h&h exam 1- lecture 1b hypothalamus & pituitary gland
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
How much does the pituitary gland weigh
600mg
where is the pituitary gland located
within the sella turcica (turkish saddle)
Are the hypothalamus and pituitary gland located within the blood brain barrier? Why
No! because it needs access to blood so it can release hormones into the bloodstream
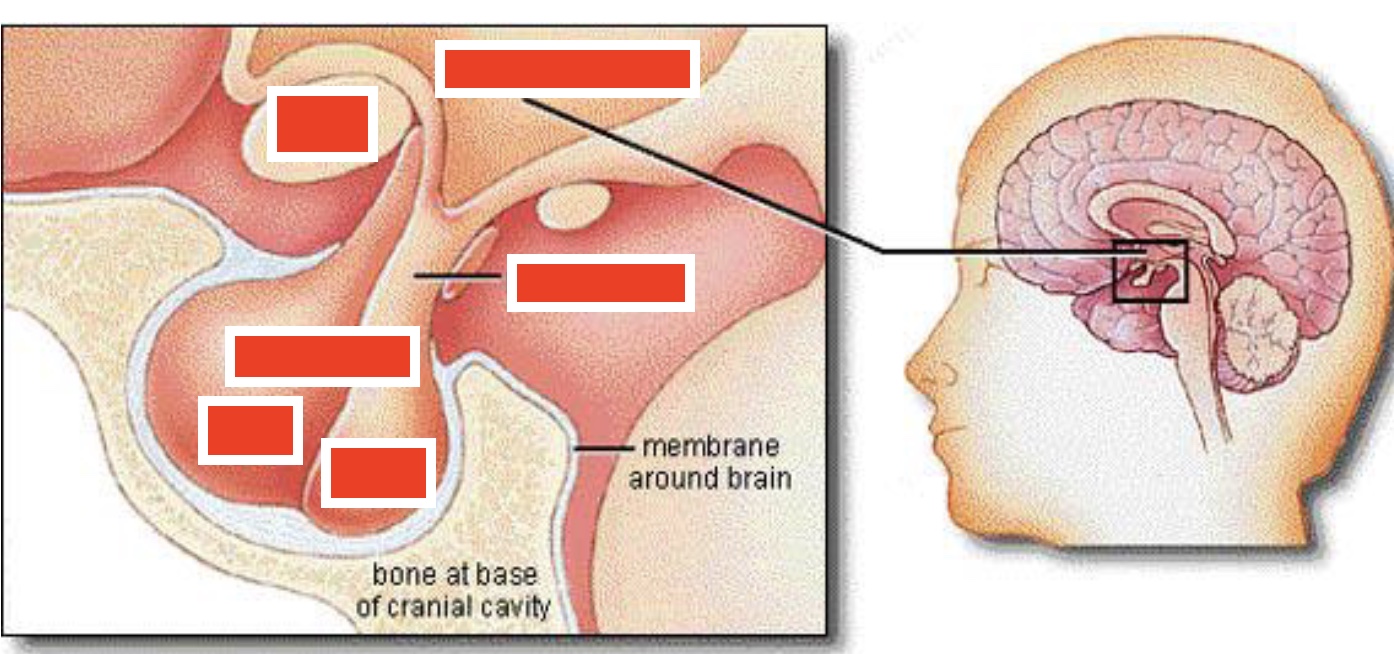
label (top two, middle, bottom 3)
top: optic chiasm, hypothalamus
middle: pituitary stalk
bottom: pituitary gland: anterior lobe (left) and posterior lobe (right)
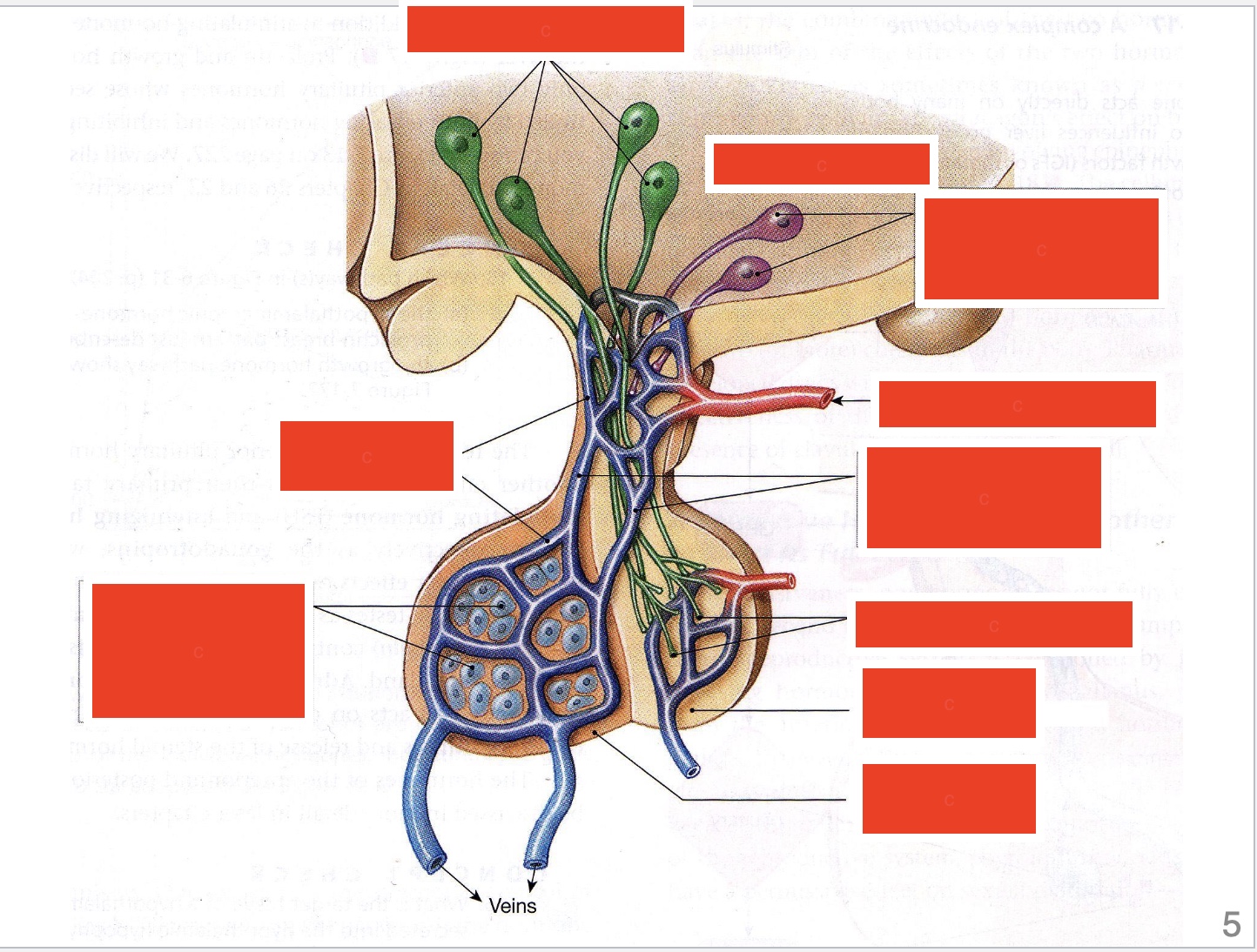
label: top 3 (top to bottom) (last one has description of function as well)
neurons synthesizing posterior pituitary hormones, hypothalamus, neurons synthesizing trophic hormones release them into capillaries of the portal system

label left two (bottom one has description of function as well)
capillary beds, endocrine cells release their hormones into the second set of capillaries for distribution to the rest of the body

label right column bottom 5 (top to bottom) (2nd has description of function as well)
artery, portal vessels carry the trophic hormones directly to the anterior pituitary, terminals of hypothalamic neurons, posterior pituitary, anterior pituitary
portal circulation description
passage of blood by a vein from one to a second capillary bed
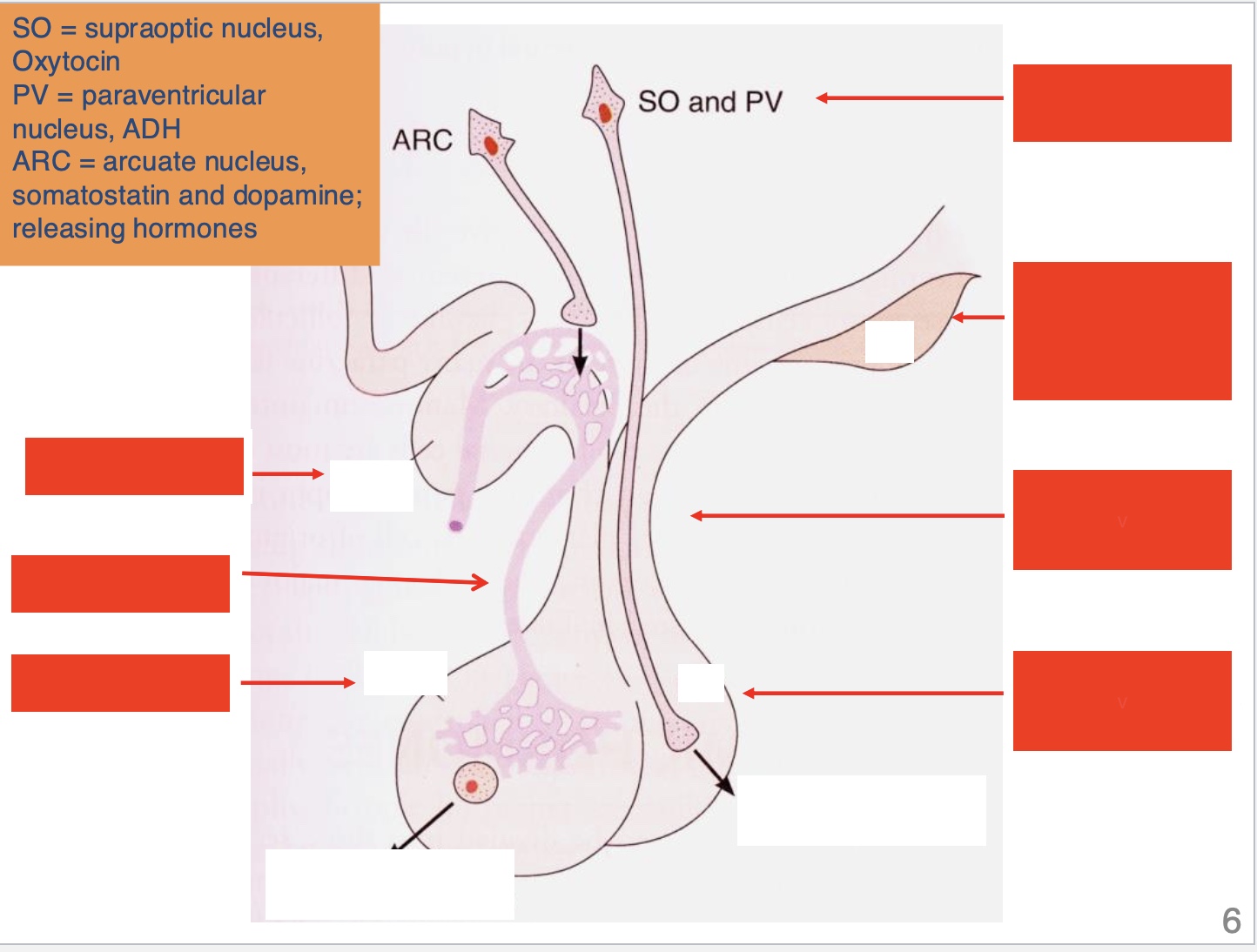
Label the red, left column
optic chiasma, portal vein, anterior lobe

Label the red, right column
hypothalamic nuclei, mamilary body (gray matter of the brain), pituitary stalk, posterior lobe
most basic functions of the anterior and posterior pituitary
anterior pituitary: portal system
posterior pituitary: neurosecretion
basic differences between anterior and posterior pituitary (3)
anterior: endocrine cells, contains capillary bed, portal system
posterior: no endocrine cells but has nerve endings from the hypothalamus, neurosecretion
Hypothalamus releasing hormones → anterior pituitary examples (6)
GHRH - GH
Dopamine - Inhibiting release of PRL (prolactin)
Somatostatin - Inhibiting release of GH
Thyrotropin-RH (TRH) - TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
Corticotropin-RH (CRH) - ACTH
Gonadotropin-RH (GnRH) - 1) LH (Luteinizing Hormone), 2) FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
Hypothalamus (hormones released in) → posterior pituitary examples (2)
AVP (cell bodies) - ADH
SO (cell bodies) - oxytocin
somatostatin description
somatotropin release inhibiting factor
Anterior pituitary important point regarding the amount of blood that is there
the amount of blood is really small (only a few capillaries) so even a few hormones can have effects on a local level, can easier change concentrations with smaller amounts of molecules
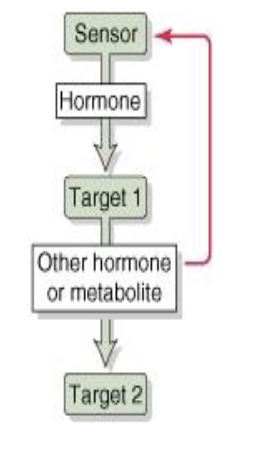
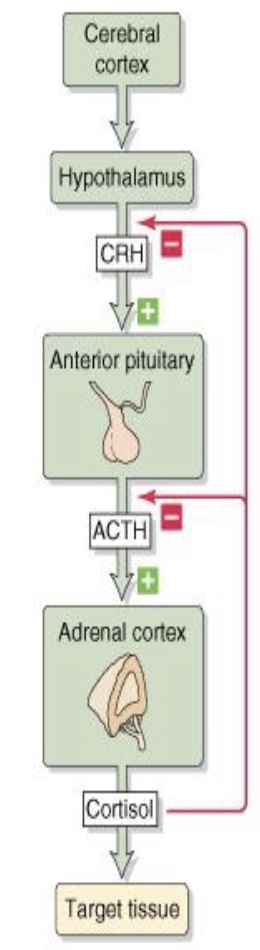
what is this an example of
simple feedback loop
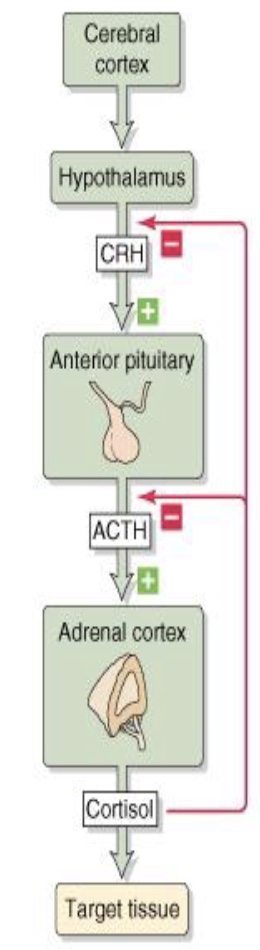
What is this an example of?
Hierarchical control
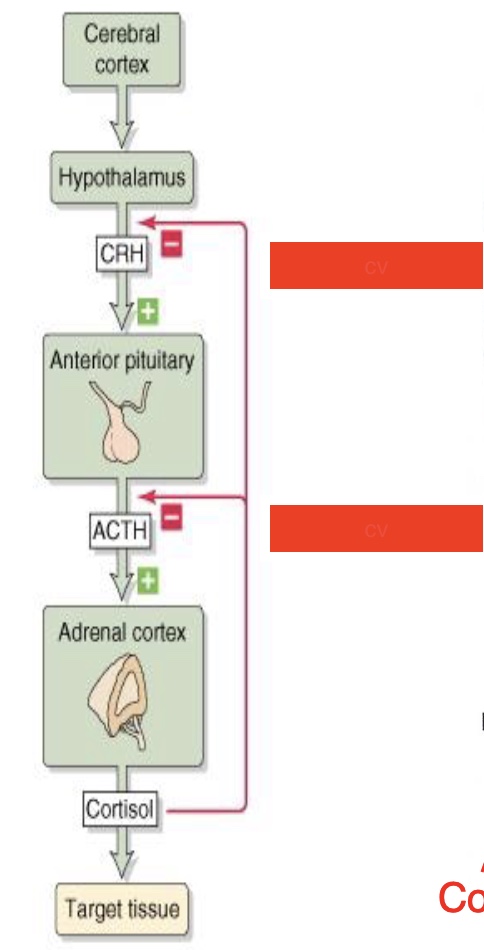
label
long-loop feedback, short-loop feedback
HPA axis simple (8 steps) (things in brackets are hormones that are released by the preceeding structure)
cerebral cortex - hypothalamus - (CRH) - ant. pituitary - (ACTH) - adrenal cortex - (cortisol) - target tissue
What is the HPA axis an example of?
Hierarchical control
HPA axis long
hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis
primary function of HPA axis
regulate the stress response
CRH long
corticotropin releasing hormone
ACTH long
adrenocorticotropic hormone
Cortisol effects on the HPA axis
short loop feedback: on the anterior pituitary releasing ACTH
long loop feedback: on the hypothalamus releasing CRH
Relation between ACTH and cortisol secretion
they have an episodic, pulastile pattern, ACTH normally increases first and then cortisol follows, except around 5am where cortisol peaks before ACTH (getting ready to wake up)
Hormones of the neurohypophysis & their actions (2)
vasopressin (effect on the kidney, effect on fluid maintenance, thirst)
oxytocin (love and bonding)
deficiencies of vasopressin secretion and action
diabetes insipidus, adipsic hypernatremia
adipsia meaning
absence of thirst
excess vasopressin secretion and action
hyponatremia
What is the neurohopophysis
posterior pituitary gland
Posterior pituitary description
axons originate in the hypothalamus, peptide hormones released by exocytosis in the posterior pituitary into the blood stream
Similarities between ADH and oxytocin
both contain 9 amino acids
actions of oxytocin (5)
uterine myometrium contraction (final stages of pregnancy) (cause of onset of labour is debated), suckling (milk ejection), maternal behaviour, possible: sexual and mating behaviour, oxytocin as a neurotransmitter
social-psychological effects of oxytocin (8)
trust (contested), sexual arousal, receptor polymorphism (sociopaths, etc), reduced function linked to autism, romantic attachment/mate bonding, improved memory for faces, empathy, dog’s attachment to humans
Dogs attachment to humans and oxytocin
after long petting session concentration of oxytocin in cerebro spinal fluid (CSF) of dog and human rose significantly
Trust and oxytocin
when administered nasally, subjects displayed “highest level of trust” twice as often as controlled (contested though)
oxytocin and romantic attachement (3)
positive correlation between oxytocin plasma levels and self-perceived romantic attachment; in praire vole - oxytocin administered in the CNS increases monogamy; reduces incidence of infanticidal behavior in animals
oxytocin and autism (2)
correlation between some forms of autism and deletion of oxytocin receptor gene; people with some forms of autism fail to produce oxytocin, nasally administered oxytocin decreased some of the symptoms
oxytocin and social behaviour and empathy (4)
administered intranasal oxytocin induces improved memory for (happy) human faces, increased empathy, improved recognition for +ve social cues over threatening social cues, increased generosity
MDMA and oxytocin
100mg of MDMA increased oxytocin levels significantly in humans, activation of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors → secretion of oxytocin
oxytocin and sexual stimulation
plasma levels of oxytocin rise during sexual stimulation up to orgasm
Pheromones in humans
testosterone derivative (AND) activates the hypothalamus in females but not in males, estrogen-like compound (EST) did the opposite