3.3.4 Normal profits, supernormal profits and losses
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
proft
total revenue -total costs
how to maximise profits
produce up to the level of output where marginal cost =marginal revenue
normal profit
total revenue = total costs
breakeven
economic profit of zero
occurs when extra revene left after costs is equal to firms opportunitys costs of factors of production that havent been paid for
minimum level of profit needed to keep resources in their current use in the long run
supernormal profit
total revenue is greater than costs
revenue generated from using factors of production in this way is greate than could have been generated by using them in any other way
incentive for other firms to joing industry
loss
total revenue is less than total costs
short run shut down point
if the seeling price(average revenue is higher than average variabke cost the firm should keep producgin if the selling price falls to the AVC it should shut down
short run shut down point graph
The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output (Q) where MC=MR
At this level, the P = AVC
This means that there is no contribution towards the firm's fixed costs
The selling price literally only covers the cost of the raw materials used in production
There is no point in continuing production and the firm should shut down
long run shut down point
n the long-run, if the selling price (AR) is higher than the average cost (AC) the firm should remain open (AR > AC)
if the selling price (AR) is equal to or lower than the average cost (AC), the firm should shut down (AR = AC)
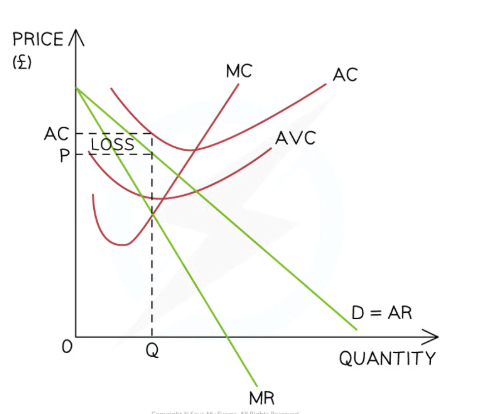
long run shut down point graph
he firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output (Q) where MC=MR
At this level, P < AC
It could continue operating in the short-run as the AR > AVC, but in the long-run they are making a loss and the firm will shut down