11.1 The Musculoskeletal System
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
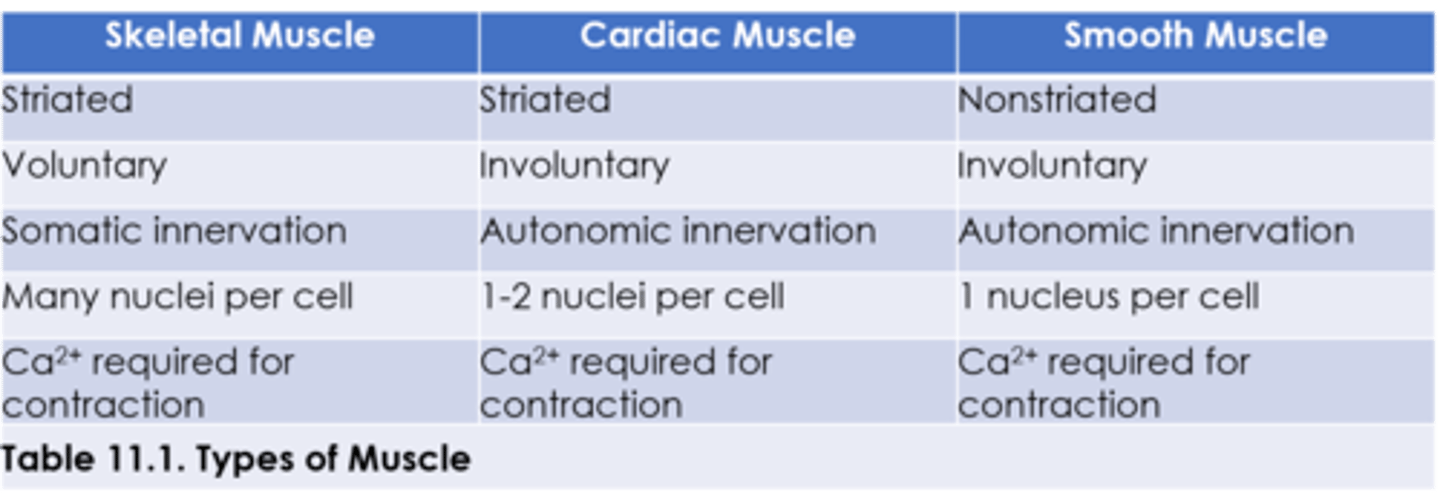
Skeletal Muscle
The muscle type that is responsible for voluntary movement by the somatic nervous system. Actin and myosin are in repeating units called sarcomeres, making it appear striped or striated. They are multinucleated due to the fusion of muscle cells during development.
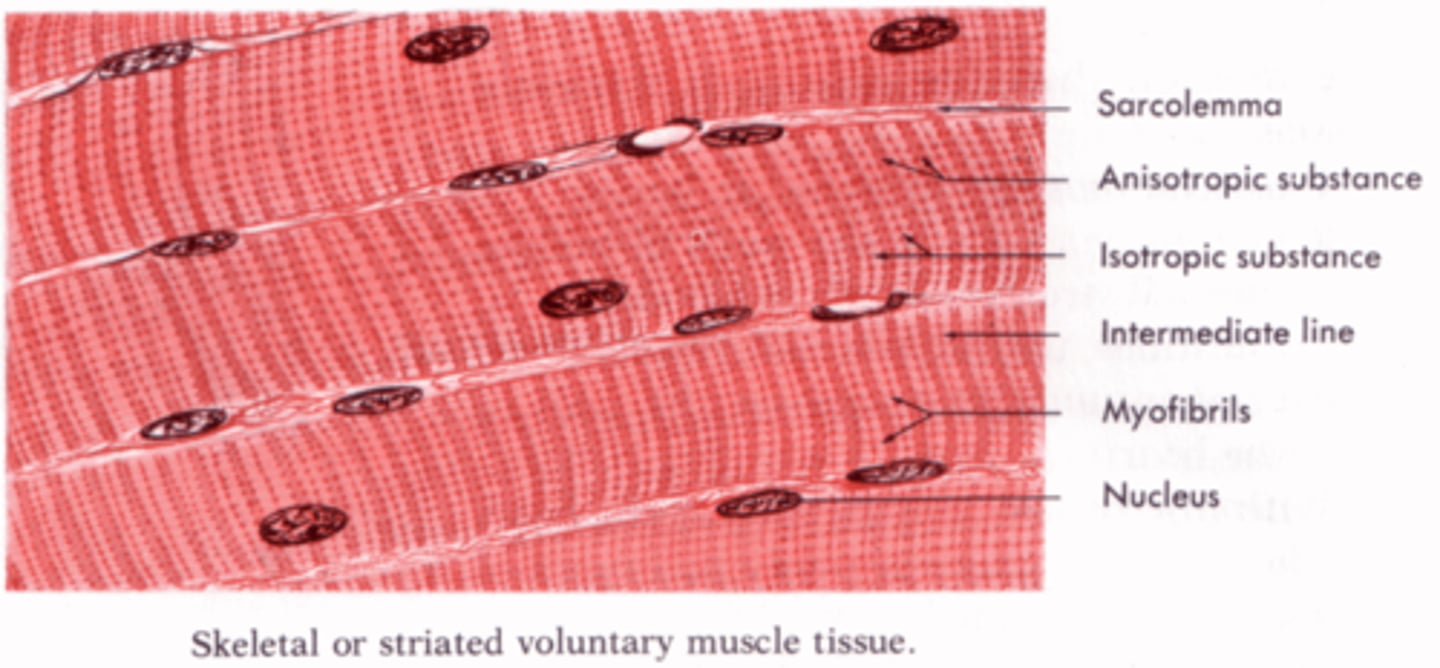
Sarcomeres
Repeating units of actin and myosin.
Striation
The striped appearance of skeletal muscle under a microscope due to the presence of sarcomeres.
Slow-Twitch Fibers
Red fibers, which have high myoglobin content and primarily derive their energy aerobically. Found primarily in muscles that contract slowly or act to hold a posture, they can sustain activity for extender periods of time.
Red Fibers
Slow-twitch fibers also have a lot of mitochondria for carrying out oxidative phosphorylation.
Myoglobin
An oxygen carrier that uses iron in a heme group to bind oxygen, imparting a red color.
Fast-Twitch Fibers
Contain much less myoglobin, making the color lighter. Found primarily in muscles that contract rapidly, but fatigue quickly.
Smooth Muscle
Responsible for involuntary action. It is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Can be found in the respiratory tree, digestive tract, bladder, uterus, blood vessel walls, and multiple other locations.
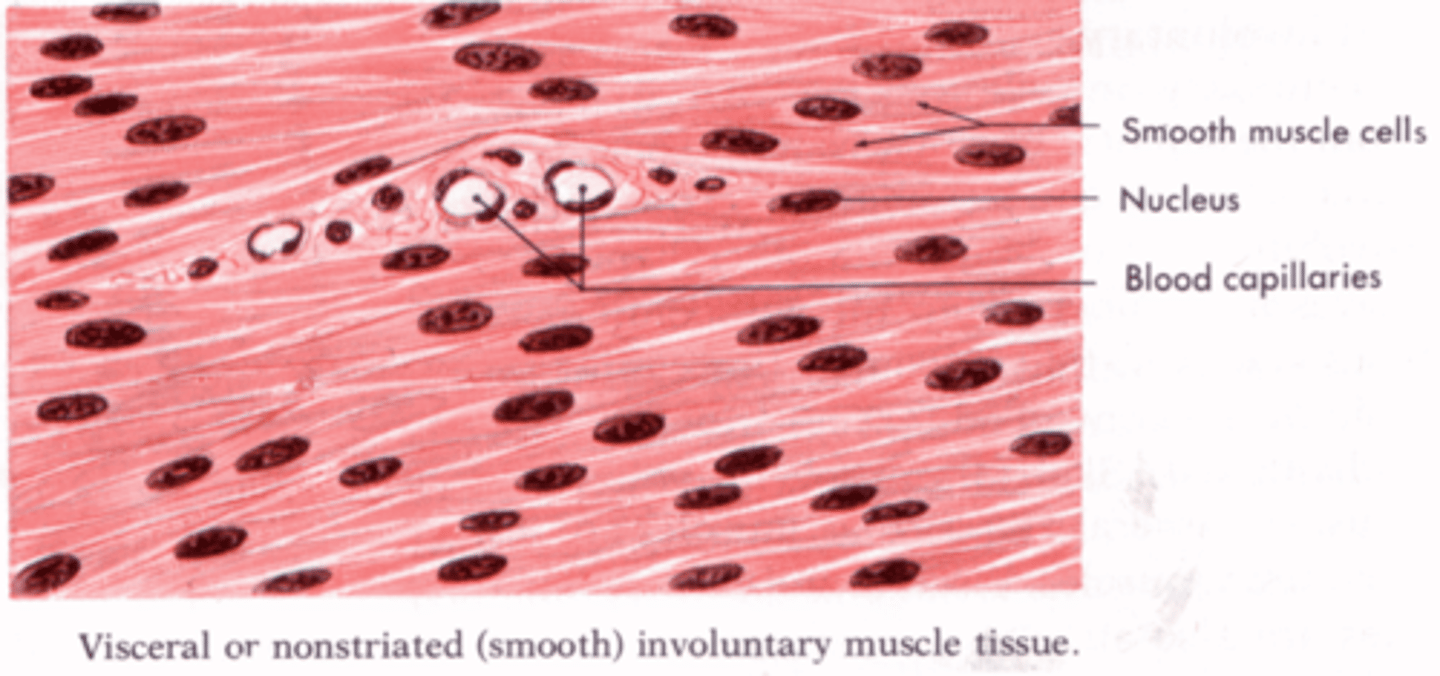
Uninucleated
Smooth muscle cells only have one nucleus.
Actin and Myosin in Smooth Muscle
The fibers are not as well-organized as skeletal muscle, so there are no visible striations.
Tonus
Smooth muscle is different from skeletal muscle in that it can handle sustained contraction, a state of low-level contraction, as can be seen in the blood vessels.
Myogenic Activity
Characteristic of smooth muscle AND cardiac muscle in which their cells can contract without nervous system input. These muscle cells can contract directly in response to stretch or other stimuli.
Cardiac Muscle
Shares characteristics with both smooth and skeletal muscle. Primarily it's uninucleated, but cells may contain two. It is involuntary and innervated by the autonomic nervous system.
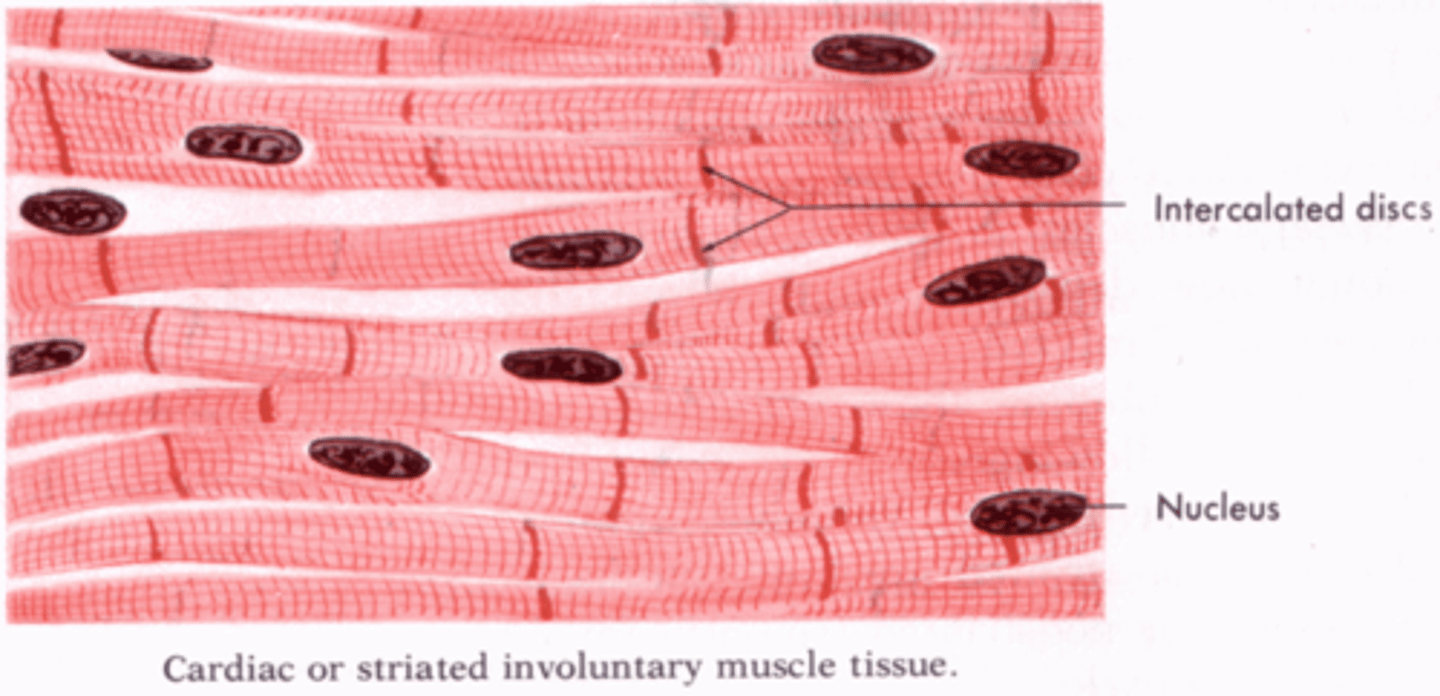
Intercalated Discs
Cardiac muscles are connected by these structures which contain many gap junctions.
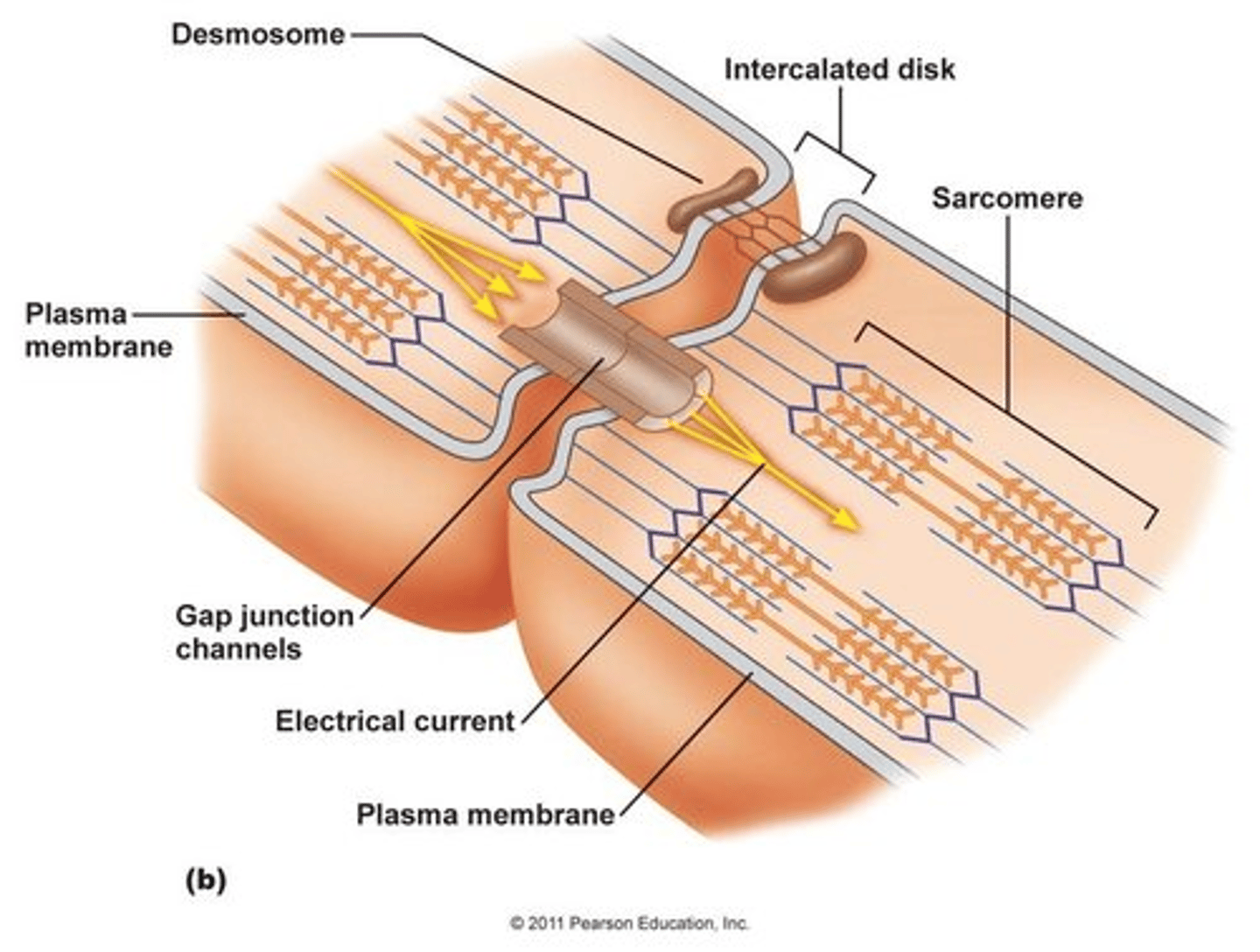
Gap Junctions
Junctions that provide a channel between the sarcoplasm of adjacent cardiac muscle cells in intercalated discs through which ions can flow. This allows for rapid and coordinated muscle cell depolarization and efficient contraction of cardiac muscle.
Cardiac Muscle Cells Maintain Their Own Rhythm Through Myogenic Activity
Starting at the SA node, depolarization spreads using conduction pathways to the AV node. From there, the depolarization spreads to the bundle of His and its branches, and then to the Purkinje fibers. The gap junctions allow for progressive depolarization to spread via ion flow across the gap junctions between cells.
Nervous and Endocrine Systems in Cardiac Muscle Contraction
The vagus nerve provides parasympathetic outflow to the heart and slows the heart rate. Norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons or epinephrine from the adrenal medulla binds to adrenergic receptors in the heart, causing an increased heart rate, and greater contractility.
Epinephrine
Hormone released from the adrenal medulla that increases heart rate and causes greater contractility. It does this by increasing intracellular calcium levels within cardiac myocytes.
Types of Muscle