Astrophysics - Test 1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Other name for variable stars
Other name for cepheids
Variable stars characteristic
Brightness varies with time
Who and why used cepheids ?
Shapely to determine the distance of various globular clusters
Cepheids function
Distance indicators
How many techniques to find double stars
Three techniques
Optical binaries
DS
Seen as two (naked eye or telescope)
Spectroscopic binaries
DS
Spectroscopy : wDetected because of the Doppler effect : Motion of the stars causes a blueshift, a redshift, a blueshift, …
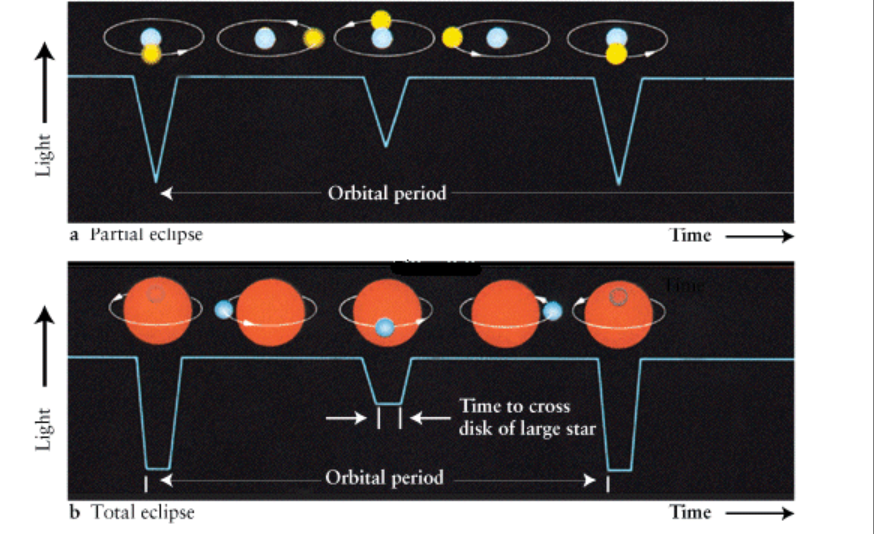
Eclipsing binaries
DS
Photometry : Detected by the variation of the brightness (mv). One star eclipse the other.
Eclipsing binaries graph
Classification basis of stars
Surface temperature (K)
Main spectral types
O, B, A, F, G, K, M
*Oh ! Be a fine guy, kiss me !
Hot satrs color
Blue
Cold stars color
Red
Luminosity classes
I : Supergiant
(II : Bright giant)
III : Giant
(IV : Sub-giant)
V : Dwarf or Main-sequence
Absorption line
When light is absorbed by elements, leaving a dark mark in spectral data
Most luminous stars class
I : Supergiant
White dwarfs characteristics
Small luminosity, small radius, very high temperature.
What star class shows a correlation between L and T ?
Only main-sequence shows correlation between those two characteristics
For main sequence, what is the correlation between L & T
The more luminous a star is, the hotter it is
Key factor in main sequence stars
Mass
Axis of HR diagram
Luminosity and Temperature axis
HR diagram type of graph
Log-log graph
3 main luminosity classes
I : Supergiant, III : Giant, V : Main sequence
Life cycle of stars
Born
V : main sequence
III : Giant
Drop in luminosity
I : Supergiant
POWW !!
White dwarf
Types of deep-sky objects ?
(10)
Open star clusters, Globular star clusters, Planetary nebulas, Supernova remnants, Bright nebulas, Dark nebulas, Spiral “nebulas”, Elliptical galaxies, Irregular galaxies, Quasars
Population classification
I : Normal (like the Sun)
II : Ionized once (different from the Sun)
III : Ionized twice (completely different from the Sun)
Open star clusters example
The Pleiades
Open star clusters characteristics
Contains 100 - 10 000 stars
Relatively weak concentration of stars
May contain some interstellar gas
Tend to be young objects with newly formed stars (of population I)
Tend to break up into individual stars
Distributed in the disk of spiral galaxies
Globular clusters example
M13
Globular star clusters characteristics
10 000 - 1 million stars (very luminous)
Strong concentration of stars
Do NOT contain interstellar gas
Tend to be old objects with old stars (of population II)
Do not break up, remain stable (because of the many stars)
Distributed in the halo of galaxies
Planetary nebula example
M57 : Ring nebula
Planetary nebula
Explosion of a star
Gas expelled by a star that becomes a white dwarf
Expand with time
Gas ionized (switch in energy level which causes light) by the hot central star
Get dispersed astronomically rapidly : in ~10 000 years
Supernova remnants example
M1 : Crab nebula
Supernova remnants characteristics
Gas expelled by a star that collapses into a neutron or into a black hole
Type I : white drawf that collapses