SLP 534 Week 8 Quiz
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
When do we assess?
when initially evaluating a client, while we're seeing a client, and when we are done seeing a client.
what is a screening
a brief evaluation of whether a person has a problem that may benefit from further professional attention and, if so, what the problem may be and what type of services might help
assessment
More comprehensive than a screening but not as comprehensive as an evaluation. It may look at specific areas. Identifies area of need and determines best level of care: planning and individualization and plan of care. It is an ongoing examination over time. Determines referrals: collaborators may include teachers, physicians and other skilled therapists
evaluation
Most comprehensive. Assesses all areas of suspected in addition to other areas that may influence performance (i.e., looks at speech, language, cognition, oral/motor, and swallowing as well as influencing factors such as hearing and vision). Includes: screening tests, assessments, interviews of qualitative and quantitative. Involves other professionals as indicated
what is MOCA?
Montreal Cognitive Assessment
an adult screening measure
Standardized/Qualitative
Qualitative methods of assessment are ways of gathering information that can be observed but cannot be easily measured by or translated into numbers. This form of assessment looks at subtleties that cannot be described by numbers, it looks deeper... the feelings, behaviors, support, community and/or family life that affect the current situation.
standardized/quantitative
Assessments that have a normative data and entail explicit instructions for test administration and scoring, enabling comparison of individual results to group results
Non-standardized/qualitative
Qualitative methods of assessment are ways of gathering information that can be observed but cannot be easily measured by or translated into numbers. This form of assessment looks at subtleties that cannot be described by numbers, it looks deeper... the feelings, behaviors, support, community and/or family life that affect the current situation.
criterion-referenced
indices used to gauge a person's own ability without direct comparison to others
norm-referenced
indices compared to a sample of a population with similar traits
dynamic assessment
Evaluation that allows tailoring of assessment materials to the interests, ability, level, and cultural and linguistic background of the person being assessed
purpose of assessment
Supporting initial and ongoing intervention
b. Contributing to the diagnostic process
c. Indexing and describing the severity and nature of a disorder
d. Indexing and describing the various impacts if language and related cognitive impairments
e. Help inform prognosis
f. Informing decisions to recommend further assessment, treatment, discharge from treatment, referrals to other professionals and to do patient and family education and counseling
g. Planning intervention with substantial patient and family input
h. Measuring, describing, and documenting baselines and progress during treatment
i. Justifying treatment to payers
j. Determining when a person has met goals
k. Collecting data to document clinical outcomes
differential diagnosis
Process of discerning which disorder, disease, or disability labels apply or do not apply to an individual according to an evaluation of their body structure
confounding factor
Any characteristic of a person’s abilities or any aspect of an assessment tool, procedure, or situation that could lead to an invalid assessment results
what is a process analysis?
Examines each part of the process for completing a given task
Considers the ability, skill, or construct we wish to assess, in light of tasks used to assess it
Analyzes the other aspects of performance that may also reflected in what is assessed
what is meant by Person Centered Care?
we include the person from the start in learning about challenges and priorities, and collaborate with the person in decision-making about goals and treatment directions.
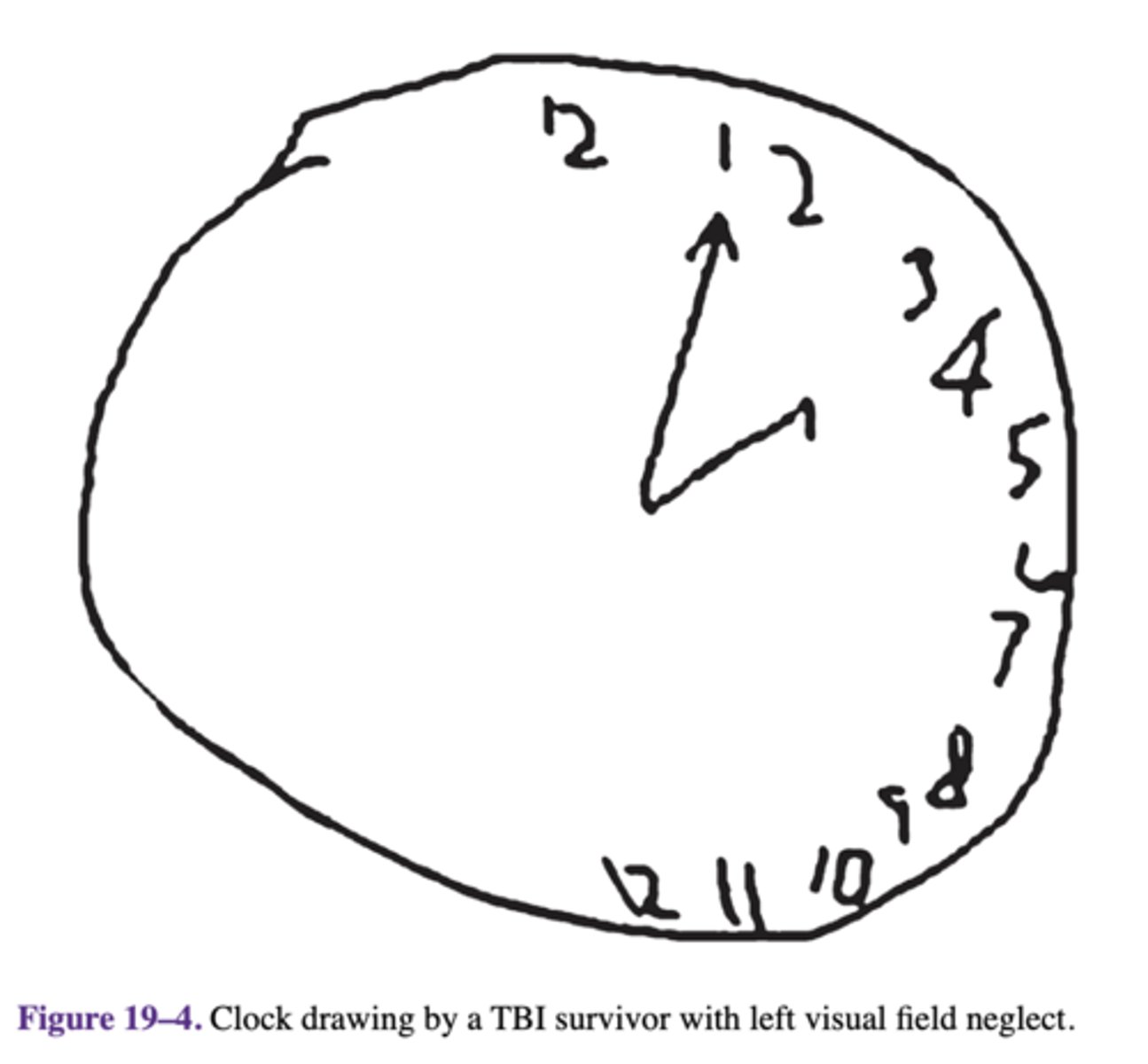
visual field neglect
a common neurological syndrome in which patients fail to acknowledge stimuli toward the side of space opposite to their unilateral lesion.
Scenario: A tendency to draw the numbers and hands of the clock on one side of the clock's face suggests that the opposite side is neglected.
visual field neglect
what is standardized testing?
these tests include directions for how many and what types of cues can be given, how many times any item may be repeated, and ceiling/floor rules.