Gen Physics Q3 - L3: Electric Fields, Electric Flux, Gauss's Law
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Electric Field
Exerts a force on other charged objects even if they are distanced from each other
Electric Field Space
Surrounds the charged body and displaces charged particles in it, causing electric force
Electric Field Lines
Used as a guide in mapping out direction of electric field forces
Michael Faraday
Pioneered the use of electric field lines of force
Positive Electric Field Charge
Field lines are directed outward
Negative Electric Field Charge
Field lines are directed inward
Origins of Electric Field Lines
Start from positively charged particles and end on negatively charged particles
Paths of Electric Field Lines
The lines neither intersect nor break as they pass from one charge to another
Strength of Electric Field Lines
Greater lines means a stronger electric field
Point Charge
Region of space around a source charge, when another object enters this field it experiences electric force
Electric Field due to Point Source Charge Formula
E = Fe/q0
where E = electric field
where Fe = electric force exerted on point charge
where q0 = electric charge
Electric Field Intensity
Strength of electric field at a point due to the source charge
Electric Field due to Point Charge Formula
E = k |q|/r²
where E = electric field
where k = Coulomb’s Constant
where q = Electric Charge
where r = Radius
Electric Flux
Number of field lines passing through a surface
Fluxus
Means to flow
Test Charge
Charge that experiences an electric charge after entering an electric field
Getting Electric Flux
Dot product of Electric field and area vector
Direction of Area Vector
Vector perpendicular to the area
Electric Flux Formula
θ = E . A
E . A = EA cos Θ
θ = Flux
E = Field
A = Area
Θ = Angle
(only use cos if there is an angle)
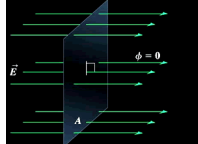
Cross Section Electric Flux
E (field) is perpendicular to A (area), and the angle between E and the line perpendicular to the surface is zero (Flux = EA) (theta = 0)
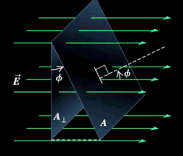
Titled Section Electric Flux
A (area) is tilted at an angle theta from the perpendicular line to E (field) (Flux = EA cos theta)
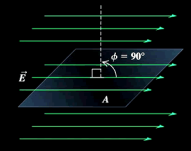
Vertical Section Electric Flux
A (area) is parallel to E (field) which is tilted at 90 degrees from the line perpendicular to E (Flux = EA cos 90 = 0)
Gauss’s Law
Total electric flux through a surface is total electric charge (qtotal) inside the surface divided by 𝝐0
Carl Friedrich Gauss
Related electric field, flux and charge together as one
Permittivity of free space constant (𝝐0)
8.8542 × 10^-12 c² / N . m²
Total Electric Flux
Φ𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 = 𝑬𝑨 𝒄𝒐𝒔 theta
or
Φ𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 = 𝒒𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝝐𝟎