5. pigmented lesions
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what are the 10 categories of pigmented lesions discussed?
amalgam tattoo
medication induced pigmentation
systemic metallic intoxications
oral melanotic macule
post inflammatory hypermelanosis
oral melanocanthosis
syndromes and systemic causes of pigmentation
melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
nevus
melanoma
what are the categories for differential diagnosis?
developmental
reactive
autoimmune/immune-mediated
infectious
metabolic/systemic
neoplastic
premalignant/malignant
what are five sources of pigment?
melanin (melanocytes)
vascular structures
saliva/mucin
cystic fluid (pathology)
foreign material
what are the two main categories of pigmented lesions?
non-melanin associated and melanin associated
what category of pigmented lesions?
exogenous
endogenous
non-melanin associated
what category of pigmented lesion?
developmental
reactive/inflammatory
infectious
autoimmune and immune mediated
metabolic/systemic
neoplastic
premalignant/malignant
melanin-associated
which category of non-melanin associated pigmented lesions?
amalgam tattoo (focal argyrosis)
graphite and other foreign body tattoos
medication-induced pigmentation
exogenous
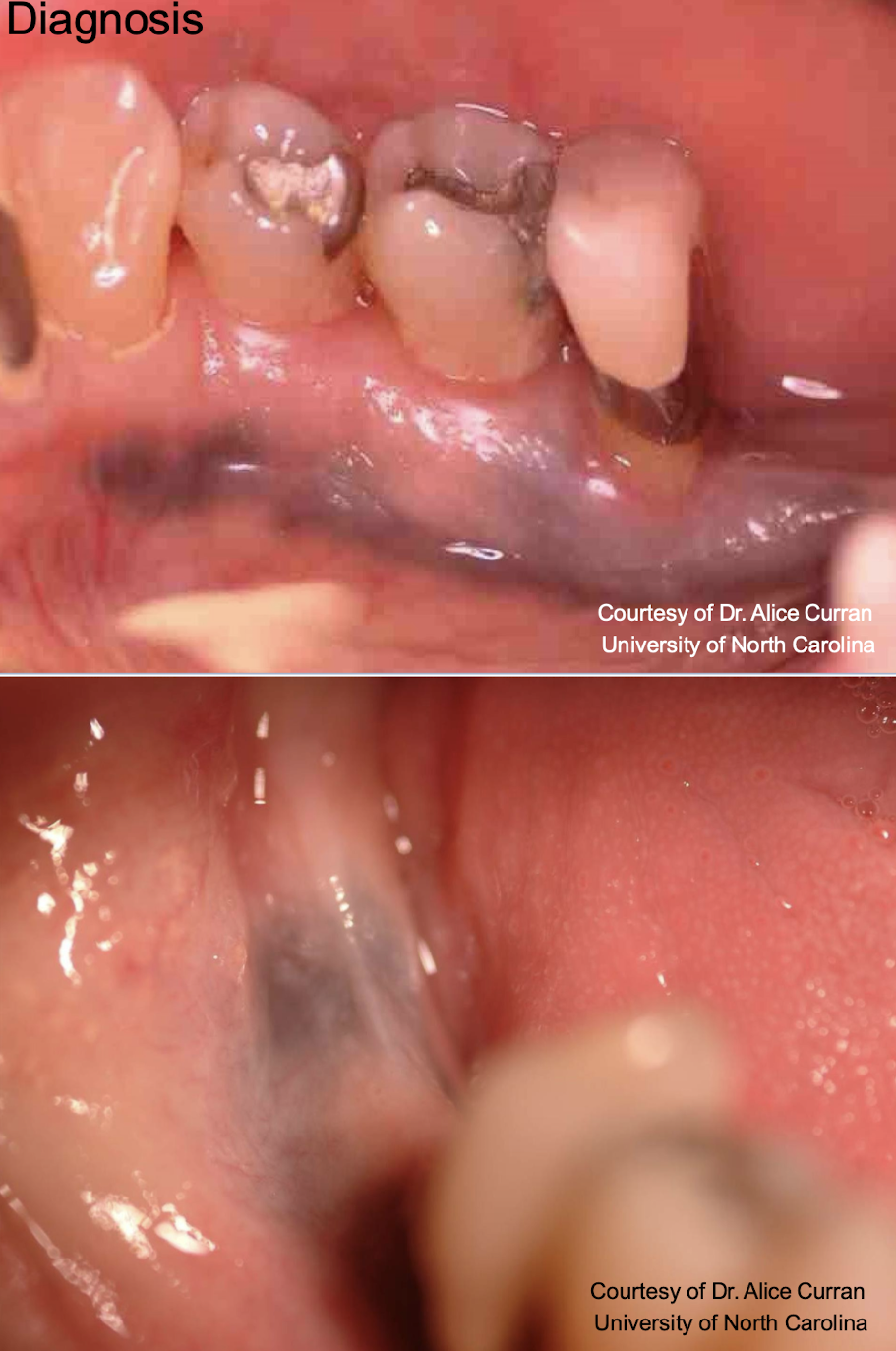
amalgam tattoo aka
focal argyrosis (silver, looks blue)
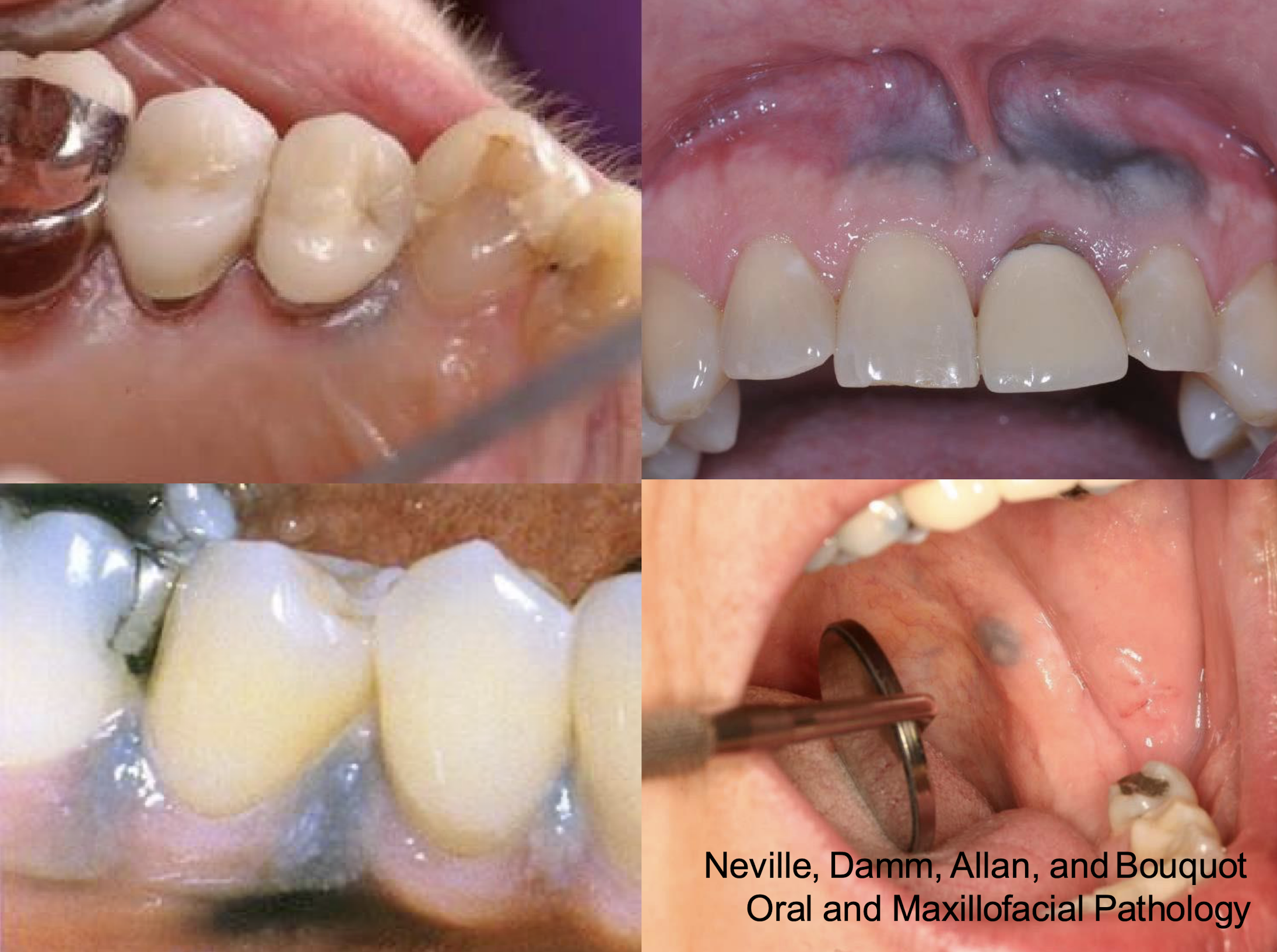
which pigmented lesion?
clinical features
Asymptomatic, localized
Blue-gray macule
Gingiva/alveolar ridge mucosa (50%)➔ buccal mucosa ➔floor of mouth
Localized around areas with: (blank) restoration
amalgam tattoo (exogenous, non-melanated)
which pigmented lesion
amalgam tattoo
amalgam tattoo,
L: purple epithelial lining and the pink the middle is the scar you can see through epithelium (graphite won’t do this)
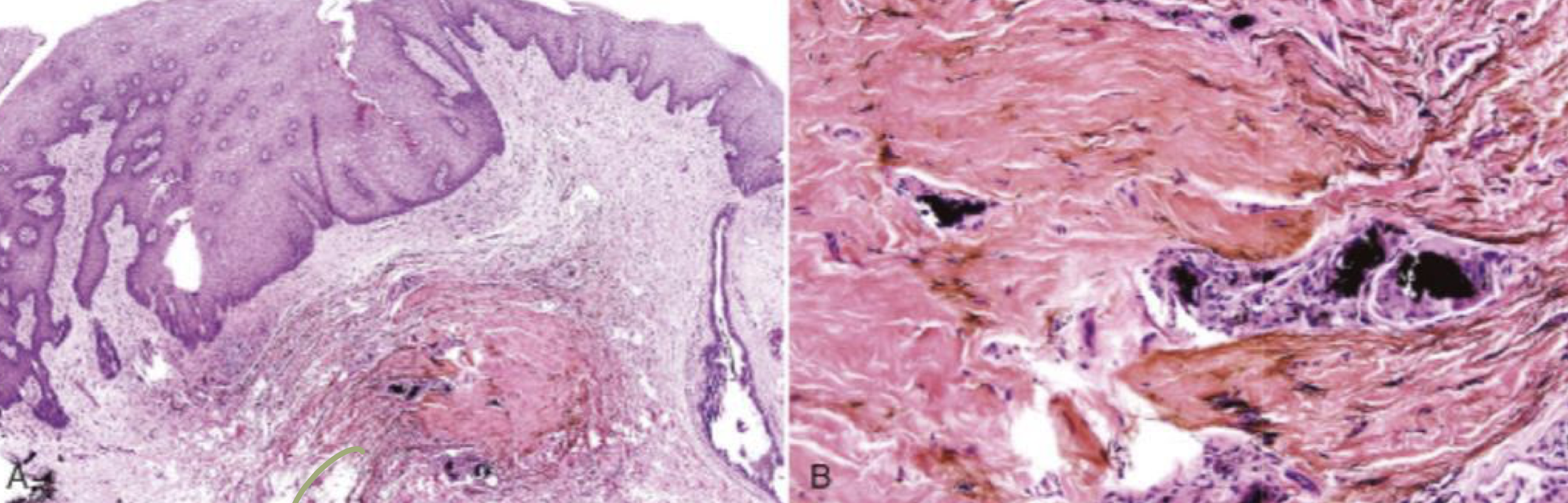
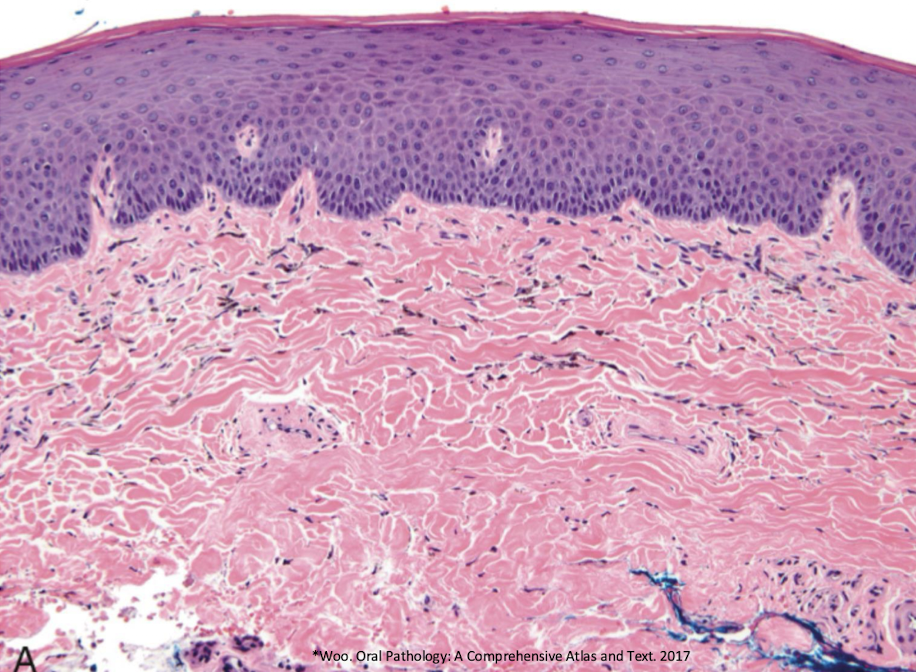
which pigmented lesion histopathological features?
pigmented fragments
staining of reticulin fibers
large fragments surrounded by fibrosis
amalgam tattoo (exogenous, non-melanated)
what can be done to treat amalgam tattoo?
laser
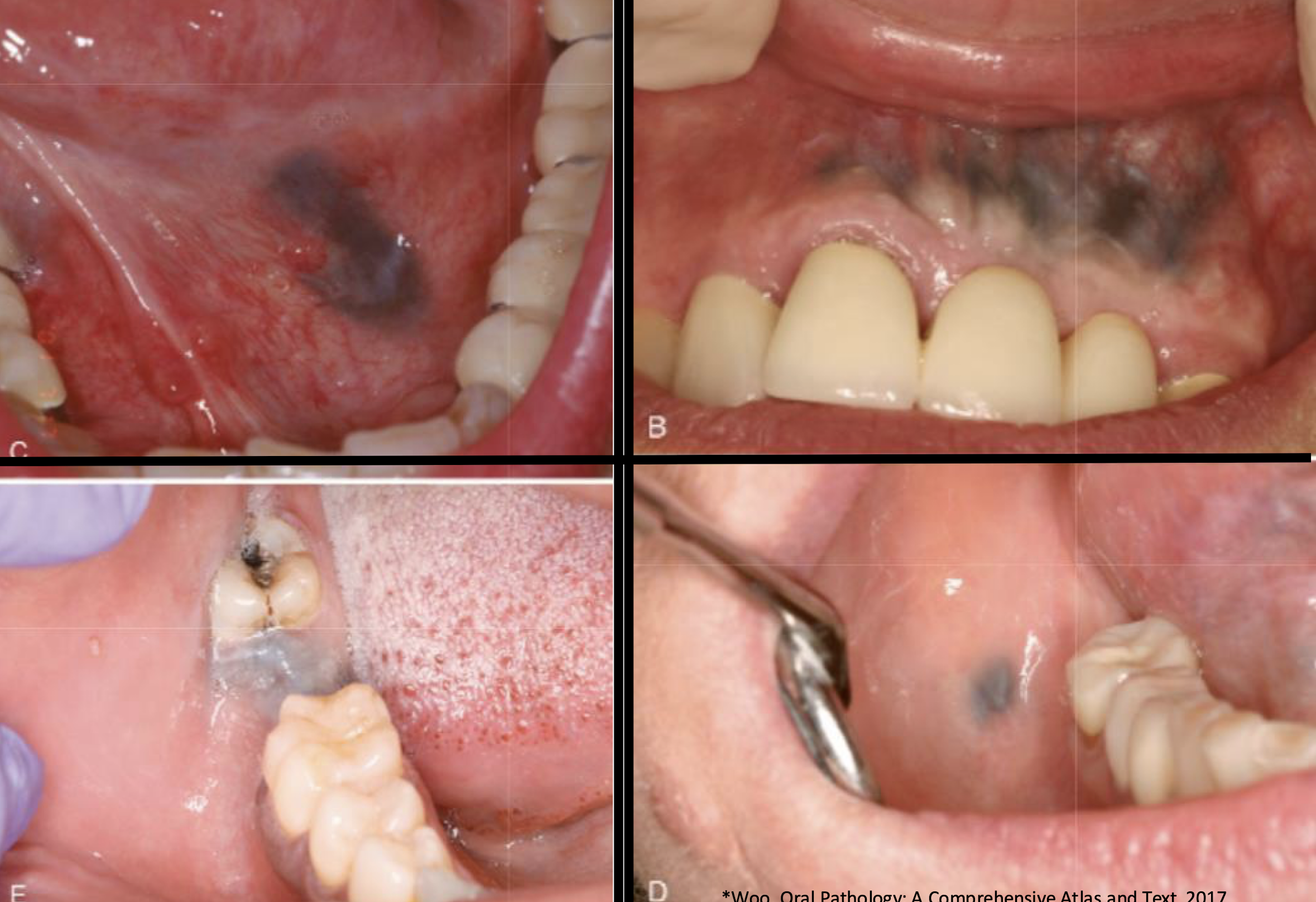
graphite and other foreign body tattoos (non-melanated, exogenous)
where does tattoo pigmentation housed?
in macrophages
which pigmented lesion etiopathogenesis?
Accumulation of melanin
Increase in melanin production (more like accumulation of med or agent itself and iron)
Decrease in melanin clearance
Accumulation of medication (ie. antimalarial for lupus)
Synthesis of special pigments (I.e. Lipofuscin)
Deposition of iron
medication-induced (non-melanated, exogenous)
clinical features of which pigmented lesion?
diffuse, painless, symmetric bluish-gray macule
melanonychia (nail bands) and skin lesions
medication-induced pigmentation
amalgam tattoos appear where 50% of the time?
gingiva/alveolar ridge mucosa
unlike amalgam tattoos where do medication-induced pigmentations occur?
on palate and usually larger
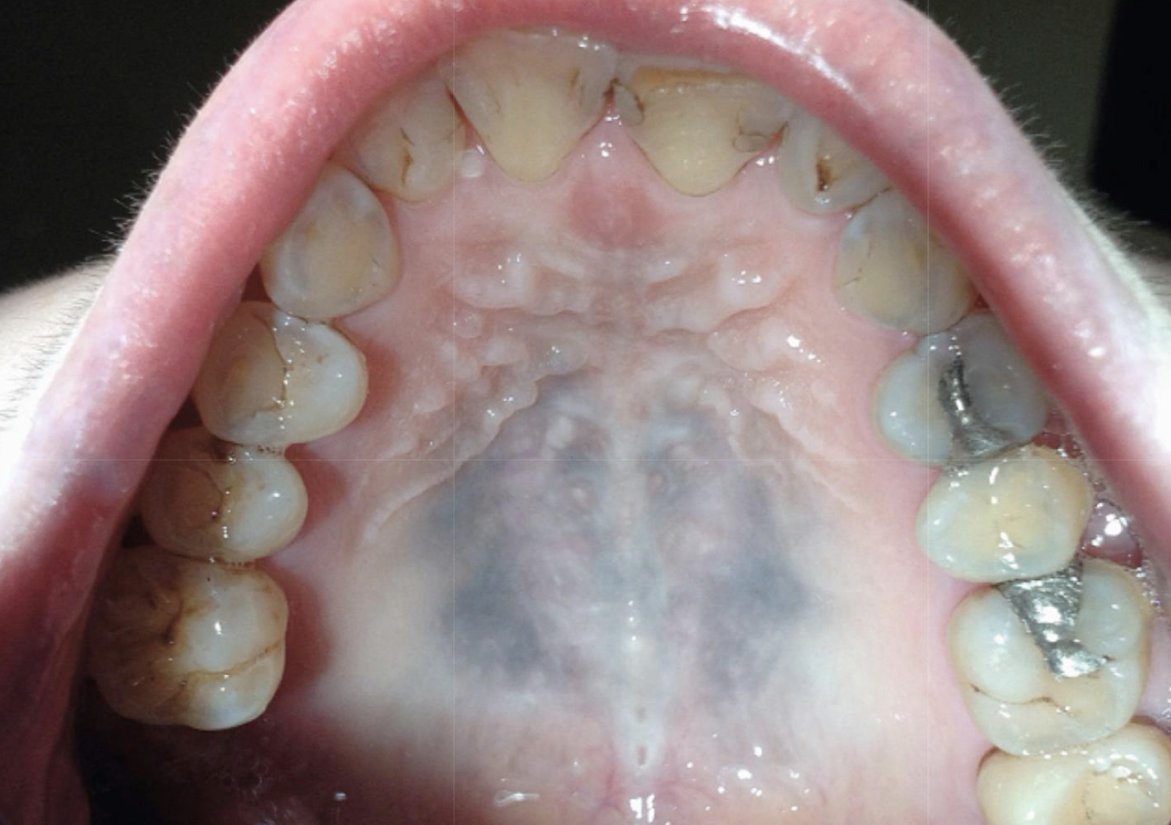
medication-induced
what are the medications associated w hyperpigmentation?
minocycline
antimalarials
clofazimine
tranquilizers
hormones
heavy metals
amiodarone
which medication proposed source of pigmentation: hyperproduction of melanin, complex w iron, or stained bone?
minocycline
which medication proposed source of pigmentation: hyperproduction of melanin?
antimalarials and hormones
which medication proposed source of pigmentation: chelated metabolites of med?
clofazimine
which medication proposed source of pigmentation: med/metabolites and/or accumulation of melanin?
tranquilizers
which medication proposed source of pigmentation: granules of metal distributed throughout blood vessels?
heavy metals
which medication proposed source of pigmentation: increased production of lipofuscin?
amiodarone

imatinib-induced hyperpigmentation
what is the worry with pigmented lesions?
melanoma
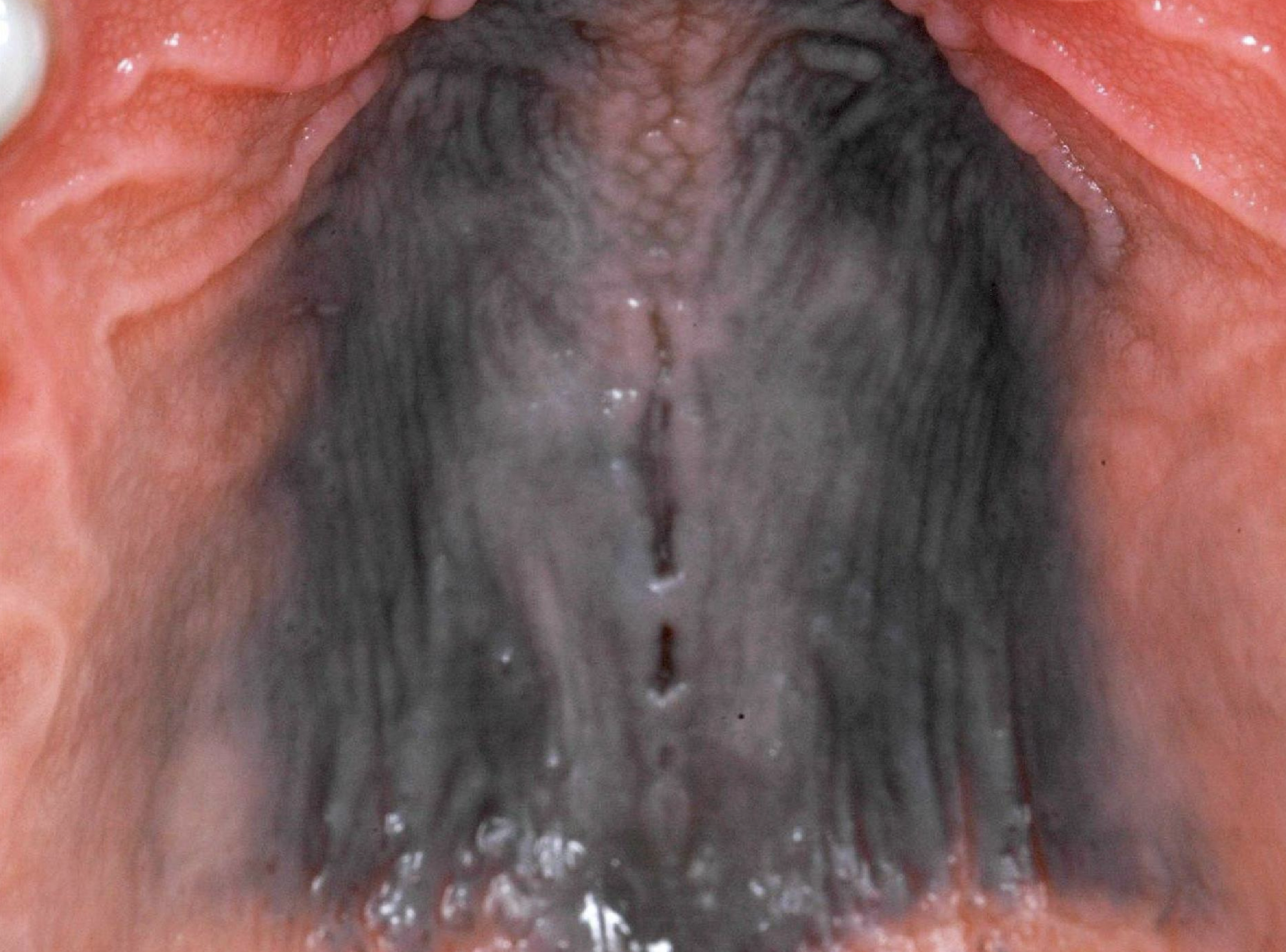
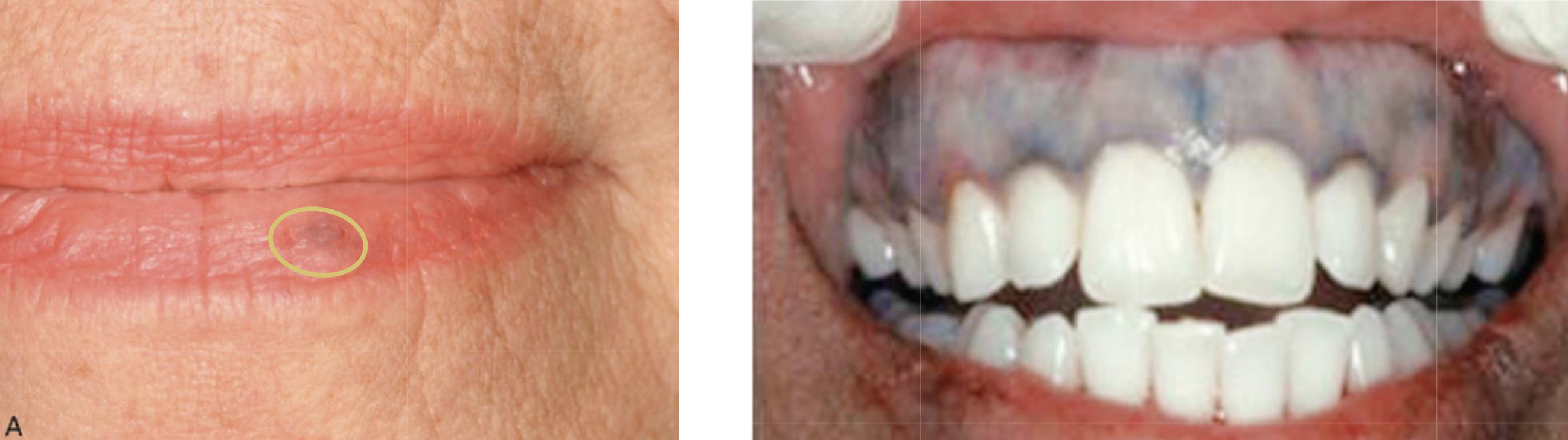
medication-induced pigmented lesion
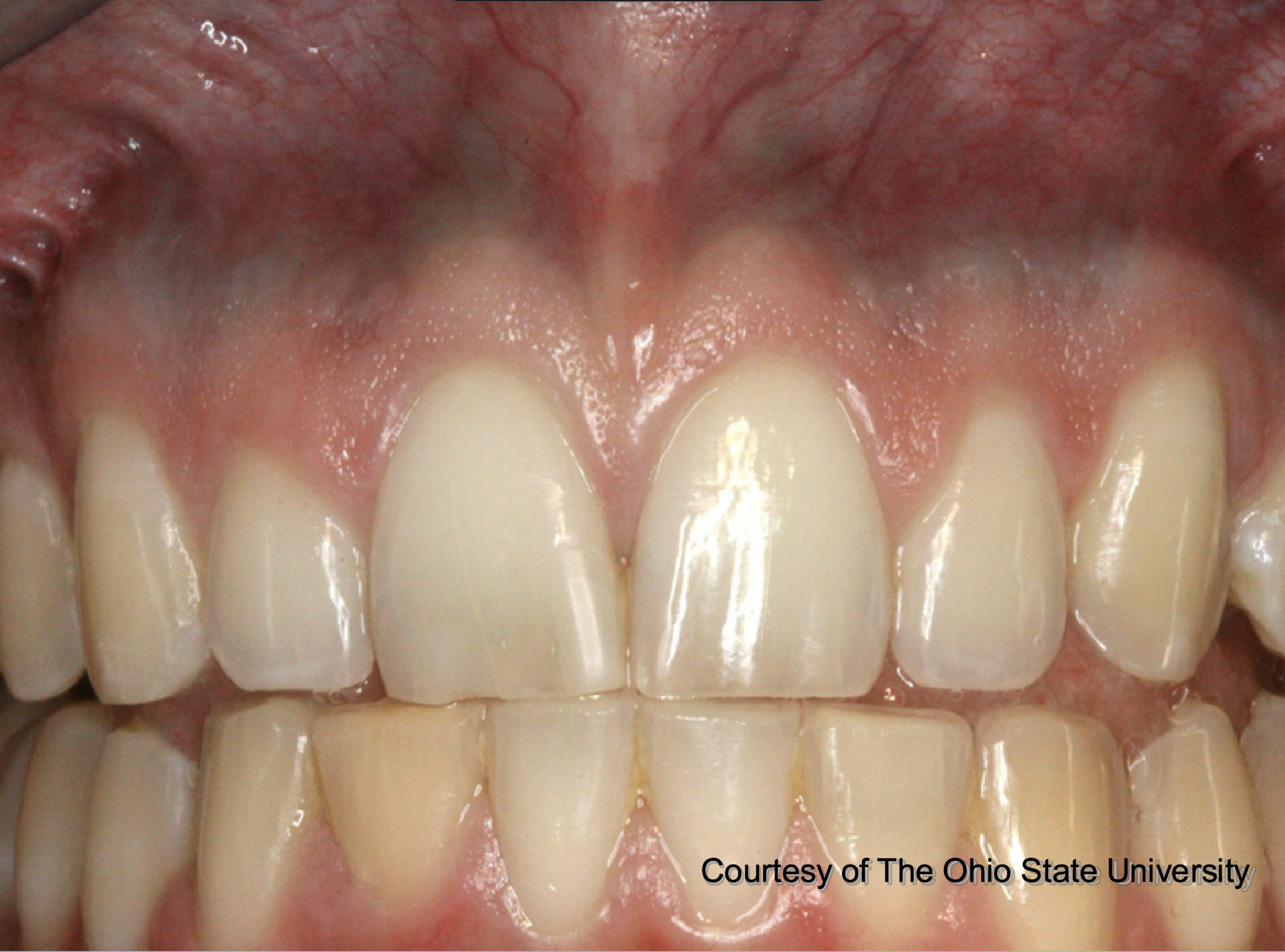
pt also has pigmented lesions in vestibule, on palate, tori, etc
medication-induced pigmented lesion
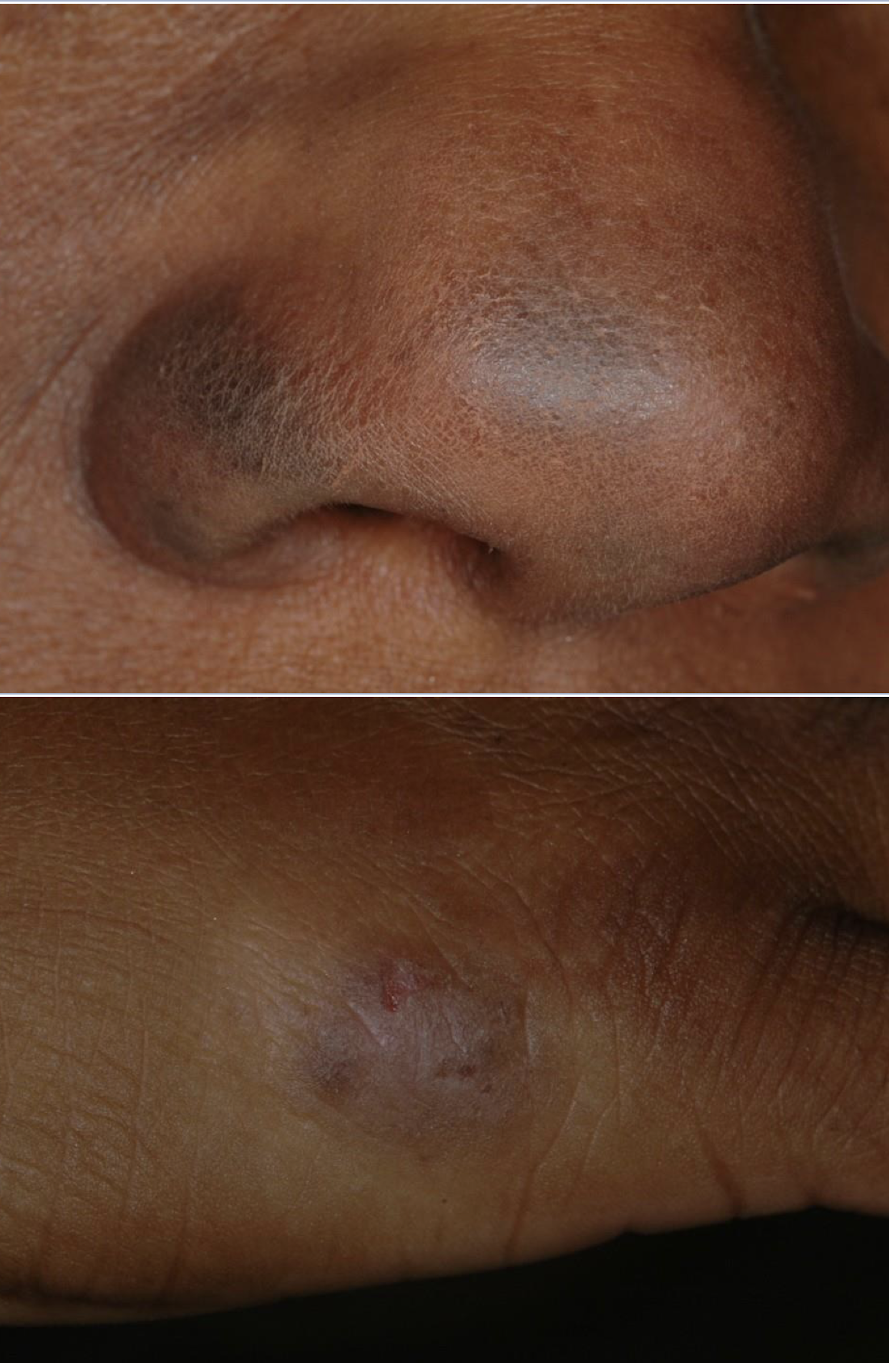
medication-induced pigmented lesion can appear on skin
amalgam tattoo
antimalaria for immune related purposes, milatinab or quinone
no scarring unlike amalgam tattoo

bluestain = iron, medication-induced pigmented lesion
the most common meds to cause drug-induced gingival pigmentation include all except:
A. minocycline
B. chloroquine (malaria)
C. cyclophosphamide (leukemia, lymphoma immunosuppressant)
D. corticosteroids
E. azidothymidine (AZT, HIV antiviral)
D. corticosteroids
what is heavy metal toxicity and what are the relevant metals?
Pigmentation of marginal gingiva, tongue tremor, metallic taste, excessive salivation, trichotillomania, bruxism
Lead, mercury, silver, bismuth, gold

heavy metal toxicity, leeches through saliva and GCF
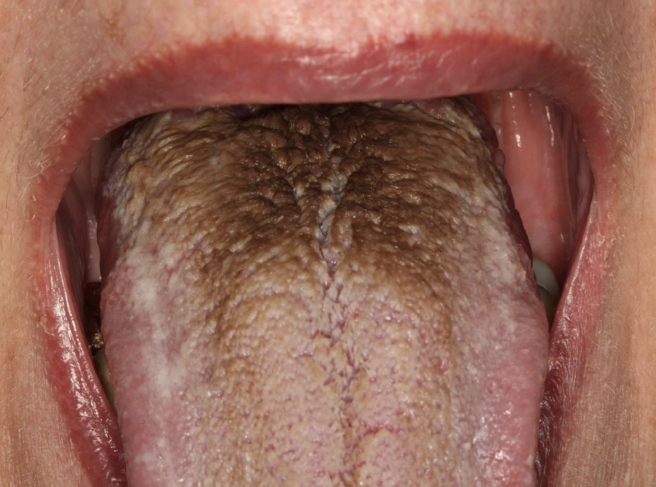
coated (hairy) tongue
non-melanated
exogenous: accumulation of keratin build on the filiform papillae; color from trapping of bacteria, yeast, or debris
coated (hairy) tongue
what are the two types of non-melanated endogenous pigmented lesions?
hemosiderin and bilirubin
what is hemosiderin?
a brown-yellow pigment that accumulates in tissues when red blood cells break down. It is composed of iron oxide and protein.
what is bilirubin?
a yellowish pigment formed when old red blood cells are broken down. It is a waste product that is processed by the liver and excreted in bile, which gives feces their color

hemosiderin
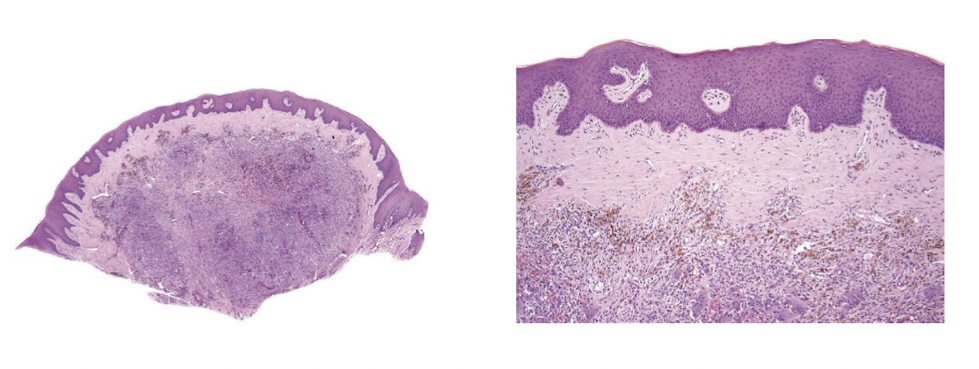
hemosiderin

bilirubin (liver, bile - also in blood and when levels too high = jaundice)