Muscle Histology & Skeletal Muscle Identification
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
characteristics of muscle tissue
excitability, contractility, extensibility, elasticity
functions of muscle tissue
-providing body movement
-supporting organ structure
-protection
-thermogenesis
-blood circulation
Another name for muscle cells is a ________.
myocyte
The three types of muscle tissue are ______, ______, and _______.
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
skeletal muscle function
responsible for body movement
skeletal muscle location
attached to bones
skeletal muscle is under ____ control
voluntary
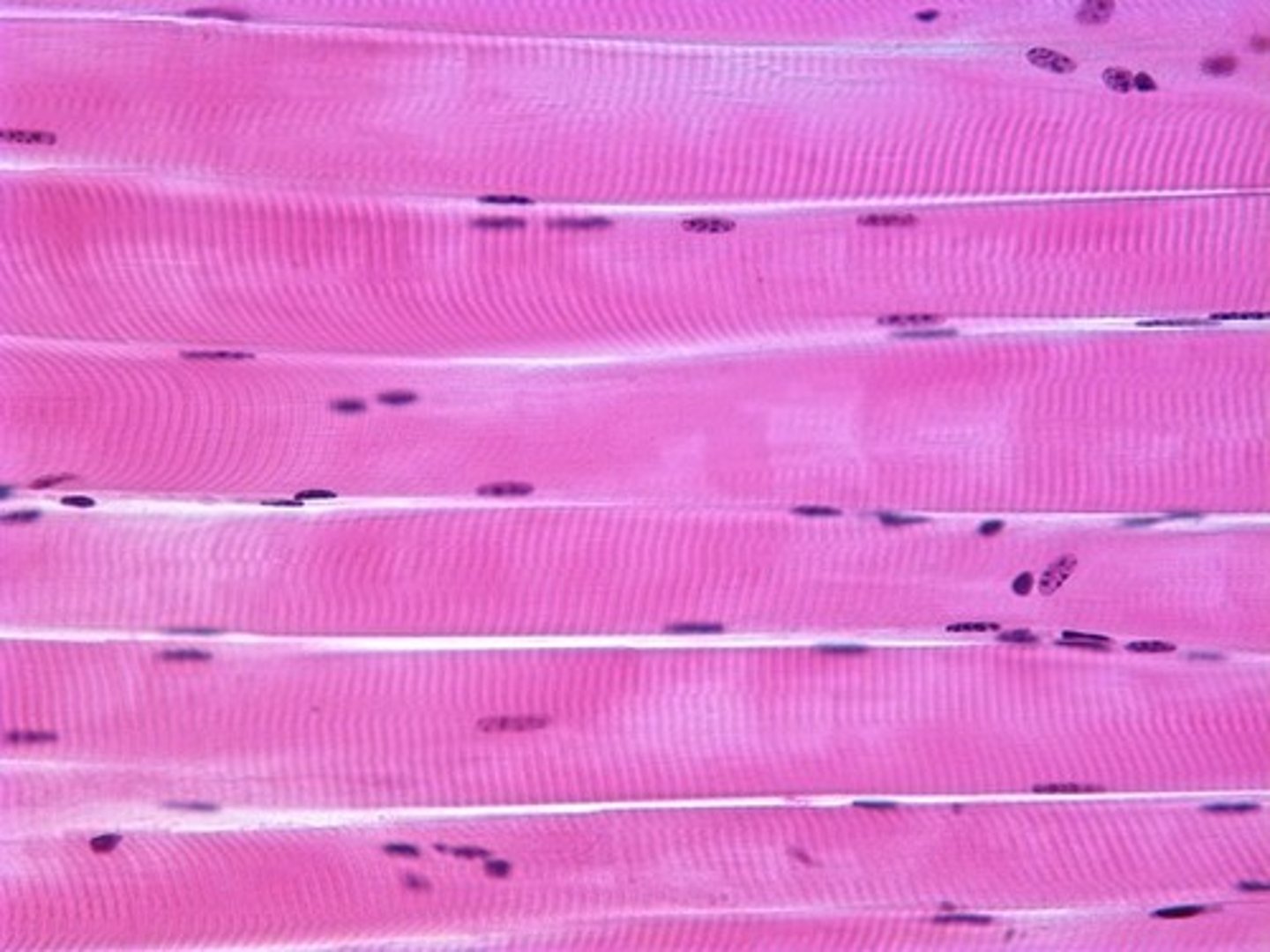
skeletal muscle is ______-nucleated
multi-nucleated
skeletal muscle is
a. striated
b. un-striated
a. striated
skeletal muscle
cardiac muscle function
pump blood
cardiac muscle location
forms the bulk of the heart
cardiac muscle is under ________ control
involuntary
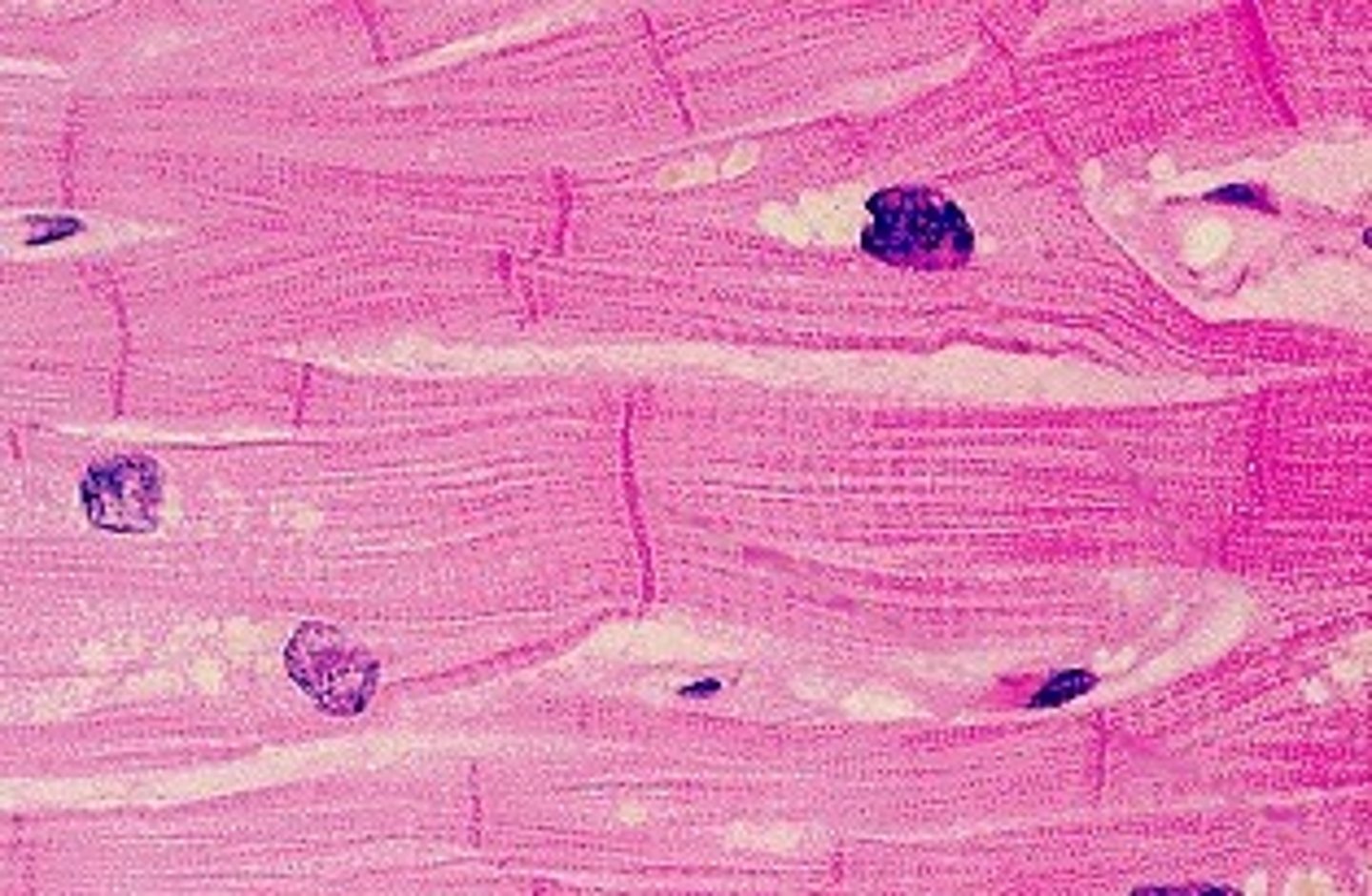
cardiac muscle is _____-nucleated
mono-nucleated (1 nucleus)
cardiac muscle is
a. striated
b. un-striated
a. striated
cardiac muscle
smooth muscle function
propels substances or objects along internal passageways
smooth muscle location
forms walls of hollow organs (ex: esophagus, GI tract)
smooth muscle is under ______ control
involuntary
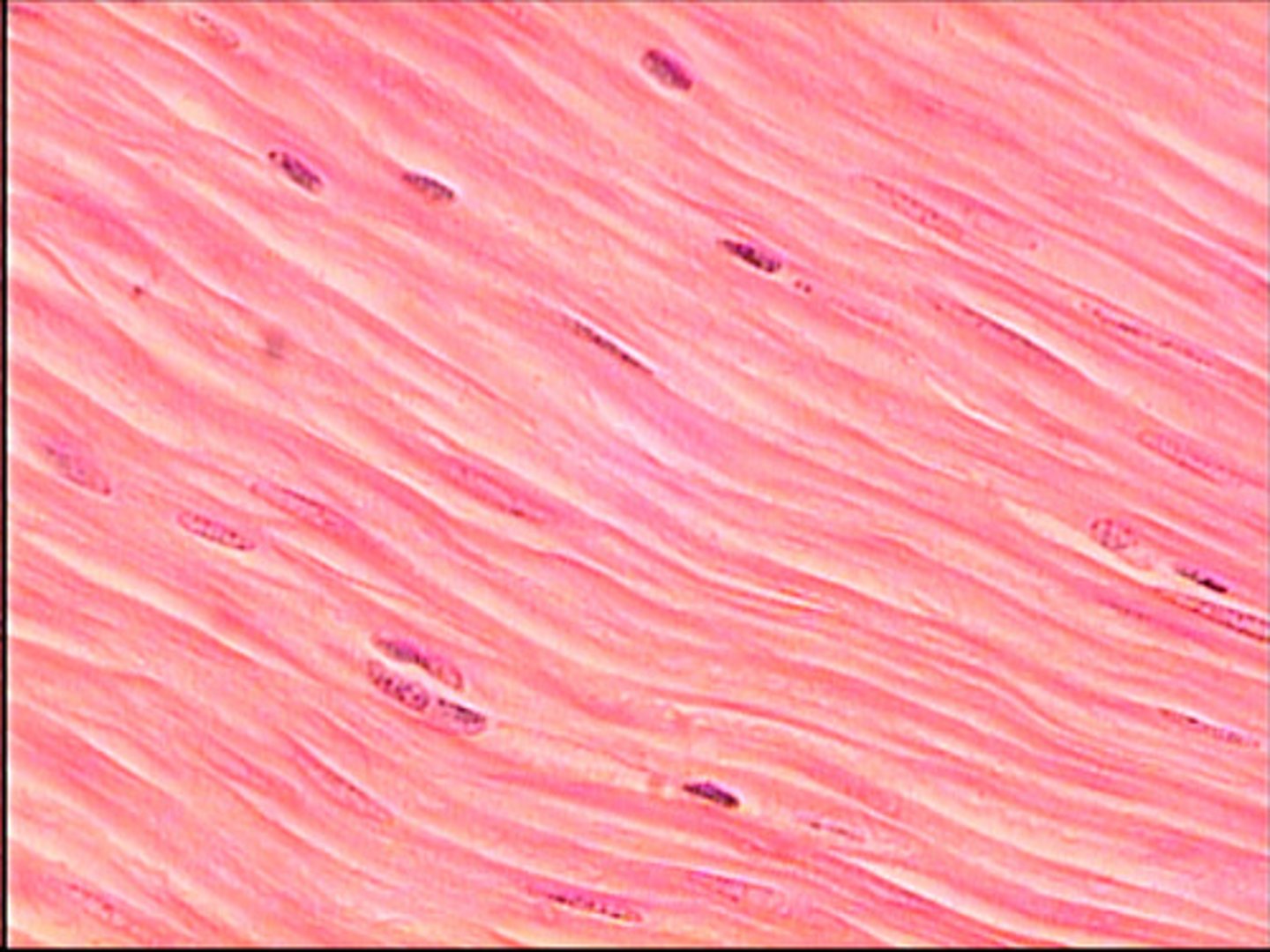
smooth muscle is _____-nucleated
mono-nucleated (1 nucleus)
smooth muscle is
a. striated
b. un-striated
b. un-striated
smooth muscle
intercalated discs
junctions between cells anchor cardiac cells
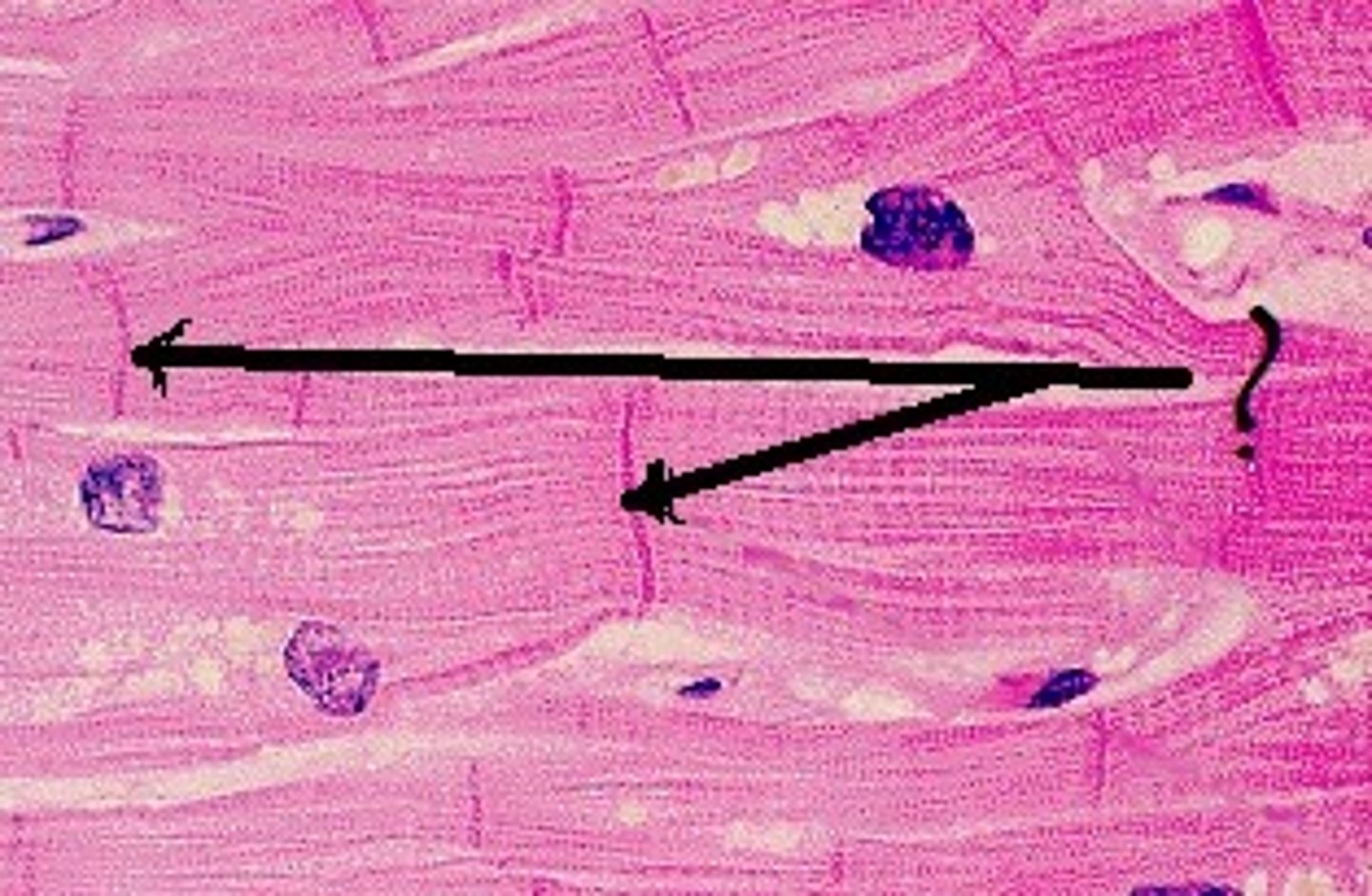
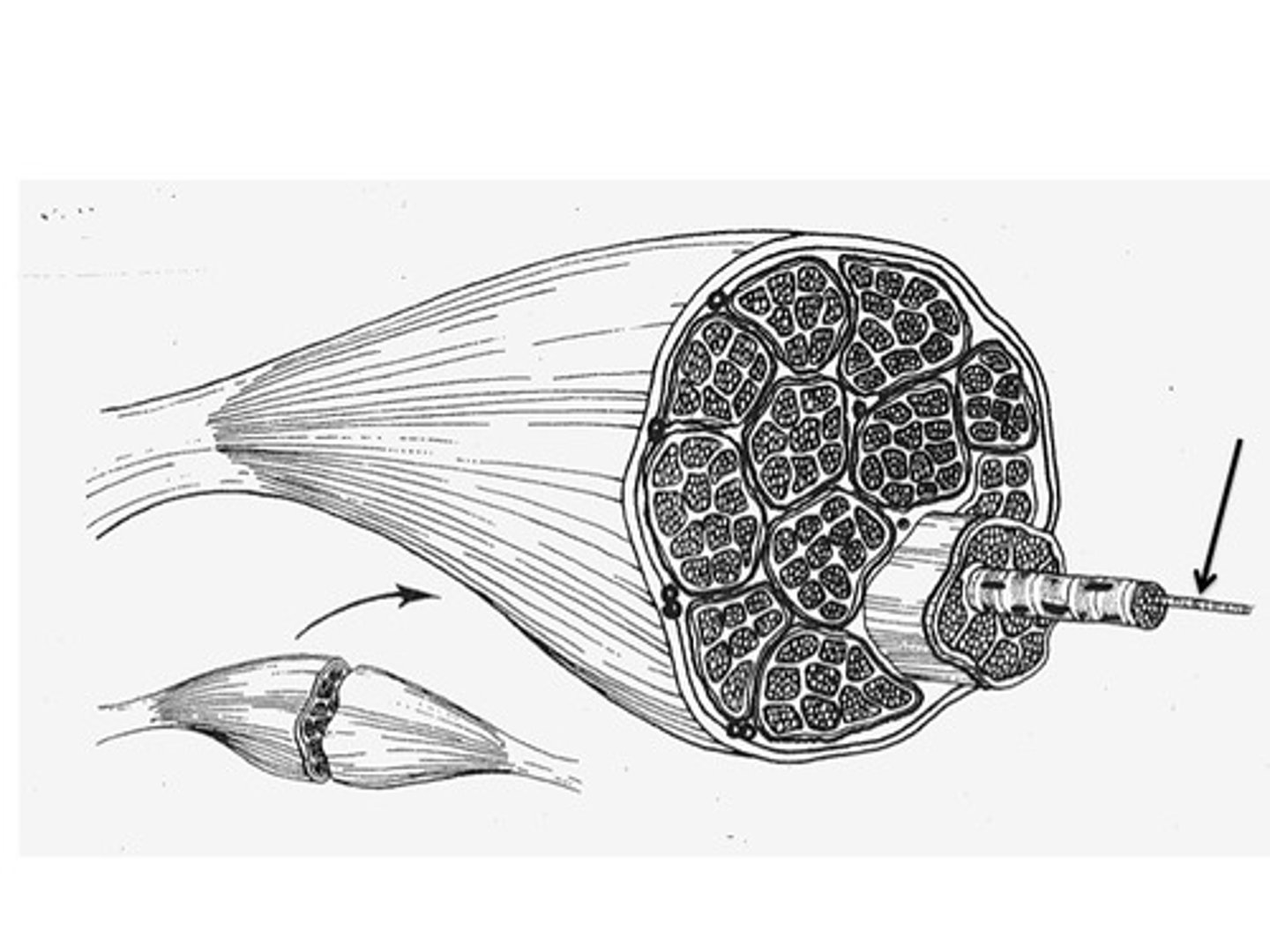
epimysium
covers the entire skeletal muscle group (outermost layer)
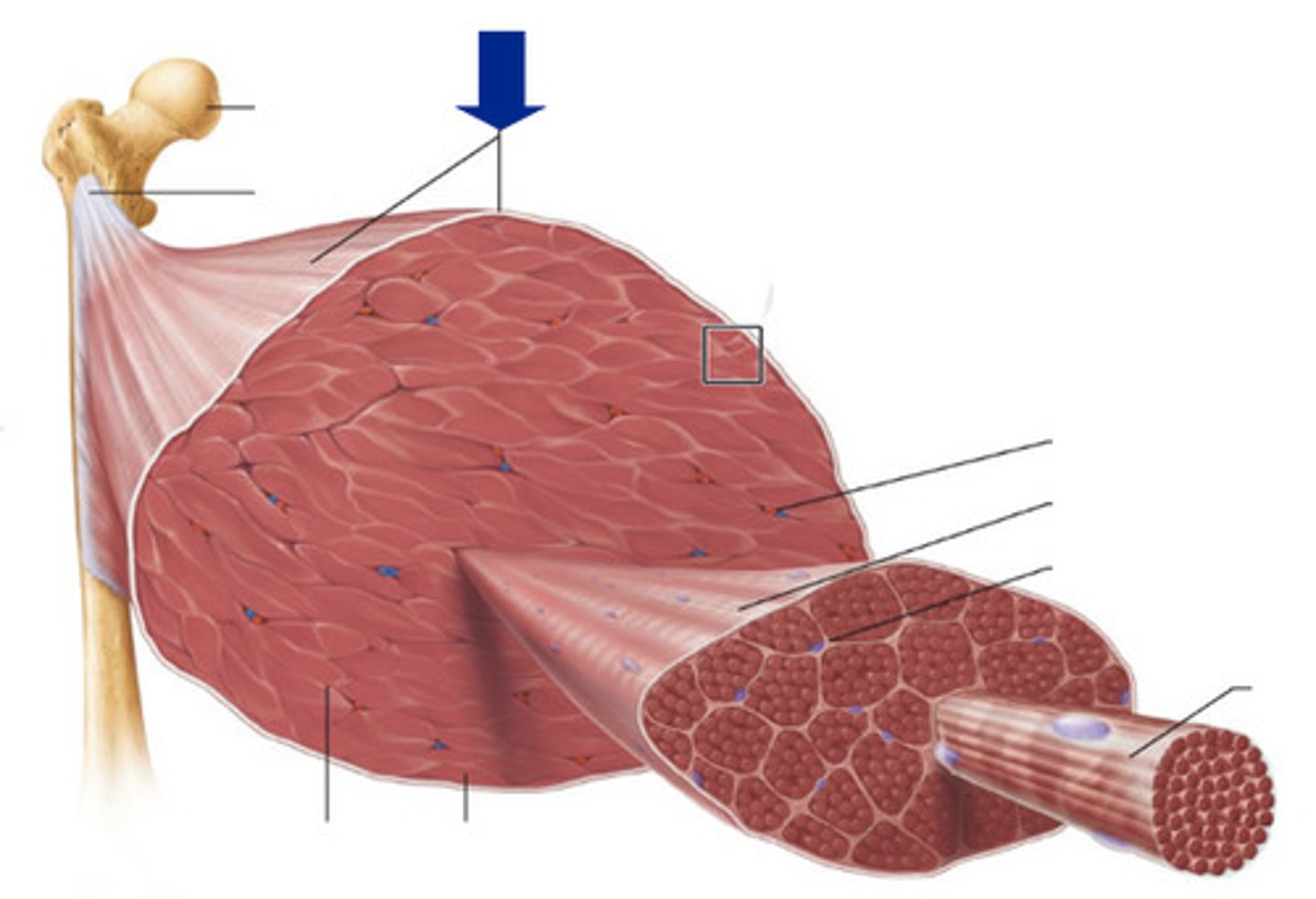
perimysium
surrounds fascicles (middle layer)
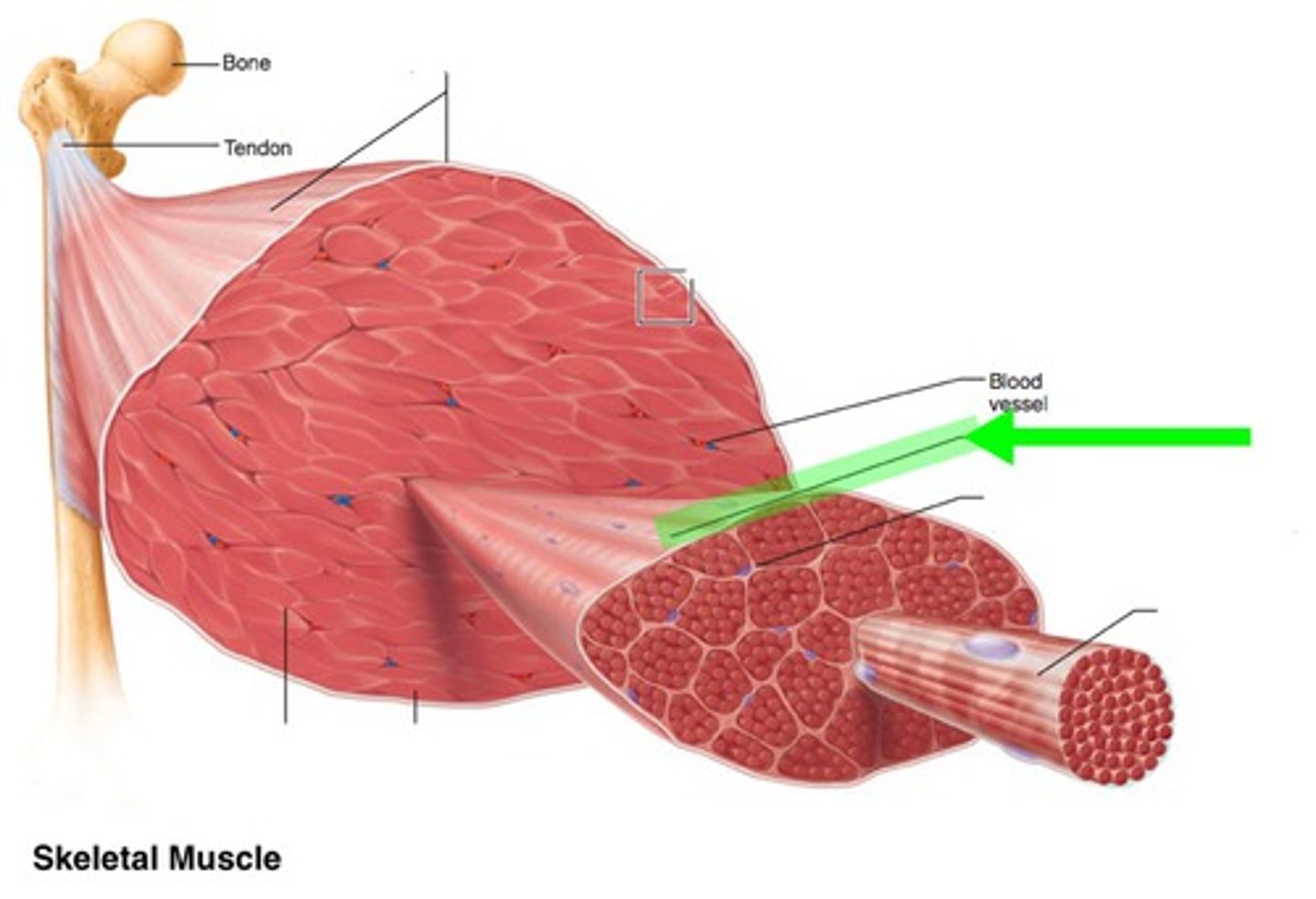
endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber (innermost layer)
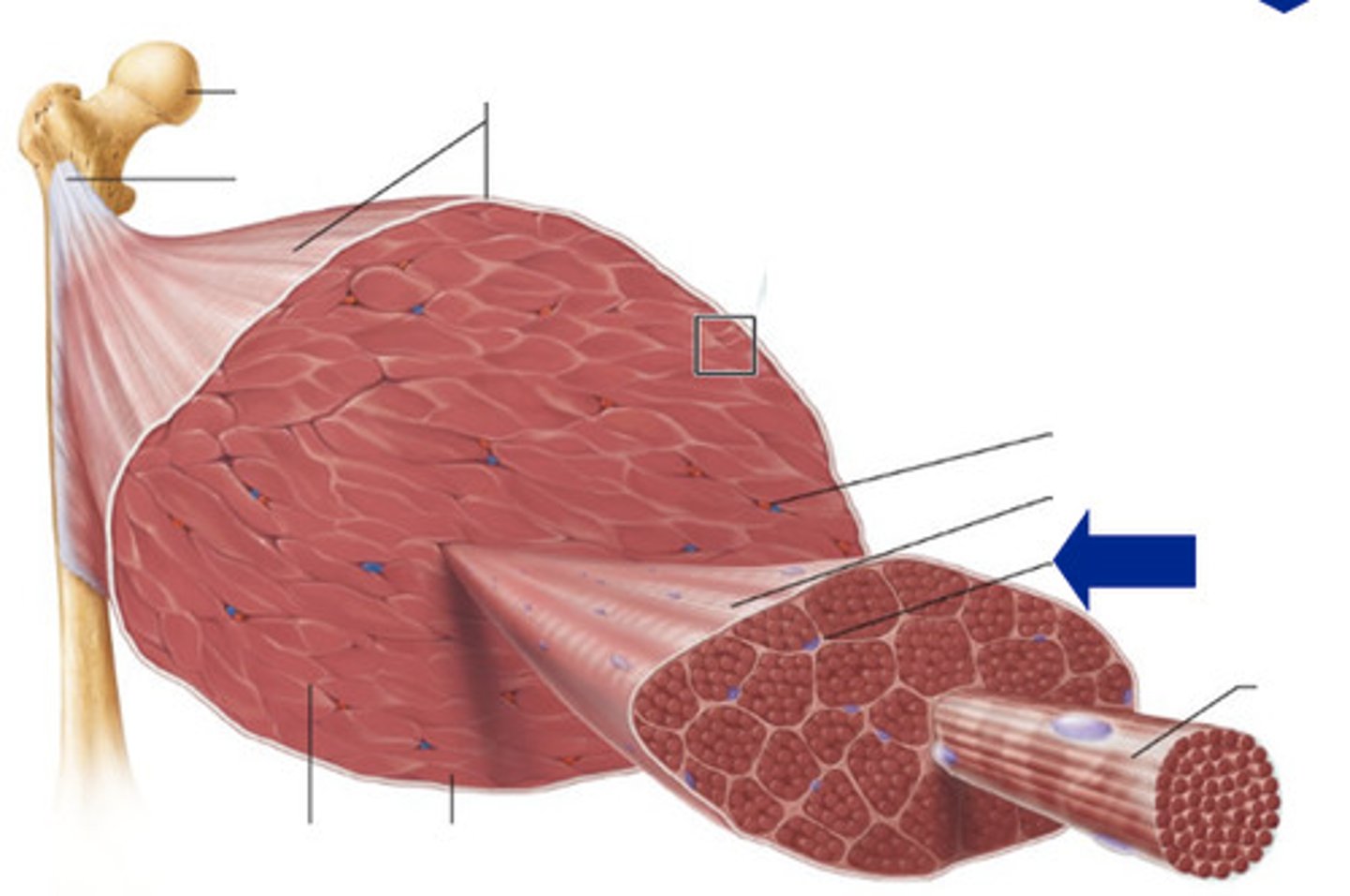
fasicle
a discrete bundle of muscle cells
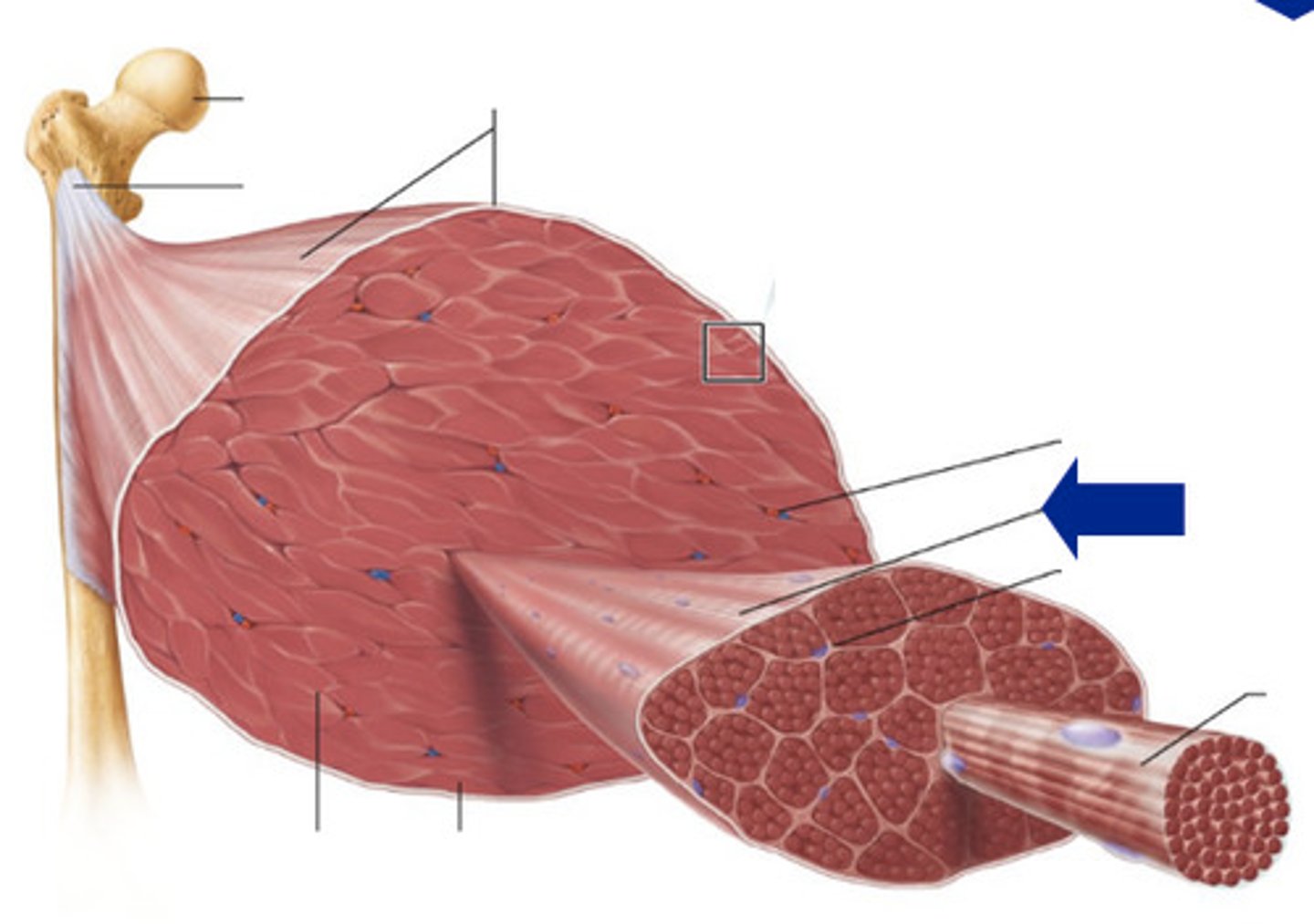
muscle fiber (cell)
bundle of myofibrils
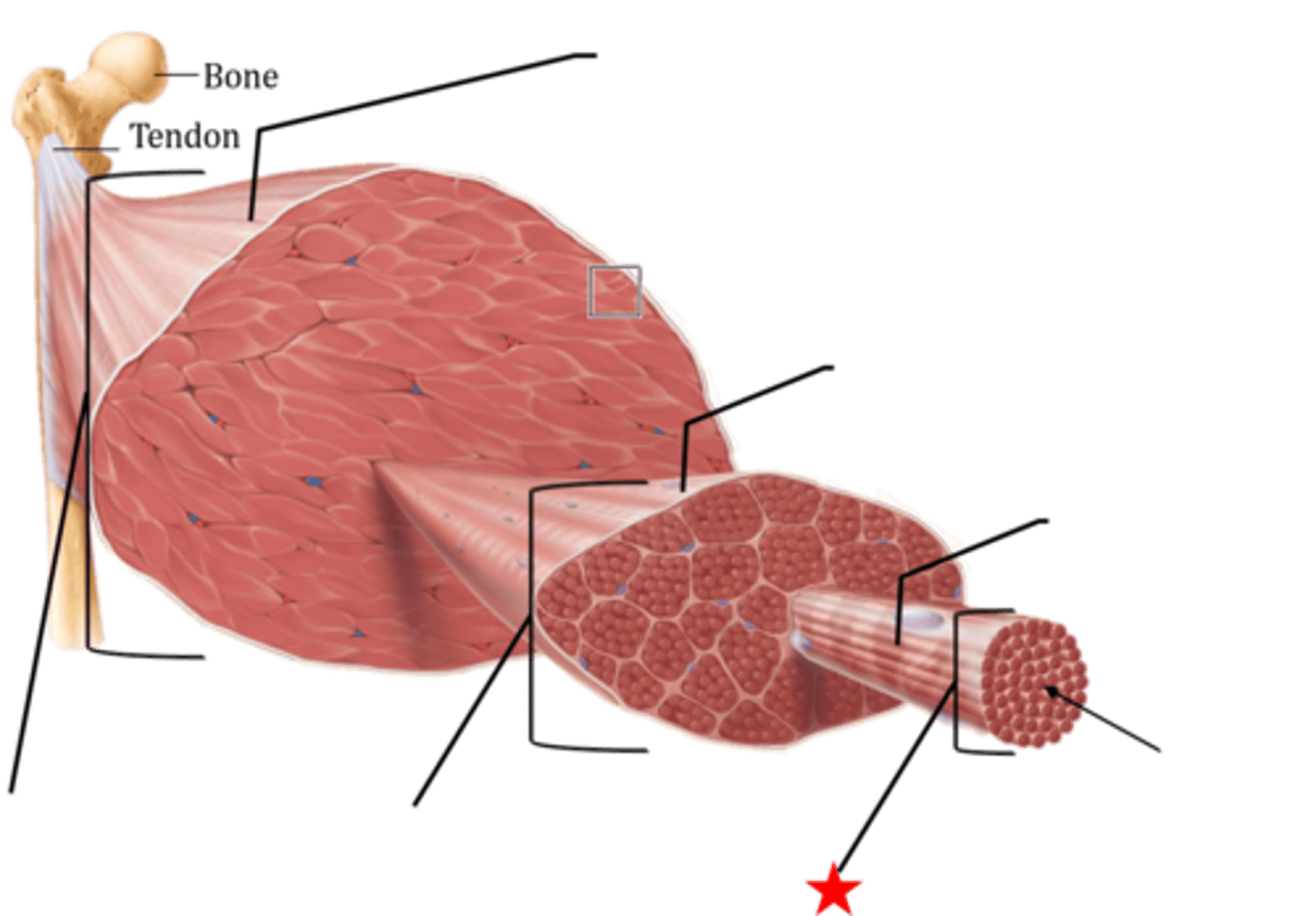
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
myofibril
tightly packed filament bundles found within skeletal muscle fibers
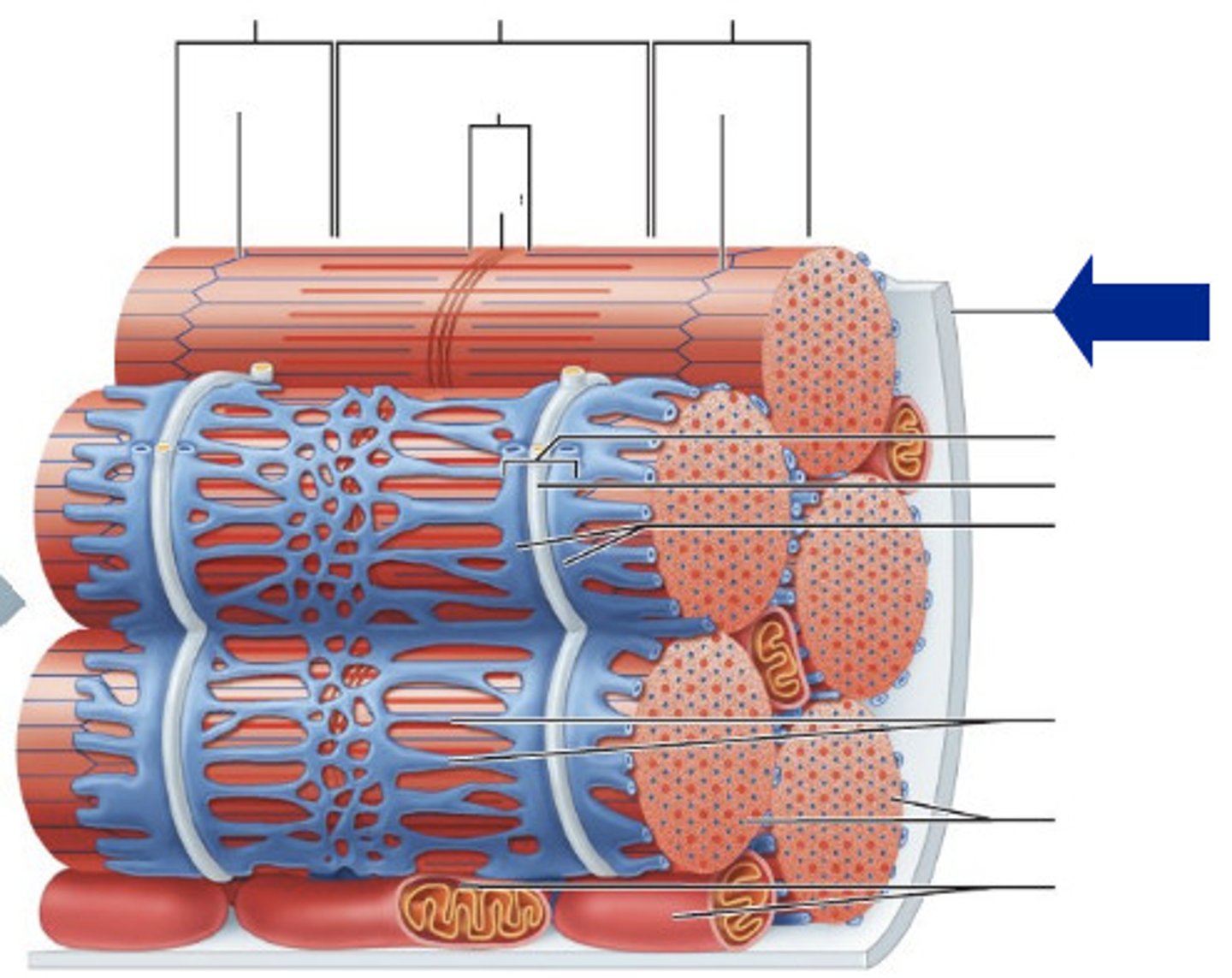
sarcomere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
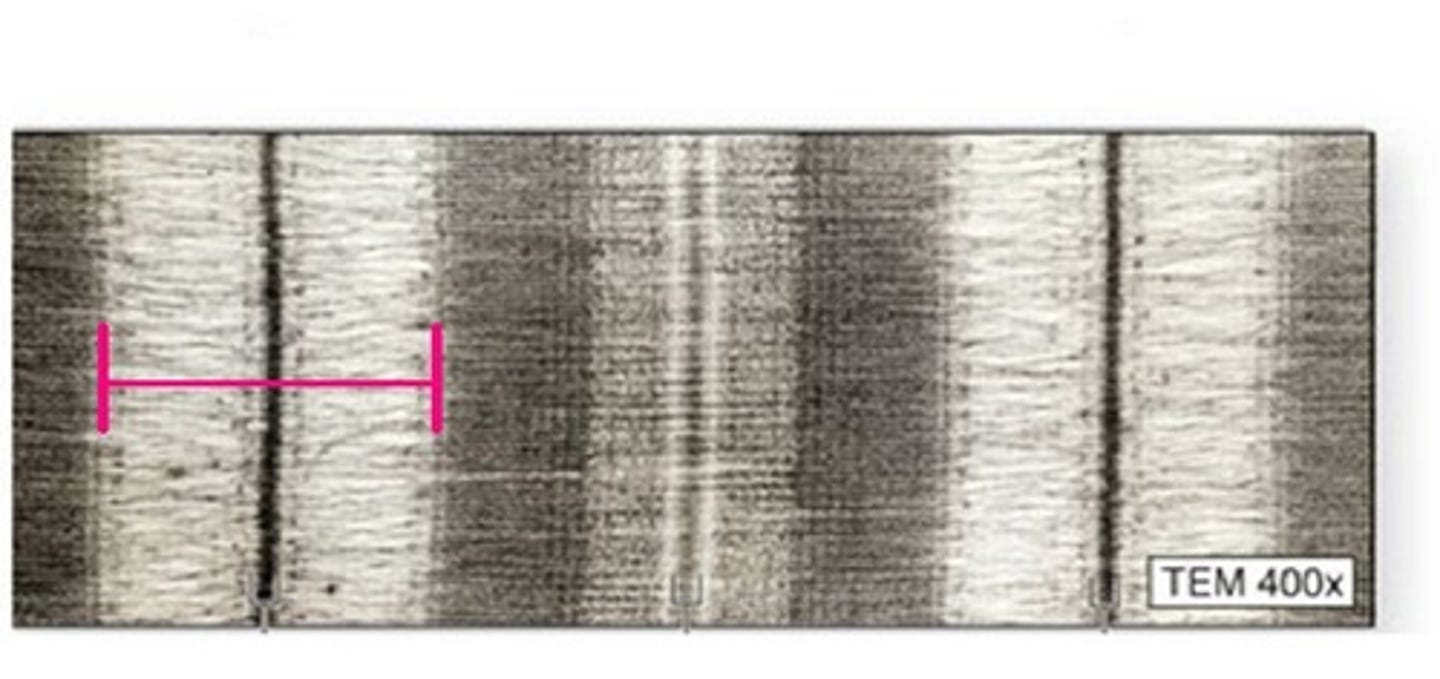
sarcomeres run from __- disc to __- disc
z-disc
z-disc
sarcomere boundary
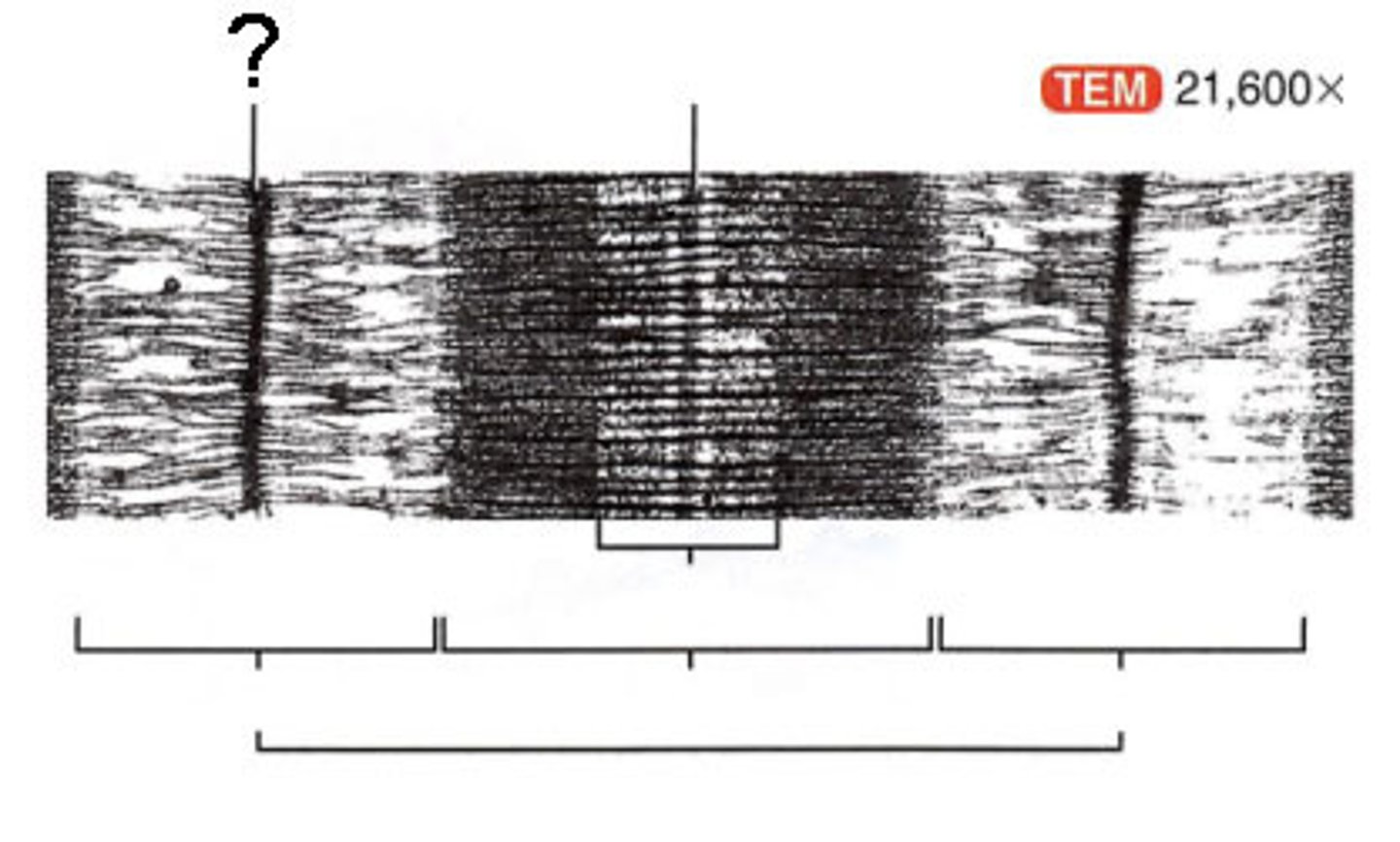

a-band
area of contraction and relaxation
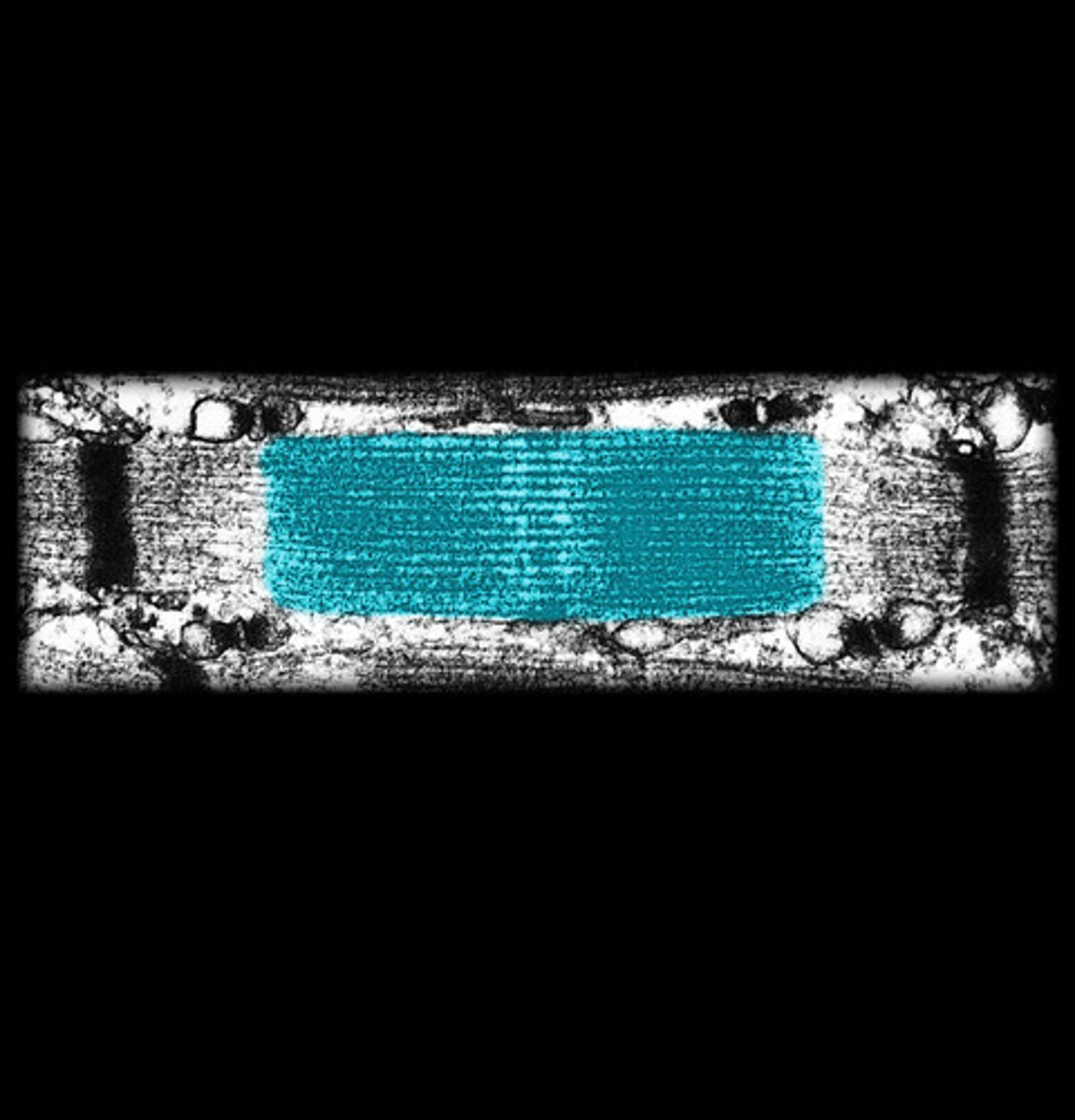
i-band
actin filaments (thin)

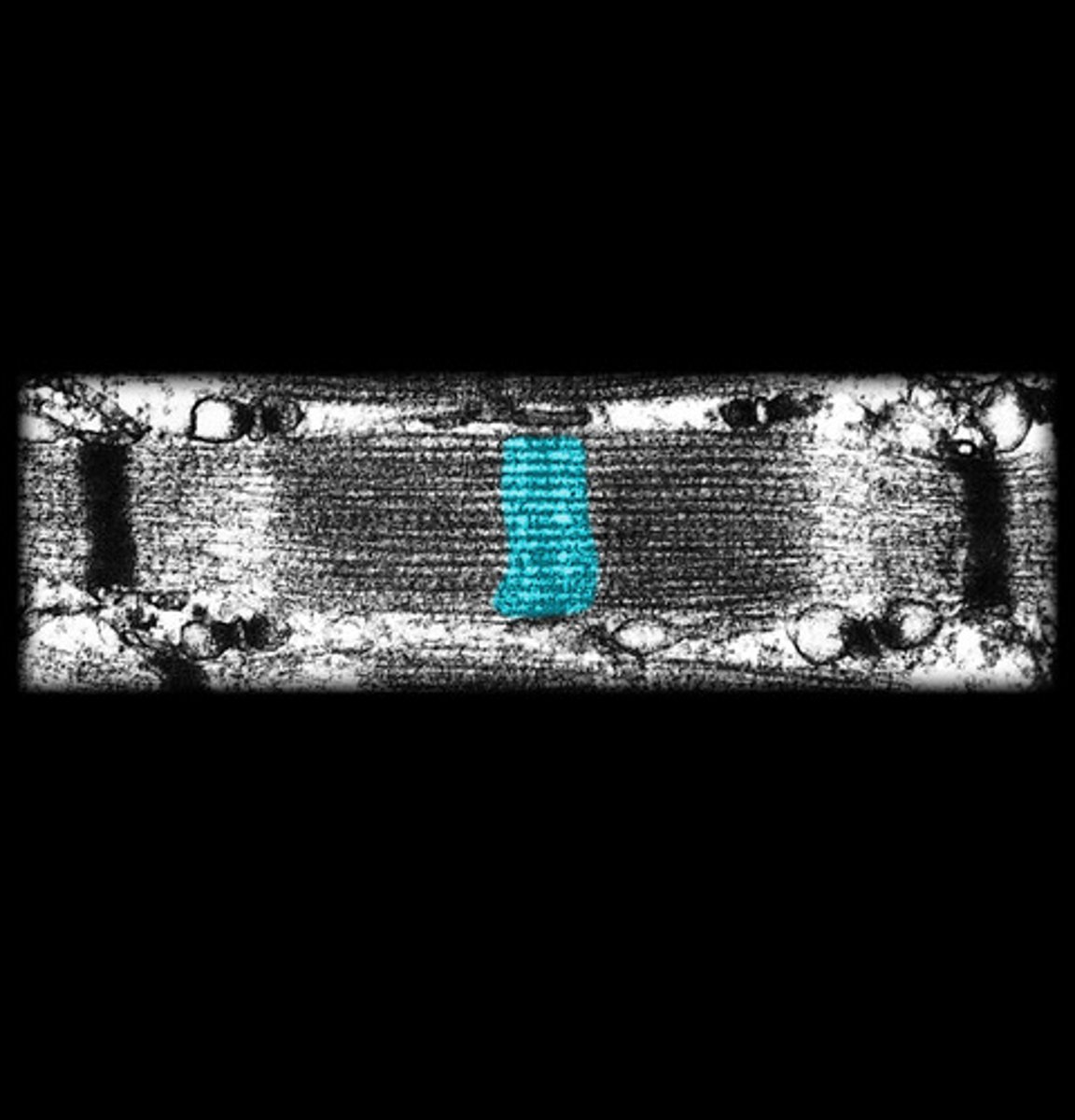
h-band
myosin filaments (thick)
origin
attachment at the stationary end
insertion
attachment at the moving end
action
the effect produced by the muscle (produce or prevent movement)
agonist (prime mover)
produces most of force
synergist
assistant to agonist
antagonist
opposes prime mover
fixator
prevents movement of bone
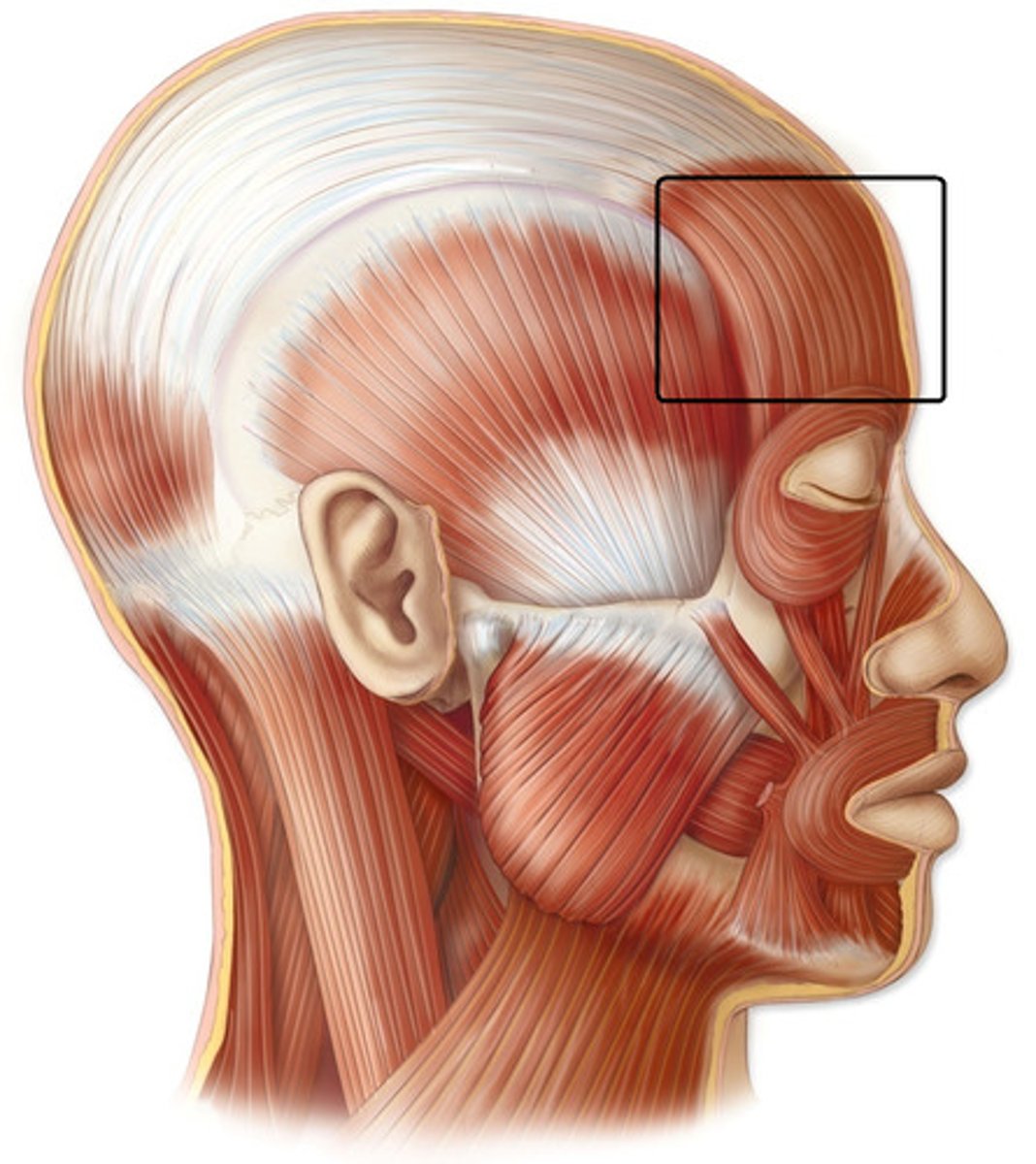
frontalis
elevates eyebrows and scalp
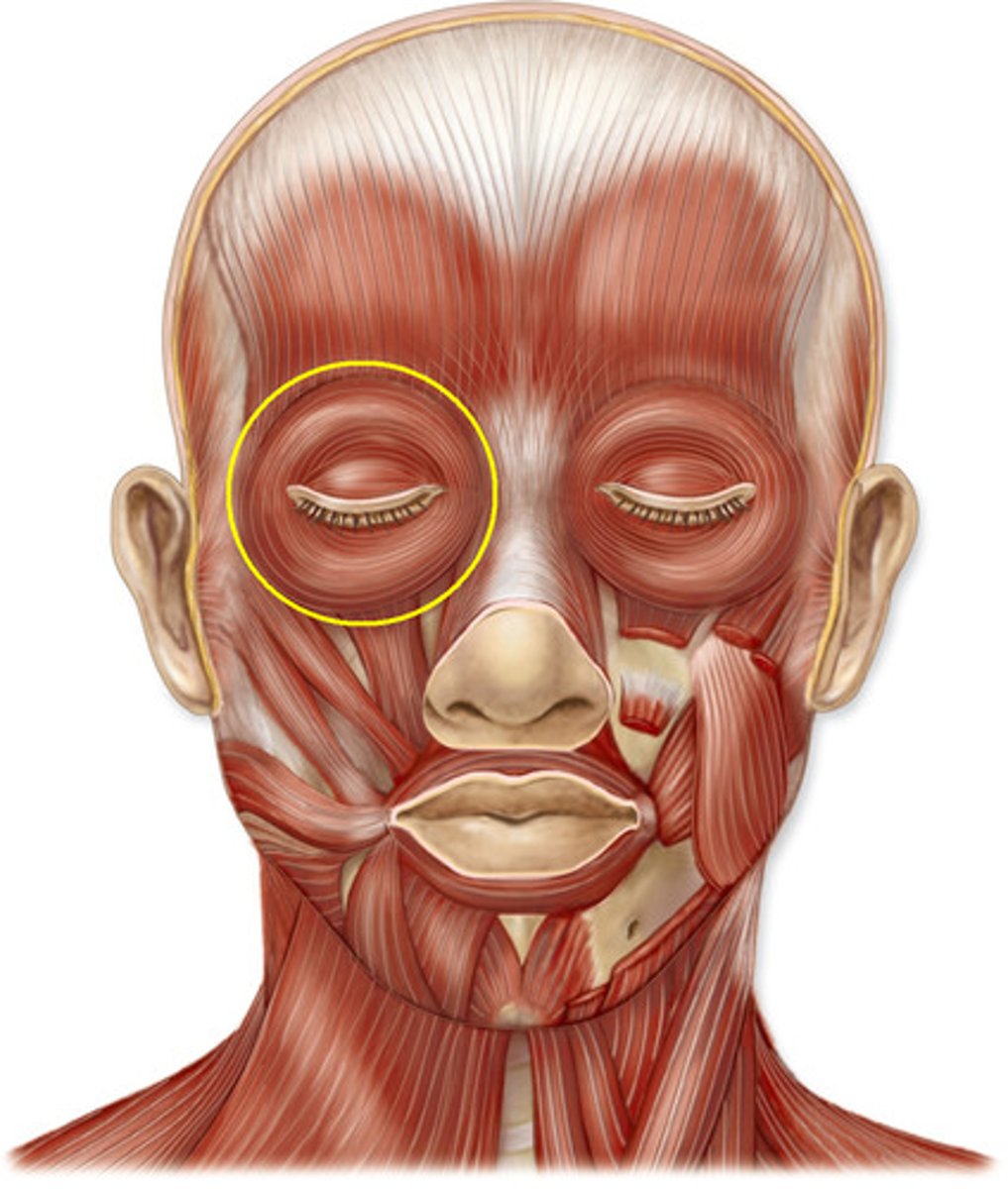
orbicularis oculi
closes the eye (blink, squint, flow of tears)
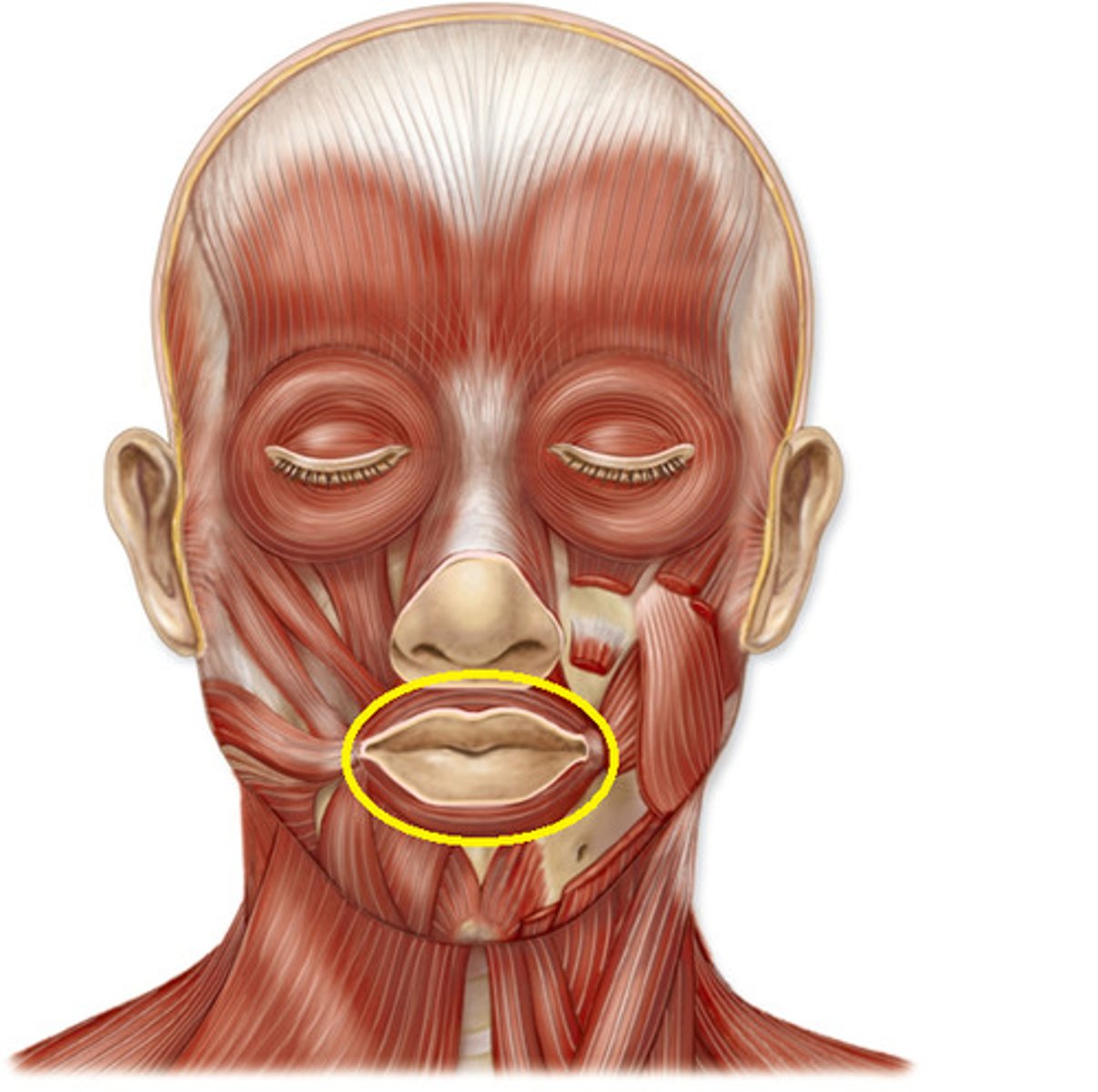
orbicularis oris
moves lips
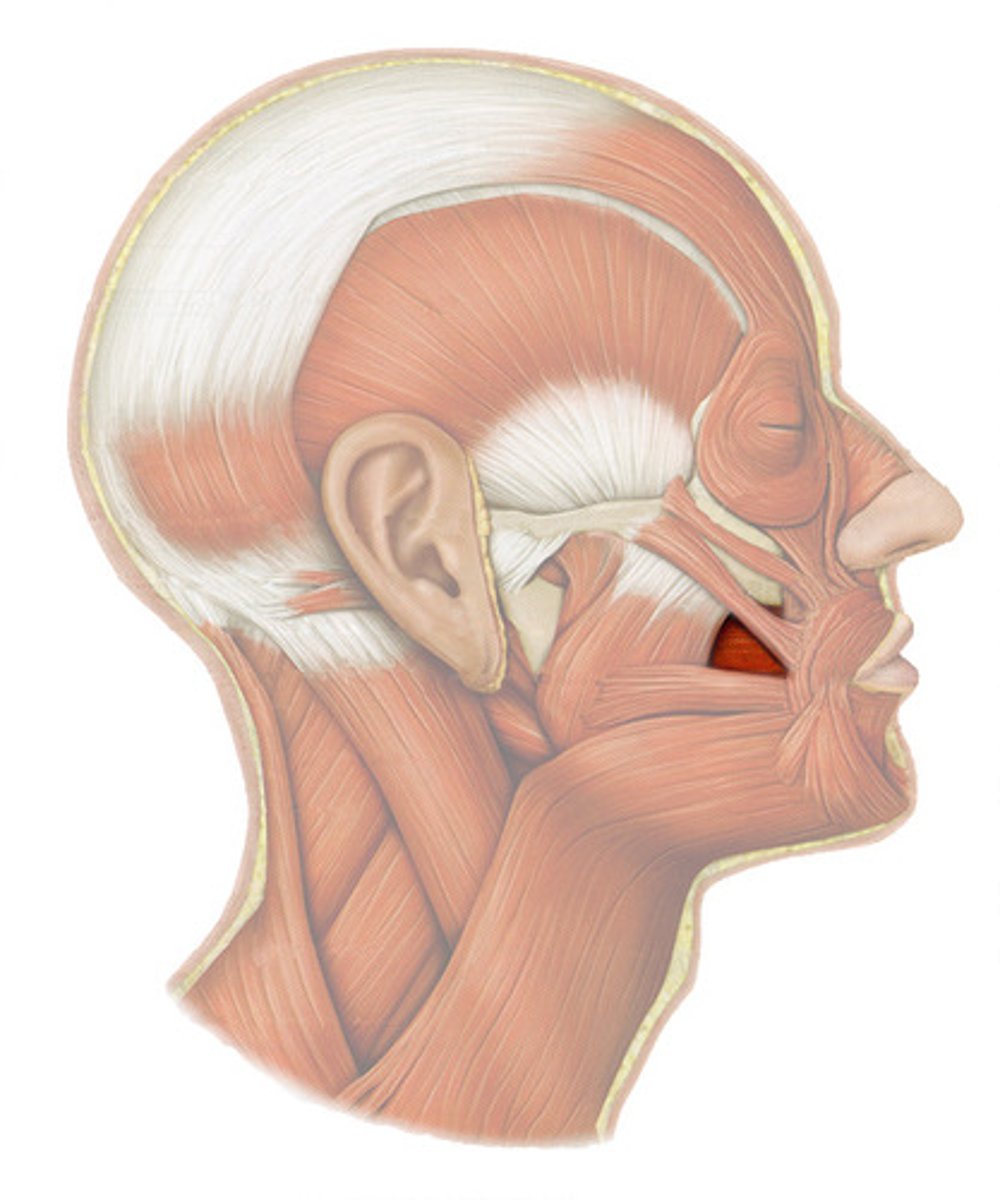
buccinator
compresses cheek (whistle, blow, drink through straw, chew)
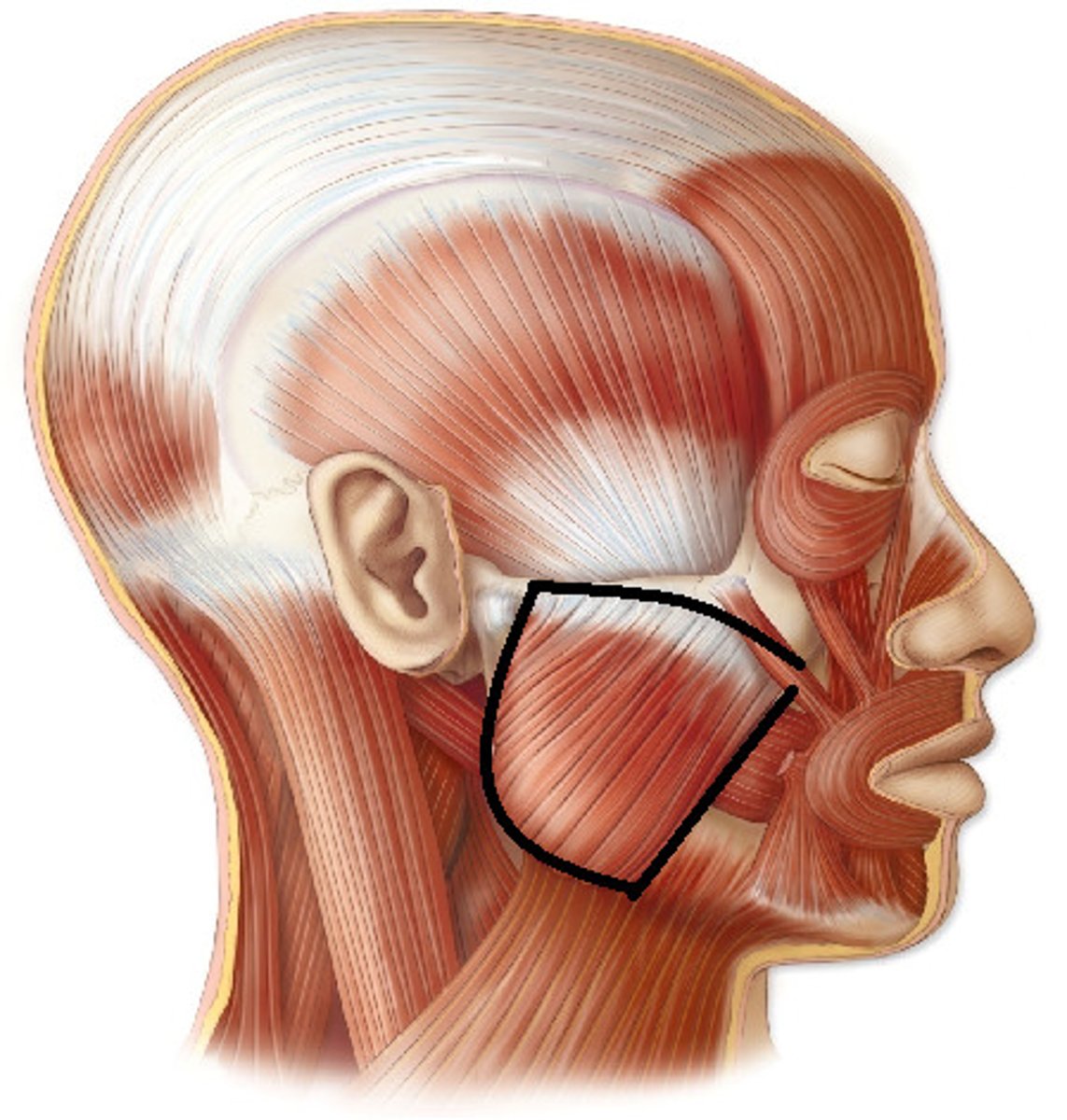
masseter
elevates mandible to close mouth
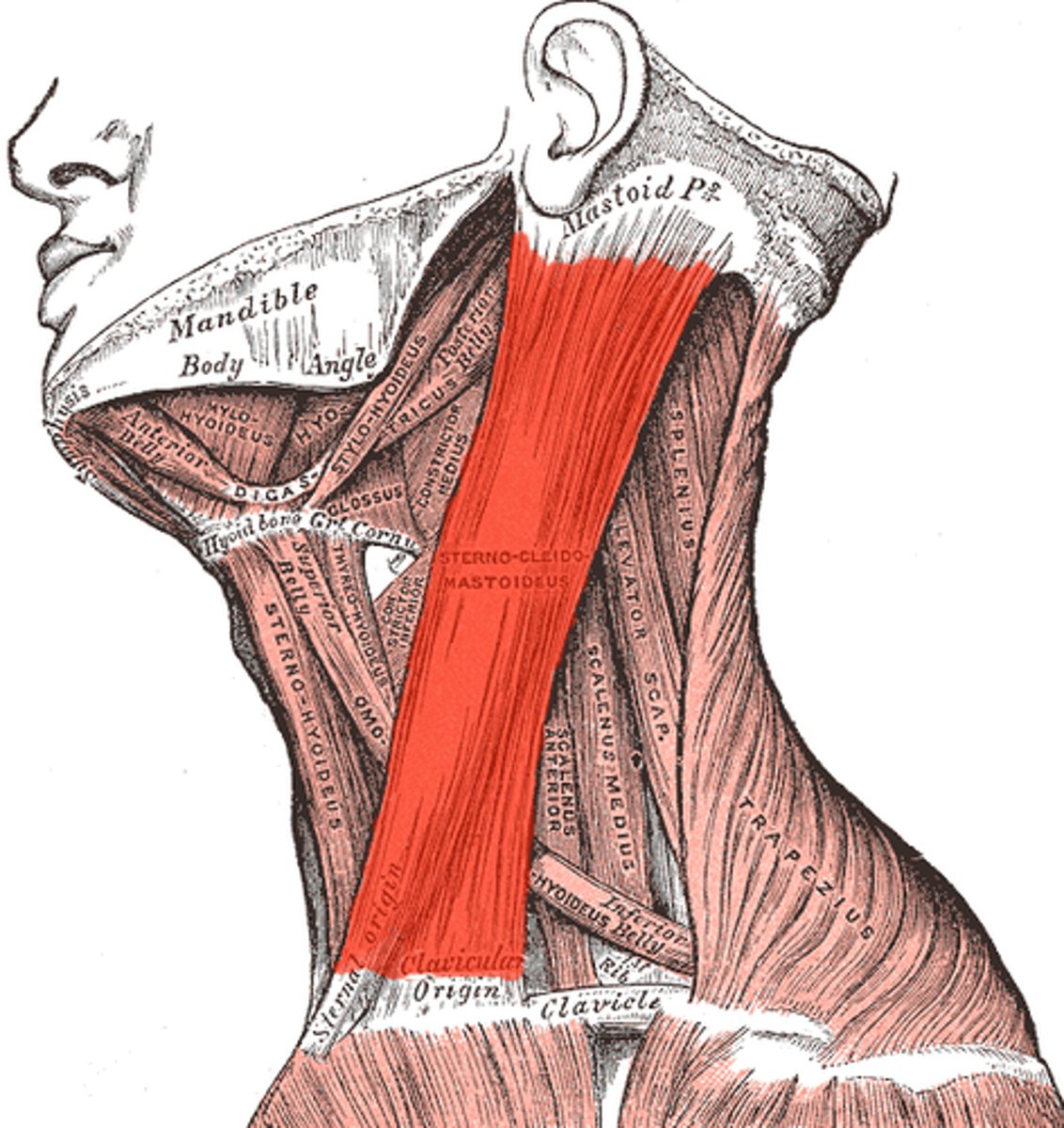
sternocleidomastoid
laterally flexes; rotates head
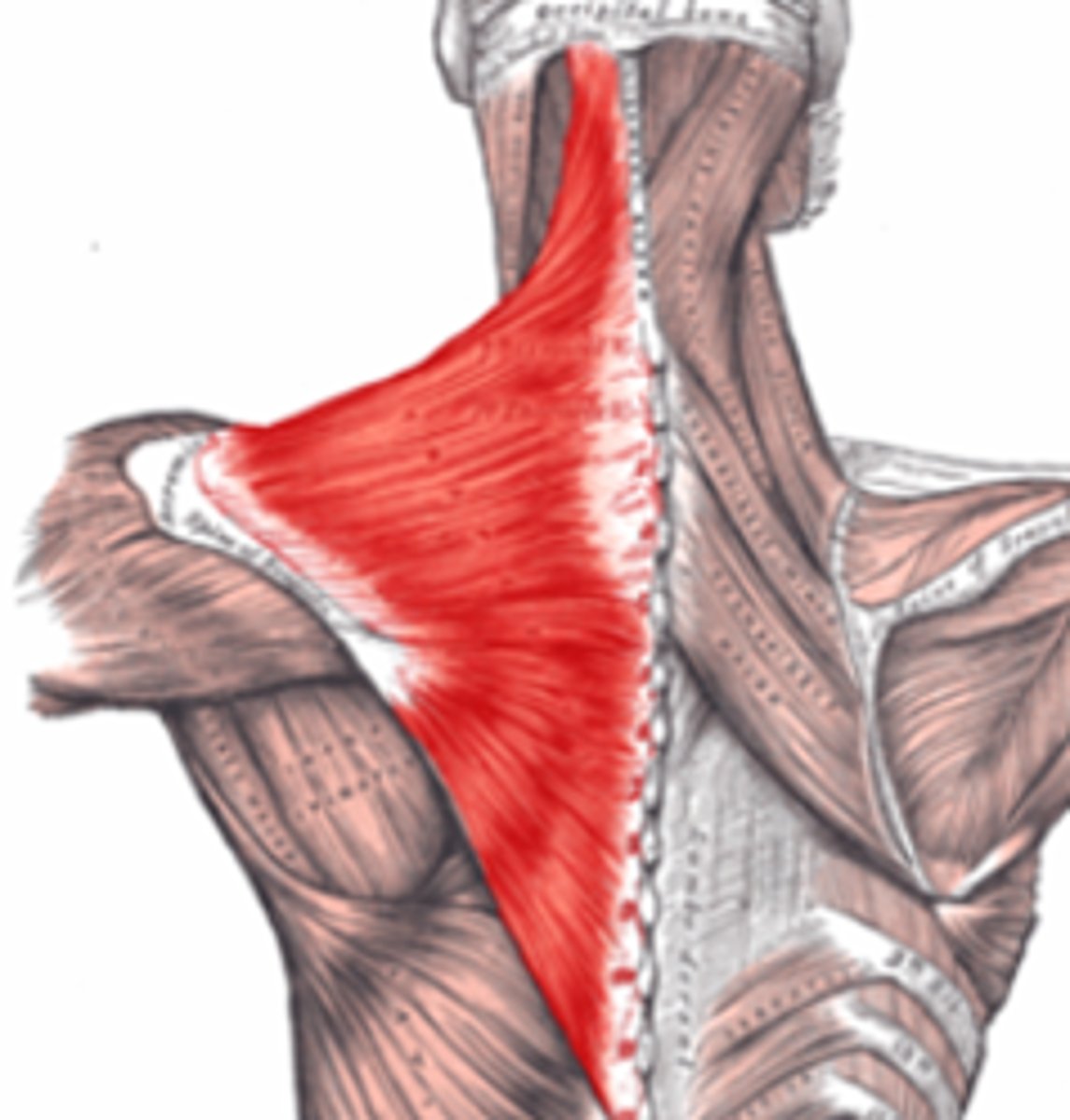
trapezius
draw head back
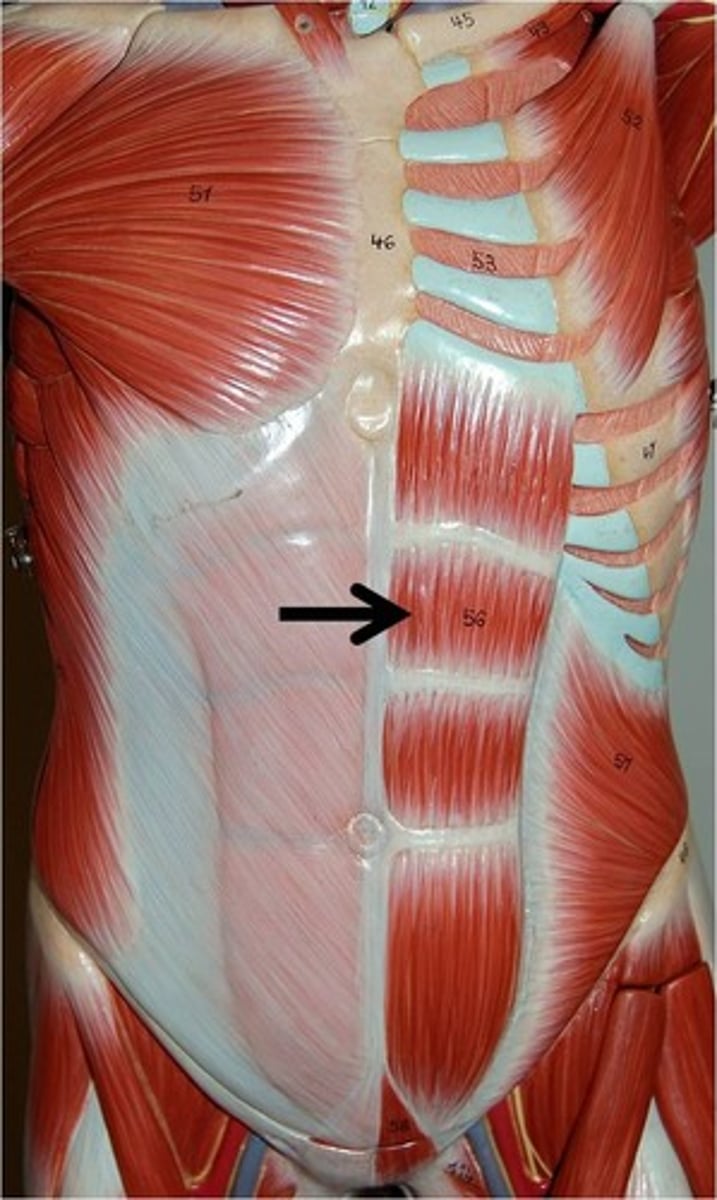
rectus abdominus
sitting up
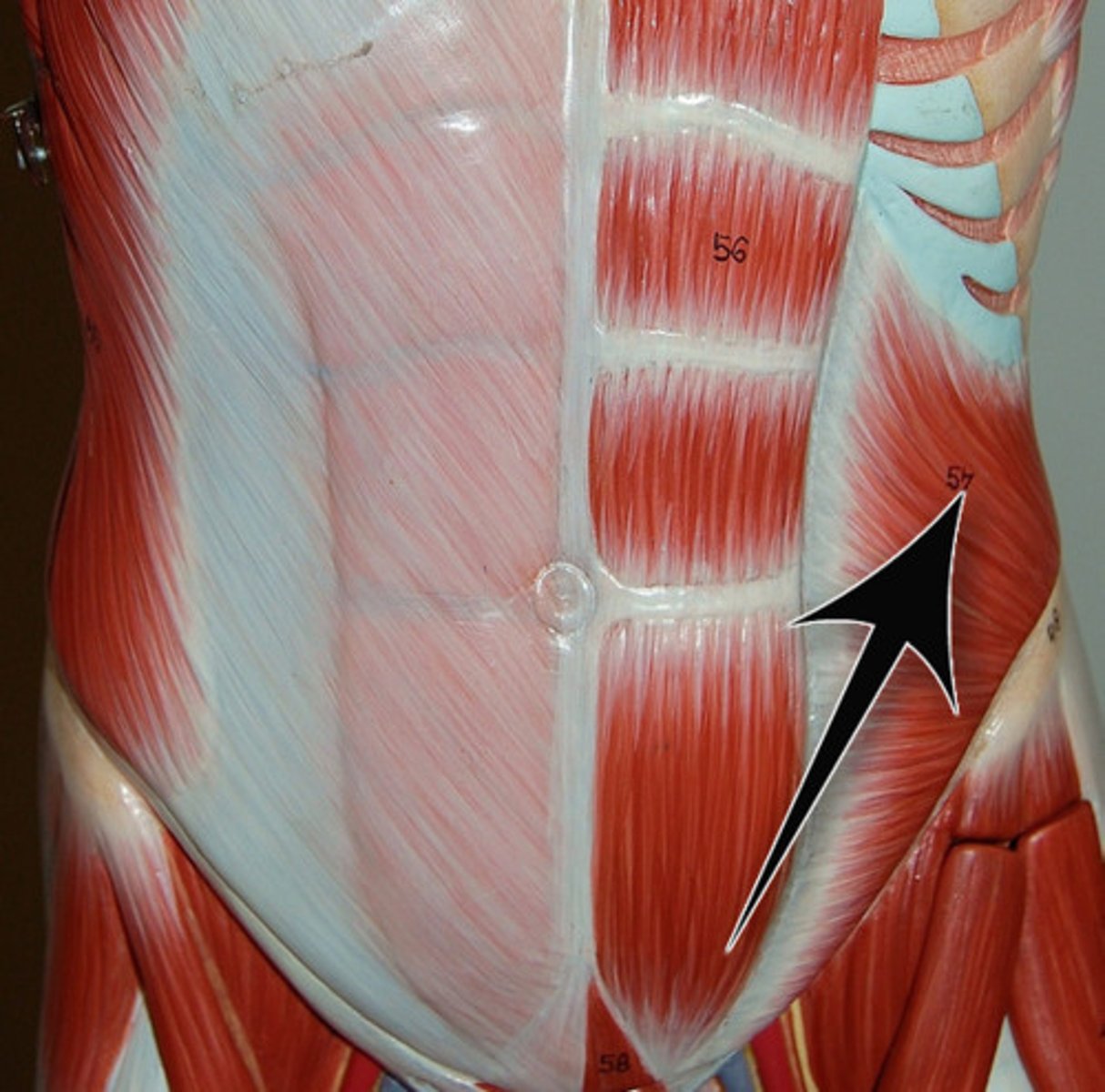
external oblique
twisting, bending to the side
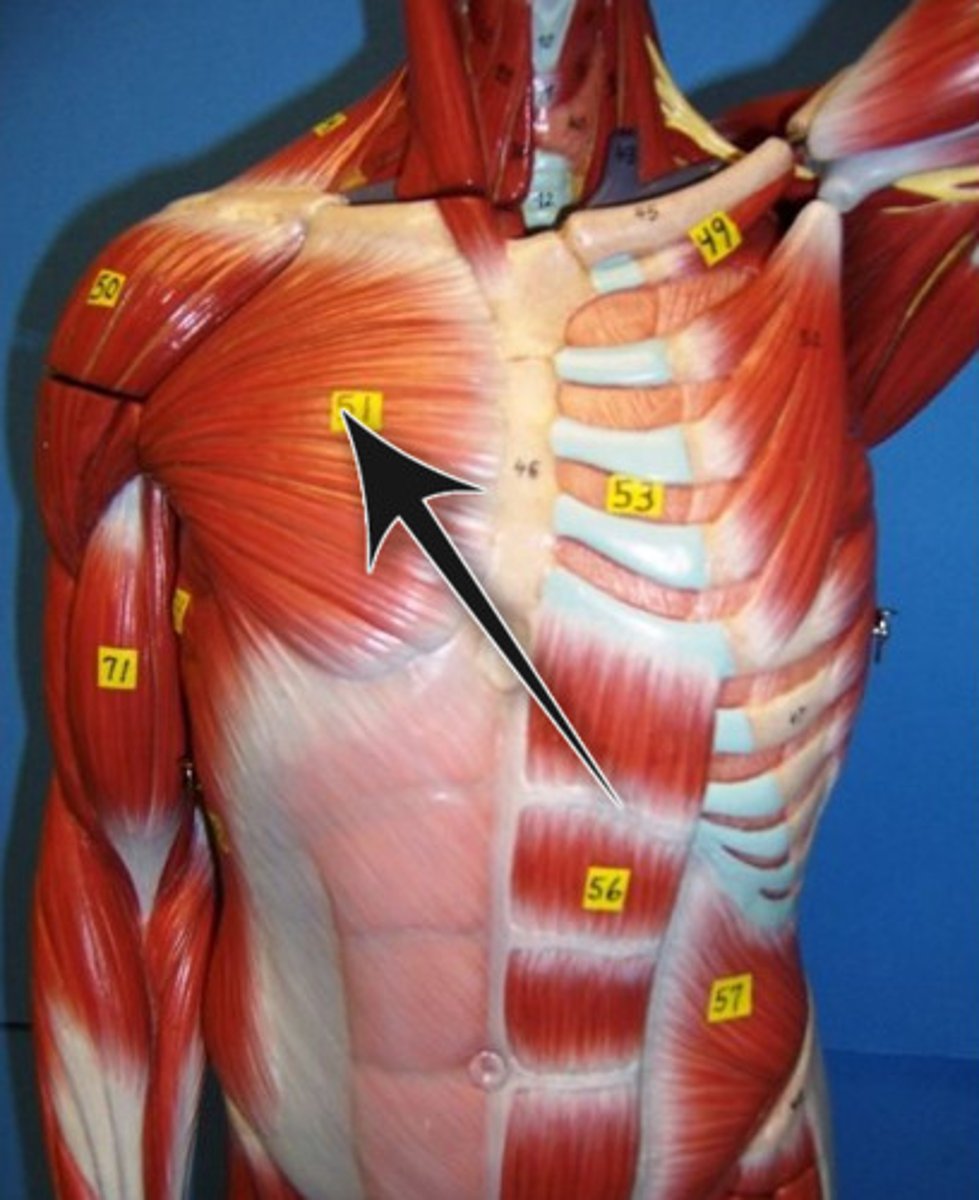
pectoralis major
brings elbows together
deltoid
lifts arms at shoulder
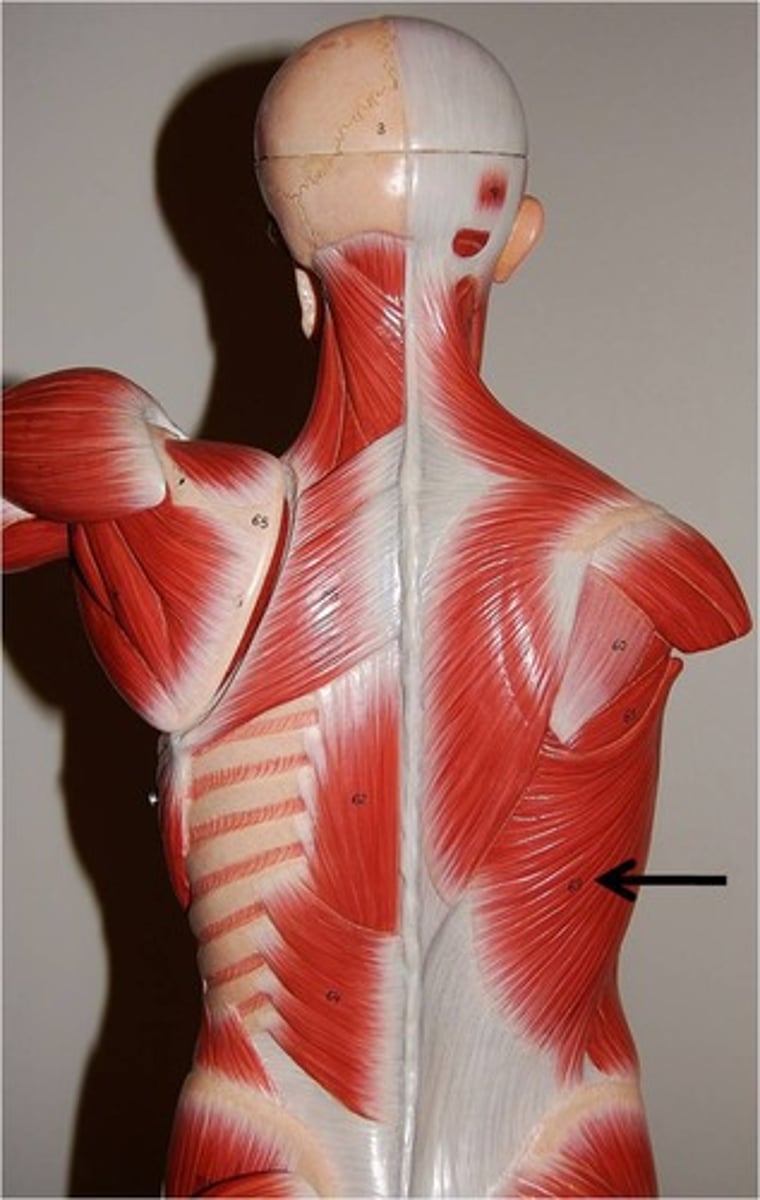
latissimus dorsi
arm movement
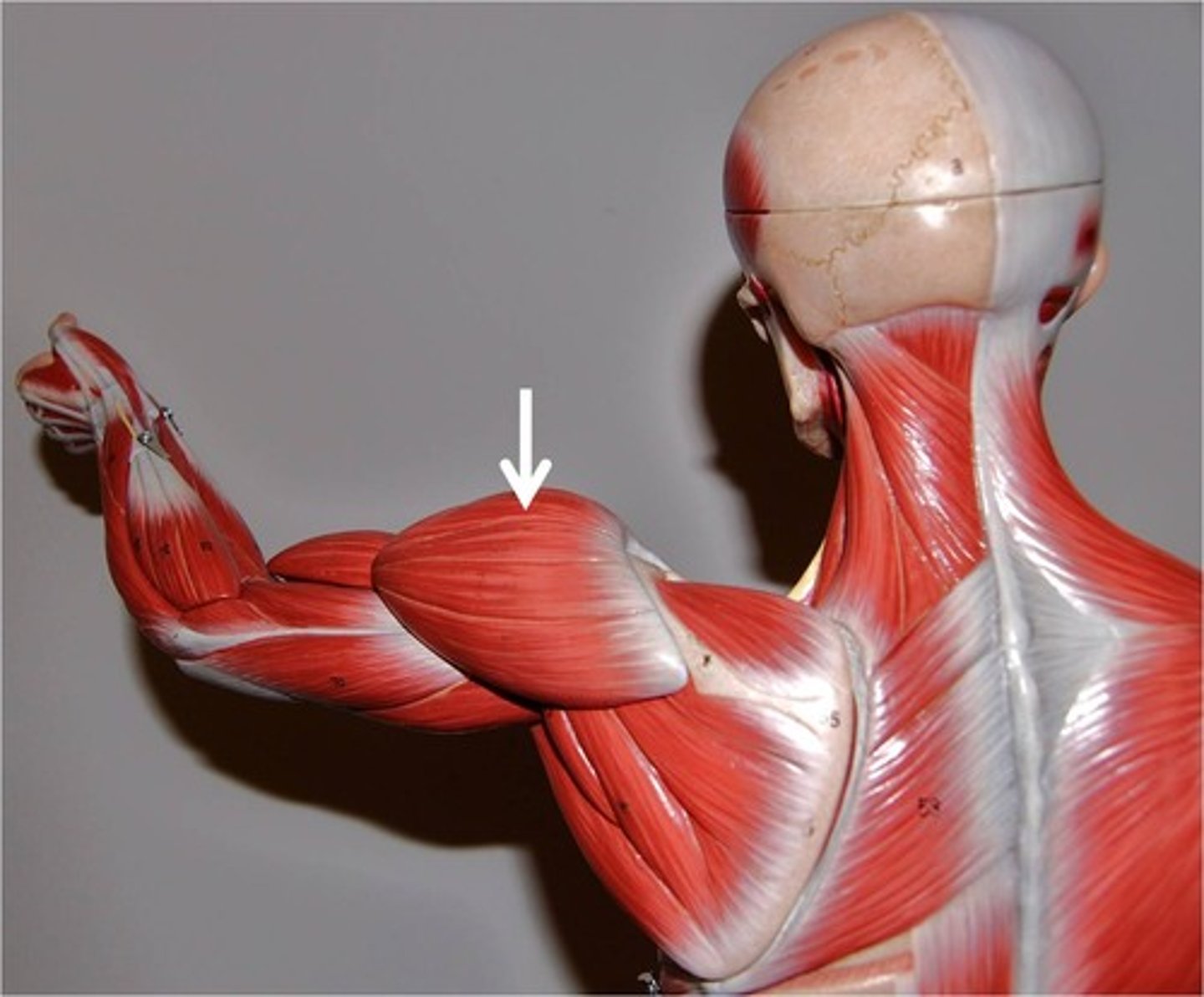
biceps brachii
bicep curl
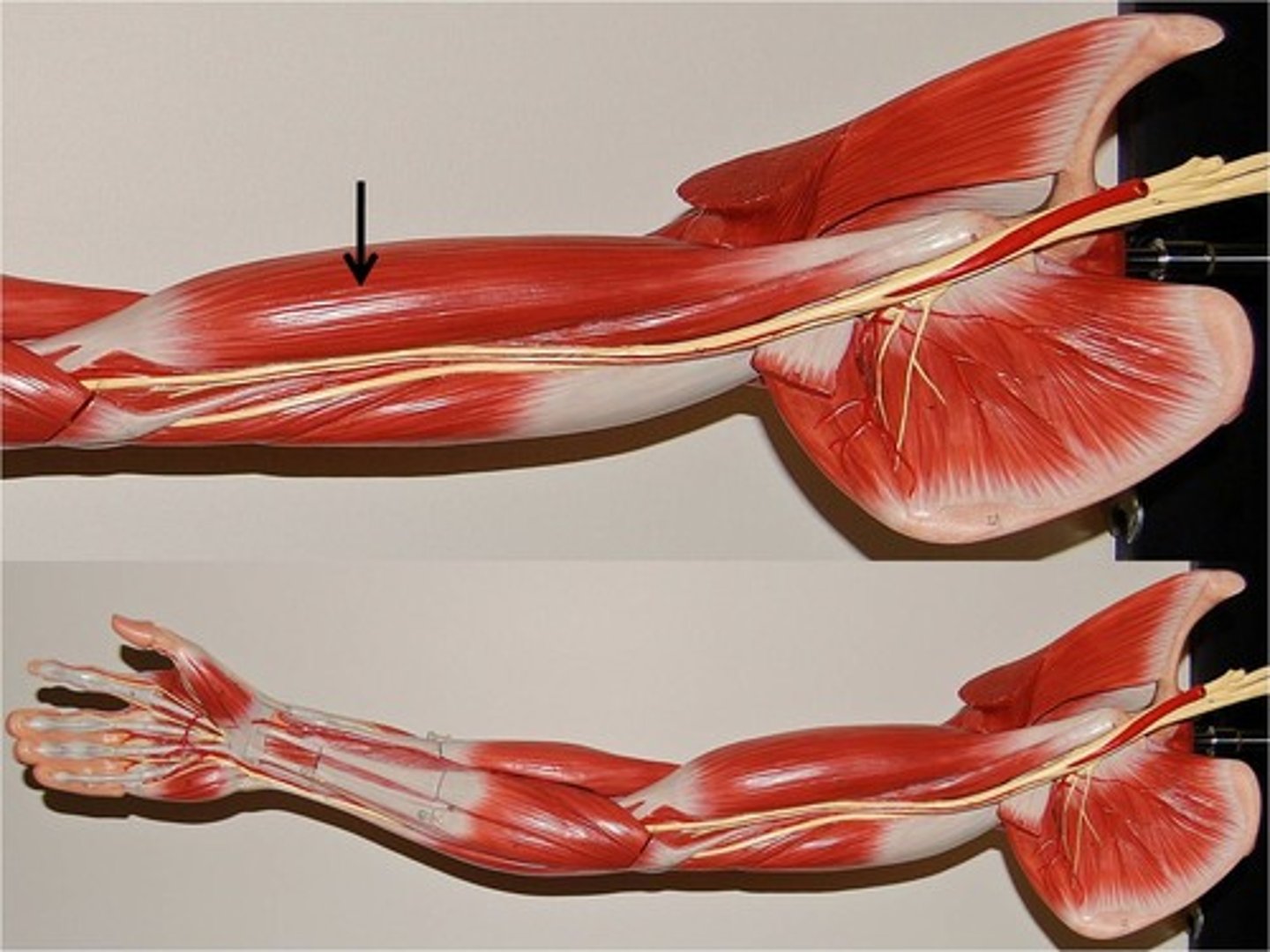
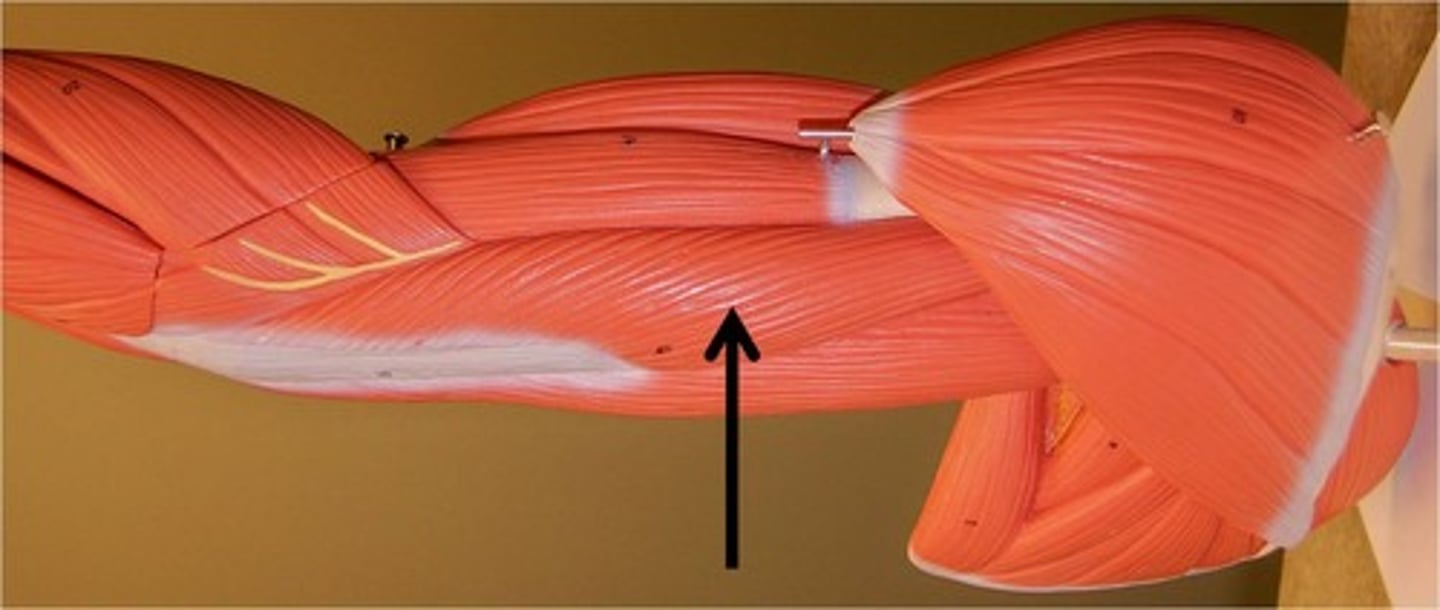
triceps brachii
extends forearm
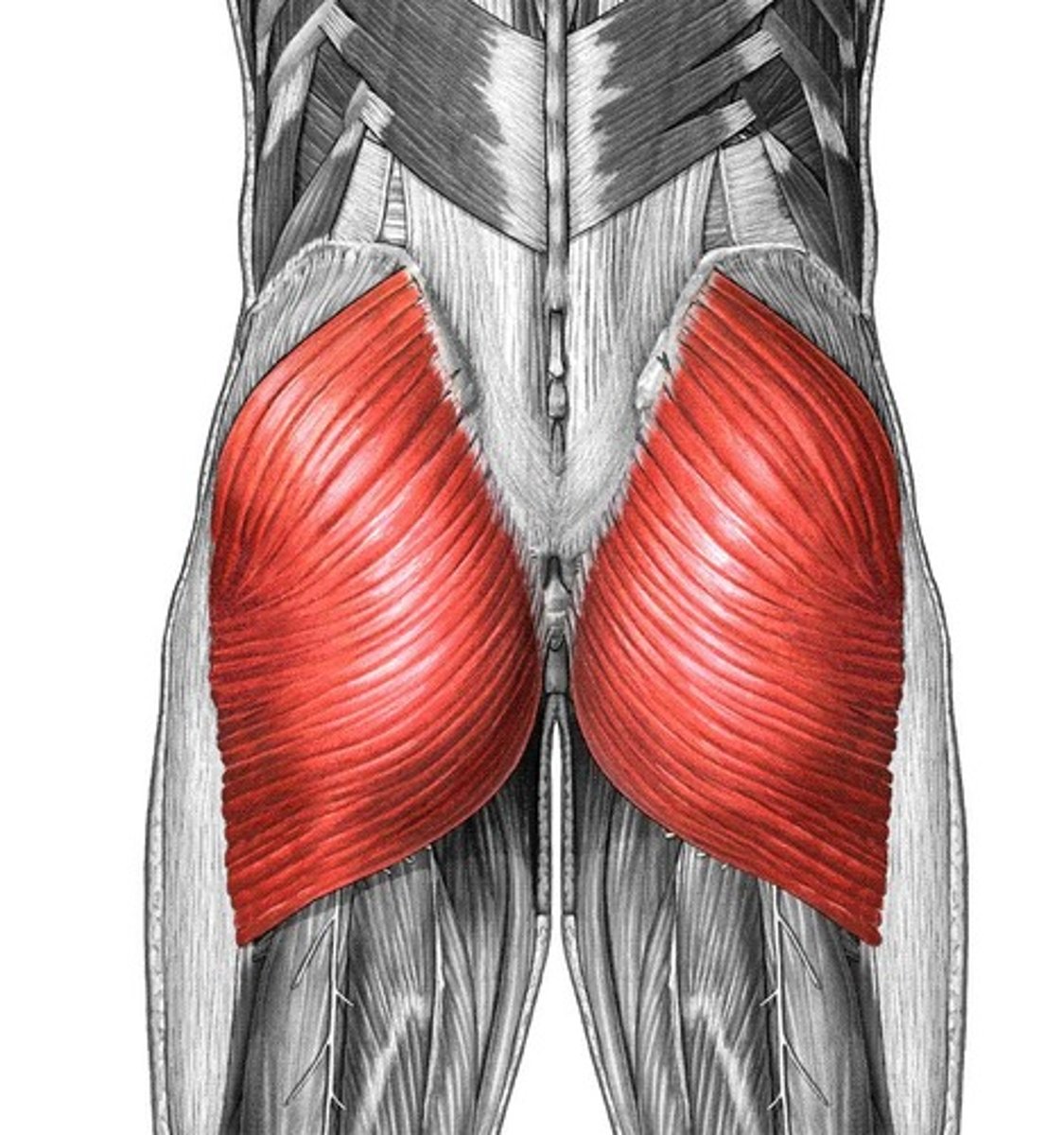
gluteal group
gluteus maximus
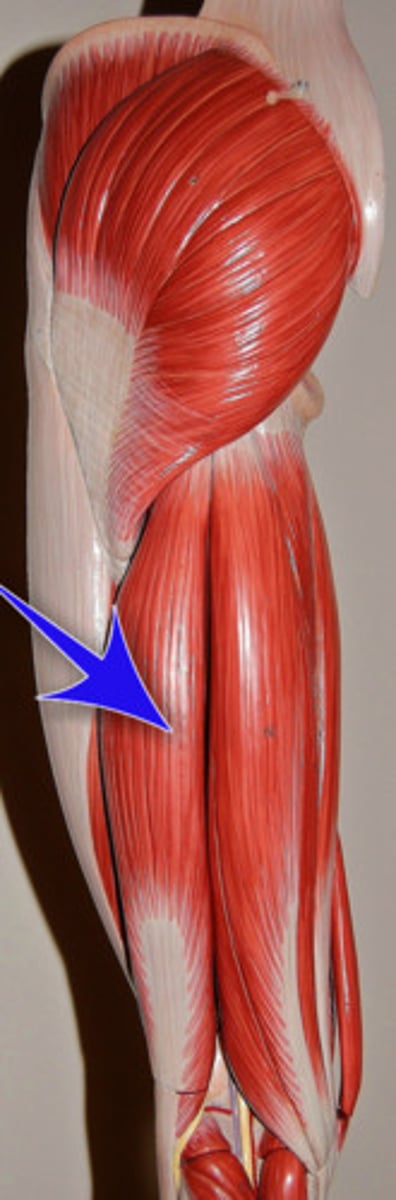
gracilis
moves thighs together
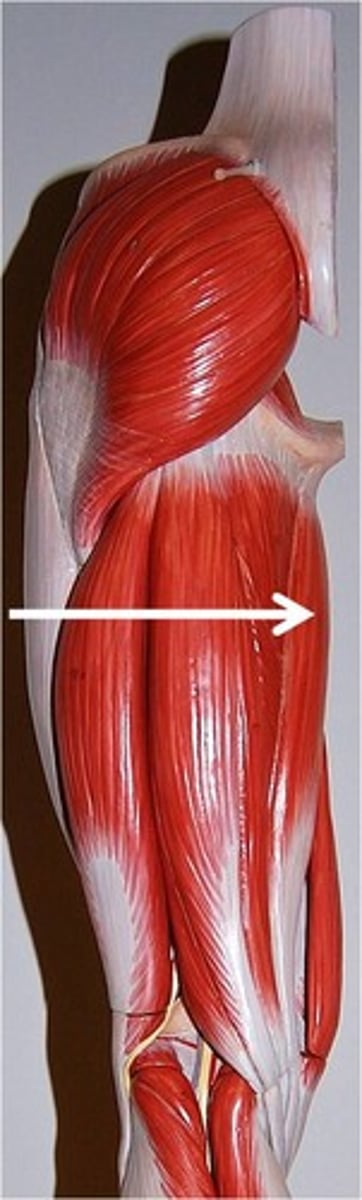
hamstring
-biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus
-all bend the knee (hamstring curls)
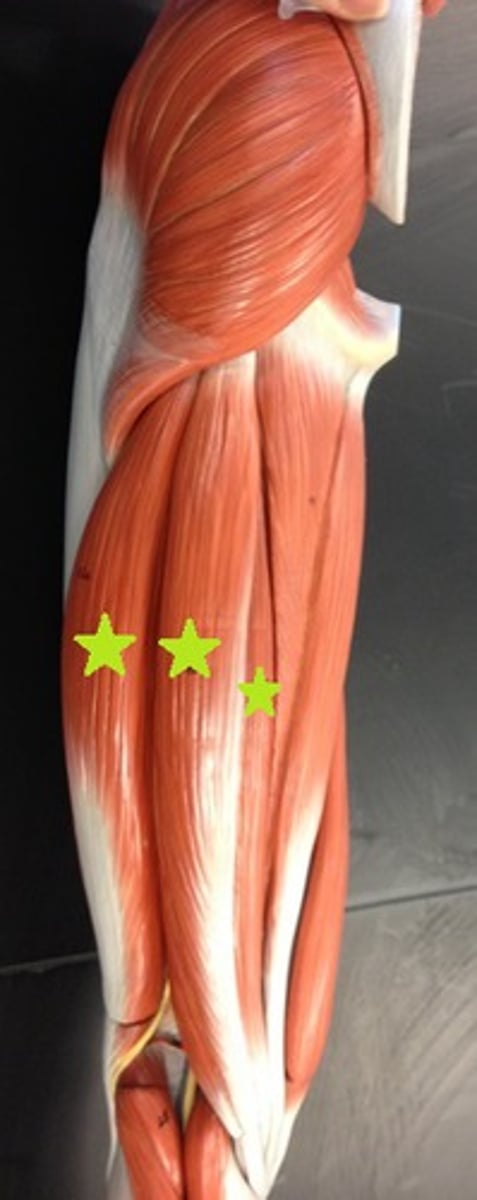
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
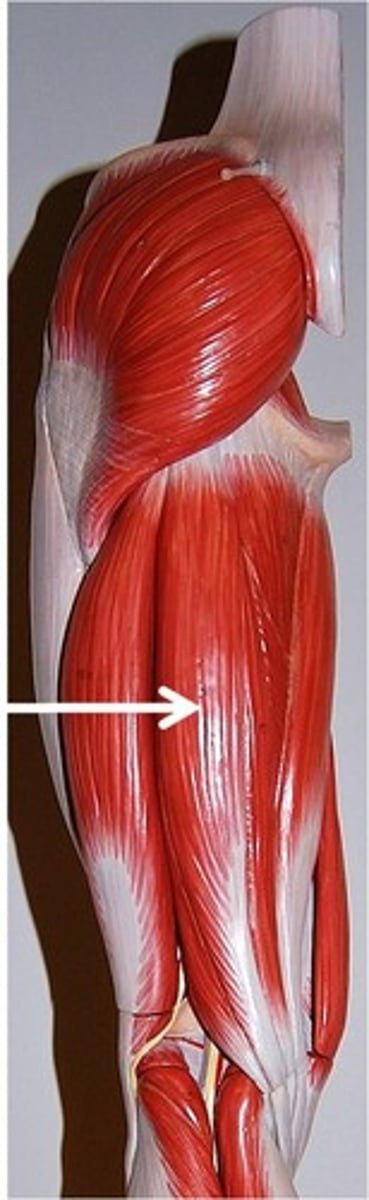
semimembranosus
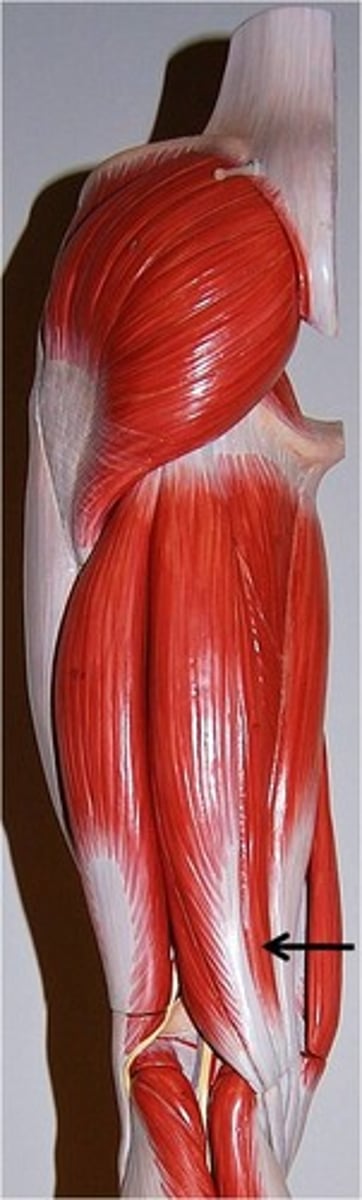
rectus (quadriceps) femoris
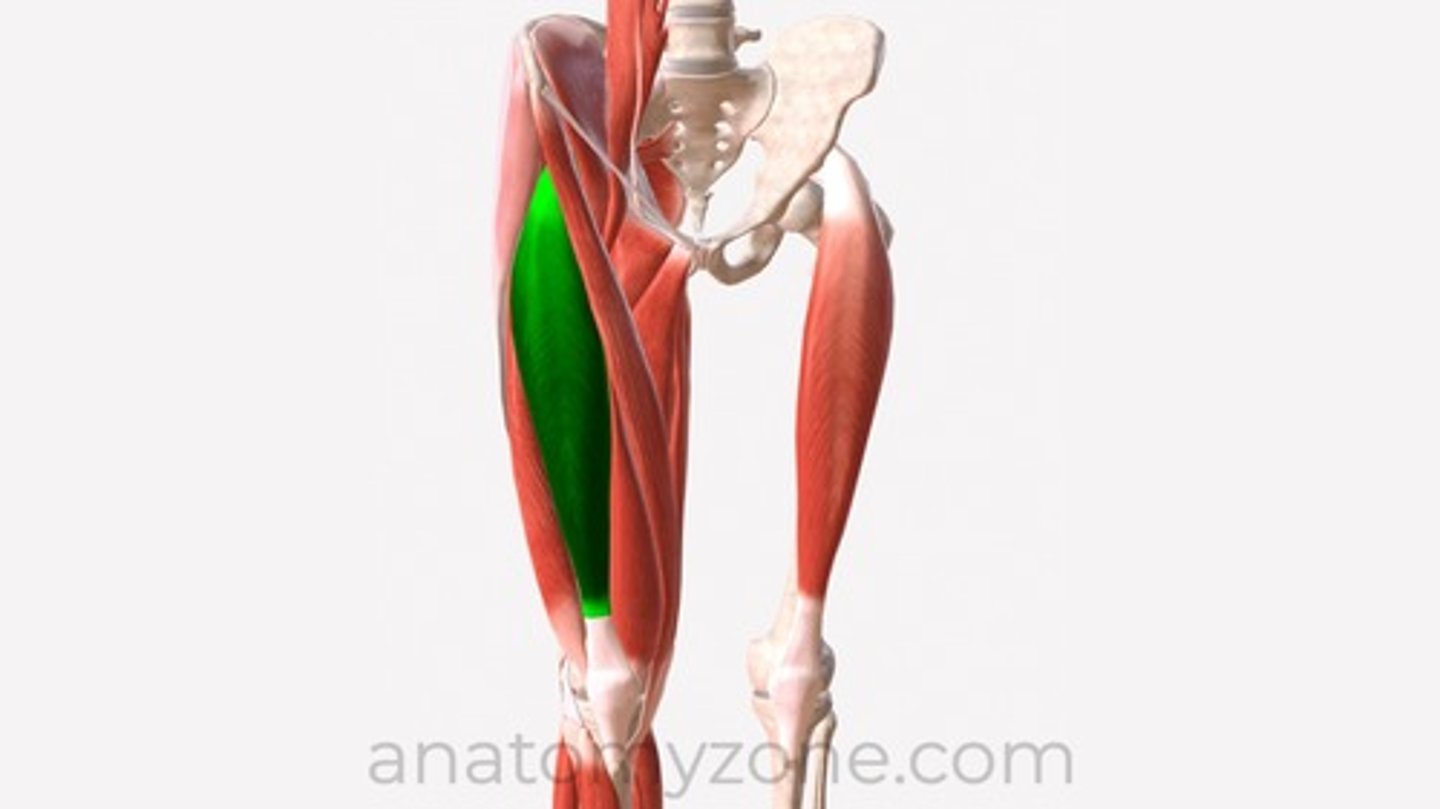
gastrocnemius
flexes foot and knee, jumping, running, walking
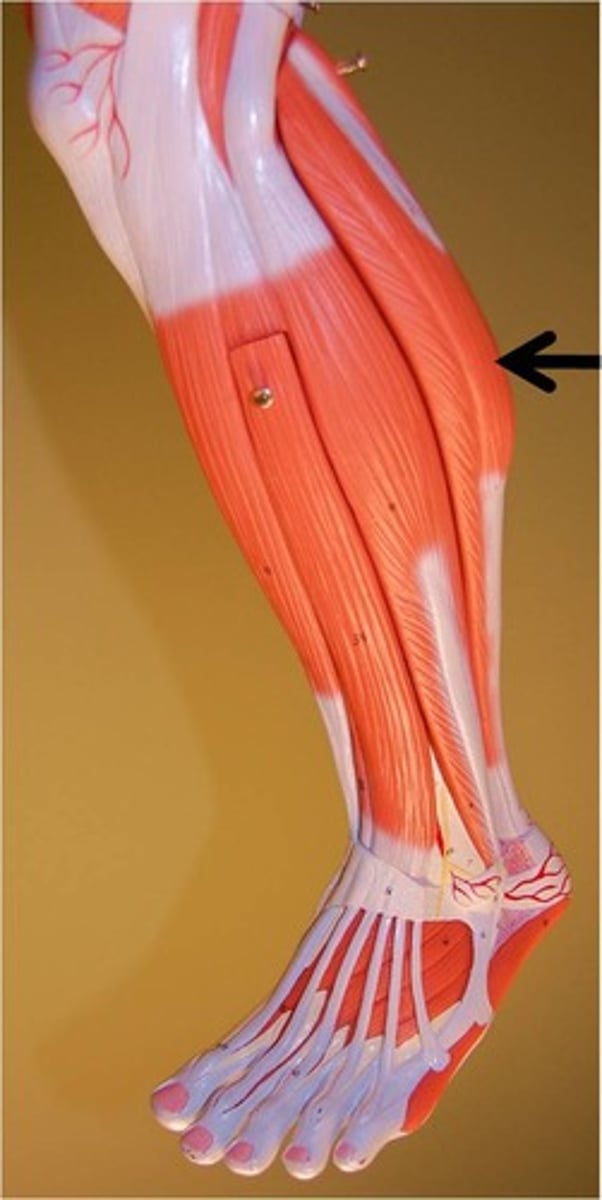
soleus
steadies leg on ankle when standing
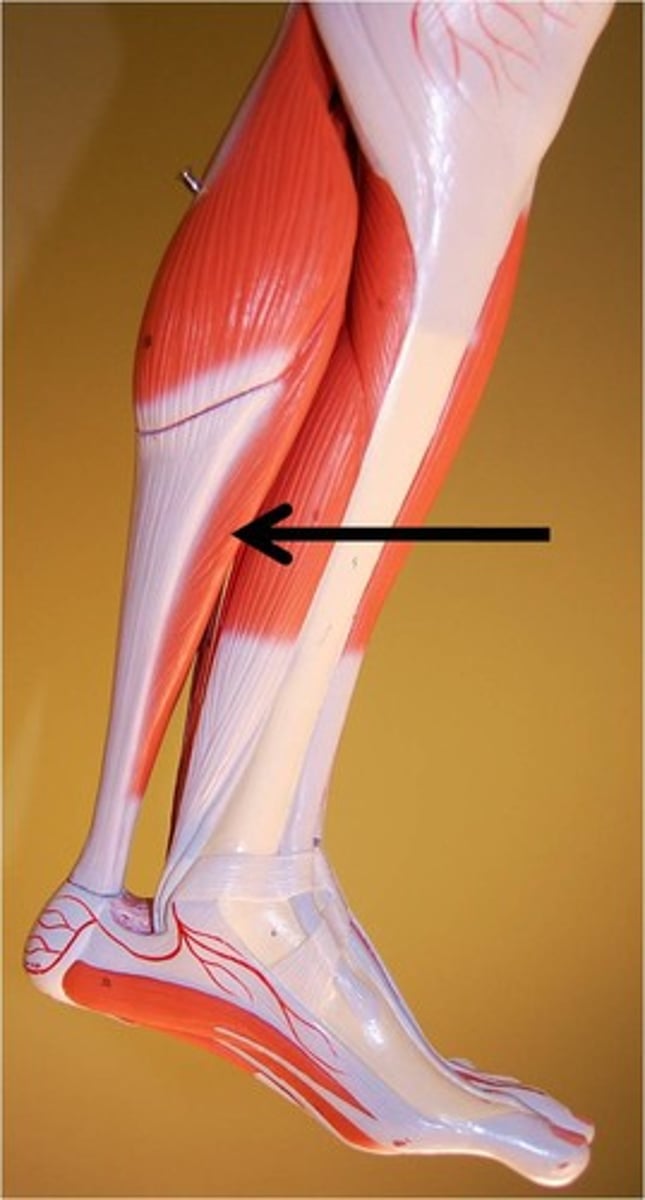
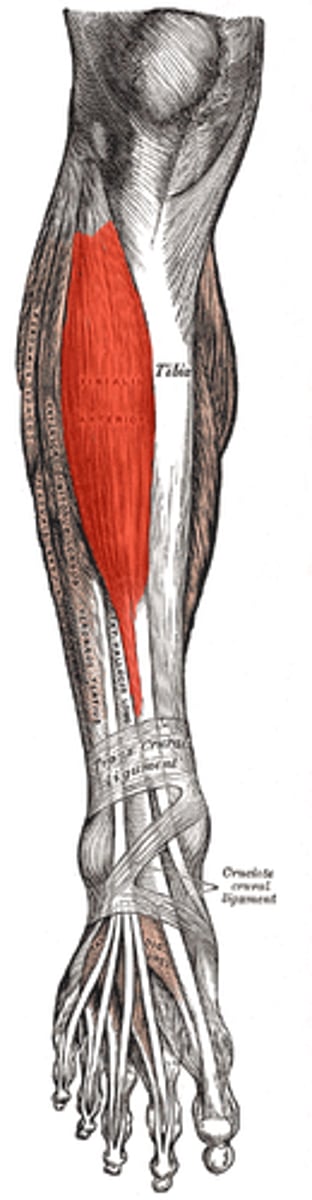
tibialis anterior
dorsiflexion of the ankle (raising toes and clears foot off ground when running/walking)