Atoms and Isotopes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What are atoms?
Very small, radius of 1 × 10-10 metres
Contain positively charged nucleus made up of protons & neutrons
Surrounded by negatively charged electrons
What electrical charge do atoms have?
Proton - +1
Electron - -1
Equal number of proton & electrons so no overall charge
Why may the energy level of an electron change?
When the atom emits or absorbs electromagnetic radiation:
Absorbing electromagnetic radiation moves electrons to higher energy level, further from nucleus
Electromagnetic radiation is emitted when an electron drops to lower energy level
How do atoms become positive and negative ions?
Atom loses one outer electron- +ion
Atom gains extra electron - -ion
What do all atoms of a particular element have?
The same number of protons
What is the atomic number?
The numbers of protons in an atom
What is the mass number?
The number of protons and neutrons in an atom
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element that has a different number of neutrons
What are two common carbon isotopes?
Carbon-12- 6 protons & 6 neutrons
Carbon-13- 6 protons & 8 neutrons
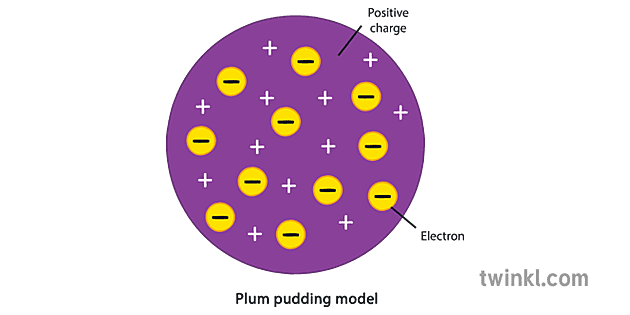
What is the Plum Pudding Model?
J.J Thompson 1897
Depicts the atom as a ball of positive charge with electrons embedded in it
What is the Rutherford, Geiger and Marsden Experiment?
Bombarded thin gold foil with alpha particles: if plum pudding model correct alpha particles pass through
Most passed through, but not all.
Some were reflected back
Must’ve been repelled by same charge alpha particles carried
Repelling charge heavier than alpha particles
Conclusion:
Mass of atom concentrated in central nucleus, positively charged
Electrons surrounded nucleus
What did Niels Bohr do?
Adapted nuclear model, suggested that electrons orbit nucleus at specific distances
What did later experiments lead to?
Idea that positive charge of nucleus can be divided into number of smaller particles, each with same amount of positive charge. Given name proton.
What did James Chadwick do in 1932?
Carried out experiments
Gave evidence that there was another particle within nucleus called ‘neutron,
Led to further refinement of nuclear model for structure of the atom