Ch. 39 Nutrition and Oral Hydration
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Nutrients provide energy for cellular metabolism, tissue maintenance and repair,
Organ function, growth and development, and physical activity.
Water is critical for all body fluid and cellular functions.
Carbohydrates provide most of the body’s energy.
1 gram of fat = 9 kcal.
A, D, E, and K.
Newborns and infants.
How much kcal/kg do infants need for the first 6 months?
108 kcal/kg.
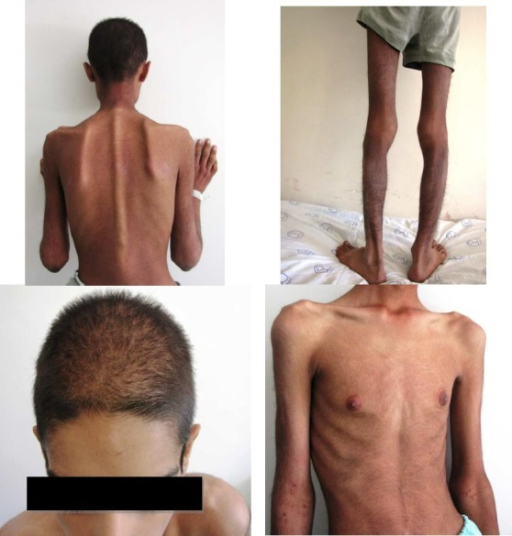
What are two characteristics of anorexia nervosa?
Significantly low body weight and
Fear of being fat.
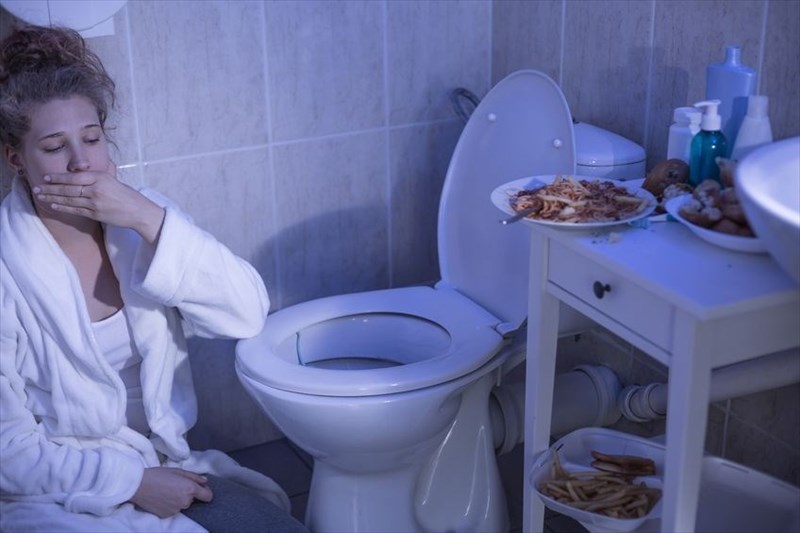

Describe bulimia nervosa.
Binge eating followed by purging, such as vomiting or using diuretics.
BMI 30 or greater.
< 18.5 is considered underweight, while a
BMI 25 to 29.9 is classified as overweight.
Normal BMI is between 18.5 and 24.9.
Illness, medications, pain, depression, and unpleasant environmental stimuli.
Increased fluid intake.
Rationale: Older adults have a decreased sense of thirst, which can lead to dehydration.
Nutrient density is more important than quantity for their growth and development.
Areas to modify in nutrient intake or caloric intake.
Which type of diet should a client with dysphagia expect?
A pureed diet with thickened liquids.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, change in weight, and weakness.
Instruct the client to tuck their chin when swallowing.
Do NOT use a straw.
Give Pureed foods and thickened liquids to help prevent aspiration.
Measure and calculate all fluid intake and output in mL.
Daily weights
Daily I&O
1 kg = 1 L of fluid.
High protein, calcium, iron, and iodine needs due to high metabolic demands.
Which of the following options are necessary for metabolism?
Proteins
Fats
Carbs
Vitamins
Vitamins: essential nutrients that aid in metabolic processes and overall health.
Fat-soluble vitamins are A, D, E, and K. The water-soluble vitamins include C and the B complex (eight vitamins). QEBP
Solid foods in infants can be introduced at which age?
Solid foods can be started at 6 months of age.
Single-grain cereals like rice or oatmeal.
Introduce one new food at a time and monitor for allergic reactions.
Nutrient density vs quantity in toddlers (1 to 3 yrs) and pre-schoolers (3 to 6 yrs)?
Nutrient density is more important than quantity.
Calcium and phosphorus are important for bone health.
Important nutritional aspects in School-age children (6 to 12 yrs) include:
They grow at a slower & steadier rate, w/ a gradual decline in energy requirements.
Tend to eat foods high in carbohydrates, fats, and salt.
Need supervision to consume adequate protein and vitamins C and A.
Factors affecting nutrition in Adolescents (12- 20 yrs) include:
Body image and appearance, fast foods, peer pressure, and fad diets influence adolescents’ diets.
Metabolic demands are high and require more energy.
Factors affecting nutrition in Older Adults (65+) include:
A slower metabolic rate requires fewer calories.
Thirst sensations diminish, increasing the risk for dehydration.
Older adults need the same amount of most vitamins and minerals as younger adults.
Calcium is important for both men and women.
Many older adults require carbohydrates that provide fiber and bulk to enhance gastrointestinal function.
A nurse in a senior center is counseling a group of older adults about their nutritional needs and considerations. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
Recommended intake of daily fiber decreases due to their lower caloric intake.
Older adults are more prone to dehydration than younger adults.
Many older adults need calcium and supplementation (to prevent bone demineralization).
Fluid Intake and Output (I&O) measurements include:
Fluid intake includes ALL liquids (oral fluids, foods that liquefy at room temperature, IV fluids, IV flushes, IV medications, enteral feedings, fluid instillations, catheter irrigants, tube irrigants).
Fluid output includes all liquids (urine, blood, emesis, diarrhea, tube drainage, wound drainage, fistula drainage).
Expected Findings of Poor Nutrition include:
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation
Flaccid muscles
Mental status changes
Loss of appetite
Change in bowel pattern
Spleen and liver enlargement
Dry, brittle hair and nails
Loss of subcutaneous fat
Dry, scaly skin
Inflammation and bleeding of gums
Poor dental health
Dry, dull eyes
Enlarged thyroid
Prominent protrusions in bony areas
Weakness and fatigue
Change in weight
Poor posture
Nursing interventions for patients with dysphagia or at risk of aspiration include?
Position in high Fowler’s position or in a chair.
Support the upper back, neck, and head.
Have clients tuck their chins when swallowing to help propel food down the esophagus.
Avoid the use of a straw.
Observe for aspiration and pocketing of food in the cheeks or other areas of the mouth.
Observe for indications of dysphagia (coughing, choking, gagging, and drooling of food).
Keep clients in semi-Fowler’s position for at least 1 hr after meals.
Provide oral hygiene after meals and snacks.
Types of therapeutic diets include:
NPO (nil per os): no food or fluid at all by mouth, not even ice chips, requiring a provider’s prescription before resuming oral intake
Clear liquid: liquids that leave little residue (clear fruit juices, gelatin, broth); can see through the glass/container.
Full liquid: clear liquids plus liquid dairy products and all juices. Some facilities include pureed vegetables in a full liquid diet.
Pureed: clear and full liquids plus pureed meats, fruits, and scrambled eggs
Mechanical soft: clear and full liquids plus diced or ground foods
Soft/low-residue: foods that are low in fiber and easy to digest (dairy products, eggs, ripe bananas)
High-fiber: whole grains, raw and dried fruits
Low sodium: no added salt, or 1 to 2 g sodium
Low cholesterol: no more than 300 mg/day of dietary cholesterol
Diabetic: balanced intake of protein, fats, and carbohydrates of about 1,800 calories
Dysphagia: pureed food and thickened liquids
Regular: no restrictions
For patients with a orders to “restrict oral fluid intake,” what should the nurse do to maintain strict I&Os?
Remove water pitcher from bedside.
Inform dietary staff of the amount of fluid to serve with each meal tray.
Inform staff of each shift of the amount of fluid clients may have in addition to what they receive with each meal tray.
Record all oral intake, and inform the family of the restriction.
Examples of foods high in fiber (whole foods) include:
Cooked barley (barely & oats)
Pureed broccoli (broccoli and cabbage in coleslaw)
Lentil soup (lentils and black beans)
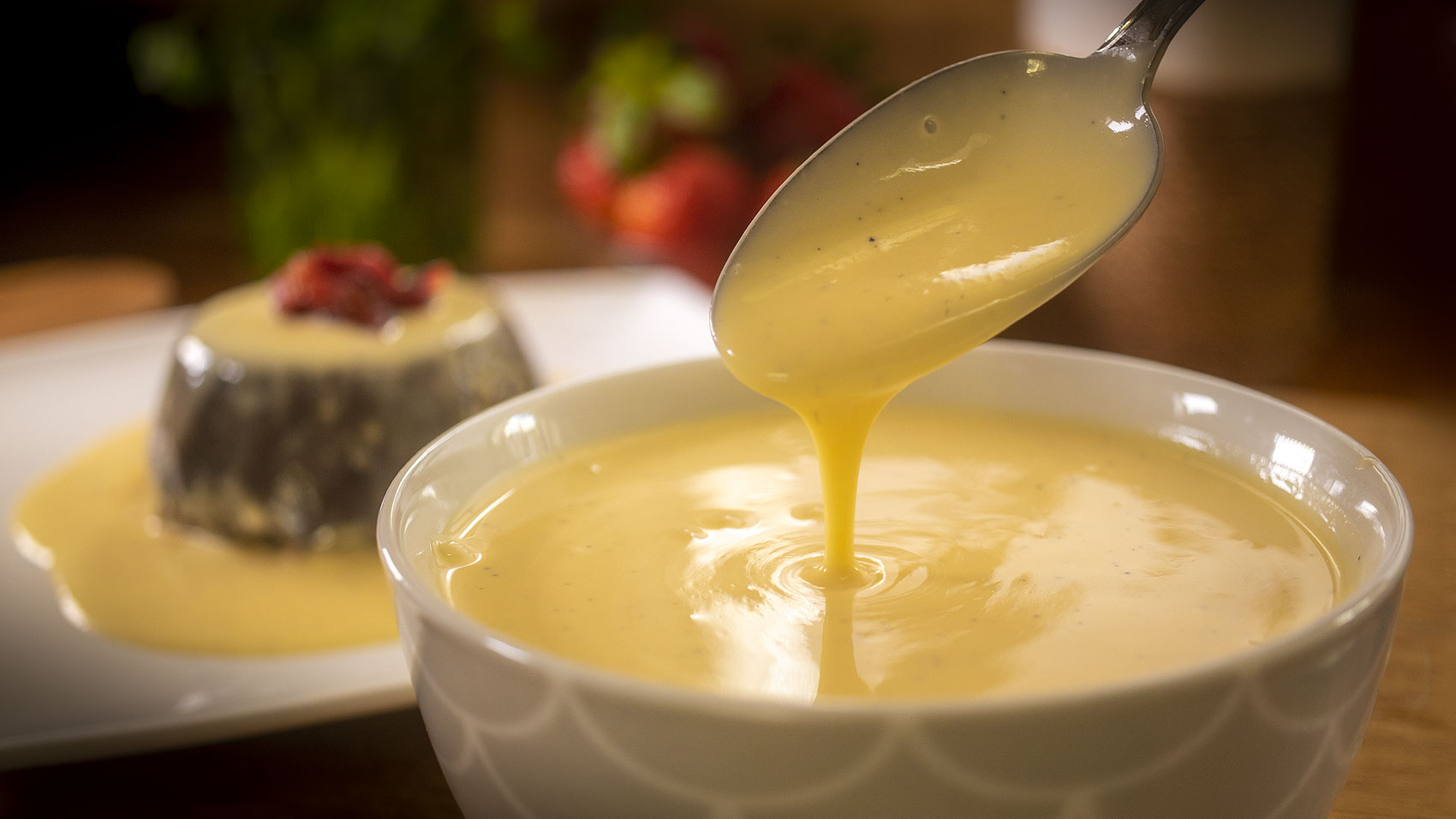

Examples of low-residue diets (low fiber) include:
Vanilla custards, yogurt
Dairy products
white rice, bananas, cooked carrots, eggs, and tender meats.