forensic science final exam study (sci205-B)(Dr.Ferko)(CBU)
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Forensic Science
Application of science to criminal & civil law.
Mathieu Orfila (1814)
Father of forensic toxicology.
Alphonse Bertillion (1878)
1st scientific sys. of personal identification through bodily measurments
Francis Galton (1892)
1st difinitive study of FINGERPRINTS & their classifications.
Leone Lattes (1915)
developed method to determine blood types & classifications from dried bloodstains
Calvin Goddard
used a comparison microscope to determine if a particular gun fired a bullet (ballistics)
Albert Osborn (1910)
developed fundamental principles of document examination
Walter McCrone
utilized microscopy and other analytical methodologies to examine evidence
Hans Gross (1893)
published a treatsie (formal doc.) on the application of scientific principles to the field of criminal investigation.
Edmond Locard (1910)
incorporated Gross' principles within a workable crime laboratory in Lyon,France.
Locard's Exchange Principle
If a criminal comes into contact w/ an obj./person a cross transfer of evidence occurs.
What is the OLDEST crime lab in the U.S?
Los Angeles Police Department
(1923)
facts abt. the FBI National Crime Lab
-established in 1932
-LARGEST lab in the world (1 million+ exams. done each year)
facts abt. California Department of Justice
-A network of crime labs established in 1972
-Regional & satelite facilities
-California Association of Criminalists
Federal Crime Labs
-FBI lab (Quantico, Virginia)
-Drug Enforcement Agency
-Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives
-U.S. Postal Inspection Services
-Defense Forensic Science Center
Basic service provided by crime labs-
-physcial sciences (chem.,physics, geology)
-biology
-fireamrs
-doc. examination
-photography
OPTIONAL services of a crime lab
-Toxicology (determines presence/absence of drugs in body)
-Latent fingerprint
-Polygraph unit (lie detector tests)
-Voiceprint analysis (voice comparison)
-Crime scene investigation unit
Functions of a Forensic Scientist
-Analysis of physical
-->Frye Standard
-Provide expert testimony
-Provide training in recognition, collection, & preservation of evidence
Frye Standard
evidence must be 'generally accepted'. Trial judges are the gatekeepers of what is admissible (Daubert case)
Other Forensic Science Services
-forensic psychiatry
-forensic odontology (dental)
-forensic engineering
-computer and digital analysis
Responsibilities of the 1ST ARRIVING OFFICER
-Preserve & protect the area
-Deal w/ violent/hazardous circumstances
-Obtain medical assisstance, evaluate condition of victs., & record statements
-Arrest prepetrators
responsibilities of OTHER officers
-isolate the area, estab. boundaries, & position guards
-identify all individuals @ scene
-detain sus. & witnesses
-exclude unatuhorized personnel-log who enters/exits scene.
Responsibilities of LEAD INVESTIGATOR
-start evaluating area
-estab. perp.'s path of entry & exit
-doc. & potograph obvious items
-walk-through to gain overview & develop srategy to examine & doc. entire crime scene.
-ensure crime scene is unaltered
spiral search method
Invetigstor starts at the perimeter of the scene and works toward the center. (good method to use when there is only one investigator)
Line Search Method
Used on large, outdoor crime scenes. Members of the search team are arranged at regular intervals, usually arm's length, and then proceed to search along straight lines.
Grid search pattern
a variation of the strip/line search pattern that is often used indoors and which overlaps a series of lanes in a cross pattern, making the search more methodical and thorough.
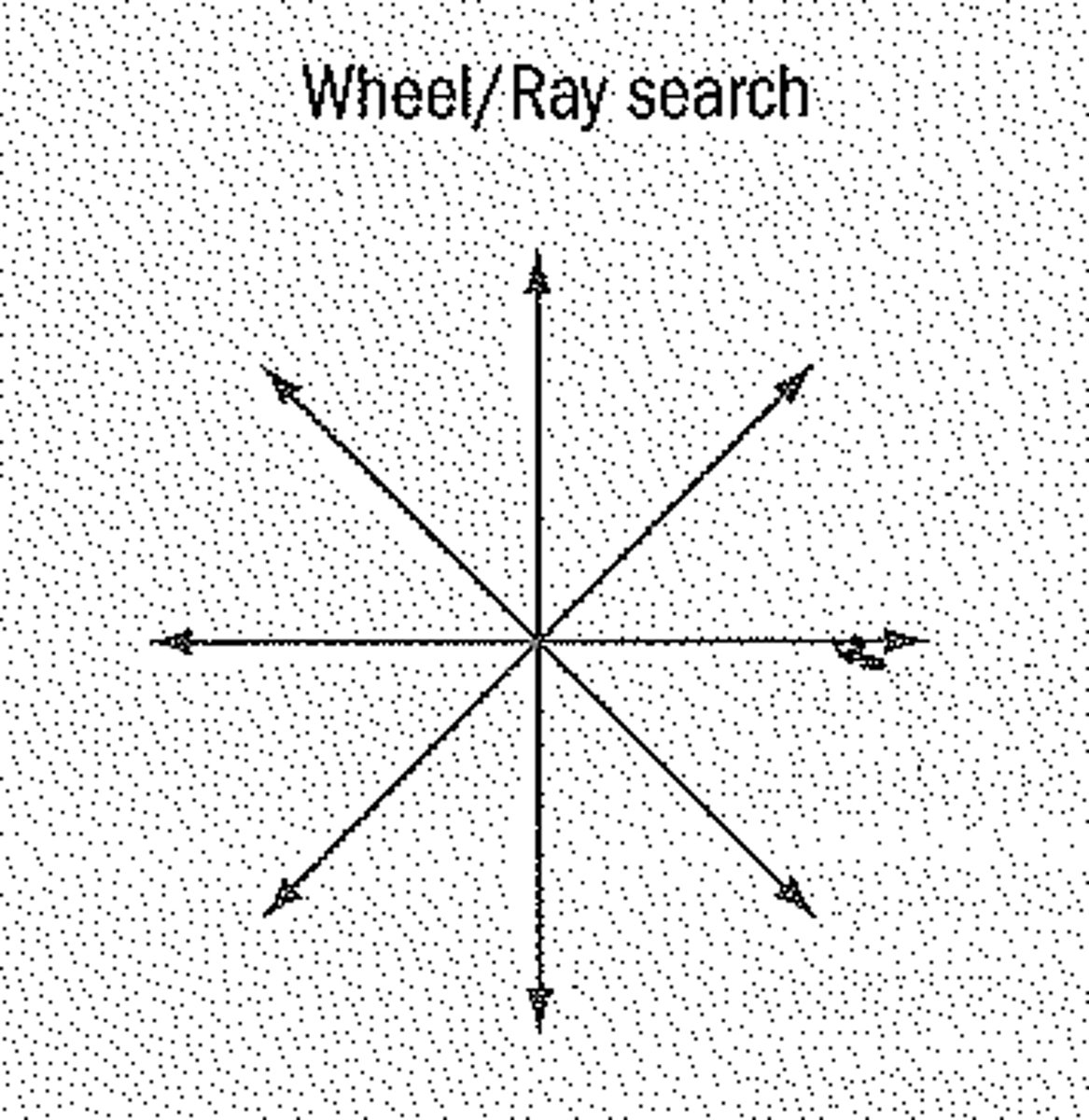
Wheel/Ray Search Pattern
SEVERAL investigators search in straight lines from the center to the boundary (outward) or from the boundary to the center (inward).
issue- misses portions in between individuals (see below)
Quadrant/Zone Search Pattern
A search method in which the crime scene is divided into smaller sections (zones or quadrants) and team members are assigned to search each section.
Fingerprint Databases
-Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification Sys. (IAFIS)
-Next Generation Identification (NGI)
DNA Databases
Combined DNA Index System (CODIS)
Ballistics Database
National Integrated Ballistics Information Network (NIBIN)
Automotive Paint Database
International Forensic Automotive Paint Data Query (PDQ)
Shoe Prints database
Shoeprint Image Capture and Retrieval (SICAR)
Physcial properties of blood (vs. water)
-(unlike water) blood is a suspension of solids & gases in a liquid
-blood (cirrcular) vs. water (tear-shaped)
-viscosity of blood lowers as its sheer rate increases (blood pumps easier @ high flow rates)
Wave Cast-Off
when a blood droplet bounces off a surface the tails of the parent & wave cast-off will point toward each other
Blood spatter analysis
-Low velocity (drop/splash)
-Medium velocity (blunt force trauma)
-High velocity (gunshot)
Blood spatter analysis can approximate
-distance from the source of the blood to the pattern
-direction from which the blood impacts
-speed the droplet was traveling
-location of the point of origin
-movement of a bleeding individual throuout the scene
Area of convergence (2d area)
a general area of convergence will appear where the strings overlap.
Transfer Bloodstains
A pattern created when a wet, bloody surface comes in contact with another surface to form a print-like pattern
Gunshot blood spatter
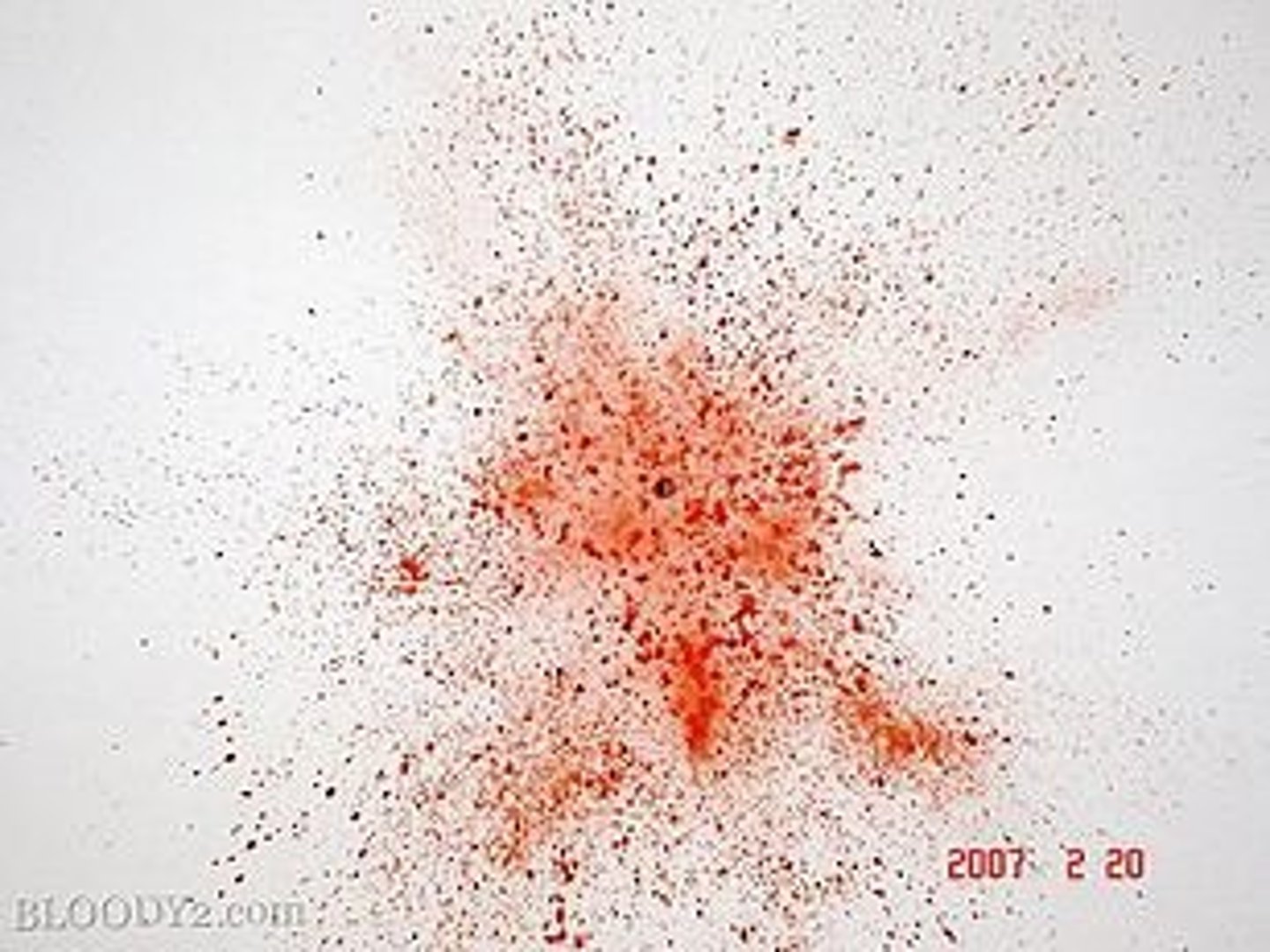

arterial spray spatter
created when a victim suffers an injury to a main artery or the heart
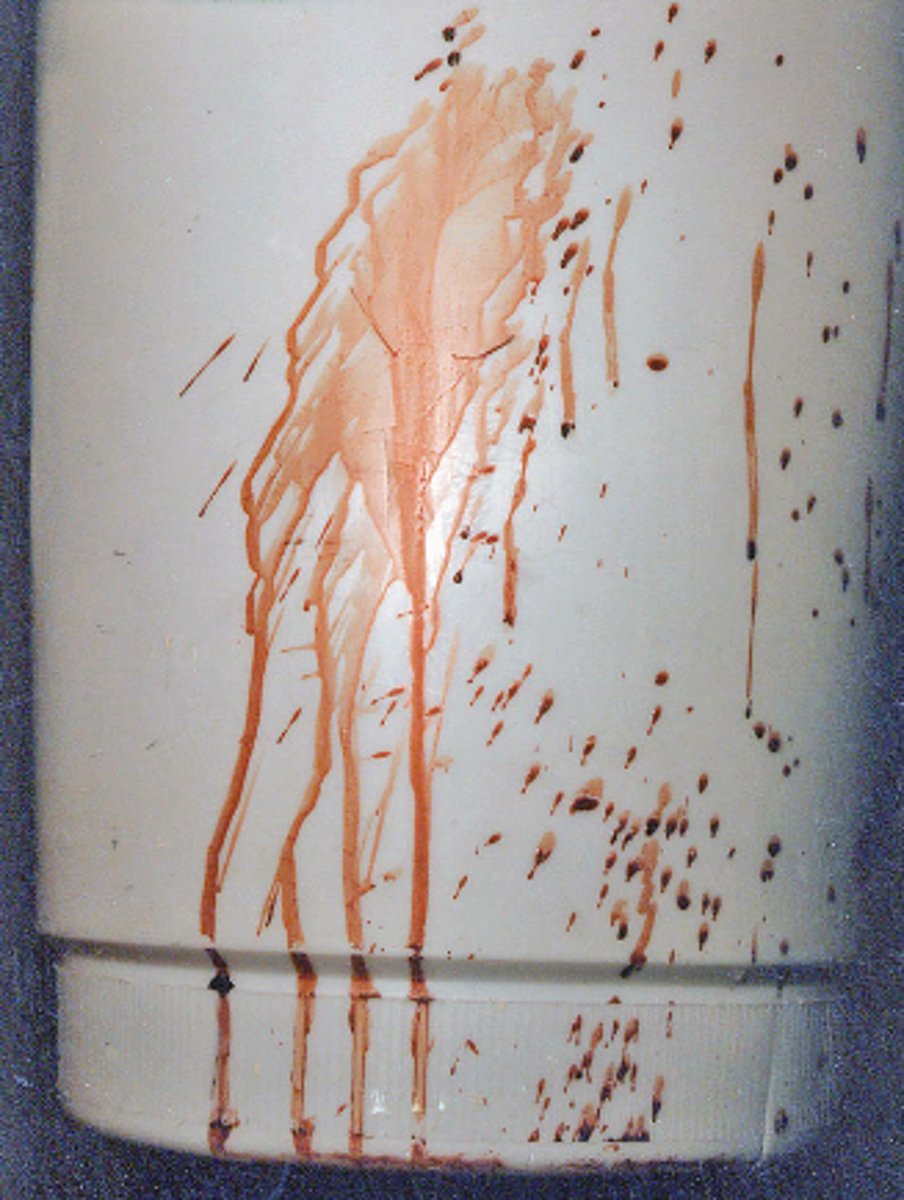

Cast-off pattern
blood projected onto a surface as a result of being flung from an object in motion
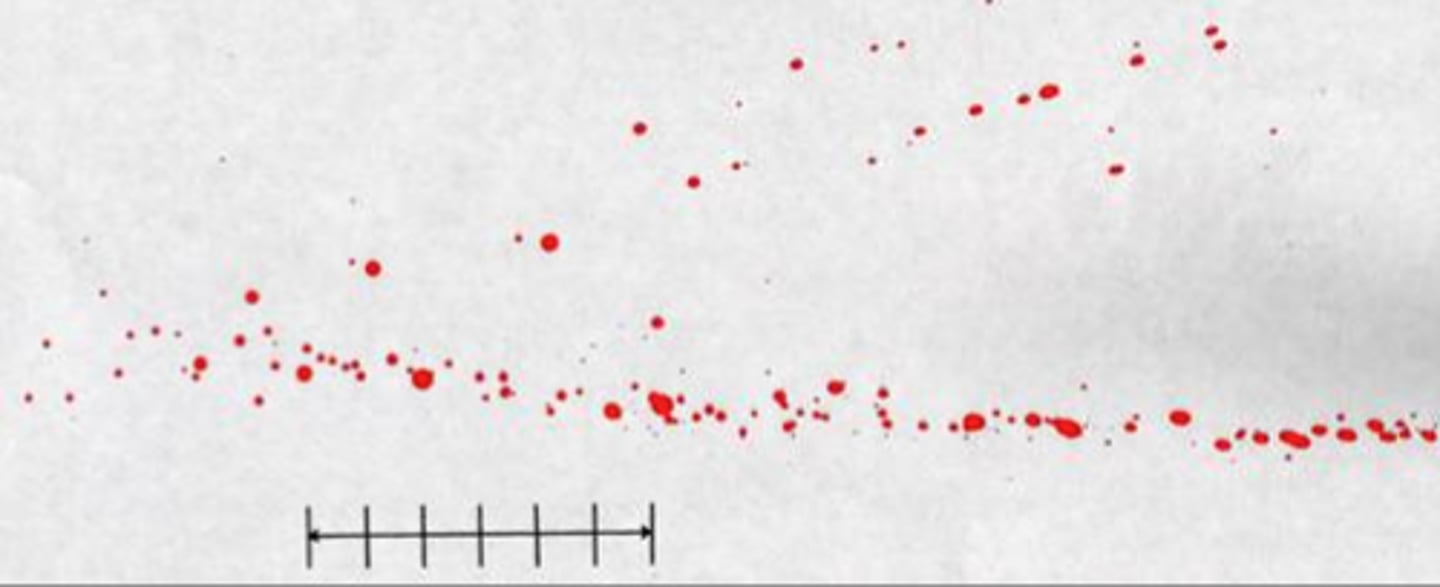

Expirated blood
Blood that is blown out of the nose, mouth, or a wound
Void blood pattern

drip trail pattern
a pattern of bloodstains formed by the dripping of blood off a moving surface or person in a recognizable pathway separate from other patterns
Forensic Pathologist (Medical Examiner)
A medical doctor who autopsies a victim to determine cause of death, manner of death, and approx. time of death
Coroner
an official who investigates violent, sudden, or suspicious deaths.
-EX. RIverside,CA
autopsy
examination of a dead body; postmortem & the goal is to examine the manner of death.
How does an M.E define 'cause' of death?
That in which initiates a series of events resulting in death.
(EX- a wound/illness that results in death years later)
laceration
a torn or jagged wound
incision (cut)
caused by a clean, sharp-edged object
stab
to injure someone with a sharp pointed object such as a knife
chop
wound caused by a heavy instrument w/ @ least one sharp cutting edge
-EX. axe
blunt force
may cause a laceration or contusion (bruise) (bat/pipe)
Sharp force injuries
cut or stab (knife/blade)
Asphyxia
interference with the intake of oxygen (fire, carbon monoxide, hanging, or smothering)
gunshot wound
range of fire (contact, burns, stippling, enterance/exit)
substance abuse
overindulgence/dependence on an addictive substance, especially alcohol or drugs.
defensive wounds
injury typically sustained by the victim. (palm, finger, forearm, upper arm, back)
Homicide
(non-accidental) death resulting from gross negligence, recklessness, or intentional actions of another person
suicide
intentionally taking one's own life
accidental
no intent to cause harm through gross negligence
Natural causes
caused by diseases or enviornment
undetermined
-No rational classification
Algor Mortis
cooling of the body to enviornmental temp.
Livor Mortis
blood pooling in parts of body closest to the ground (20 mins.-3 hours after death)
Lividity (coloring)
blue-purple where blood pools
Blanching
lividity pressed out of vessels when skin is pressed
Rigor Mortis
rigid muscles-evolves over 24 hrs; disappears after 36 hrs.
potassium eye levels
Vitreous humor(fluid in the eye)- potassium slowly released after death. Fluid compared b/t both eyes.
Autolysis
self-digestion of cells by enzymes
putrefaction
decomposition by bacteria & other microorganisms. Causes bloating, green/purple discoloration, foul smell.
Forensic Anthropology
Identification and examination of skeletal remains
Determining age and sex decedent
-sex (from size and shape of pelvic bones & cranium)
- length of bones
-(teeth for children)
-racial ancestry from shape of cranium
determining time of death
observe stage development of maggots or arrival of insects
-BLOWFLY (green/blue colored fly) arrives w/in 24 hrs
-feeds on dead tissue & lays eggs (up to 2,000 in lifetime)
-based on larvae stages, can be used to estimate death from hours to 1 month (PMI- postmortem interval)
Determining time of death (observe stage of development of maggots or arrival of insects)
-empty pupal cases & other insects (cheeseskippers)
-predator insects, beetles, omnivore insects (ants & wasps), eventually spiders
Factors that affect insect development
Geographic location, climate, weather conditions, drugs
Will and William West Case (Fort Leavenworth prison 1903)
two men w/ similar names and features were charged for incorrect crimes. (one man was convicted of a midemeanor while the other was cnvicted of murder and they were charged for each others crimes.)
Other uses of fingerprints
-(Ancient Chinese) sign legal docs.
-(William Herscel) India contracts
-(Henry Fauld) personal identification in a Japanese hospital (1880)
Francis Galton (1892)- FINGER PRINTS
-Loops, arches, whorls assigned
-No 2 prints are identical
-an individual's prints remain unchanged (unless burned, severed, chemically removed, etc.)
Dr.Juan Vucetich (1891)- Argentinian police officer
-Developed a classification sys.
-Still used in Spanish speaking countries
Sir Edward Richard Henry (1897)
-Developed classification sys.
-Still used in English speaking countries
Adoption of fingerprints in the U.S.
-New York (1901)
-FBI (1924)
-(1999) prints were deemed admissible in court as scientific evidence
Ridge Characteristics
(1st Principle: individual characteristics)
-minutiae (ridge endings)
-point-by-point comparison
-bifurcations, minutiae, enclosures, short ridges, ridge islands
Ridge Comparisons
(1st Principle: individual characteristics)
8-16 ridge comparisons needed to identify matching fingerprints

2nd Principle: Fingerprints remain unchanged
-remain unchanged through their lifetime
-Due to structure od skin:
>Epidermis, Papillae, Dermis
>Hills (ridges) and valleys (grooves)
Latent fingerprints
(2nd Principle)
Prespiration & oils transferred to a surface
Changing fingerprints
(2nd principle)
Small changes can be made but not ALL fingerprints & ridge son other parts of the palms/feet
3rd Principle: Fingerprints can be systematically identified
GENERAL PATTERN-
>Loops (65% of population)
>Whrols (30-35% of pop. - 4 types)
>Arches (5% of pop. - 2 types)
Photocopier, Fax, & Printer Examination
-defects of the device (ex. smudges/scratches on glass)
-Ink type, print mechanism (laser v. dot matrix)
Erasures & Alterations
-Paper eill be removed during erasure
-Discoloration for chem. erasure
-Alternate light sources (UV) may help to see these
Obliterations & charred docs.
-obliteration is seldom an issue (very obvious)
-charred (use alternate light sources (UV))
Gun barrels
-Rifled v. smooth
-bullets fired through the same barrel must be the same caliber as the barrel
-fired bullets will have matching striations
Markings or fired cartridges
-firing pin imprint on the primer
-breechface marking on the surface of the cartridge
-markings from the metal-to-metal contract w/ the magazine, extractor, ejector
Breechface
the rear part of a firearm barrel
DRUG-FIRE
FBI database of the cartridge casings
Integrated Ballistics Identification Sys. (IBIS)
ATF database of bullets & catridge casing
National Integrated Ballistics Information Network (NIBIN)
a joint database on ballistics
Ballistic fingerprinting
capture & store bullets & casings taken before firearms are sold
distance determination
based on the distribution of powder or spread of a shot pattern