Essentials Exam #2: Key Terms in Medicine Study Guide
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
body temperature, pulse rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure
What are the 4 vital (cardinal) signs?
pain
5th vital sign (JCAHO)
unpleasant sensory and emotional experience arising from actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage
*perception of an uncomfortable stimulus and the response to that perception
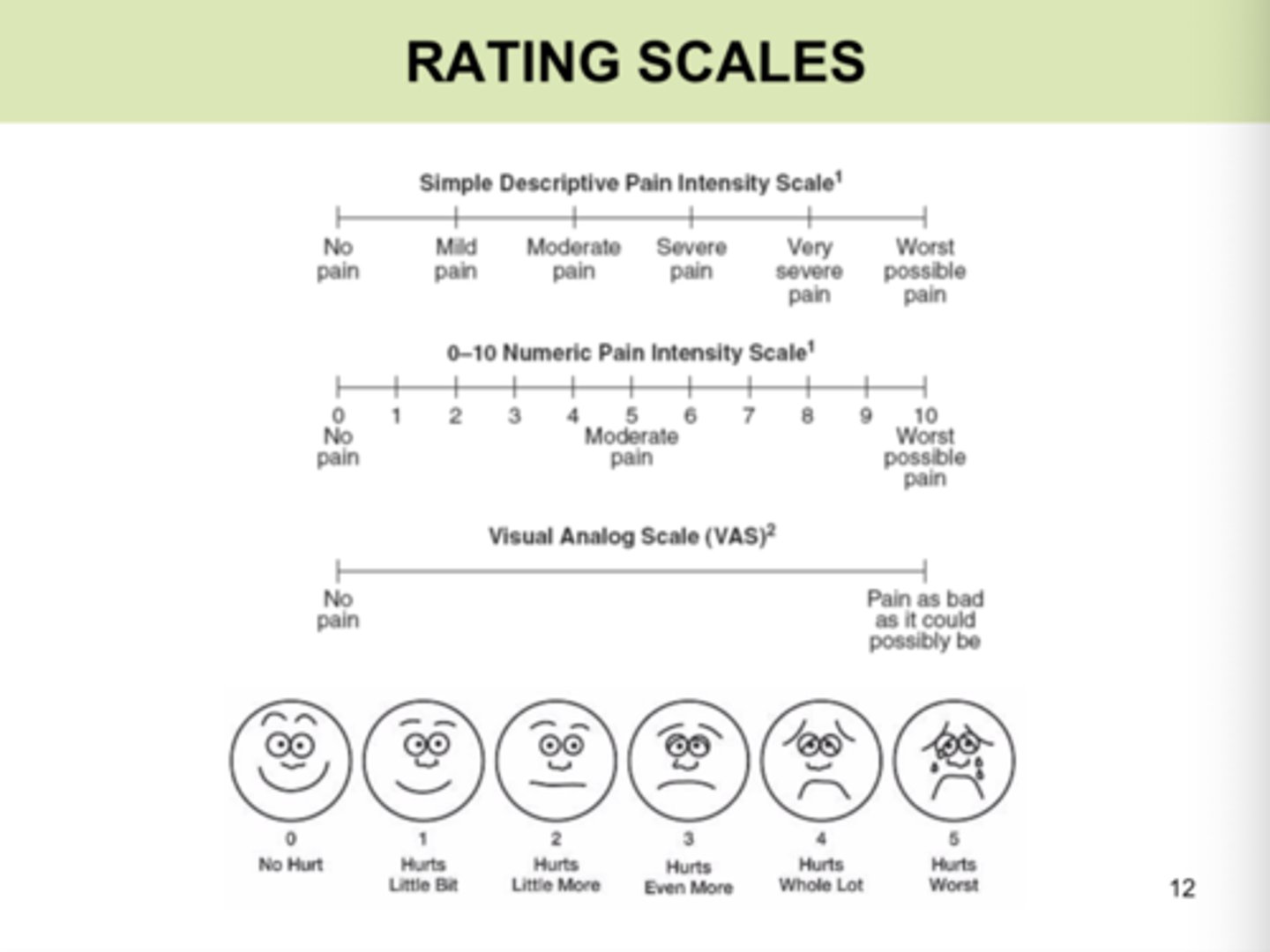
pain scales
1. visual analog scale
2. numerical rating scale
3. FACES pain rating scale
4. thermometer pain scale
BORG (rate of perceived exertion)
individual's perceived exertion
*way to monitor exercise intensity
ranges 6-20
- may correlate to HR (young healthy pple)

gait speed
functional vital sign
ASSOCIATED WITH:
- quality of life
- functional capacity
- general health status
- decreased participation
- presence of depressive symptoms
PREDICTIVE OF:
- frailty
- hospitalization/discharge destination
etc.
distance/time
walk at a comfortable pace
What instructions should a PT give a patient for a self-selected gait speed test (preferred)?
walk as fast as safely possible ("reach a bus that is about to pull out")
What instructions should a PT give a patient for a maximum gait speed test?
3
When evaluating gait speed, the patient should perform ___ trials and calculate the average.
body temperature
the balance between the heat produced by the body and the heat lost from the body
NORMAL:
98.6 degrees F (96.8-100.4)
37 degrees C (36-38)
pyrexia
increased body temperature (febrile)
S/Sx = general malaise, headache, increase pulse, increase RR, chills, piloerection (goosebumps), loss of appetite, sweating, etc.
hyperthermia--> temperature well above normal
*greater than or equal to 106 degrees F or 41.1 degrees C
**may be fatal
yes (proceed with caution)
Can a PT treat a patient with a low grade fever?
(99-100 degrees F)
102 degrees F (38.9 degrees C)
What is considered a high grade fever?
HINT: NO PT allowed
hypothermia
exposure to extreme cold
S/Sx = decrease pulse, decrease RR, cold and pale skin, cyanosis, drowsiness, etc.
- less than 94 degrees F (34.4 degrees C) = thermoregulation is impaired
- 85 degrees F (29.4 degrees C) = thermoregulation is lost
rectal, ear (tympanic), oral, axillary
What are the 4 primary measurement sites for body temperature?
ear (tympanic)
What is the most accurate measurement site for body temperature?
factors that influence body temperature
1. age
*infants higher, elderly lower
2. emotion/stress
*stimulation of sympathetic nervous system = increase epinephrine = temp
3. exercise
*strenuous exercise = increase metabolic rate
**muscle contractions = heat production source
4. external environment
*warm weather = increase temp
**humidity
***clothing
5. time of day
*circadian rhythm
6. menstrual cycle
*increase progesterone during ovulation
7. pregnancy
oral monitoring (temperature)
contraindications
- patients who are uncooperative or unconscious
- newborns/infants
- patients with notable dyspnea (SOB)
- cautionary use on patients with unpredictable seizures
*tympanic = higher, axillary = lower*
pulse rate (PR)
pulse waves of arterial blood created by contractions from the left ventricle
normal adult = 60-100 bpm
*higher in children, lower in trained athletes
radial pulse
Where is the most common peripheral pulse rate taken without issues?
bradycardia
slow heart rate (less than 60 bpm)
tachycardia
rapid heart rate (>100 bpm)
women (small body w/ small heart)
Do women or men have a faster HR?
factors influencing pulse rate
1. age
2. body size
thin = decrease
3. gender
lower in males
4. exercise
- relationship with workload intensity
- used to calculate target heart rate
- trained athletes lower resting HR
5. other factors
- stress/emotions
- medications
rhythm, volume/amplitude/quality, feel of arterial wall
Pulse rate can be described by what 3 things?
rhythm
aspect of pulse rate
describes pattern of pulsations and intervals
*regular vs irregular (patterns)
volume (amplitude, quality)
aspect of pulse rate
amount of blood pushed through artery during each contraction (cardiac output)
*strong/full vs. weak/thready vs. bounding
feel of arterial wall
aspect of pulse rate
should be smooth, elastic, soft, flexible
*with advancing age - sclerotic changes
respiration
RATE: number of breaths per minute (bpm)
normal adult = 12-20 breaths/min
*minimum of 30 seconds for testing
RHYTHM-->time interval between breaths
regular vs irregular
DEPTH--> amount of air exchanged with each breath
shallow vs deep
dyspnea
shortness of breath (SOB)
apnea
absence/interruptions of breathing
factors influencing respiration
1. age
increase in adults due to decrease in vital capacity
newborns/toddlers: 25-50 breaths/min (decreases with age)
* > 70 = alarming
2. body size and stature
men & tall/thin = low
3. exercise
increase in rate and depth
4. other
- medication
- stress/emotions
- body position on diaphragm
dyspnea scales
1. Talk Test (0, 1+, 2+, 3+, 4+)
2. MRC Breathless Scale (0-4)
MRC breathlessness scale
0 = only breathless with strenuous exercise
1 = SOB hurrying or walking up hill
2 = walks slower than same age people
3 = stops for breath walking 100+ yds
4 = too breathless to leave house
pulse oximeter
assess oxygen saturation level (%) in peripheral arterial blood
normal adult SaO2 = 95-100%
*may decrease slightly during exercise
90
An SaO2 < ____% is ABNORMAL!
*need O2, chronic condition --> requires medical attention
blood pressure (BP)
force that blood exerts against arterial wall as the heart contracts and relaxes, expressed as a fraction (in mmHg)
CO x total peripheral resistance = ?
systolic
top number
*max pressure during ventricular contraction
diastolic
bottom number
*min. pressure during ventricular relaxation
pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
peripheral resistance
resistance to blood flow within vessel
INFLUENCED BY:
1. diameter/elasticity of arteries
2. blood viscosity
cardiac output (CO)
DETERMINED BY:
1. strength, rate, rhythm of HR
2. blood volume
SV x HR = ?
normal blood pressure
systolic < 120
AND
diastolic < 80
high blood pressure stage 1
systolic: 130-139
OR
diastolic: 80-89
*start lifestyle modifications (PT intervention)
high blood pressure stage 2
systolic: 140 or higher
OR
diastolic: 90 or higher
*need medication
hypertensive crisis
systolic: higher than 180
AND/OR
diastolic: higher than 120
*consult a doctor immeadiately
factors affecting blood pressure
1. exercise
physical activity increases CO efficiency
2. cuff size
too small = false HIGH readings
too large = false LOW readings
3. arm position
should be supported with cuff at heart level
4. Valsalva manuever
5. orthostatic hypotension
Valsalva manuever
drop in BP followed by rapid increase as breath is released
orthostatic hypotension
sudden drop in BP with upright standing
laying down (blood closest to heart)
Blood pressure is highest in which position?
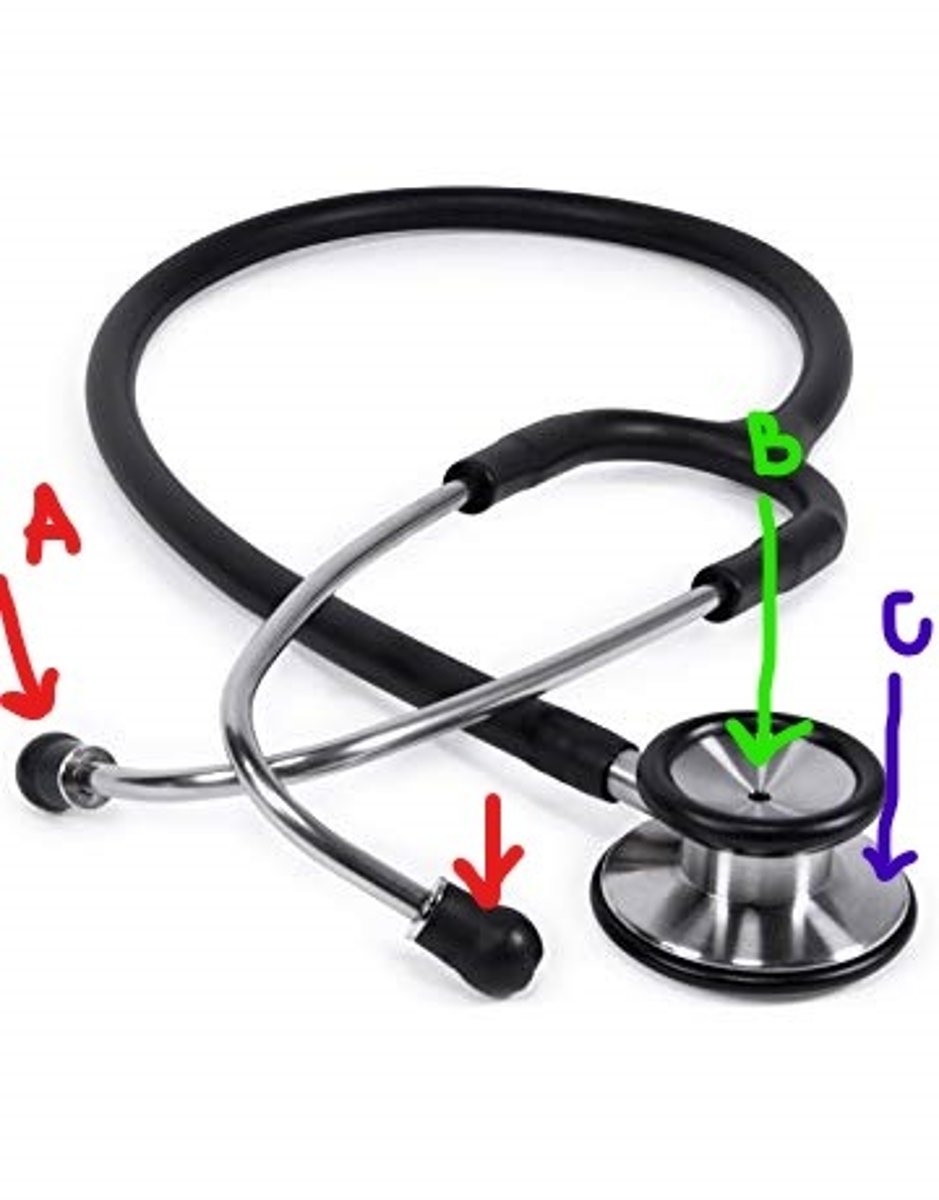
diaphragm (stethoscope)
flat endpiece (larger dome) of the stethoscope used for hearing relatively high-pitched heart sounds
*usually used for breath sounds and BP
(C IN IMAGE)
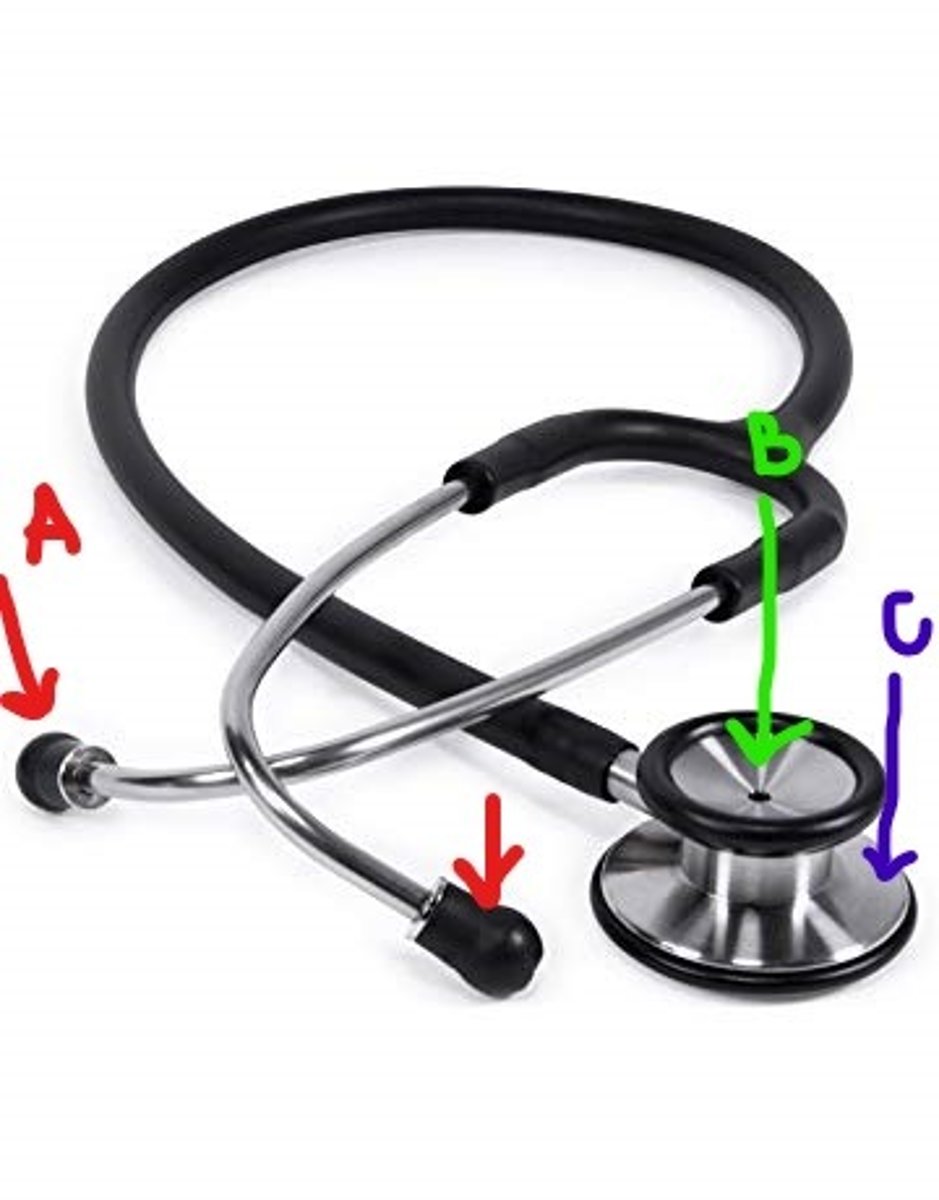
bell (stethoscope)
smaller dome used for low frequency sounds
*preferred use for heart sounds
(B IN IMAGE)
forward
The earpieces of the stethoscope should face _______________.
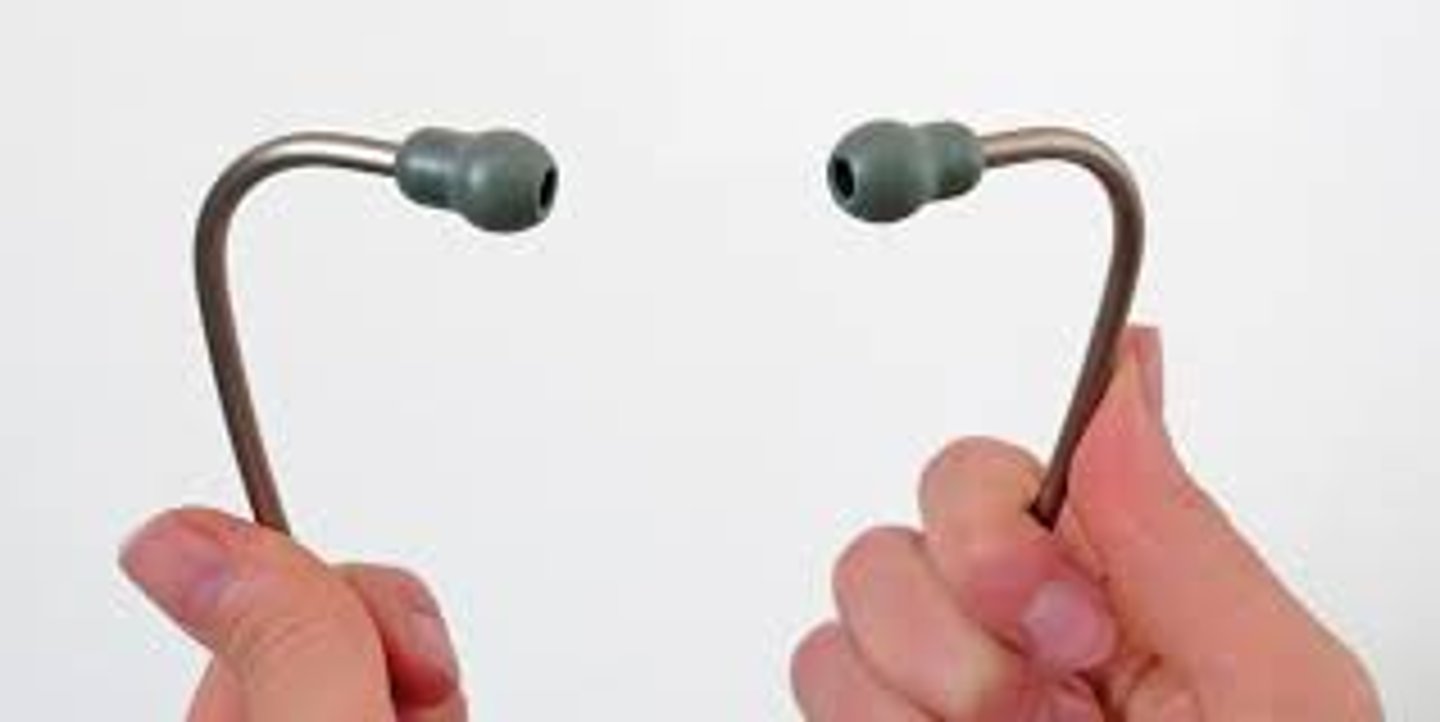

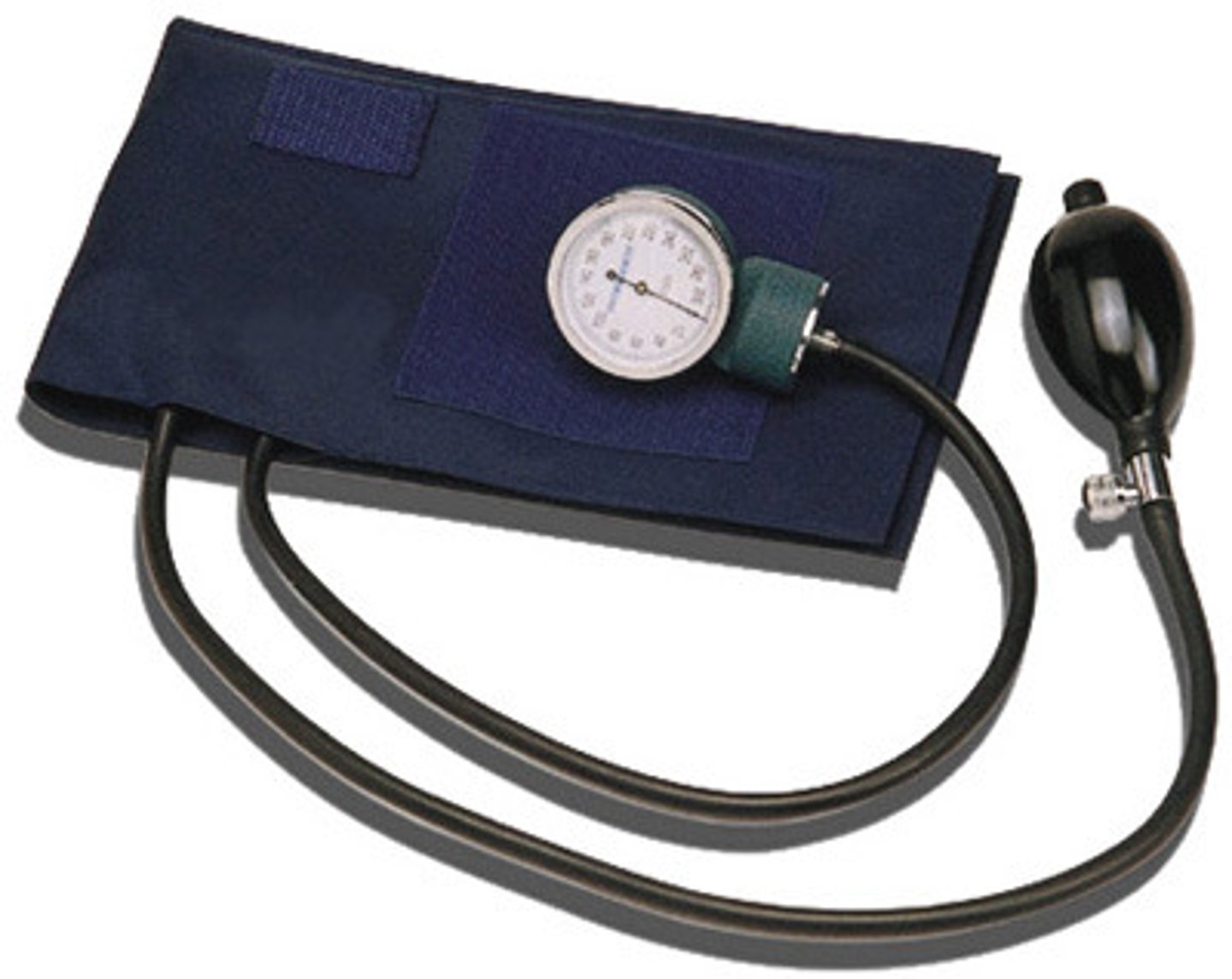
sphygmomanometer
instrument to measure blood pressure
*mercury, aneroid (USED IN CLASS), electronic
Korotkoff sounds
series of sounds heard through stethoscope when measuring BP
PHASE 1 = first clear, faint rhythmic tapping sound (SYSTOLIC PRESSURE)
PHASE 5 = last discernable sound before disappearance of sound altogether (DIASTOLIC PRESSURE)
arterial occlusion
used to estimate systolic pressure
*palpate the radial artery and pump up cuff and note when pulse disappears
**wait 60 seconds for recovery and then use this value + 30 mmHg for blood pressure
sensation
a mental process (such as seeing, hearing, or smelling) resulting from the immediate external stimulation of a sense organ often as a distinguished from a conscious awareness of the sensory process
*an impression produced by impulses conveyed by an afferent nerve (away from CNS) to the sensorium
sensory integration
organization, interpretation and use of sensory information
*provides a representation of the environment that informs and guides motor response
**occurs without conscious effort in an intact system
sensory testing
specific examination of sensory integration
WHY?
- determine location and extent of an injury
- how does the injury affect movement
- provide rationale for PT
- reassess for effective treatment
afferent, efferent
In an intact system, an ______________ signal travels from PNS to the CNS where info is processed and then relayed to the body via an _______________ signal.
afferent signal
signal going to the spinal cord/brain from the skin
*by sensory neurons
efferent signal
nerve impulses carried away from the central nervous system to effectors such as muscles or glands
impairments, activity limitations, participation restrictions
Sensory dysfunction may occur in PNS, CNS, or combined systems and may result in what 3 things?
peripheral nerve injury
sensory loss along cutaneous nerve distribution
ex. stocking glove neuropathy (impaired sensation in hands and feet)
spinal nerve root injury
sensory loss along dermatome distribution
CNS lesion
sensory loss with diffuse distribution
ex. MS, Parkinson's, etc.
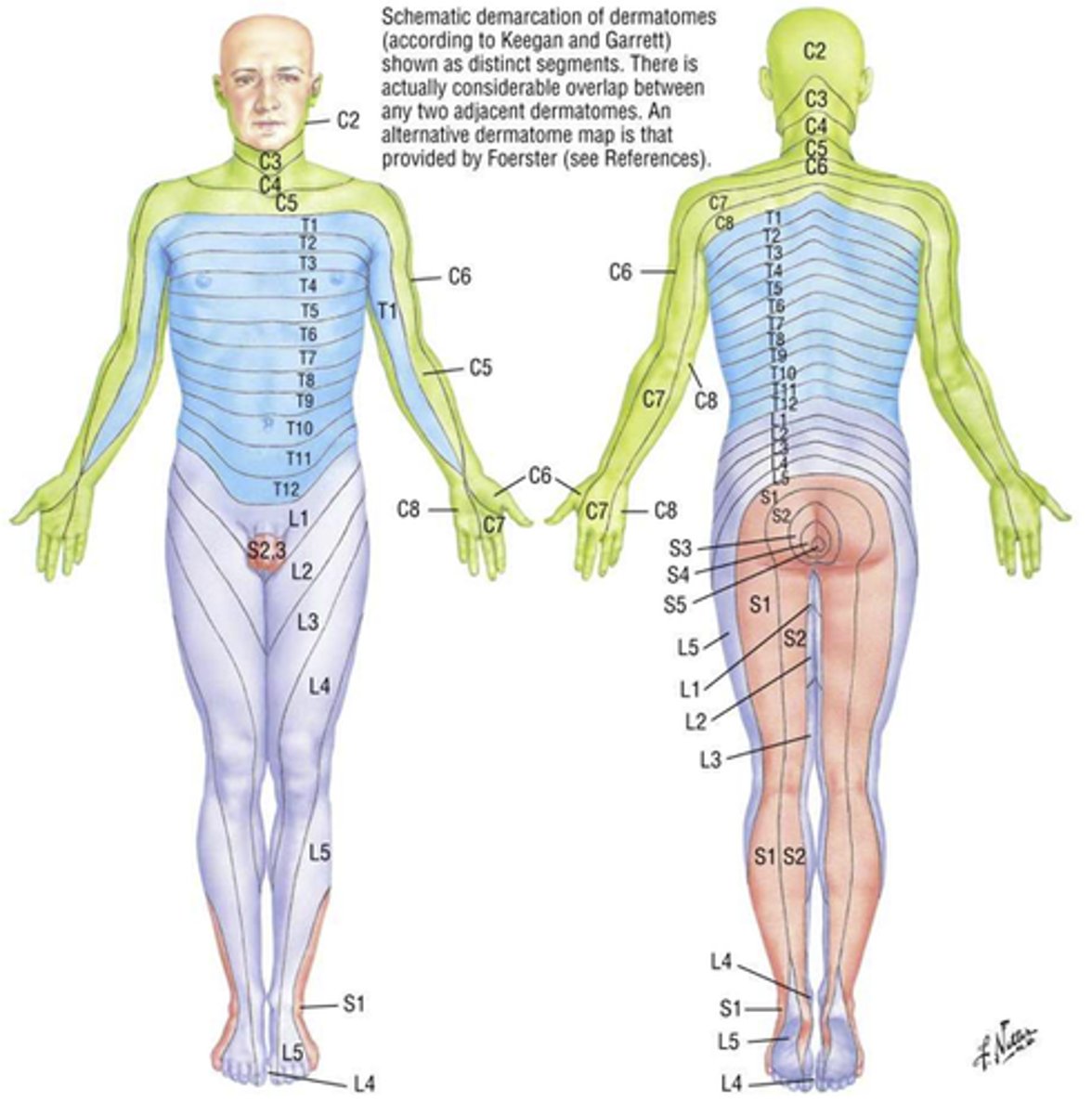
dermatome
"skin segment"
area of skin sensation supplied by one dorsal nerve root (SINGLE NERVE)
*cutaneous nerve distribution
**lesion at the level of the nerve root
superficial (exteroceptors), deep sensation (proprioceptors)
What are the 2 sensory receptor divisions?
superficial sensation (exteroceptors)
cutaneous & subcutaneous tissue
*perceive pain, temperature, light touch, pressure
deep sensation (proprioceptors)
muscle and joint
*position sense, joint awareness, kinesthesia, vibration
astereognosis
inability to determine an object by feel
abarognosis
inability to tell the weight of an object of difference between two
paresthesia
abnormal sensations
ex. pins and needles, prickly
dysesthesia
painful sensation
*burning, itchy
allodynia
hypersensitive response to painful stimulus that is not typically severe
hypoesthesia
reduced skin/tactile sensation
HINT: anesthesia--> total absence of skin sensation (med-induced or not)
hyperesthesia
increased sensitivity to (any) sensation
hypalgesia
diminished sensitivity to pain
HINT: analgesia = total absence of pain perception
hyperalgesia
extreme sensitivity to pain, usually used in context of total pain response
stereognosis
ability to recognize objects by feeling their form, size, and weight while the eyes are closed
*use small familiar objects of varying sizes

kinesthesia
awareness of movement in space
*move a joint through small ROM
"up/down", "left/right", "in/out"
proprioception
position sense at rest
*joint moved in small increments
**patients asked to identify or demonstrate contra-laterally at a static point
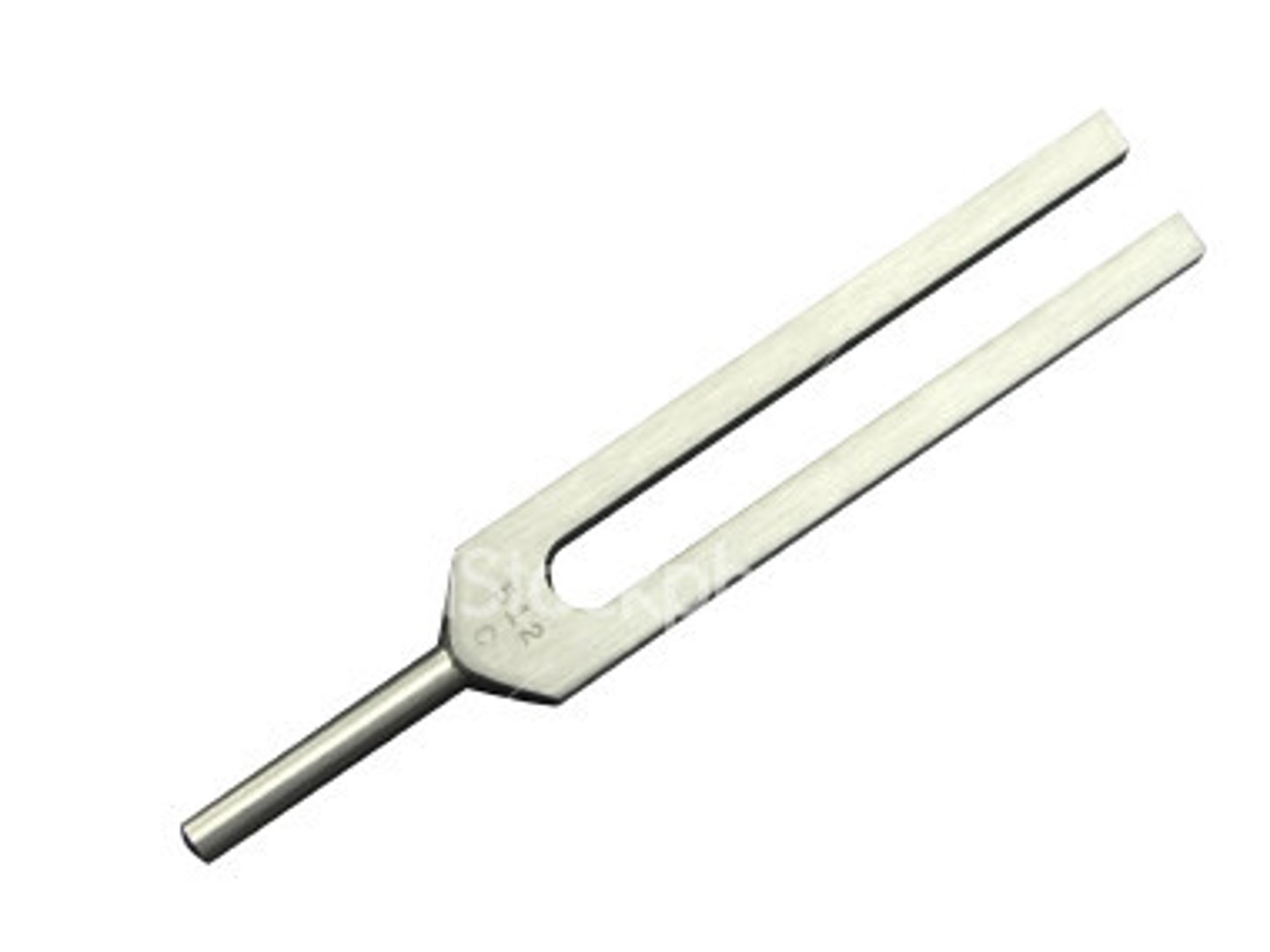
vibration
use a 128 hz tuning fork
*base on bony prominence
**can be used to detect fractures (sometimes missed by x-rays)

two-point discrimination
perception of two points of contact simultaneously
*mostly used for upper extremity
**"one" or "two" response
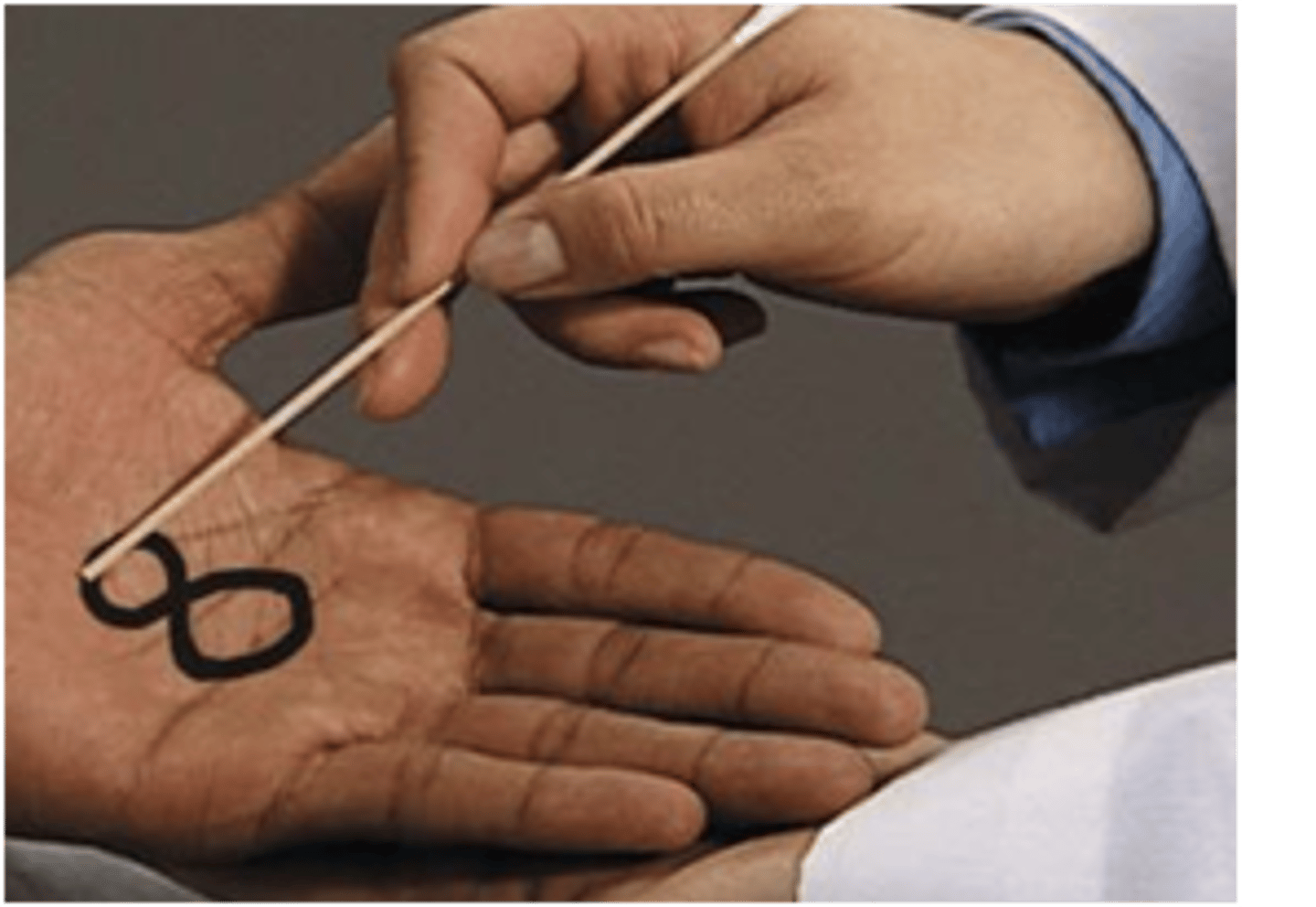
graphesthesia
trace figure identification
*letters, numbers, shapes "drawn" on palm
**use finger, eraser end of pencil
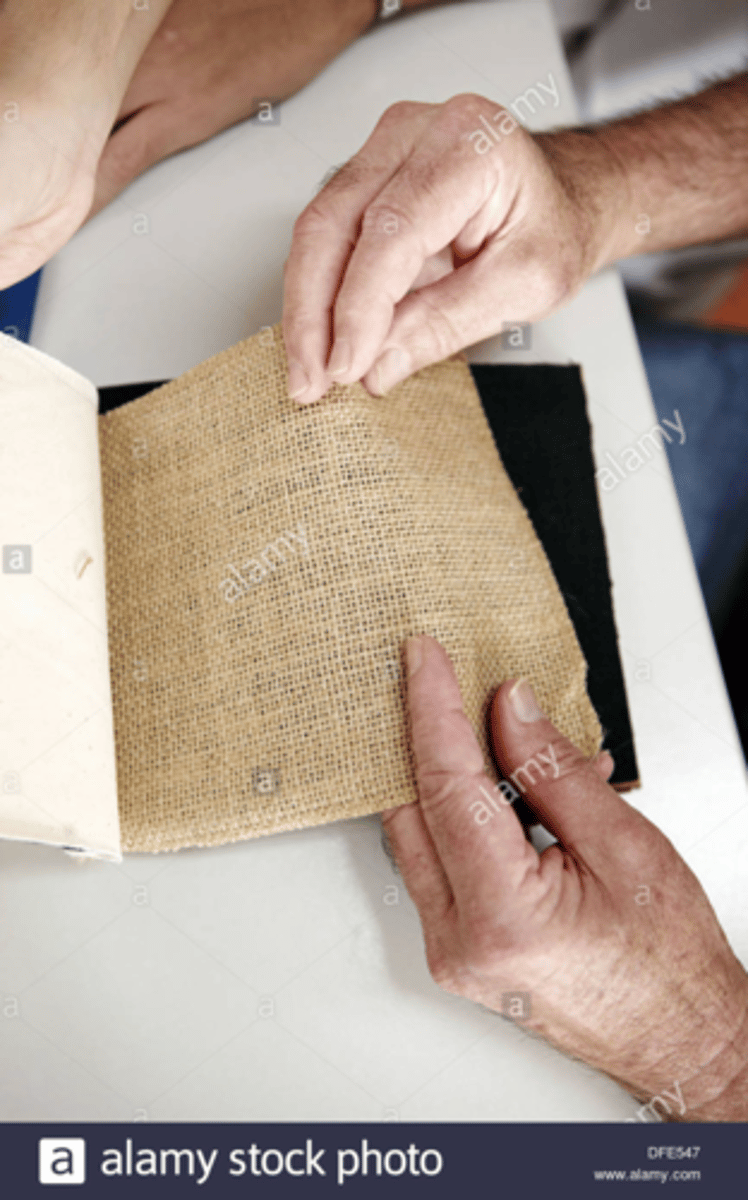
texture recognition
"familiar" fabrics used
*silk, cotton, wool
**identify actual fabric or describe texture (soft, smooth, rough, etc.)

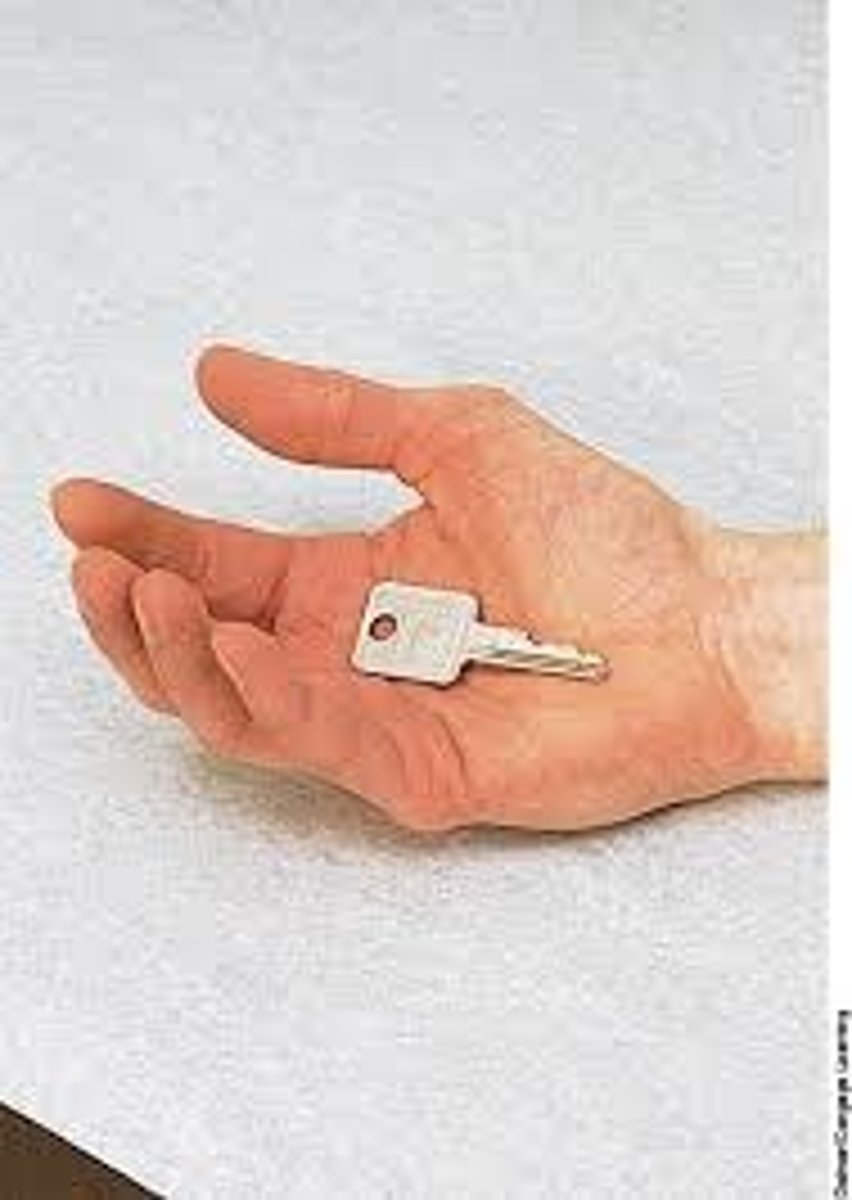
barognosis
weight recognition test
*different weights placed in palm (individually or simultaneously)
**"heavier" or "lighter" response
spinal nerve
area of skin supplied by the spinal afferents of a single nerve - therefore there is almost more than one nerve root involved
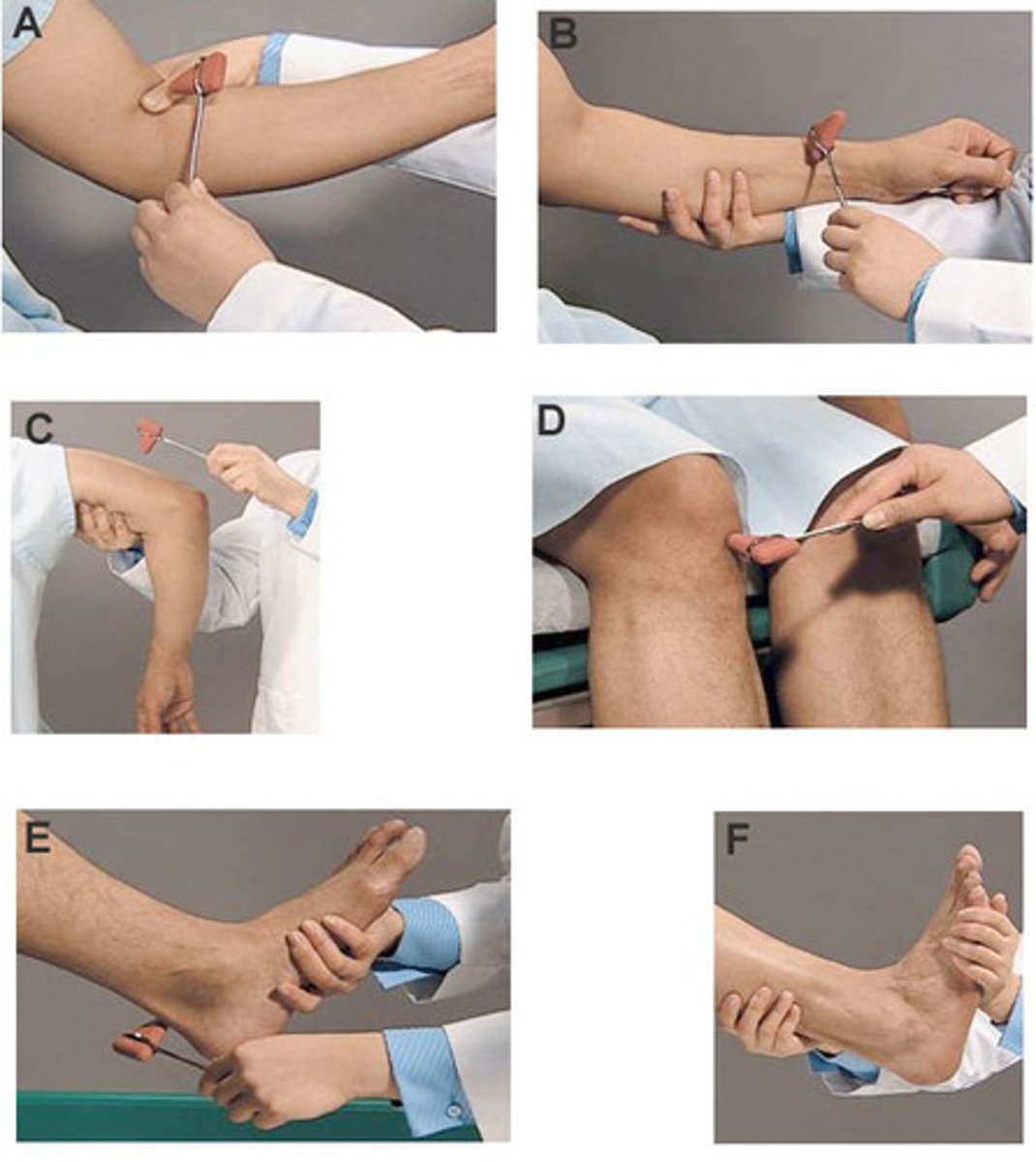
deep tendon reflexes (DTR)
aka muscle stretch reflex, myotatic reflex, monosynaptic reflex
involuntary muscle contraction in response to striking muscle tendon with reflex hammer
*results from stimulation of the stretch-sensitive IA afferent nerves of neuromuscular spindle
**produces a contraction via monosynaptic path
reflex
an involuntary, predictable and specific response to a stimulus that requires an intact reflex arc
biceps, brachioradialis, triceps, achilles, patellar
List the 5 deep tendon reflexes we tested in lab.
2+
What is the "normal" value rating for a DTR?
HINT: must test both sides
Jendrassik maneuver
hooks fingers together and try to pull hands apart
*reinforces knee jerk reflex when patellar ligament is tapped
neuron replacement, conduction velocity, axon size, Meissner's corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles
What 5 sensory changes are decreased as a person ages?