the rock cycle
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
formation of igneous rocks
-melting and solidification of lava/magma (depending on intrusive or extrusive)
characteristics of igneous rocks
-hard
-vesicles (small holes)
-smooth
-no layers
-crystals (size depends on cooling time, more time = bigger crystals)
types of igneous rocks
-intrusive (caused by slow magma cooling inside of Earth)
-has larger crystals due to a longer cooling period
-extrusive (rapid lava cooling outside of Earth)
-small mineral grains or none ar all due to shorter cooling period
examples of igneous rocks
-granite (intrusive)
-obsidian (extrusive)
-basalt (extrusive)

what type of rocks are these?
-igneous rocks
formation of metamorphic rocks
-heat & pressure after underground burial
characteristics of metamorphic rocks
-relatively hard
-may or may not have layers
-squashed
-banding
types of metamorphic rocks
-foliated (has layers)
-unfoliated (no layers)
examples of metamorphic rocks
-gneiss (foliated)
-marble (non-foilated)
-quartzite (non-foilated)

what types of rocks are these?
-metamorphic
formation of sedimentary rocks
-small pieces of sediment (caused by erosion and weathering) cement together and get compacted to form a rock
characteristics of sedimentary rocks
-layers
-small sediments
-crumbly
-fossils
-pieces with sediment between them
types of sedimentary rocks
-clastic (compacted broken rocks)
-chemical (compacted dissolved materials)
-organic (compacted biogenic matter)
examples of sedimentary rocks
-sandstone
-limestone
-coal
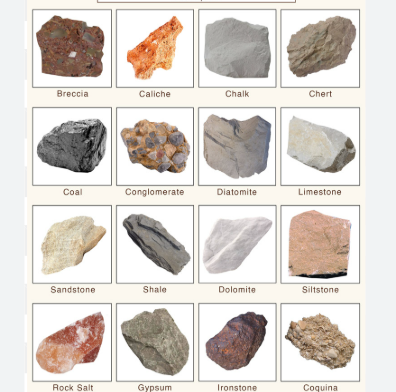
what type of rocks are these?
-sedimentary rocks
magma
-liquid rock inside of Earth
lava
-liquid rock outside of earth
burial
-the process where layers of accumulated sediment are covered by new, overlying layers
-the weight of the materials lead to increased pressure and temperature in the buried layers, triggering the physical and chemical changes that transform loose sediment into solid rock
-processes called lithilication
compaction and cementation
-process where sediments are squeezed together under pressure
-the "gluing" of sediment grains together by new mineral crystals
sediments
any solid material broken down by weathering and erosion
weathering and erosion
-the process of breaking down or dissolving rocks, soil, and minerals without movement
-the process that picks up and moves weathered material from its original location
heat and pressure
forces that transform existing rocks into metamorphic rocks
melting and cooling
-process magma goes through to achieve igneous rocks
strata
-distinct layers of sediment in sedimentary rocks
-clastic
-compacted broken rocks
chemical
compacted dissolved materials
organic
compacted biogenic matter