Level Up RN and Book Exam 1, Week 2 Content
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Med Surg 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
What is an MI?
30+ min chest pain due to ischemia
What causes an MI?
Atherosclerosis= occluded blood flow
What are the primary S/S of an MI?
Chest Pain 30+ min
SOB
Diaphoresis
Dizzy
What are female S/S of MI?
Fatigue
N+V
Shoulder/Back/Jaw Pain
What are the diagnostics for an MI?
Myoglobin
Troponin I
Troponin T
What is the earliest marker for cardiac enzymes?
Myoglobin (No longer after 24 hr)
What is the range and time for Troponin I?
7-10 days
0.03
What is the range and time for Troponin T?
10-14 days
0.4
What are the two types of MI?
NSTEMI (Non-Elevated ST)
STEMI (Elevated ST)
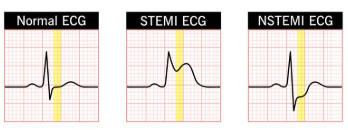
What are the main medications for an MI?
Morphine Sulfate
Oxygen
Nitroglycerin
Aspirin
What other medications can be given with an MI?
Clopidogrel
Metoprolol
Heparin
Eptifibatide (ATE)
What are surgical interventions for MI?
PCI, CABG, Atherectomy, Cardiac Cath
What happens with a cardiac cath w/ MI?
catheter in femoral vessel
injection of contrast media
What absolutely needs to happen before a cardiac cath?
Informed Consent
NPO 8 hours
What needs to be monitored with nitroglycerin?
Orthostatic Hypotension
NO erectile dysfunction meds (24-48 hr)
How many doses of nitroglycerin at 5 minute intervals?
3 doses max (sublingual)
What is the most common adverse effect of nitroglycerin?
Headache
When taking nitroglycerin if pain is NOT relieved in 5 minutes what should you do?
Call 911 and continue taking next doses
What should you monitor when giving morphine sulfate?
Resp Depression (Less than 12 BPM)
Who should you NOT give morphine sulfate to?
Asthma and Emphysema Patients
What needs to be monitored with metoprolol?
Bradycardia and Hypotension
What needs to be done with both Metoprolol and Nitroglycerin?
Change positions slowly
Who should you NOT give metoprolol to?
Asthma patients
HR under 60 BPM
What is the biggest risk with thrombolytics?
Bleeding and Bruising
What medication should nitroglycerin be given at the same time as?
Aspirin
What is an indication of aspirin toxicity?
Tinnitus
What lab needs to be monitored with heparin?
aPTT
When should oxygen be administered with an MI?
O2 Sat under 90%
When does cardiogenic shock or failure occur?
40% blockage
What are the S/S of cariogenic shock?
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Low UO
Hypotension
Cool/Clammy Skin
Weak Pulses
What does percutaneous coronary intervention do?
Open coronary arteries
How long after onset of MI symptoms can a PCI be done?
2 hours after onset
What happens with a PCI?
Balloon in femoral
Balloon inflated
Stent placed
After a PCI what is super important to do?
Check distal perfusion
(Color, Cap Refill, Pulses)
What are complications of PCI?
Artery Dissection/Reocclusion
Cardiac Tamponade
What are S/S of aortic dissection/reocclusion?
Chest Pain
SOB
Tachypnea
Tachycardia
What are S/S of cardiac tamponade?
Hypotension
JVD
Muffled Heart Sounds
10 mmHg BP variance
What is the treatment for a cardiac tamponade?
Pericardiocentesis (aspirate fluid)
What diagnostic tests confirm cardiac tamponade?
Chest X-Ray and Echocardiogram
(See fluid)
What medication is given prior to a stress test?
Adenosine
What is the antidote for heparin?
Protamine Sulfate
What is given before and after a PCI?
Before: Clopidogrel
After: IV Heparin
What is the leading cause of death after an MI?
Dysrhythmias
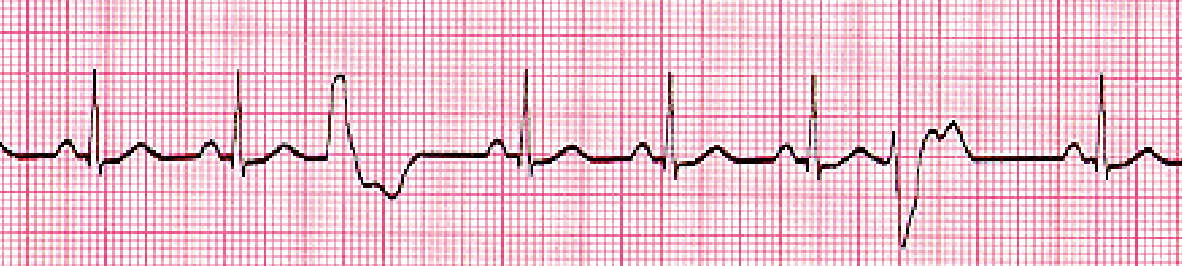
What does a PVC look like?
P wave: Normal expect before QRS
QRS: Wide and early (>0.12)
Pause before next beat
What is a CABG?
bypass one or more coronary artery
What is the criteria for a CABG?
50% blockage
Heart failure and disease
Persistent ischemia
Heart Valve Disease
What is preprocedure for CABG?
Baseline assessments
Informed Consent
Prophylactic ATBs
Diazepam/Lorazepam
What is client teaching before CABG?
Cough and Deep Breath
Splint with pillow
Arm and Leg Exercises
Early Ambulation
What is super important that the nurse does before a CABG?
Help with anxiety for patient and family
Before a CABG when should diuretics be stopped?
2-3 days before
Before a CABG when should aspirin and anticoagulants be stopped?
1 week before
What medications can be continued with a CABG?
K+ supplements
Amiodarone
Metoprolol
Insulin
What is intraop teaching with CABG?
Cardiopulmonary Bypass
Heart is stopped with cardioplegic
Pacemaker wires placed
Catheter placed
Chest tubes placed
What is a concerning drainage from chest tubes?
150+ mL/hr
Notify Provider
What is post-op teaching with CABG?
Monitor F+E
Monitor Vitals
What F+E is most important to monitor with CABG?
Potassium levels
What does hypertension cause with CABG?
Bleeding from grafts and sutures
What does hypotension cause with CABG?
graft collapse
Why is temperature control important after CABG?
Hypothermia (help w/ rewarming)
What should be given for pain for CABG?
Morphine and Fentanyl
After a CABG when should a patient be in a chair?
24 hours post-op
By day 1 post-op how far should a patient walk after a CABG?
25-100 feet (3x day)
How long after a CABG can you return to work?
week 2 (part-time)
What are common complications after a CABG?
Cardiac Tamponade
Hypovolemia
Left Ventricular HF
What is a heart healthy diet after CABG?
low fat
low cholesterol
low salt
high fiber
What are the two methods of CABG?
Saphenous= Leg Vein
Internal Mammary= Left anterior artery
What is ischemia?
insufficient oxygen
What is infarction?
necrosis or cell death
What is stable angina?
Occurs with exercise or Stress
“Strangling of Chest”
What is stable angina relieved by?
Rest or Nitroglycerin
What causes angina?
Atherosclerotic Plaque
What is unstable angina?
Occurs with exercise or rest
Increases in duration, severity, and occurrence
What is variant angina?
Coronary Artery Spasm (rest)
What is pre-infarction angina?
chest pain days or weeks prior to MI
How long does angina last?
15 minutes or less
What is super important teaching with nitroglycerin?
NO SUN
3 month shelf life
How is angina pain often referred?
Squeezing, heavy pressure, constricting
How to decipher between unstable and stable angina?
Stable= Anticipated (w/ exercise or stress)
Unstable= Random (either exercise or rest)
What diagnostics for angina?
EKG
Stress Test (Adenosine)
Coronary Angiogram
What is valvular heart disease?
abnormality or dysfunction of valve
What is stenosis?
Narrowed opening
What is insufficiency?
Regurgitation (backflow)
What are risk factors for valvular heart disease?
HTN
Rheumatic Fever
Infective Endocarditis
What happens to the heart with valvular heart disease?
Hypertrophy
Murmur
Increased pulmonary artery pressure
What are S/S of valvular heart disease?
Murmur
Extra Heart Sounds
Dyspnea
Fatigue
Orthopnea
What is unique with mitral stenosis?
A-Fib
JVD
Hepatomegaly
What is unique with mitral insufficiency?
S3 sounds
JVD
Hepatomegaly
What is unique with aortic stenosis?
S4 sounds
Angina
Narrow pulse pressure
What is unique with aortic insufficiency?
Nocturnal Angina
Widened pulse pressure
Bounding pulse
Elevated systolic
What diagnostics for valvular heart disease?
Chest X-Ray
Echocardiogram
TEE
Stress Test
What medications for valvular heart disease?
Diuretics (watch K+)
-pril
-sartan
Digoxin
Anticoagulants (Heparin)
What surgical procedures for valvular heart disease?
Percutaneous Balloon
Valve Replacement
Valve Repair
What must be given before every procedure with valvular heart disease?
Prophylactic ATBs (dental/resp procedures)
After a mechanical valve is placed what needs to be monitored frequently?
Prothrombin time
What is infective endocarditis?
Infection of the endocardium
Who is infective endocarditis common for?
Cardiac Malformations
Pacemakers
Prosthetic Heart Valve
IV substance abuse
What are the findings for infective endocarditis?
Flu-Like
Murmur
Petechiae (Mouth+Trunk)
Splinter Hemorrhage (Red Streak on nails)
What diagnostic test for infective endocarditis and pericarditis?
Echocardiogram and EKG
What is pericarditis?
Inflammation of pericardium
What are the findings for pericarditis?
Chest pressure from breathing, coughing, swallowing
Friction Rub
SOB
Relief when sitting upright or leaning forward