3.1 Pulmonary Pathology
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What are the 4 physical properties of the lungs
compliance
elasticity
surface tension
resistance to airflow
define compliance
the ability of the lings to expand/distend
Why is it essential that the residual volume remain in relation to compliance
having a little bit of air within the lungs before trying to inflate will cause the lungs to be more compliant
Compliance ____ as you reach TLC
decreases
define elasticity
the ability of an object/material to resume its normal shape after being stretched or compressed (ability to recoil)
What causes elasticity
change in pressures and the elasticity of the lung tissue
What is the risk with lungs becoming over compliant
decrease elasticity
what causes surface tension
the air/water interaction
Why can moisture in alveolar sacs be dangerous id not properly gerring air in
the sides can come together and cause the sac to collapse
What is the role of surfactant
keeps the sacs with unequal pressures open by equalizing the pressures/changing the refill times
What causes an increased resistance to flow
bronchoconstriction
PSNS
mucous and edema in airway
What causes a decrease in resistance to flow
SNS
bronchodilation
What is resistance to flow mainly based off of
vasomotor tone
Absolute lung volume factors
height/weight
age
gender
ethnicity
What are the affects of height on absolute lung volume
taller: larger
shorter: smaller
What are the affects of weight on absolute lung volume
increased central waist: smaller
decreased central waist: larger
What are the affects of age on absolute lung volume
lung function peaks at 25 y/o and decreases over time
What are the affects of genderon absolute lung volume
males have typically larger lungs
What are the affects of ethnicity on absolute lung volume
European decent: larger
African decent: smaller
Clinical signs of pulmonary pathology
abnormal PFT
Chest XR
ABGs
Auscultation
CV (bradycardia or hemorrhage)
vital signs
cor pulmonale
What are signs
objective tests done to show pathology
What are symptoms
what the pt is experiencing to indicate pathology
Clinical symptoms of pulmonary pathology
respiratory pattern
nasal flaring
grunting
crying with decreased volume/strength (silent)
cyanosis
dyspnea
cough
weight loss
define ventilation
movement of air (gas) in and out of lungs
normal resting RR
12-20 breaths/min
normal resting TV
~350-500 mL/breath
how is ventilation calculated
=volume/min
normal ventilation rate
~5 L/min
define tidal volume (TV)
volume of air inhaled and exhaled with each breath
define inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
additional volume of air that can be taken in beyond normal tidal inhalation
define expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
additional volume of air that can be let out after normal exhalation
define residual volume (RV)
volume of air that remains in the lungs after a forceful expiratory effort
What is considered the top of a resting breath
in
what is considered the bottom of a resting breath
out
define inspiratory capacity (IC)
maximum amount of air that can be inhaled after normal tidal exhalation
What volumes make up the IC
TV + IRV
define functional capacity reserve/functional residual capacity (FCR)
the amount of air remaining in the lings at the end of normal tidal exhalation
What volumes make up the FCR
ERV+RV
define vital capacity
max amount of air that can be exhaled following a max inhalation
What volumes make up the VC
IRV+TV+ERV
define total lung capacity (TLC)
max volume to which the lungs can be expanded
What volumes make up the TLC
TV+IRV+ERV+RV
What is the typical TLC
5-6L
What percentage of the TLC is IRV
50%
What percentage of the TLC is TV
10%
What percentage of the TLC is ERV
20%
What percentage of the TLC is RV
20%
What is the purpose of the pulmonary function test (PFT)
can indicate type/progression/reversibility of disease
What is important for us to keep in mind when running a pt through PFT
make sure they are giving appropriate effort
how many attempts does the pt have to perform the PFT
3
What is FEV1
forced expiratory volume in 1 sec
instructions to give pts for the PFT
keep lips tight over mouth piece
breath in as much as you can
then breath out as fast as you can
then breath in again
What does a PFT graph look like
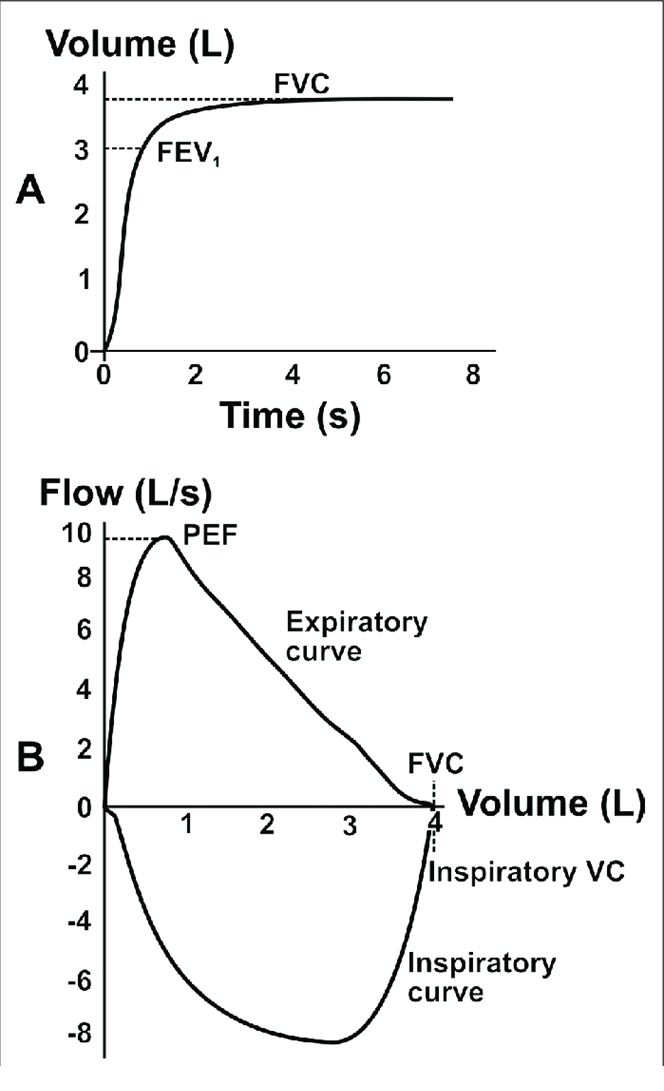
What is the importance of the FEV1/FVC ratio
can show us potential pathology
What are the types of pathology
obstructive, restrictive, combined
What does a PFT graph look like for obstructive pathologies
large volume (wide), with delayed expiration (concave)
What does a PFT graph look like for restrictive pathologies
very small volume, but shape appears normal
What does a wheeze sound like
high pitched, musical
What causes a wheeze sound
airway obstruction/narrowing
What pathology correlates to wheeze
asthma
What does a rhonchi sound like
low pitched and potential gurgle (snoring)
What causes a rhonchi sound
secretions
What pathology correlates to rhonchi
COPD, Bronchitis
What does a pleural friction rub sound like
low/deep grating (sand paper)
What causes pleural friction rub sounds
inflammation
What pathology correlates with pleural friction rub
pleuritis
What does stridor sound like
barking cough with potential wheeze (seal)
What causes stridor sound
obstruction/foreign body
what do crackles sound like
bubbling, popping
What cause course crackle sound
excessive fluid
What causes fine crackle sound
small airway disease
What pathology correlates with crackles
PNA, pulmonary edema, ARD, HF
What is the main cause of Kussmaul breathing
diabetic ketoacidosis
WHen is Cheyne-stokes breathing seen
in sleep apnea or toward the end of life
Describe Cheyne-stokes breathing
slow → rapid → no breathing
Decribe Biot’s breathing
no breaths followed by irregular/rapid breaths
describe Kussmaul breathing
rapid, deep, labored breathing