In sickness and in Health
4.8(11)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:28 AM on 12/14/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
Do substances move into and out of cells?
true
2
New cards
What is homeostasis
the ability for organisms to maintain a steady sate when the external environment changes
3
New cards
what are examples of homeostasis
sweating or shivering
4
New cards
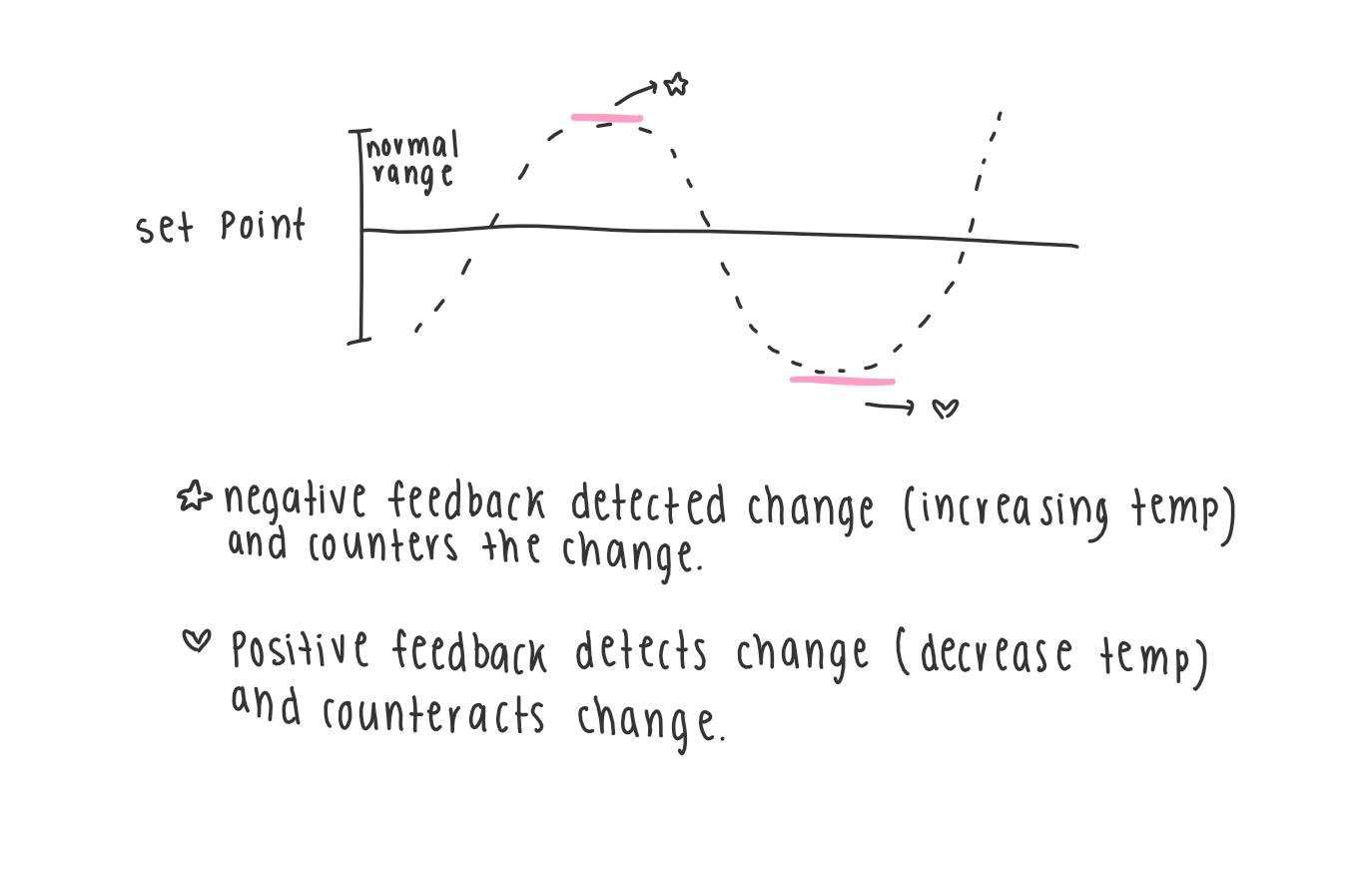
what is set point?
a normal or target value
5
New cards
what is normal range?
a range of values, around the target value, that are normal or healthy
6
New cards
what system closely monitors and coordinates
the endocrine system and the nervous system
7
New cards
what does the nervous system control
all body activities
8
New cards
what does the endocrine system do
it secretes hormones that regulate activities that the nervous system controls
9
New cards
what does the organ system do
it supplies body cells with all the substances, they also keep temperature pH, and other conditions at the optimal levels
10
New cards
what is the respiratory system
high concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood --> triggers faster breathing --> lungs exhale more --> removes carbon dioxide from the body fast
11
New cards
what is the excretory system
low level of water in the blood --> triggers retention in kidneys --> kidneys produce more concentrated urine --> less water lost from body
12
New cards
what is the endocrine system
high concentration of sugar in the blood --> triggers secretion of insulin from pancreas -->
13
New cards
what is insulin
hormone that helps cells absorb sugar from the blood
14
New cards
what is negative feedback
response to a stimulus that keeps a variable close to a set value, it shuts off or turns on.
15
New cards
what are the steps of negative feedback
1. a change in the body is detected --> temp or gluc level
2. a message is sent to a gland or organ
3. a response is initiated --> body returns to normal state
2. a message is sent to a gland or organ
3. a response is initiated --> body returns to normal state
16
New cards
is negative feedback involved in the maintenance of blood sugar
true
17
New cards
what hormone is released when there is a rise in blood sugar levels
insulin which comes from the pancreas
18
New cards
whats is positive feedback
when a change from normal state triggers a reaction that results in the change being amplified
19
New cards
what is an example of positive feedback
contraction :D
20
New cards
what does the kidney do
filter blood, remove nitrogenous waste, regulate salt and water balance, regulate sugar levels
21
New cards
what are receptor cells
receptor cells are a nerve cell that identifies change in the environment both inside and outside the body
22
New cards
chemoreceptor
a sensory receptor that responds to chemical stimuli (tongue)
23
New cards
photoreceptor
a receptor that responds to light (eye)
24
New cards
mechanoreceptor
responds to pressure or distortion (skin, inner ear)
25
New cards
thermorecepetor
responds to heat (skin)
26
New cards
what is the nervous system
senses the environment, controls action
27
New cards
what does the central nervous system consist of
the brain and spinal cord
28
New cards
what does the central nervous system respond to
muscles and glands
29
New cards
what does the peripheral nervous system consist of
the bundles of nerves that relay messages between the sense organ, central nervous system and the muscles and glands.
30
New cards
where is the peripheral nervous system located
it is spread out through the entire body
31
New cards
what are neurons
cells that transmit messages in the form of electrical signals from the central nervous system.
32
New cards
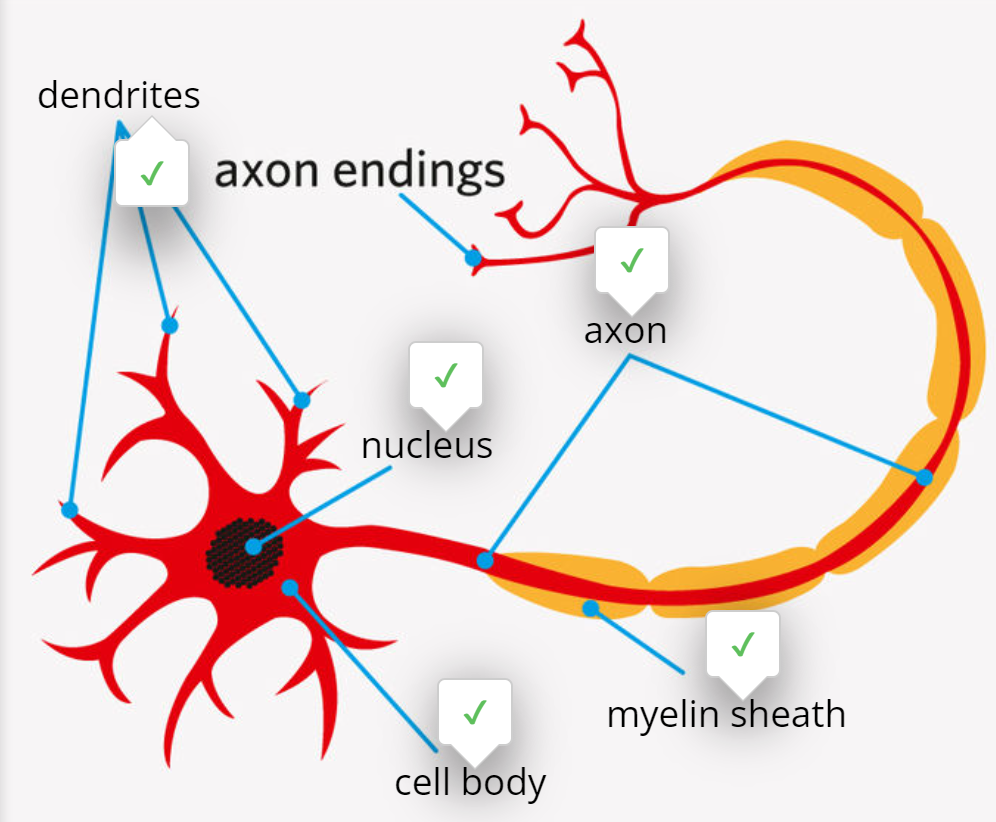
what is a cell body
where the nucleus is located
33
New cards
what are denrites
branches that receive messages
34
New cards
what are axon
a thread like structure that carries impulses to other neurons
35
New cards
what are myelin sheaths
a fatty later that sometimes insulates the axon and sometimes a dendrite.
36
New cards
general structure of a neuron
general structure of a neuron
37
New cards
what so the sensory neuron do
transmit messages from the sensory organs to the central nervous system
38
New cards
what does the interneuron do
transmit messages from sensory neurons to motor neurons
39
New cards
what does the motor neuron do
transmit messages from the central nervous system to effectors such as muscle and glands to initiate a response.
40
New cards
what is the speed of messages in the endocrine system
slow, generally takes longer to have an effect
41
New cards
what is the speed of messages in the nervous system
fast, generally has a rapid effect
42
New cards
what is the length of response for the endocrine system
often long lasting
43
New cards
what is the length of response for the nervous system
usually short lived
44
New cards
what is the spread of effect in the endocrine system
the hormones travel to all parts of the body via the bloodstream. BUT only affect the receptors for that particular hormone
45
New cards
what is the spread of effect in the nervous system
very localised
46
New cards
how do messages travel through the body in the endocrine system
in the blood stream
47
New cards
how do messages travel through the body in the nervous system
along nerves
48
New cards
what type of messages in the endocrine system
hormone (chemical)
49
New cards
what type of messages in the nervous system
electrical impulse, neurotransmitter (chemical)
50
New cards
adrenaline
source gland --> adrenal
target --> whole body
main effects --> increases heart rate shuts down digestion makes energy available to muscles
target --> whole body
main effects --> increases heart rate shuts down digestion makes energy available to muscles
51
New cards
thyroxine
source gland --> thyroid
target --> whole body
main effects --> makes cells consume more oxygen and nutrients increases body temperature
target --> whole body
main effects --> makes cells consume more oxygen and nutrients increases body temperature
52
New cards
thyroid-stimulating hormone
source gland --> pituitary
target --> thyroid
main effects --> stimulates thyroid hormone production
target --> thyroid
main effects --> stimulates thyroid hormone production
53
New cards
follicle-stimulating hormone
source gland --> pituitary
target --> gonads (ovaries or testicles)
main effect --> stimulates egg production in females stimulates sperm production in males
target --> gonads (ovaries or testicles)
main effect --> stimulates egg production in females stimulates sperm production in males
54
New cards
what is the sugar the body relies on for energy
glucose
55
New cards
glucose levels in the blood need to be kept within a certain range for the body to maintain homeostasis
true
56
New cards
what happens if there is too much glucose in the body
insulin yay :D —> it is produced by the pancreases
57
New cards
what is it called if the body can't use insulin effectively
diabetes
58
New cards
what is type 1 diabetes
the pancreas can’t produce enough insulin to control blood glucose levels
59
New cards
what do people with type 1 diabetes need
regular injections of insulin
60
New cards
what is type 2 diabetes
the target cells of insulin stop responding properly —> insulin resistance
61
New cards
what do people with type 2 diabetes need to do
change diet
62
New cards
what is artificial insemination
injection of sperm into the women’s uterus close to to time of ovulation
63
New cards
where else has artificial insemination been used for besides humans
It has also been used in agriculture in the production of prime farm animals, and in the breeding programs for endangered species
64
New cards
what is In-vitro fertilisation (IVF)
It is when the egg and semen are combined outside the mother's body in a dish.
65
New cards
what can be done if a man does not have enough sperm or a woman does not have enough eggs for a reproductive technology.
they can get it from a donor :D
66
New cards
what is the controversy surrounding reproductive technology
- some people believe it goes against nature
- religion may play a part in determining someone's views
- its very expensive
- Donors do not get paid
- religion may play a part in determining someone's views
- its very expensive
- Donors do not get paid
67
New cards
what is a pathogen
an organism which causes a disease to its host
68
New cards
what are organisms which can only been seen with a microscope
microbes
69
New cards
are pathogens infectious diseases
yup
70
New cards
what is a macro parasites
they are multicellular, do not typically multiply but instead produce transmission stages.
71
New cards
what is fungus
they are unicellular, they reproduce
72
New cards
what is protozoan
are single- celled organisms whose DNA is inside a membrane-bounded nucleus
73
New cards
what is bacterium
single celled organisms whose DNA is not contained inside a membrane-bounded nucleus
74
New cards
what is a virus
can not reproduce unless inside a host cell
75
New cards
what is a prion
are thought to be incorrectly folded proteins
76
New cards
can a disease disrupt the normal homeostasis of your body
yes
77
New cards
what is a non-infectious disease
they are not caused by pathogens and can NOT be transmitted from one organism to another.
78
New cards
how can infectious diseases be spread?
sneezing, coughing, physical contact with an infected organism, contaminated objects, contaminated water supply or vectors
79
New cards
is the common cold an infectious or non-infectious disease
infectious disease
80
New cards
is cancer and infectious or non-infectious disease
non-infectious disease
81
New cards
what is the first line of defence also known as
the barrier defences
82
New cards
what does the first line of defence do
prevents pathogens from entering the body. it consists of both physical and chemical barriers
83
New cards
what are some physical barriers
skin, cilia, hair, urine, and mucous
84
New cards
what are some chemical barriers
saliva, tears, strong acid, and acidity in your skin
85
New cards
what is the second line of defence
it is NON SPECIFIC !!!
86
New cards
what is the thing which takes up and digest any pathogen which enters the body
white blood cells also known as phagocytes
87
New cards
what is a macrophage
large white blood cell which eats pathogens
88
New cards
what is the general responses for the second line of defence
fever, inflammation, and phagocytes
89
New cards
what is a fever
the increase of body temp (above 38) --> slows down and kills pathogens
90
New cards
what is inflammation
painful redness and swelling in the affected area --> more blood = more white blood cells
91
New cards
what is the two main roles of the third line of defence
- identify and destroy specific pathogens
- build long-lasting immunity against the pathogen in case they
infect the body again
- build long-lasting immunity against the pathogen in case they
infect the body again
92
New cards
all pathogens have the same structure
false
93
New cards
what is an antibody
a type of protein that can bind to a pathogen
94
New cards
what does it mean to be immune to a disease causes by a pathogen
- the immune system has formed a memory of the pathogen
- the immune system can fight the pathogen more quickly and effectively
- the immune system can fight the pathogen more quickly and effectively
95
New cards
what does a vaccination do
- prevent the spread of a viral diseases and some bacterial disease
- trains the body
- trains the body
96
New cards
what does a vaccine contain?
a weakened or killed version of the particular pathogen
97
New cards
what is an antibiotic
a way of treating some bacterial diseases once people have gotten them
98
New cards
do antibiotic stop the growth of, or kill bacteria
yes
99
New cards
when were antibiotics first discovered
1928 by Alexander Fleming
100
New cards
good luck guys ily