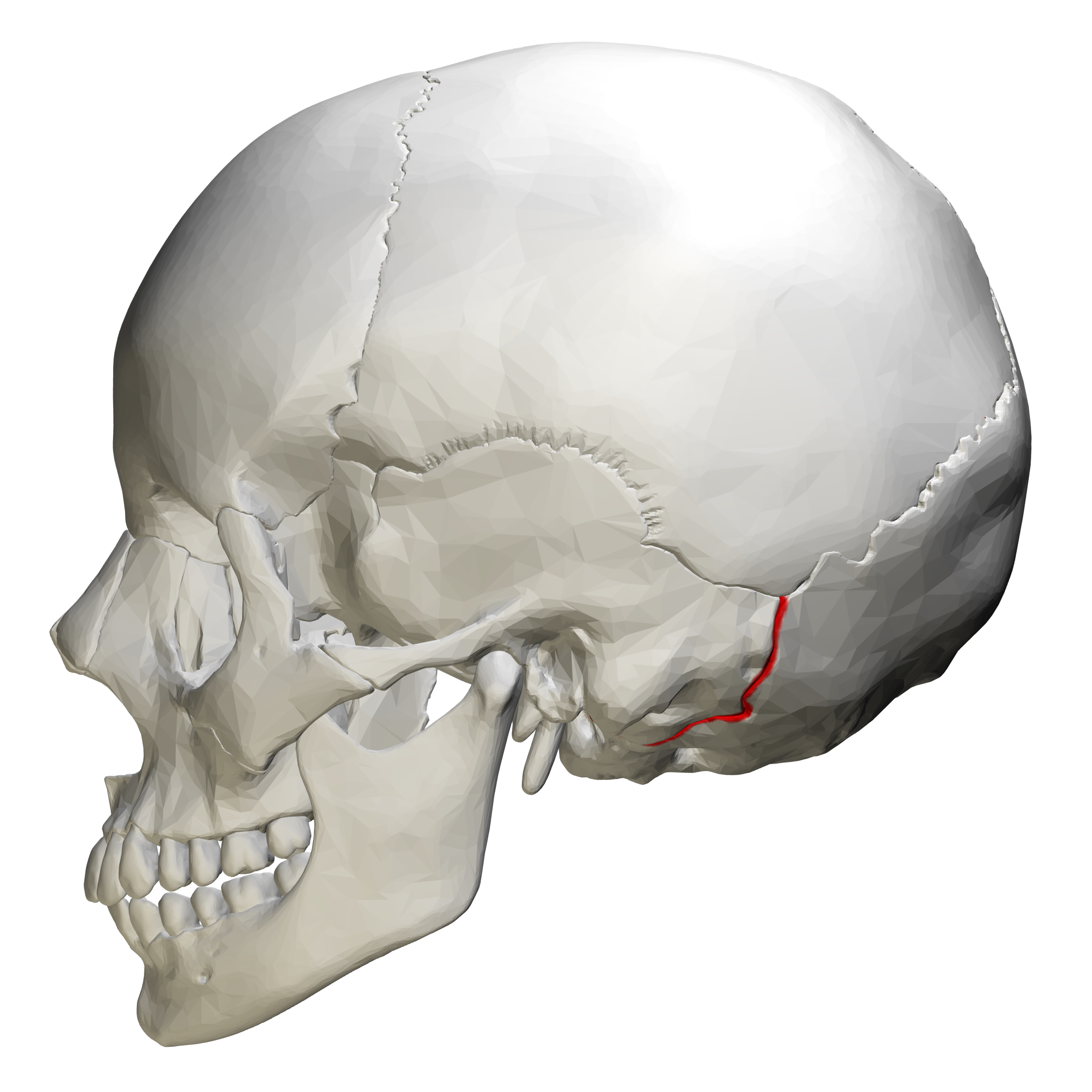
Temporal Bone: Occipitomastoid Suture
between occipital and temporal bones
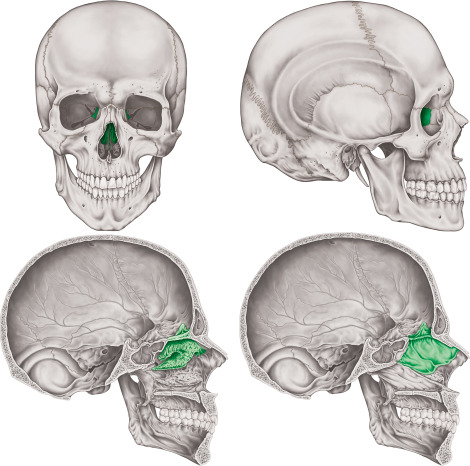
Cranial Bones: Ethmoid Bone
unpaired bone
*separate nasal and cranial cavities
many foramen for olfactory nerve fibers-CN1
forms the *superior nasal septum
forms the superior and medial nasal concha
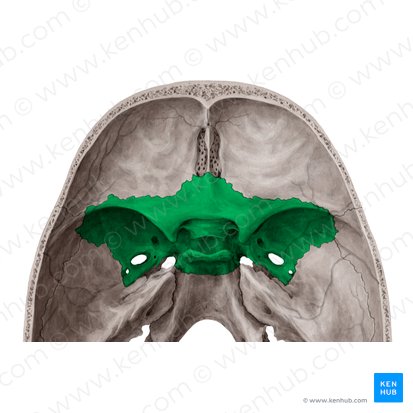
Cranial Bones: Sphenoid Bone
unpaired bone
Cavities of Vocal Tract
oral
buccal
nasal
pharyngeal
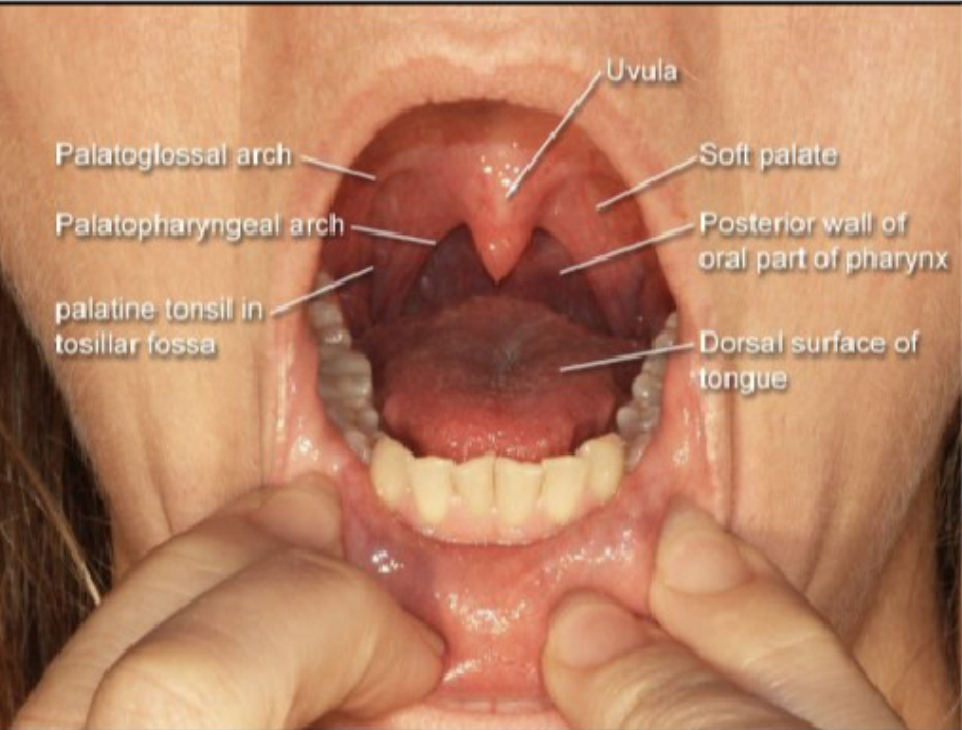
Oral Cavity
most important for the articulation system
contains the most articulators
nearly all sounds exit the mouth (except for nasal sounds)
Oral Cavity: Hard Palate
maxillary/palatal bone
separates oral/nasal cavity
Hard Palate: Landmarks
Alveolar Ridge
Rugae
Median Raphe: line running anterior/posterior
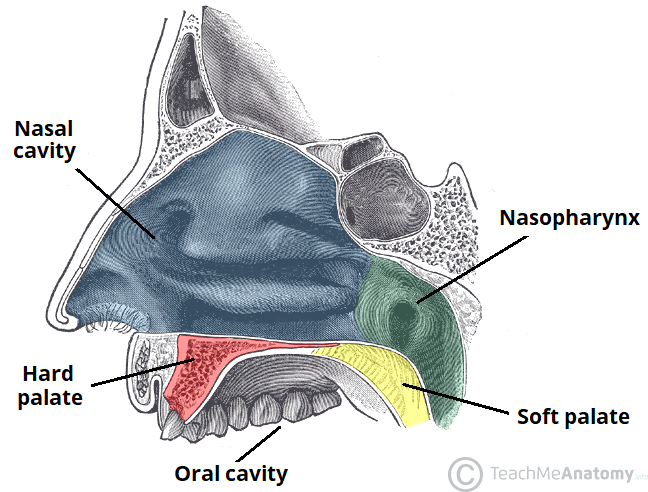
Oral Cavity: Velum (soft palate)
extends posteriorly from hard palate (palatine bone)
moveable structure separating oral/nasal cavities
uvala
terminal extension of velum
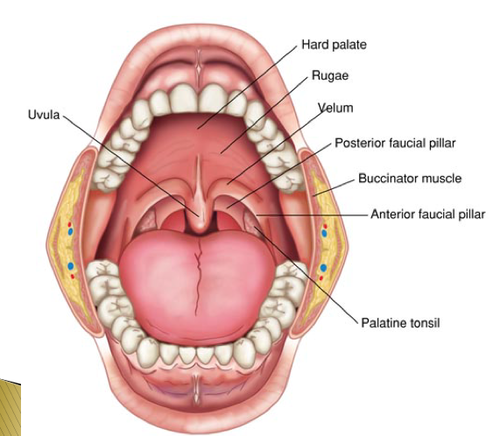
Oral Cavity: faucial arches
tissue bands extending downward from velum
anterior arches (palatoglossal arch)
posterior arch (palatopharyngeal or facial arch)
faucial arch from the posterior border of oral cavity
Buccae
Cheeks
Buccal Cavity
Lateral Sulcus: space between gums and cheeks
lateral to oral cavity
dysphagia can occur (pocketing of food in the buccal cavity)
Dentition
arrangement of teeth
16 per arch for adult teeth
Incisors
cutting
central incisors (2 per arch)
lateral incisors (2)
Cuspid
canine/eyetooth
single cusp
used for tearing
has the longest root
2
Bicuspid/Premolar
4 per arch
2 cusps
present only in adults
Molars
6 in total
1st molar: largest
2nd: 3-4 cusps
3rd: wisdom teeth
multiple roots
Deciduous Teeth
baby teeth; milk teeth
typically erupt between 6-9 months
10 teeth per arch
only 2 molars per side
shedding occurs (6-9 years)