Data Structures and Algorithms
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Orange - Examples of Data Structures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Data Structures
These are a particular way of organizing data in a computer to be used efficiently. It is the arrangement of data in the memory locations to represent values of the carrier set of an abstract data type.
These are also based on the ability of a computer to fetch and store data at any place in its memory, which is specified by a pointer
Pointer
A bit string representing a memory address that can be stored in memory and manipulated by the program.
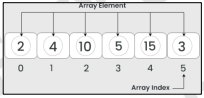
Array
A fixed-length, ordered collection of values of the same type stored in contiguous memory locations. The collection may be ordered in several dimensions. It consists of elements identified by at least (1) array index.
It can be considered as the simplest type of data structure and can be either a one-dimensional or a two-dimensional array (matrix).
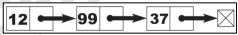
List
An abstract data type that represents a sequence of values, where the same value may occur more than once.
Instance of a list- is a computer representation of the mathematical concept of a finite sequence.
Streams - (potentially) infinite analog of a list.
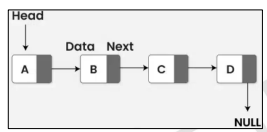
Linked List
Consist of chains of nodes where each node contains information such as data and a pointer to the next node in the chain.
They are among the simplest and most common data structures that can be used to implement several other common abstract data types.
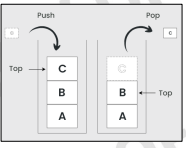
Stack
A kind of abstract data type or collection in which the principal operations on the collection are the addition of an entity to the collection (push) and the removal of an entity (pop). It is a Last-In-First-Out (LIFO).
it is said to be full if it does not contain enough space to accept an entity to be pushed, and it is then considered to be in an overflow state.
Last-In-First-Out
Data structure that the last element added to the structure must be the first one to be removed.
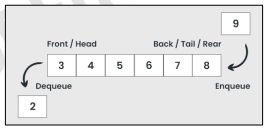
Queue
A kind of abstract data type or collection in which the entities in the collection are kept in order, and the principal operations on the collection are the addition of entities to the rear terminal position and the removal of entities from the front terminal position. It is a First-In-First-Out (FIFO)
First-In-First-Out (FIFO)
A data structure where the first element added to the queue will be the first one to be removed.
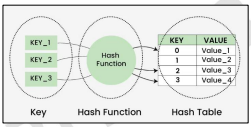
Hashing
A method for storing and retrieving records from a data base. It allows one to insert, delete, and search for records based on a search key value.
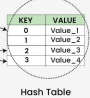
Hast Table
It is a hash system stores records in an array. It works by performing a computation on a search key K.
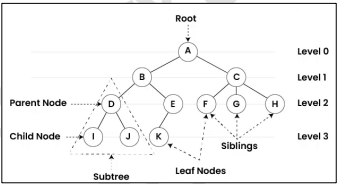
Trees
A data structure made up of nodes or vertices and edges without having any cycles.
It can be defined recursively as a collection of nodes (starting at a root node), where each node is a data structure consisting of a value, together with a list of references to nodes (the “children”), with the constraints that no references is duplicated, and none points to the root.
Abstract Data Type
It is a mathematical model for a certain class of data structures that have similar behavior, or for certain data types of one or more programming languages that have identical semantics.
It is defined only by the operations that may be performed on it and by mathematical pre-conditions and constraints on the effects of those operations.
Algorithm
It is a finite sequence of steps for accomplishing a computational task. It must have steps that are simple and definite enough to be done by a computer, and it must terminate after a finite number of steps.
Human Language
Expressing algorithms to it means describing a sequence of steps or instructions using plain, natural language instead of formal programming code or mathematical notation.
Pseudocode
An informal high-level description of the operating principle of a computer program or other algorithm. It is a procedure for solving a problem based on the actions to be executed and the order in which those actions are to be executed.
Flowchart
A type of diagram that represents an algorithm, workflow, or process. It shows the steps in the form of boxes of various kinds and their order by connecting them with arrows.
Linear data structure
It is a data structure where elements are organized sequentially, wherein each element is positioned in a linear order, and traversal typically follows one direction (from start to end).
Array
It is a fixed-length, ordered collection of values of the same type stored in contiguous memory locations.
It is considered as the simplest type of data structure, and can be either a one-dimensional or two-dimensional.
Static arrays
These are data structures with a fixed size. Once an array is created, its size cannot be changed or altered.
Dynamic arrays
It is a resizable arrays, can change size during runtime.
Linked List
consist of chains of nodes, where each node contains information, such as data, and a pointer to the next node.
Each node is composed of data and a reference (a link) to the next node in the sequence.
Singly Linked List
It consists of nodes where each nodes contains a data filed and a reference to the next node in the linked list.
Doubly Linked List
It allows traversal of the list in both direction, as each node in the list contains a pointer to the previous node and a pointer to the next node.
Traversal
It means visiting each node in the linked list one by one to read, display, or process its data. In java, it is typically done using while loop that follows the next references from the head to the end of the list.
Insertion
It means adding a new node to a linked list. It’s one of the core operations supported by all types of linked lists.
Deletion
It is the operation of removing a node from a linked list.
Search
It means finding a node that contains a specific value by traversing each node one-by-one starting from the head.
Sort
It means arranging its nodes’ values in ascending or descending order.