Paper 1 physics
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
Energy 1 & 2
10 types of energy changes
- magnetic
- kinetic
- thermal/heat
- light
- grav potential
- chemical
- sound
- electrical
- elastic potential
- nuclear
what is a system?
an object/group of objects working together
what is energy?
the ability to do work
What is magnetic energy?
due to the magnetic fields around magnets
What is kinetic energy
moving object/particle
what is thermal energy?
energy is transferred from one object to another bc of temp difference between the two objects
What is light energy?
kind of kinetic energy with the ability to make types of light visible to human eyes.
what is gravitational potential energy?
above the earths surface = potential (stored)
what is chemical energy?
energy stored in bonds of chemical compounds
what is sound energy?
vibrations/movement of energy through a substance
what is electrical energy?
kinetic energy caused by moving electric charges
what is elastic potential energy?
energy stored as a result of applying a force to deform an elastic object
What is nuclear energy?
Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
Energy transfers:
energy carried from one place to another
Types of energy transfers
- mechanical
- electrical
- by heating
- by radiation
mechanical transfers
when force moves through a distance
electrical transfers
when charge moves through a pd
by heating transfers
because of temp difference
by radiation
eg light, microwaves, sound
Efficiency
- when energy is changed from one form to another, some energy is changed into forms that are not useful. A system is more efficient if it can produce the same output energy with less input.
Why are some light bulbs given a higher energy rating than others?
less of the input energy becomes heat/wasted
how can we make a light bulb more efficient?
reduce heat produced so we can get same amount of light for less input
what are some washing machines given a higher energy rating than others?
can do the same job using less input energy
why are the brakes on a car so hot?
the brakes do not work on the kinetic energy and converts it into chemical energy
Conservation of energy
energy cannot be created/destroyed, only transferred from one form to another. Sometimes transferred into useless forms.
Useful energy
- Do some exercises on sanky diagrams##
the width represents the amount of energy, as the width split, arrows should add up to width of starting arrows, this shows conservation of energy
Energy supplied =
useful energy delivered + energy wasted
efficiency (%) =
useful energy/ total energy x 100
Thermal energy
is transferred from hot to cool areas by conduction, convection or radiation
Conduction
movement of heat through a substance by the collision of particles. Hotter particles vibrate faster and these increased vibrations are transferred through the substance.
Convection
is what happens when warmer fluids rise up through cooler fluids because they are less dense than the cooler surroundings
Radiation
All warm objects emit infrared rays in all directions. These rays travel ar the speed of light.
Metals
good conductors
Non-metals
bad conductors, good insulators
Conduction of heat
The conductivity of materials can be compared by examining the time taken to transmit energy through them, this is called their thermal conductivity.
It has applicants to areas in modern life such as the design and construction of buildings.
Why is air a bad conductor of heat?
Conduction involves collisions of particles, it takes longer to pass on the energy in air bc the particles are far apart = bad conductor.
What are u-values?
measures how effective a material is as an insulator. The lower the u-value is, the better the material is as an insulator.
Cavity wall
u-value of 1.6W/m^2
Solid brick wall
u-value of 2W/m^2
Double glazed window
u-value of 2.8W/m^2
What is power?
the rate at which work is done/energy is transferred
power =
workdone or energy transferred/ time taken
power -
W watts
Time taken-
s, seconds
work done -
J, joules
Work done =
force (N) x distance(m)
ways in which insulation reduces energy costs in houses
1) cavity wall insulation
2) double glaze windows
3) loft insulation
what is payback time?
amount of time taken to recover the cost of an investment - like a new method of insulation.
Non-renewable energy resources
- will eventually run out
- not replaced at same rate it's used
- ex = coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear
Renewable energy resources
- will not run out
- can be replaced at same rate it's used
- ex = solar, tidal, wave, wind, geothermal, biofuel, hydroelectric.
Coal
+ enough available for demand
- releases CO2, climate change, eventually will run out
nuclear fuel
+ reliable, lot of energy from small mass, no polluting gases
- waste is dangerous/difficult/expensive to deal with, expensive to run/shut down
Solar energy
+ can be used in remote places, cheap, no waste product/polluting gases
- unreliable, expensive initial set up, can't control supply
tidal power
+ no polluting gases/waste products, reliable, produce large amounts of electricity, cheap
- harm marine habitats, expensive initial set up, hazard for boats, energy amount varies on time of month
Wave turbines
+ no polluting gases/waste products, cheap
- unreliable, depend on weather, expensive initial set up harm marine habitats, can't be used in large scales
Wind turbines
+ free, high power output
- unreliable, depends on weather, noise pollution, takes up space
Geothermal energy
+ no polluting gases, low cost
- expensive initial set up, available in few locations
biofuels
+ carbon neutral, reliable
- expensive to produce, use land/water, might need to grow food
Hydroelectric power
+ no polluting gases/waste products, cheap, reliable
- expensive initial set up, dams harm/destroy marine habitats
Gravitational potential energy
- when you lift an object up, you exert force = to its weight(mg) , through a distance equal to the height raised(h). Therefore you have done work equal to mg x h.
- Law of conservation of energy, the gravitational potential energy gained is = to work done
grav potential energy(J) =
mass x grav field strength x height
(kg) x (9.8 N/kg) x (m)
Elastic potential energy
When we stretch a spring, work is done & energy is stored within the spring, assuming no energy is lost, work is done = energy stored.
The more the spring is stretched, more work is done and more energy is stored.
Force & extention
Force is directly proportional to extension.
Elastic potential energy(J) =
1/2 x spring constant x extention^2
1/2 (N/m) x (m)
Kinetic energy depends on speed
Doubling the speed of an object, quadruples the kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the speed of an object squared.
Kinetic energy (J) =
1/2 x mass x velocity^2
1/2 x (Kg) x (m/s)
Current electricity:
Inside atoms
centre of atoms is a nucleus containing protons & neutrons.
Protons
relative charge is +1, relative mass is 1
Neutron
relative charge is 0, relative mass is 1
Electron
relative charge is -1, relative mass is 1/2000
Adding electrons to an uncharged atom
makes it negative, because there are more electrons than protons.
Removing electrons to an uncharged atom
makes it positive, because there are more protons than electrons
Electrical charges; charged rods
charge polythene and acetate rods by rubbing with a duster. One rod should be balanced on an upturned evaporating basin before bringing the other rod up to it. So the rubbed sides of both rods are close.
Friction transfers electrons
Polythene rod and polythene rod
Repel
Acetate and acetate
Repel
Polythene rod and acetate
attract
Like charges
repel
Different charges
attract
Charge is measured in
coulombs
Uncharged objects
Have equal no. of positive & negative charges, this means they have no overall charge and can be described as being neutral.
Charged objects
Charged objects either have more negative charges than positive charges or more positive charges than negative charges.
How can insulator can become charged with static electricity?
- if you have two insulators, rub together and causes friction.
- Friction transfers electrons
- The insulator that receives electrons has a net negative charge
- The insulator that loss electrons has a net positive charge
Balloon sticking to a wall:
1) The balloon and the wall has no overall/net charge; they are neutral
2) Rub the balloon and the friction transfers electrons to the balloon, negative charge
3) Balloon is near the wall and the negatively charged electrons are repelled
4) The surface of the wall is positively charged
5) The balloon and the wall attract
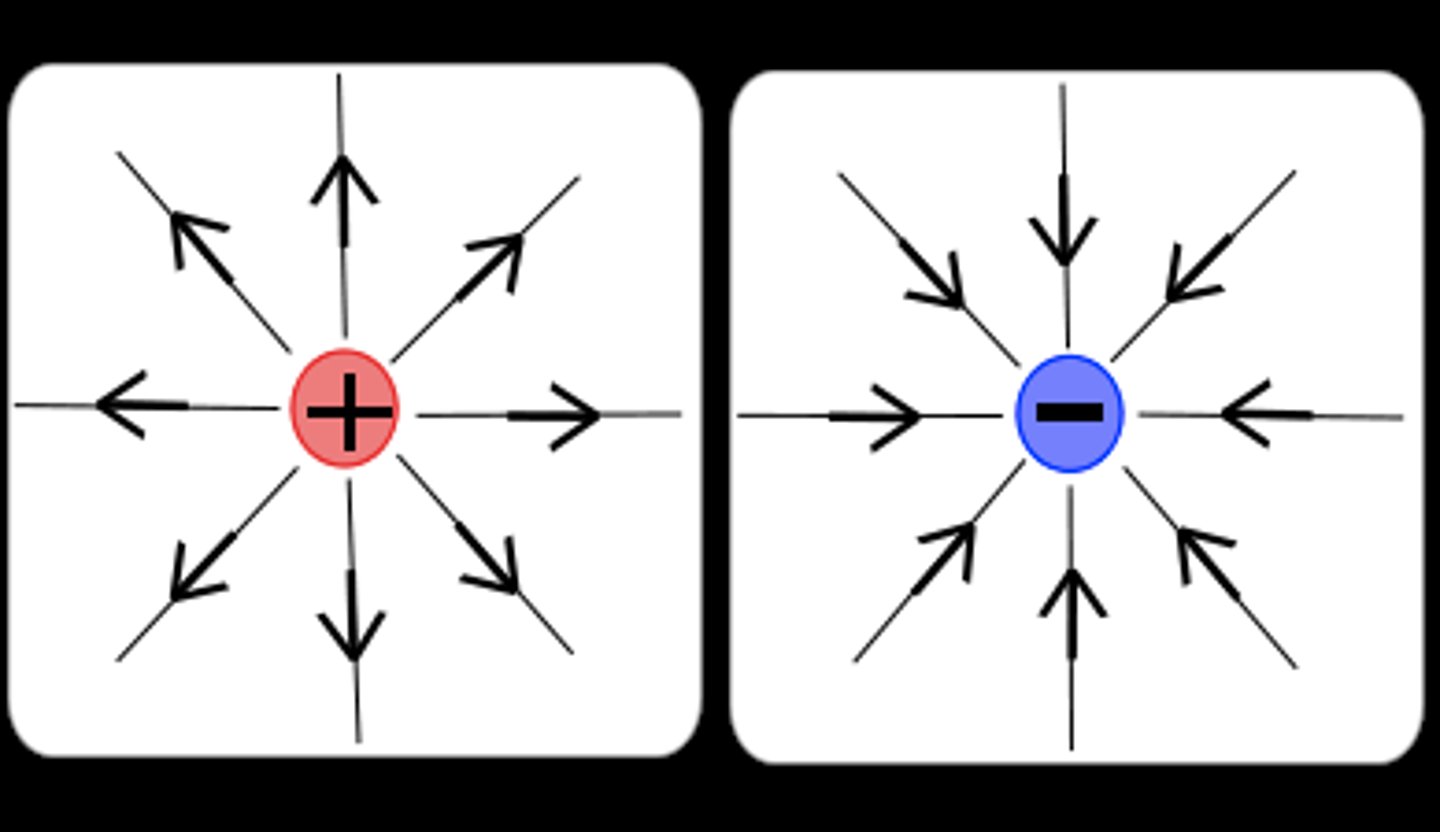
What is an electric field?
The region in which a charged object. They produce non-contact forces between charge objects.
Electric fields
+ charges repel each other, - charges attract.
Arrows represent the direction that a positive charge will feel a force.
The force of the field is strongest dose to the surface, the field lines are closer together.
The closer the object is to the field, the strength of field will be stronger. Field is stronger at the surface of electrons will distance.
SPARK
Has to be a high enough PD between the charged object and the earth, the air becomes ionised, the electrons jump between the charged object and the earth. energy is released as heating light.
When polythene is rubbed with wool
- some electrons leave the cloth & move on to the polythene rod so that the polythene becomes negatively charged and the wool is left positively charged.
Uncharged object
- a negatively charged object attracts a piece of paper bc it repels electrons away from the surface of the paper.
- This leaves the surface of the paper positively charged so that it is attracted to the object.
- A positively charged object attracts a piece of paper bc it attracts electrons towards the surface of the paper.
- This makes the surface of the paper negatively charged so that is it attracted to the object.
What are conductors?
Conductors allow electrons charges to flow through them.
What are insulators?
Don't allow electron charges to flow through them.
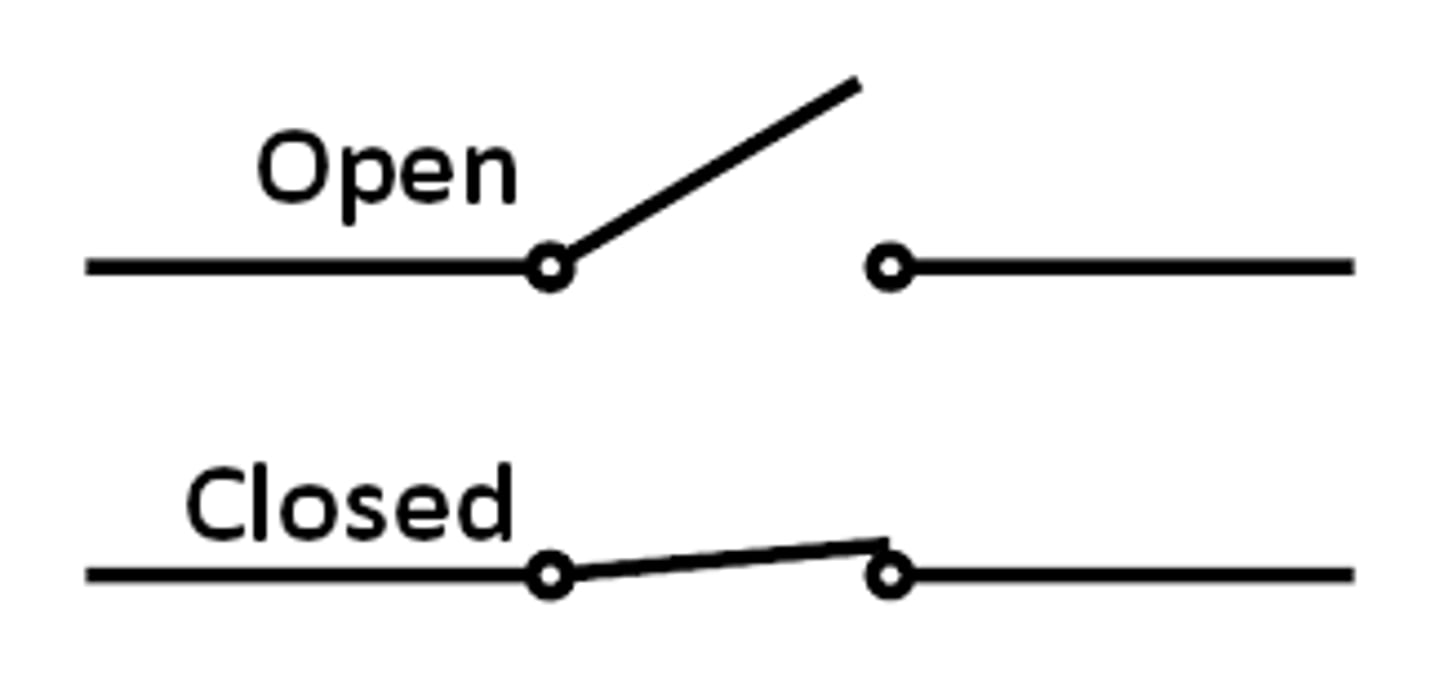
Open/close switch
Current doesn't flow unless opened
Cell
Supplies energy and current
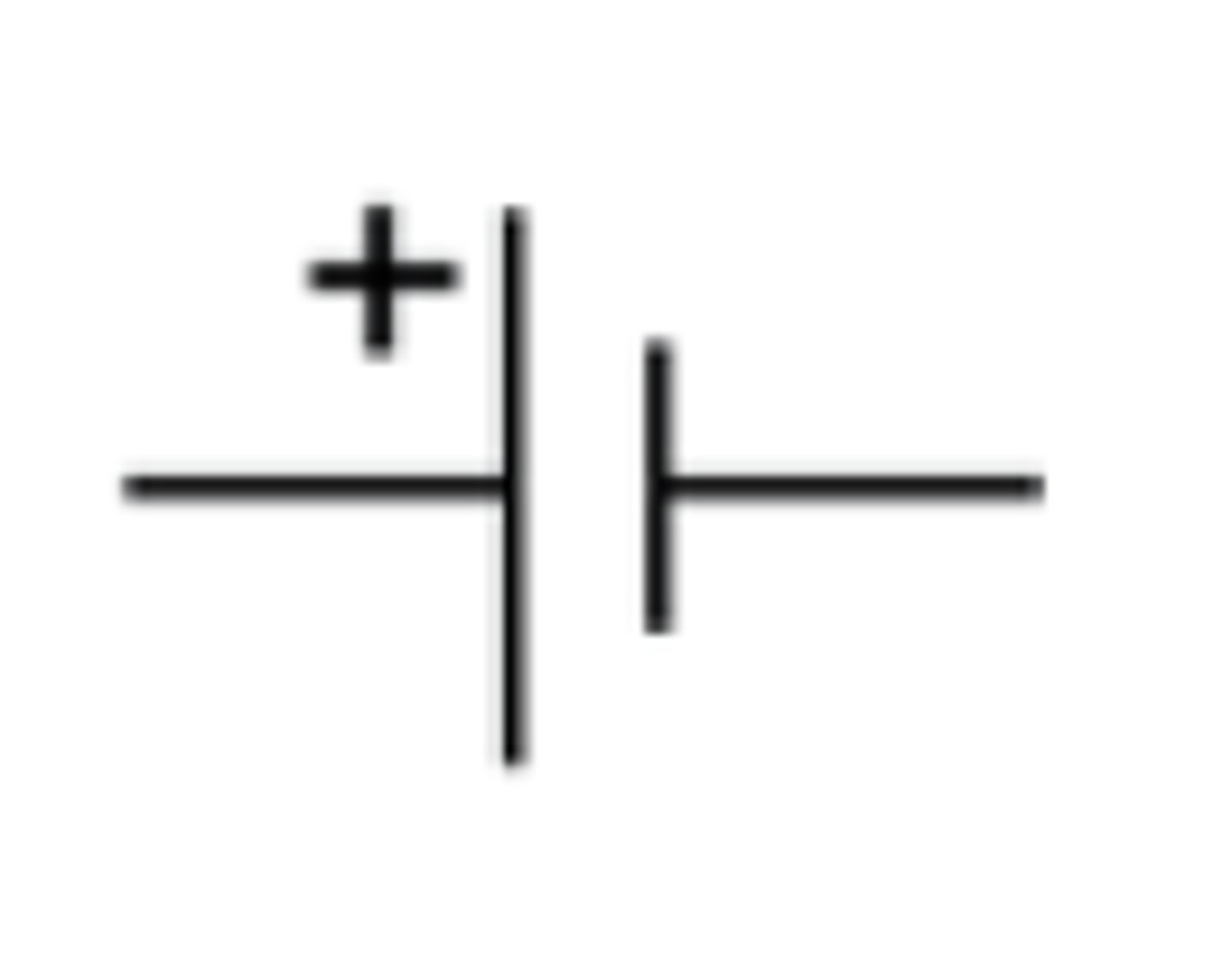
Battery
2/more cells

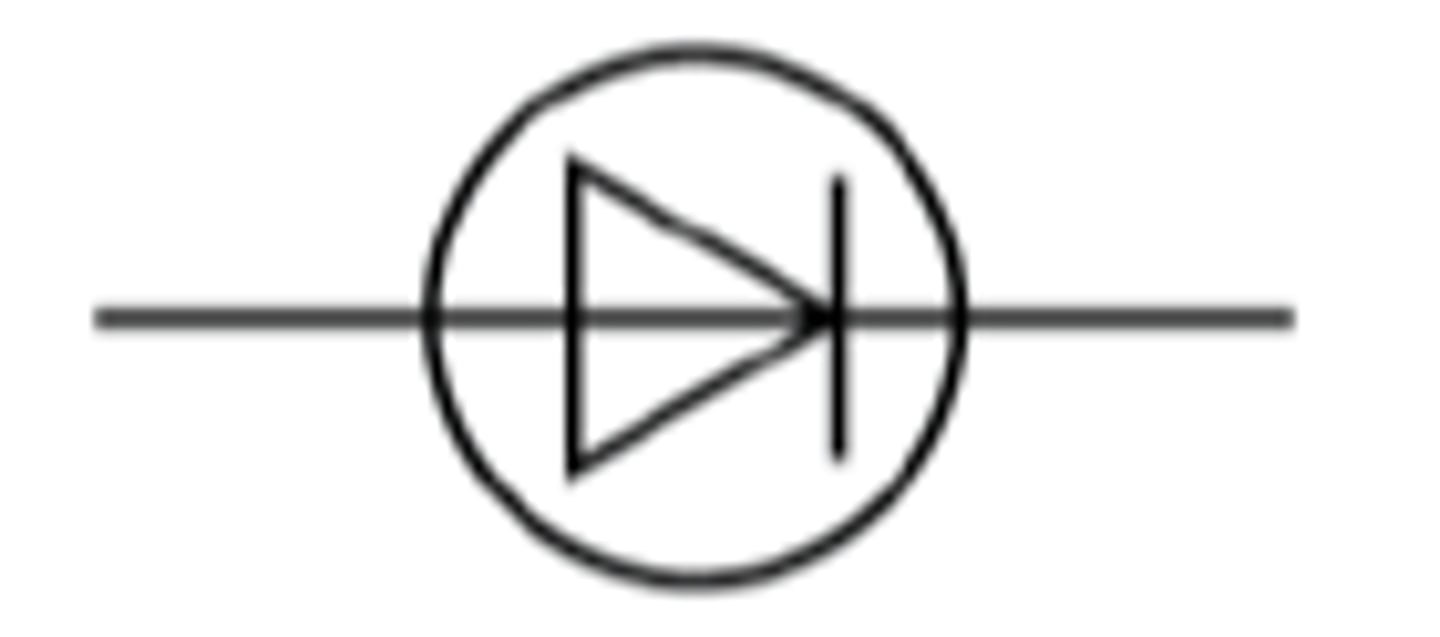
Diode
Current can only pass in one direction
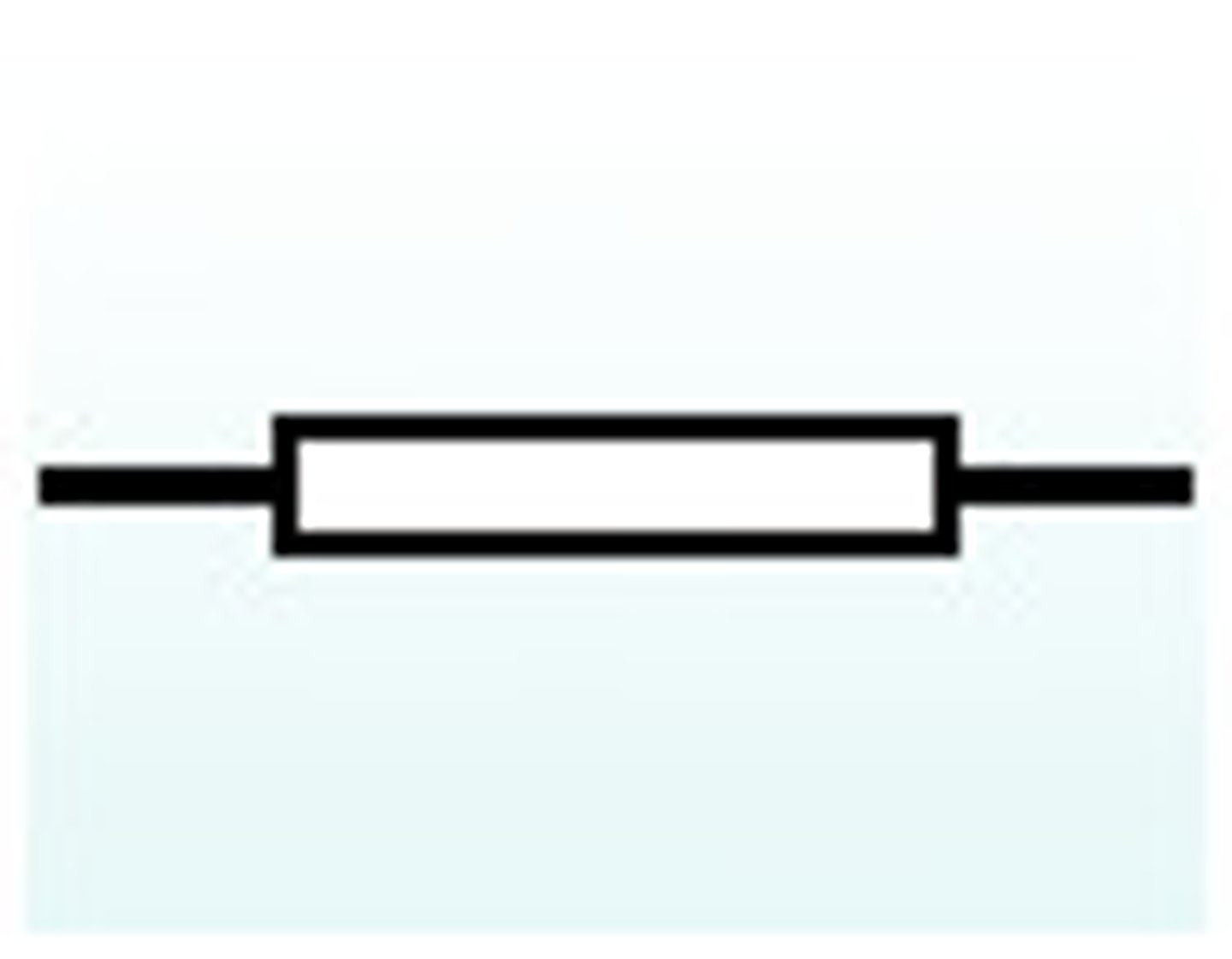
Resistor
Reduces current flow
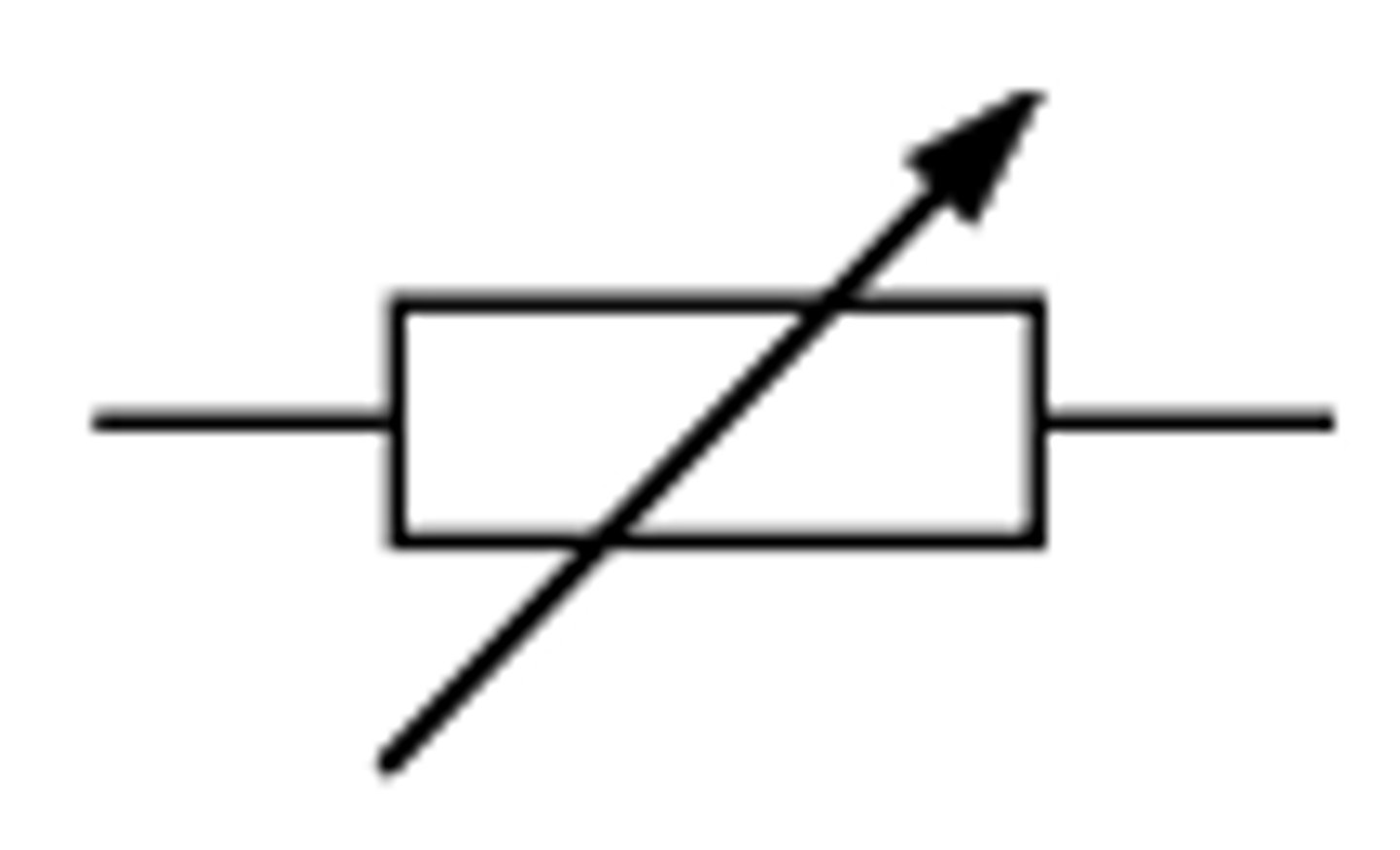
Variable resistor
Amount of resistance can change
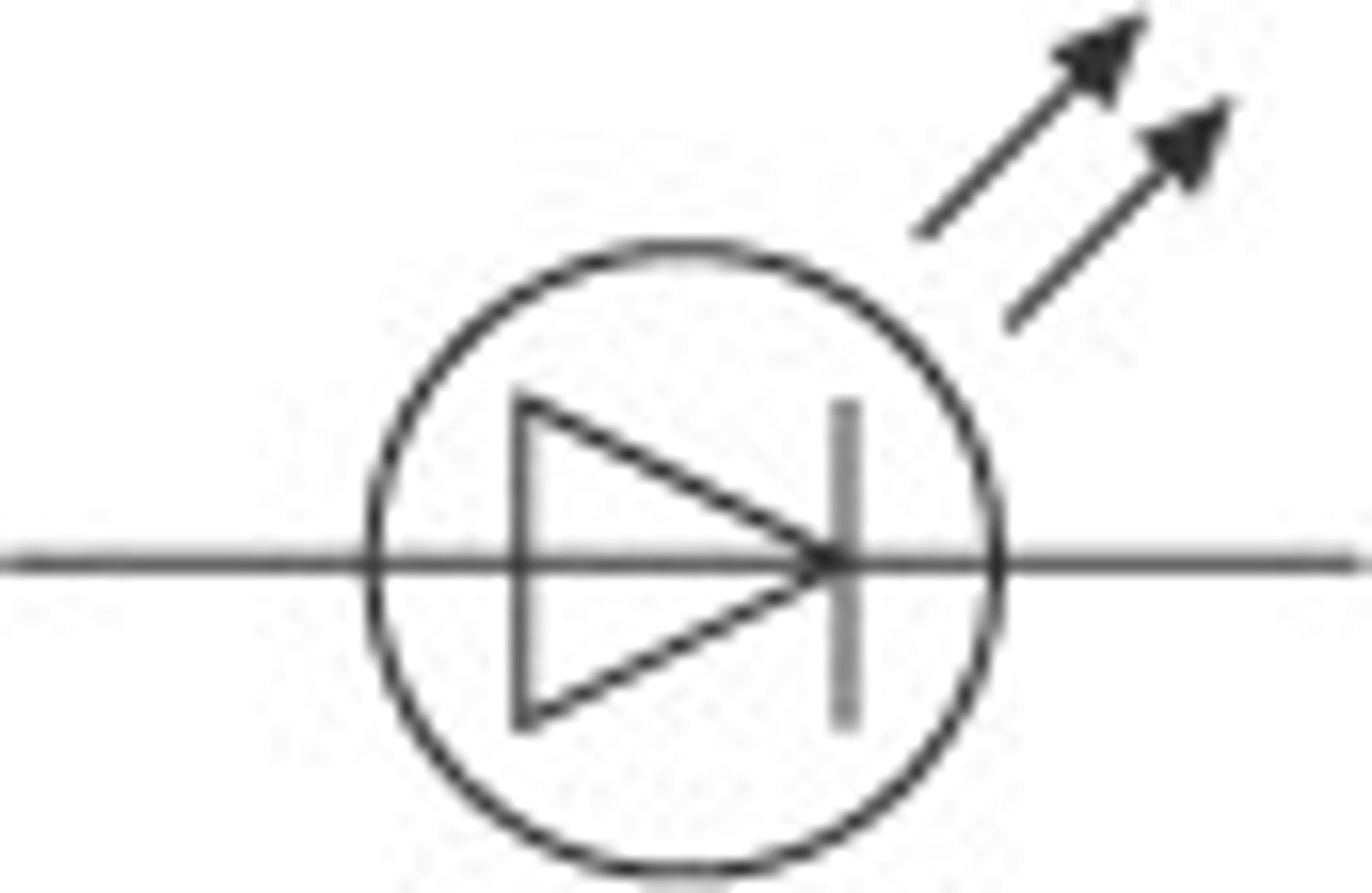
Light emitting diode
Emits light when a current flows in one direction
Fuse
'blows' if too much current flows
