Prescribing in pregnancy and breastfeeding
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
What would you advise women wishing to become pregnant to avoid?
avoid OTC, prescription and herbal remedies where possible, avoid alcohol, smoking, vitamin A products and exposure to hazardous substances/radiation
What health advice would you give women wishing to become pregnant?
Weight management where appropriate, healthy diet, decrease caffeine intake, stop use of illicit drugs if able to do so
What supplement is advised to be taken as prophylaxis against neural tube defects?
Folic acid 400 micrograms per day
What conditions mean folic acid should be prescribed by a GP or other clinician at a dose of 5mg per day?
Women with epilepsy, sickle cell disease, thalassaemia, diabetes, coeliac disease, BMI 30kg/m² or more or has a child previously with neural tube defects or a family history of NTDs
What immunisations should women wishing get pregnant be checked for?
Rubella - dangerous to unborn foetus and chicken pox/shingles
What should women wishing to become pregnant do if they have a chronic illness?
Speak to GP as dosages of regular medications may need to be adjusted
What is the length of an average pregnancy?
38-40 weeks
When is the first trimester in pregnancy?
0-12 weeks
When is the second trimester in pregnancy?
12-28 weeks
When is the third trimester in pregnancy?
28-40 weeks
What happens in the pre-embryonic stages of foetal development (days 1-17)?
Time taken from fertilisation through cell division to arrive at the embryonic stage
What is the embryonic stage in foetal development? (Days 18-56)
Organogenesis - development of primary organs occurs during this time period
What is the foetal stage in foetal development (day 56+)?
Maturation, development and growth
What happens to blood pressure in pregnancy?
Vadcular resistance changes from conception - decrease until midway through 2nd trimester around 24 weeks, BP then rises again towards pre-pregnancy levels
What is the decreased vascular resistance compensated by?
Gradual increase in heart rate and stroke volume during pregnancy and labour
How does the blood change during pregnancy?
Plasma volume increases by around 40% - RBC volume increases by 15% but decreases blood viscosity.
How does the coagulation cascade change in pregnancy?
Increase in coagulation factors and decrease in fibrinolysis
Why do the changes to blood happen in pregnancy?
Minimise blood loss during labour
What is a consequence of the blood loss in pregnancy?
Increase risk of VTE
How do the increased plasma volume levels have an affect on the kidneys in pregnancy?
Increases renal blood flow and therefore increases glomerular filtration rate - renally excreted drugs are cleared faster and upwards dose adjustments may be needed
What protein levels in the blood are affected during pregnancy?
Serum albumin - 80% of normal by the end of pregnancy so drugs that are extensively plasma bound should be adjusted
What effects do the increased progesterone levels have during pregnancy?
Relaxes smooth muscle - including in oesophageal sphincter and gut - leading to a higher likelihood of constipation and bloating
What does upward pressure from the uterus and relaxation of the oesophagus sphincter result in in pregnancy?
Oesophageal reflux
What are congenital disorders?
Structural or functional anomalies that occur during intrauterine growth
What can congenital disorders be caused by?
Genetics, environment or unknown
When does most foetal damage occur in pregnancy?
During the first trimester when organogenesis is in process
What does teratogenicity mean?
Describes the effects of drugs causing birth defects
What are the most common teratogenic effects?
Spine bifida, cleft lip/palate, renal failure and growth retardation
What is a diagram to show cleft lip and palate?
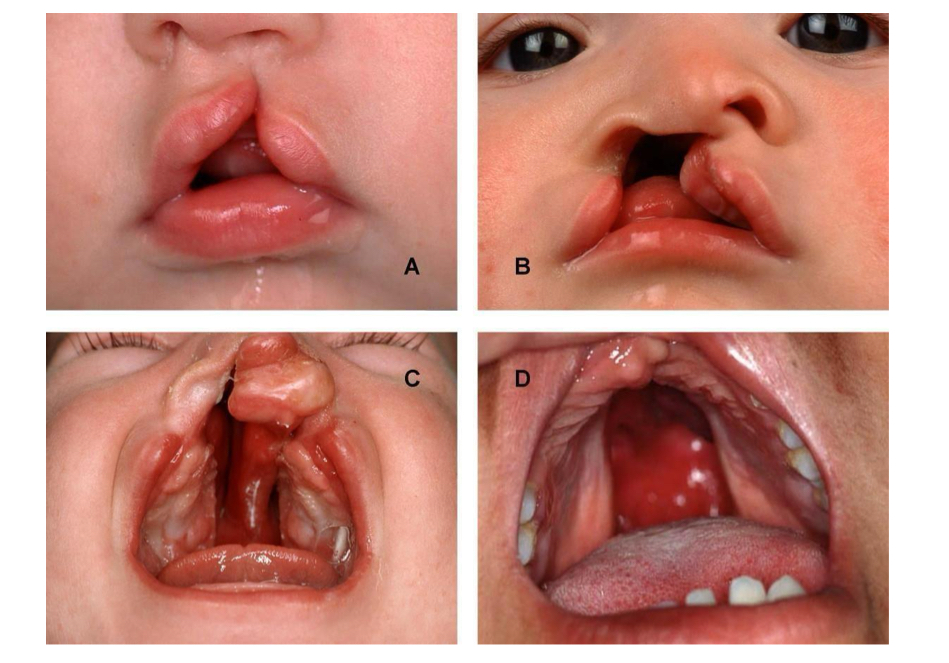
What is a diagram to show myelomeningocele as the most severe form of spine bifida?
A portion of the spinal cord protrudes itself through the back
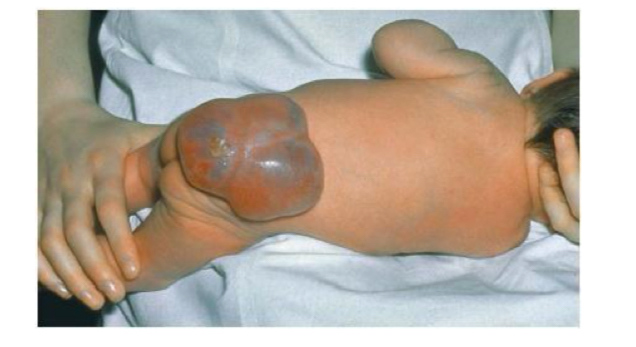
What is spina bifida?
Incomplete closure of the spinal column - can have tissues and nerves exposed
What are the most common teratogenic drugs?
anti-epileptics such as phenytoin, valproate and carbamazepine
Lithium
Warfarin
Retinoids e.g., isotretinoin
Danazol
What drugs affect later in pregnancy?
ACE inhibitors, antithyroid drugs, benzodiazepines, Beta blockers, NSAIDs and warfarin
What are the effects of ACE inhibitors on the foetus?
Causes renal failure
What are the effects of antithyroid drugs such as carbimazole on the foetus?
Causes hypothyroidism in the foetus
What can the effects be of taking benzodiazepines in the third trimester?
Can cause severe benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome in the neonate
What are the symptoms of severe benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome?
Hypotonia, reluctance to suck, apnoeic spells, cyanosis, seizures and impaired metabolic responses to cold stress and can persist from hours to months after birth
What are the effects of atenolol and predicted from other beta blockers in pregnancy?
Can cause growth retardation - can also cause neonatal hypoglycaemia and bradycardia
What beta blocker is commonly prescribed for hypertension in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy?
Labetalol
What can NSAIDs cause when used in later pregnancy?
Can close ductus arteriosus
What is the ductus arteriosus?
Foetal blood vessel which joins the aorta and pulmonary artery in utero and allows respiratory circulation to be bypassed
What does warfarin cause when used in later pregnancy?
Bleeding into the foetal brain
What drugs have been known to not cause harm yet in pregnancy?
Paracetamol, penicillins, antacids, steroid inhalers, bronchodilator inhalers
What is the only non-prescription analgesic recommended during pregnancy?
Paracetamol!
What are the safer antibiotics in pregnancy?
Penicillins and cephalosporins
When should nitrofurantoin be avoided in pregnancy?
At full term
What is the second line treatment for UTIs in pregnancy?
Cefalexin
What treatment for a UTI should be avoided in pregnancy?
Trimethoprim
What class of antibiotics should be avoided in pregnancy?
Tetracyclines
Why should care be taken when recommending antacids to pregnant women?
Recommend products that have a low sodium content to prevent hypertension
Why is it imperative for asthma to be controlled in pregnancy?
An asthma attack can reduce oxygen the mother receives but also reduces the amount the foetus gets
What is hyperemesis also known as?
Morning sickness
Approximately how many women are affected by morning sickness in their first trimester?
70%
What is the cause of hyperemesis gravidarum?
Unknown
What is hyperemesis gravidarum?
A more severe form of morning sickness
What are the dangers of hyperemesis gravidarum?
Severe nausea and vomiting can result in dehydration, weight loss and hospitalisation
What are some non-pharmacological ways of managing morning sickness?
Eating smaller meals more frequently
Avoiding spicy foods
Avoiding caffeine
Preventing fatigue
Emotional support provision
How can oesophagul reflux be managed in pregnancy non-pharmacologically?
Eating smaller meals more frequently, avoiding caffeine and spicy foods
What can be prescribed as first line options for hyperemesis in pregnancy?
Antihistamines such as cyclizine or promethazine, or a phenothiazine/prochlorperazine
What are the second line treatments for hyperemsis in pregnancy?
Metoclopramide or ondansetron for a maximum of 5 days
Why is metoclopramide only used for up to 5 days for a second line treatment of hyperemesis?
Risk of neurological extrapyramidal side effects - restlessness, trembling, muscle stiffness or spasm
What can happen if using metoclopramide towards the end of the third trimester?
Can cause extrapyramidal side effects in newborn babies
What risks does ondansetron have when used in first semester?
Small increased risk of cleft lip/palate
What is first line management of acid reflux in pregnancy?
Avoidance of trigger factors e.g., spicy/fatty foods, tight clothing, big meals and smoking
What is second line treatment if non-pharmacological methods do not work for acid reflux in pregnancy?
Pharmacological treatments such as an antacids with/without an alginate
What antacids are not recommended in pregnancy?
Those containing sodium bicarbonate or magnesium trisillicate
What are some examples of second line pharmacological therapy in acid reflux in pregnancy?
Omeprazole or ranitidine - manufacturer advises avoid unless essential
What is pregnancy induced hypertension?
A BP of greater than 140/90 mmHg beyond 20 weeks of pregnancy resolving upon delivery
What is pre-eclampsia?
New hypertension presenting after 20 weeks accompanied by pregnancy-induced proteinuria
What should all pregnant women have done at every antenatal appointment for hypertension and pre-eclampsia?
Have their BP taken and urine dipped for protein
What is the pharmacological treatment of pregnancy-induced hypertension?
Labetalol
What drugs can be used for PIH if labetalol is not tolerated?
Nifedipine or methyldopa
What can detect gestational diabetes in pregnant women?
Urine dipstick test at each antenatal appointment
What risks are increased if gestational diabetes is left untreated?
Risks of PIH, pre-eclampsia, premature birth and neonatal hyperglycaemia
What are the first line treatments of gestational diabetes?
Diet and lifestyle modifications
What is the target fasting blood glucose level in gestational diabetes?
5.3mmol/L
What should happen if non-pharmacological treatment for gestational diabetes is unsuccessful?
Drug treatment should be started
What is the first line pharmacological treatment for gestational diabetes?
Oral metformin
What is the second line pharmacological treatment for gestational diabetes?
Insulin therapy used alongside metformin
What should women receive early on in pregnancy to establish VTE risk?
VTE assessment to establish risk factors and initiate treatment if necessary
What should pregnant women at risk of a VTE during pregnancy be prescribed for prophylaxis?
Low molecular weight heparin
What is the safest anti-epileptic drug to be used in pregnancy according to the MHRA?
Lamotrigine or levetiracetem
What should be the aims of using anti-epileptics in pregnancy?
Lowest dose to control seizures, ideally monotherapy and counselled to plan pregnancies where possible
What should the mother be scanned for if on anti-epileptic medication in pregnancy?
Alpha-fetoprotein and should have 2nd trimester ultrasound scan
What should be injected to minimise the risk of neonatal haemorrhage associated with antiepileptics?
Vitamin k
What drugs do not distribute into breast milk?
Insulin and warfarin - very large molecules
What does the extent of transfer to breast milk depend on?
pKa - basic drugs are more likely to cross into breast milk
Protein binding - highly protein bound drugs are less likely to cross into breast milk
Lipophilicity - highly lipophilic drugs are more likely to cross into breast milk
What drugs are least likely to cross into breast milk?
Drugs that are acidic, highly protein bound and with a low lipophilicity e.g., NSAIDs
What drugs are more likely to have a higher concentration in breast milk?
Those that are basic, with low plasma binding and high lipophilicity
What reduces potential ill effects of drugs in breast milk?
Dilutional effects of breast milk and amount actually swallowed
When is it best to breast-feed a child when the mother is on drugs?
Immediately before the dose of drug is taken
What should happen if non-compatible drugs are unavoidable and must be used with breastfeeding?
Mother should express and discard any milk and wait for the elimination time for the drug (4-5 half lives) before feeding
What drugs must be avoiding when breastfeeding?
Amiodarone, aspirin, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, carbimazole, combined oral contraceptives, cytotoxics, ephedrine and tetracyclines
Are corticosteroids teratogenic?
No evidence that it has any influence on foetal endocrine system
Are oral contraceptives teratogenic?
No evidence for teratogenicity
Why is warfarin safe for breastfeeding?
Concentrations in breast milk are very low and no evidence for any ill effect