lecture 4 diseases of leukocytes and erythrocytes
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
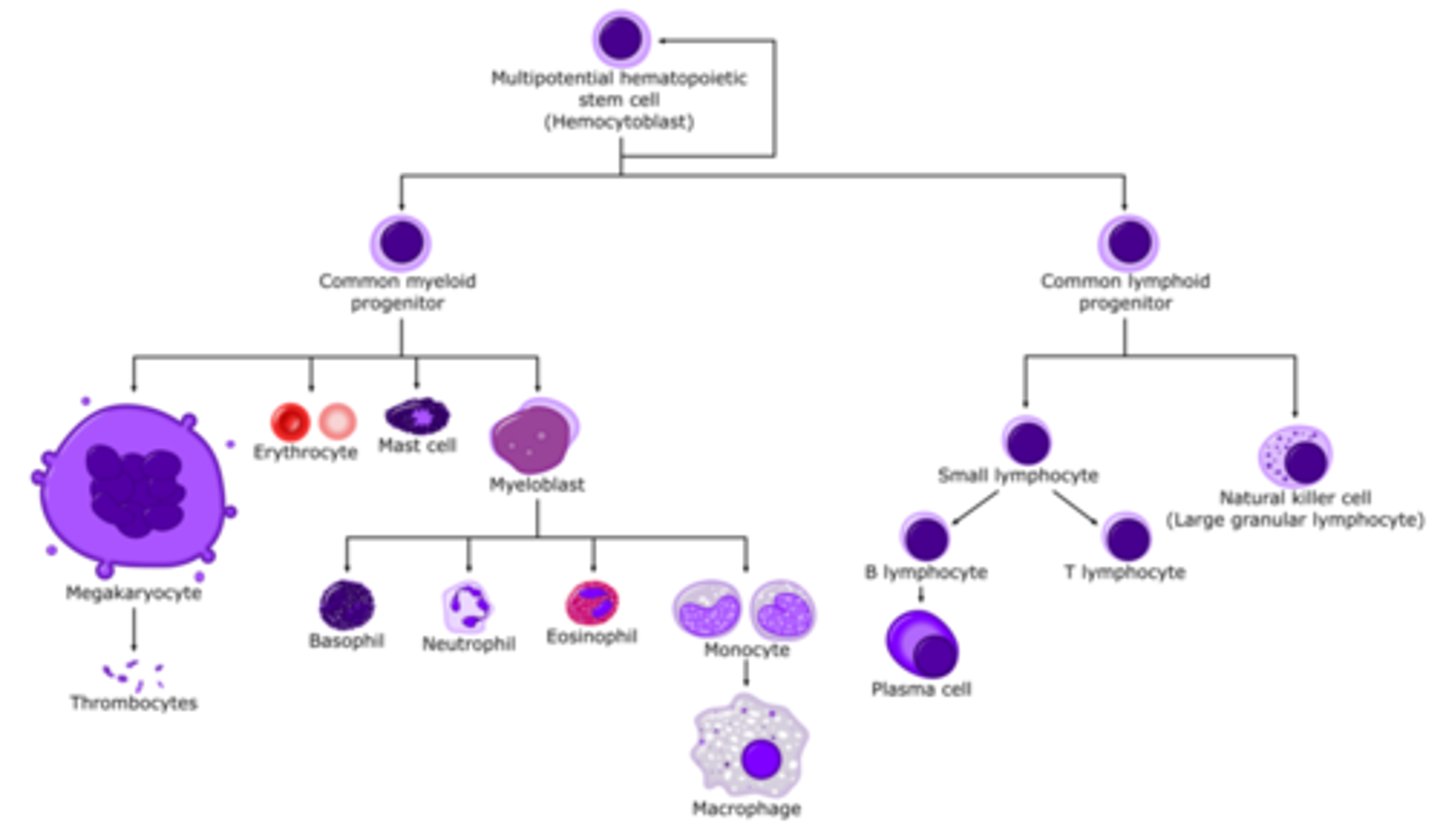
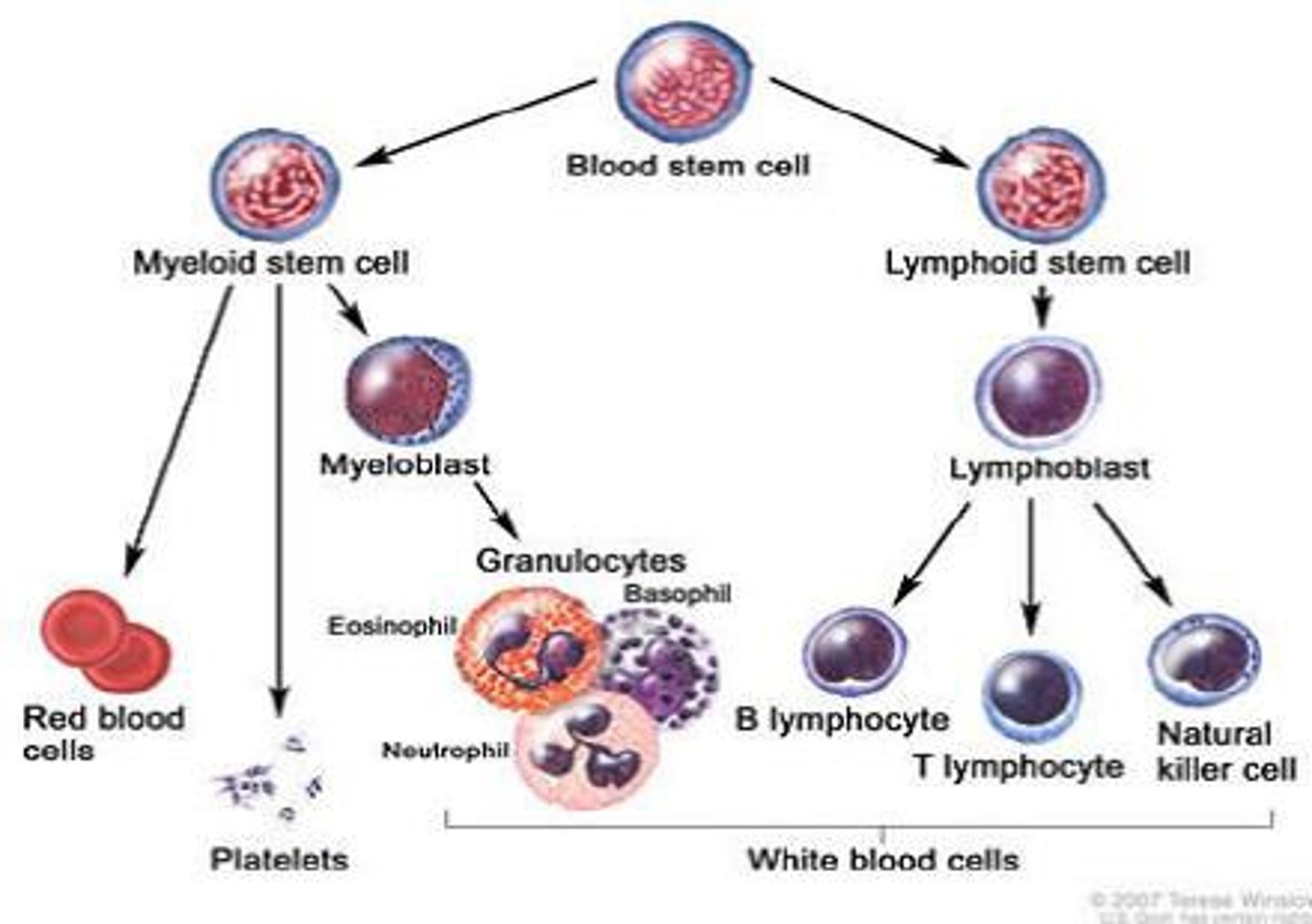
hematopoiesis
formation and development of blood cells
lineage from multipotential hematopoietic stem cell
becomes myeloid progenitor
- erythrocytes
- mast cells
- granulocytes (basophil, neutrophil, monocyte -> macrophage)
- thrombocyte (platelets)
becomes lymphoid progenitor
- natural killer cell
- t cell
- b cell
leukocyte vs lymphocyte
leukocyte - overall immune response (neutrophils, eosinophils)
lymphocyte - adaptive, specific immune response (natural killer cell, b cell, t cell)
2 types of white cell disorder
reactive - too much of these cells during an active infesion
neoplastic - ???
leukopenia
non neoplastic disorder, most common is neutropenia
causes include:
- decreased granulocyte production
- increased granulocyte destruction
lymphopenia
non neoplastic disorder, not enough b/t cells, less common than leukopenia
causes include:
- rare inherited immune disease
- HIV
- high corticosteroid treatment
reactive leukocytosis
non neoplastic disorder, too many WBCs, types include: polygamy morphonuclear leukocytosis, eosinophilic leukocytosis, monocytosis
polygamy morphonuclear leukocytosis
caused by acute bacterial infection or tissue necrosis
eosinophilic leukocytosis
seen with allergy disorders, parasitic infection, drug rxns
monocytosis
seen with chronic infection, lupus
reactive lymphadentitis
enlarged lymph node bc of foreign antigen, can have follicular hyperplasia or paracortical hyperplasia
follicular hyperplasia
enlarged secondary follicles bc of increased B cells (seen as regions)
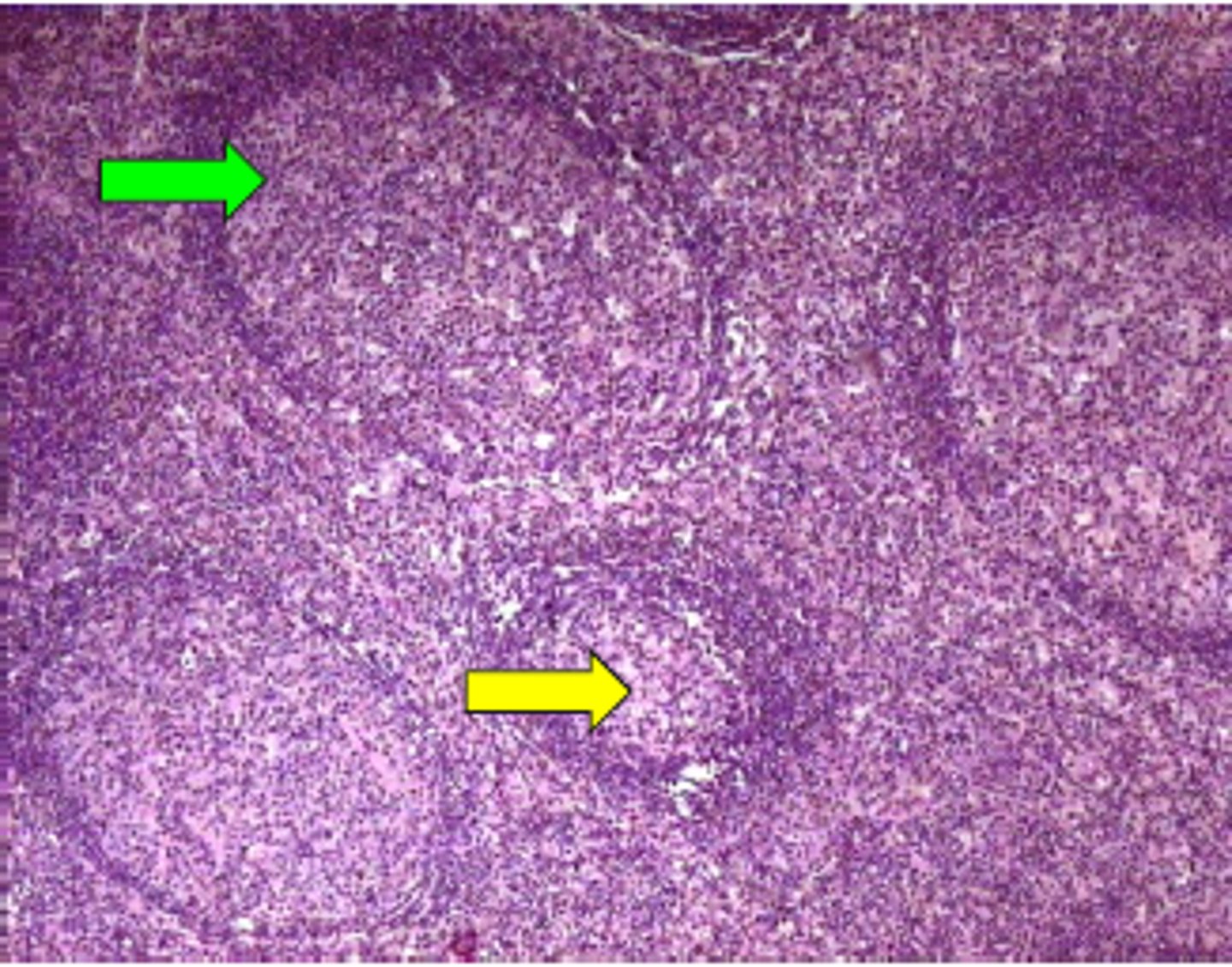
paracortical hyperplasia
enlarged tissue on outside bc of active T cell response
neoplastic disorders
most common disorder of WBCs, malignant, occurs at any age/race, 150,000 new diagnosis, can be lymphoid neoplasm or myeloid neoplasm
leukemia vs lymphoma
leukemia = malignant w/ bone marrow involvement
lymphoma = lymphoid proliferations (lymph nodes)
** not distinguished sometimes can see one with the other
leukemia
cancerous cells that overpopulate marrow and replace normal cells
- pushes out RBCs and macrophages
-can infiltrate high vascularized tissues (liver, spleen. lymph nodes)
- can be acute or chronic
acute vs chronic leukemia
acute
- bone marrow is replaced by early lymphoid or myeloid progenitors -> loses ability to make RBCs
- cells are undifferentiated and nonfunctional
chronic
- well differentiated cells
- precursor to neutrophils, specified cells
lymphoma
- B and T cells
- swollen lymph nodes
- most common 15-24 yo
lymphoid neoplasms characterization
precursor B cell -> bone marrow
peripheral B cell -> in lymph nodes
precursor T cell -> bone marrow
peripheral T cell -> in lymph nodes
what causes lymphoma and leukemia
- environmental
- chromosomal translocation
- inherited
- viruses
- chronic inflammation -> leukocytes are constantly produced in bone marrow
- iatrogenic -> caused by medical treatment like chemotherapy
- smoking
lymphoid neoplasms
- B cell origin
- causes abnormal immunity (1 B cell overmultiplies and takes over other B cells present) -> leads to loss of protective immunity
- monoclonal origin -> specific B cell causes a problem
precursor lymphomas includes
acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ALL)
B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ALL)
- transform hematopoietic cells w/o differentiation
- B cells or T cells (usually B)
- malignant B vs T can't be distinguished
- from chromosomal aberration -> affect function of TFs
B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
- most common in children
- more common in hispanics>whites>blacks
- clonal expansions of cells that aren't mature
- no immunoglobins on cell bodies
- suppresses normal hematopoiesis -> low RBCs, WBCs, platelets
- marrow has lots of lymphoblasts
- caused by chromosomal abnormalities -> Philadelphia chromosome (9+22 swap to create different promotor gene combo)
peripheral B cell neoplasms includes
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)
follicular lymphoma
plasma cell neoplasm
hodgkin lymphoma
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) similarities
- morphologically same
- mature lymphocytes that can produe antibodies
- disrupt normal immune function
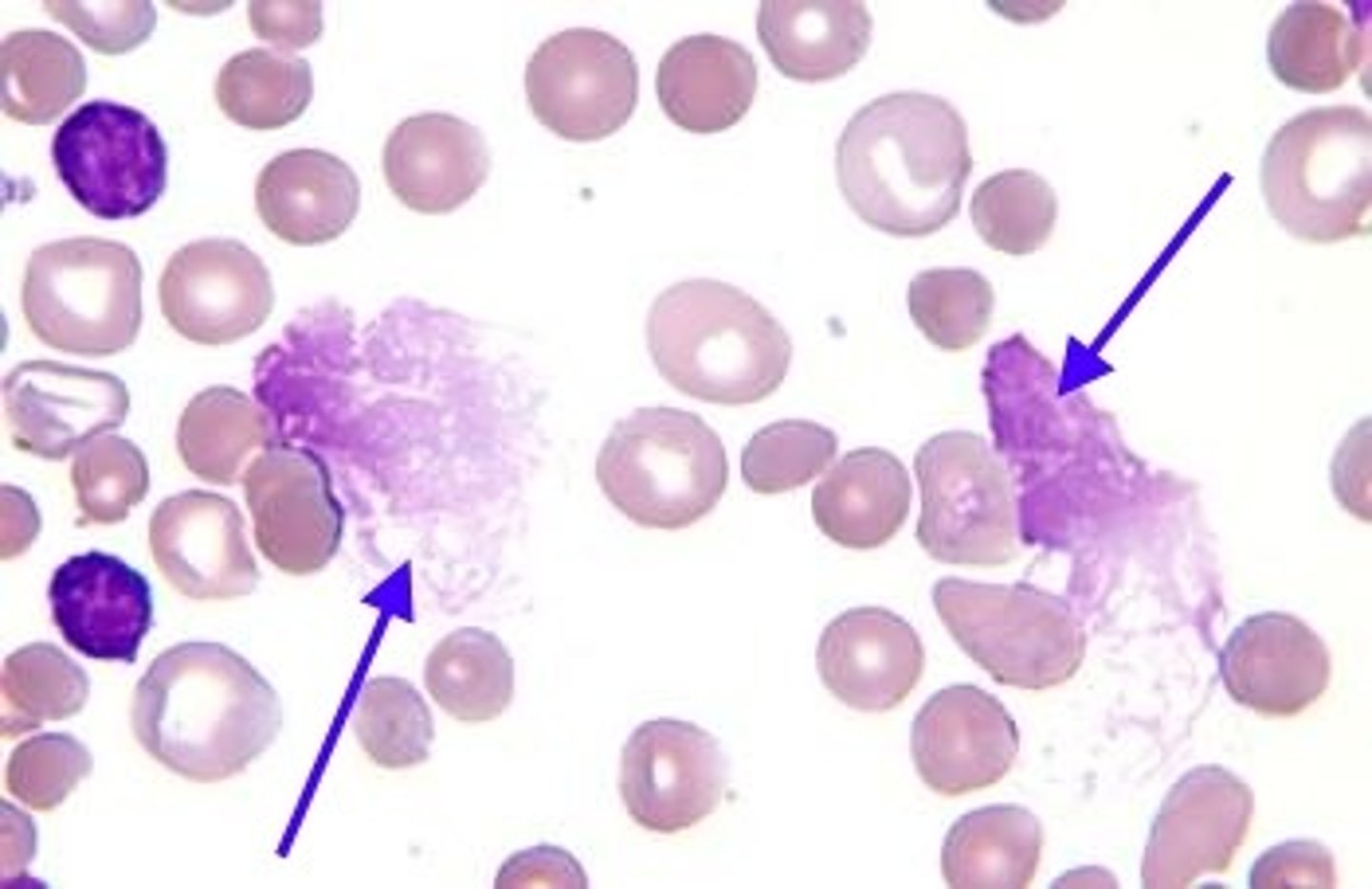
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) differences
CLL
- bone marrow involvement
- most common in old adults
- mostly B cell
- shows positive CD5 markers of T cells on B cells
- smudge cells
SLL
- in lymph nodes
- invade lymph tissue and disrupt structure
follicular lymphoma
- non hodgkin
- non tender, enlarged lymph nodes
- resemble normal B cells
- caused by chromosomal translocation (14 + 18) -> causes overexpression of BCL2
- incurable (survival time 7-10 yrs)
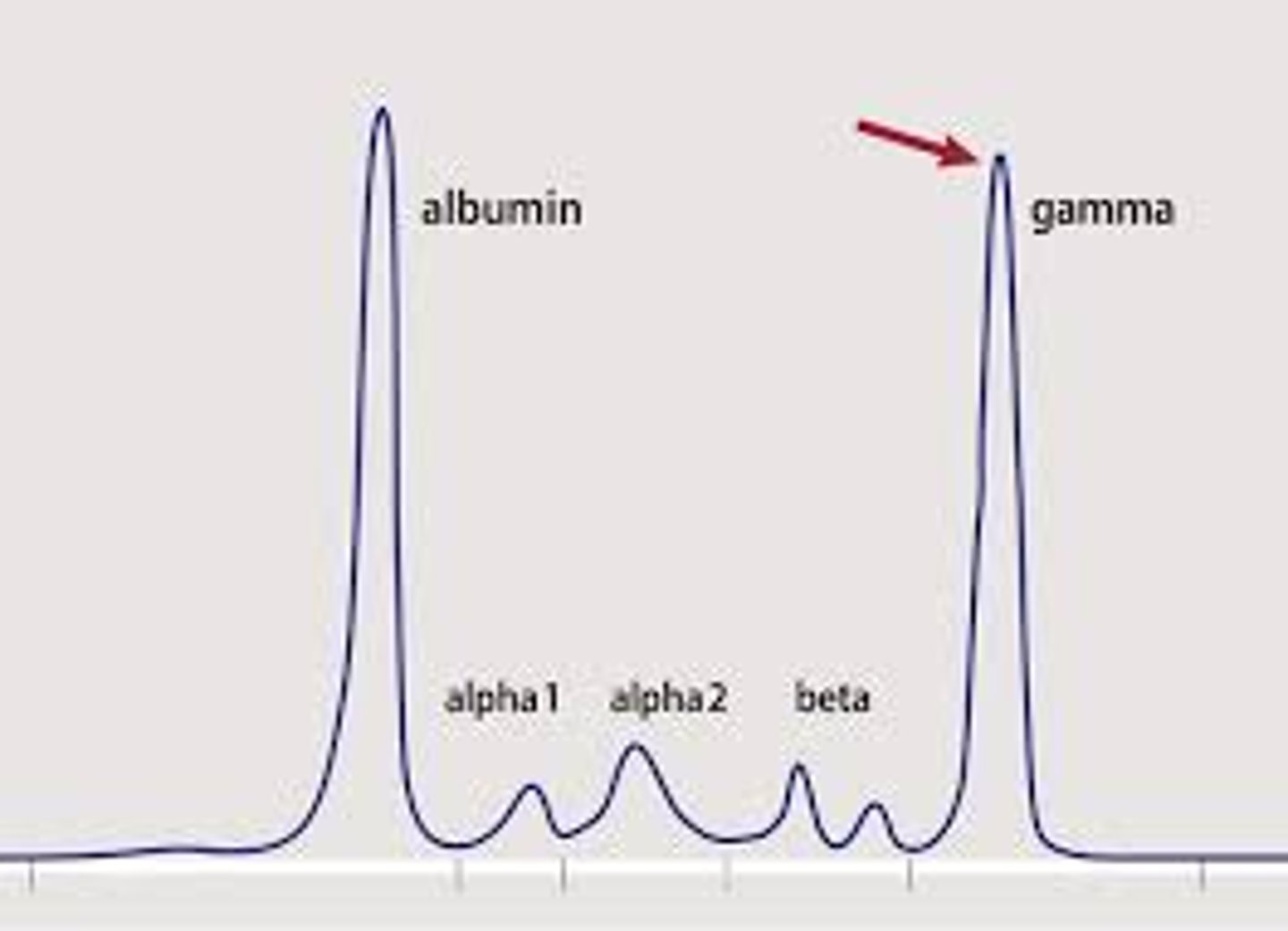
plasma cell neoplasm
- clones 1 mature B cell
- multiple myeloma (uncontrollable growth)
- breaks down bone -> causes high Ca levels -> leads to hypercalcemia and renal failure
- on graph: end spike from increased B cells of 1 types
hodgkin lymphoma
- presence of Reed-Sternberg cells (owl looking)
- starts in 1 lymph node and spreads to spleen + liver
- peaks in 20s and 50+
- treat w radiation and chemotherapy (if caught early enough can remove single lymph node)
myeloid neoplasm
- derived from hematopoietic progenitor cells in marrow
- progenitor cell for RBCs, granulocyte, monocytes, platelets
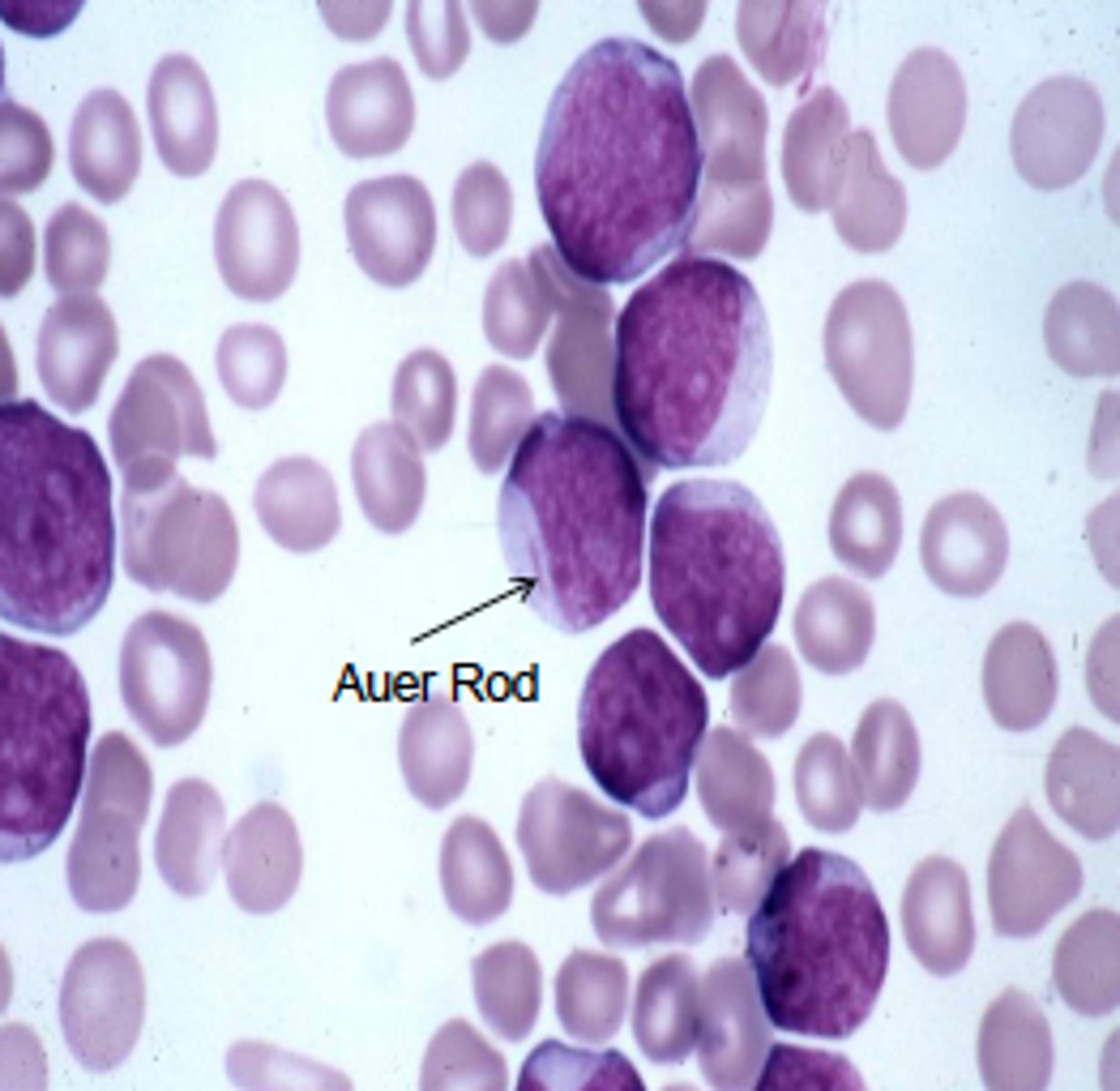
acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML)
- caused by mutation that affects differentiation
- blast cells replicate w/o differentiating
- affects committed myeloid progenitor (younger pts), pluripotent stem cell (older pts)
- peaks in 60s
- presence of Auer rod after staining
- causes anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
chronic myeloproliferative disease
- 90% have Philadelphia chromosome (9+22)
- mutant cells continue to mature -> shows inc granulocyte precursors in blood
- has 3 stages
- caused by having too much myeloid stem cell
3 stages of chronic myeloproliferative disease
1. initial stable phase (2-8 yrs)
2. accelerated phase (6-12 months) - fail to respond to treatment, inc anemia and thrombocytopenia
3. blast crisis - similar to acute leukemia
- lose adaptive immunity -> production of myeloblasts
- produce lymphoblasts
- don't repond to treatment
- fatal quickly
erythropoiesis process
produced in kidney then into bone marrow, entire process is about 1 week
Day 1: proerythroblast (committed stem cell)
Day 4: normoblast -> eject nucleus
Days 5-7: reticulocyte -> dark staining bc extra RNA to maintain hemoglobin protein, not as oxygen binding as a mature RBC
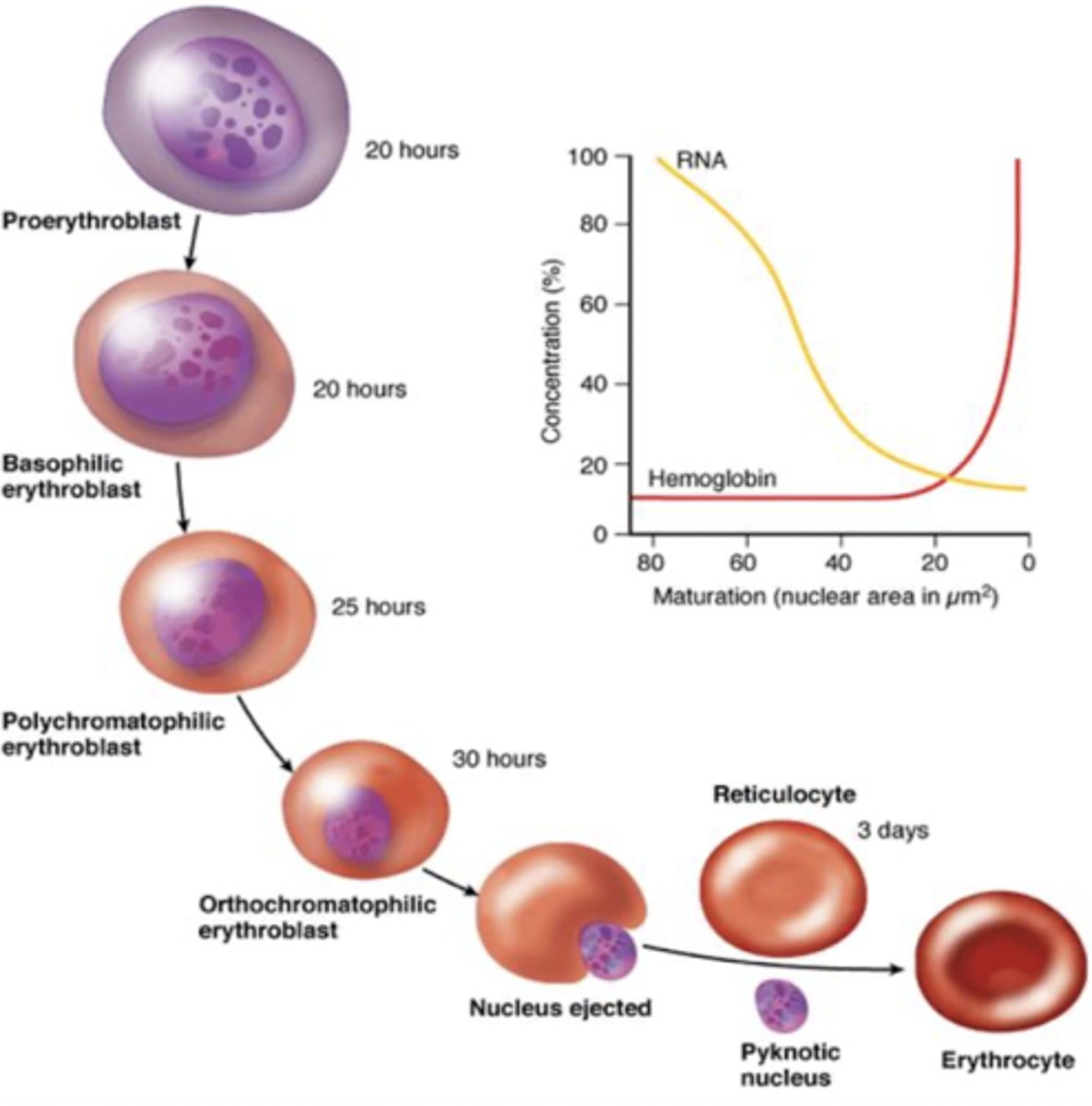
erythropoietin
hormone (signal molecule of stem cell precursor)
- regulates development of erythroid cells
- produced in kidney
- promotes growth of erythroid progenitor cells (associated w cytokines)
- stimulate release of reticulocytes from bone marrow
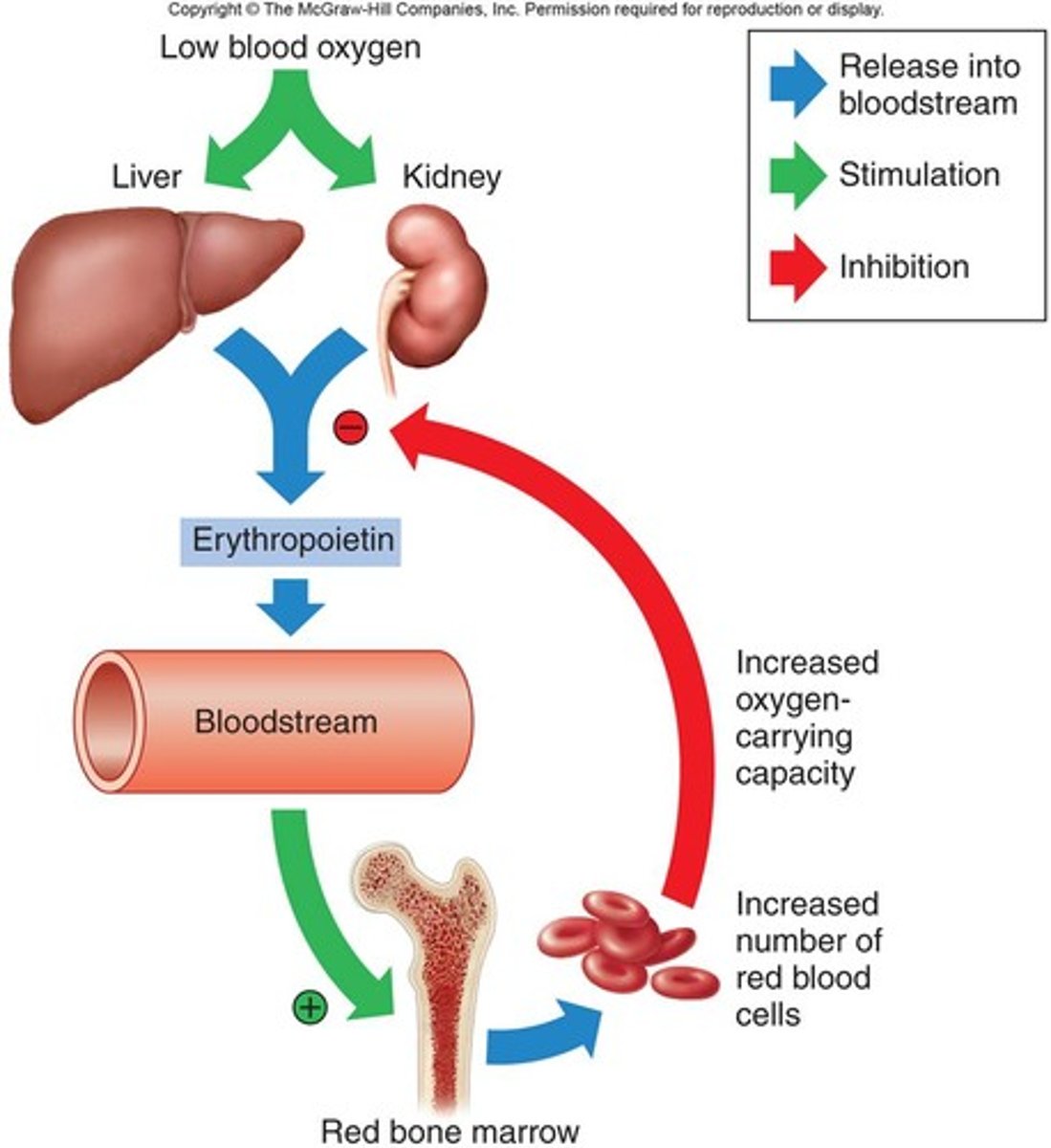
response to stress in bone marrow
- inc number of erythroid stem cells differentiating into erythrocytes (~1 week)
- dec maturation (1 week -> couple days)
- release reticulocytes into bloodstream earlier
OVERALL: needs more blood to carry 02
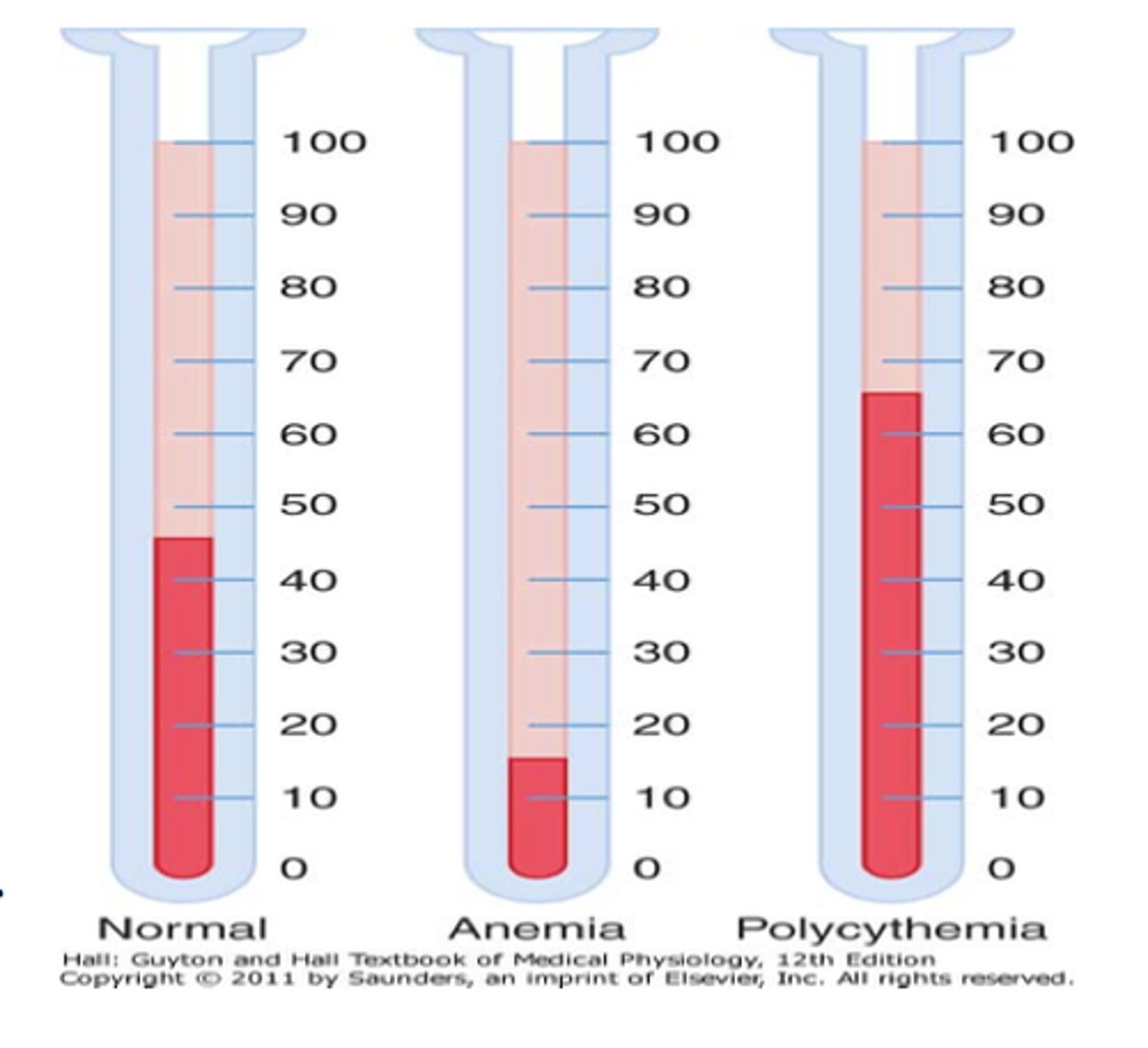
polycythemia
primary - clonal stem cell disorder, not dependent on erythropoietin levels, caused by mutation/inherited
secondary - from erythropoietin stimulation, physiologic response to low O2
anemia description
caused when the bone marrow cannot compensate for lack of O2 in the body
levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit for anemia
males
hemoglobin: < 13 gm/dL
hematocrit: < 39%
females
hemoglobin: < 12 gm/dL
hematocrit: < 36%
** difference in male and female due to muscle mass
4 compensatory mechanisms for anemia
1. decrease hemoglobin-oxygen affinity -> dec presence of 2,3 BPG (usually binds to hemoglobin to release O2)
2. increased tissue perfusion (decreases tissue perfusion to skin to send it to organs like heart and brain)
3. increased cardiac output
4. increased RBC production
clinical features of anemia
- pallor
- weakness, fatigue
- dyspnea (short breath)
- cardiac failure
ocular manifestations of anemia
- retinal hemorrhage -> leaky RBCs produced
- cotton wool spots -> portions that die off due to no vascularization
- vessel tortuosity -> squiggly vessels
- conjunctival pallor -> white under eyes
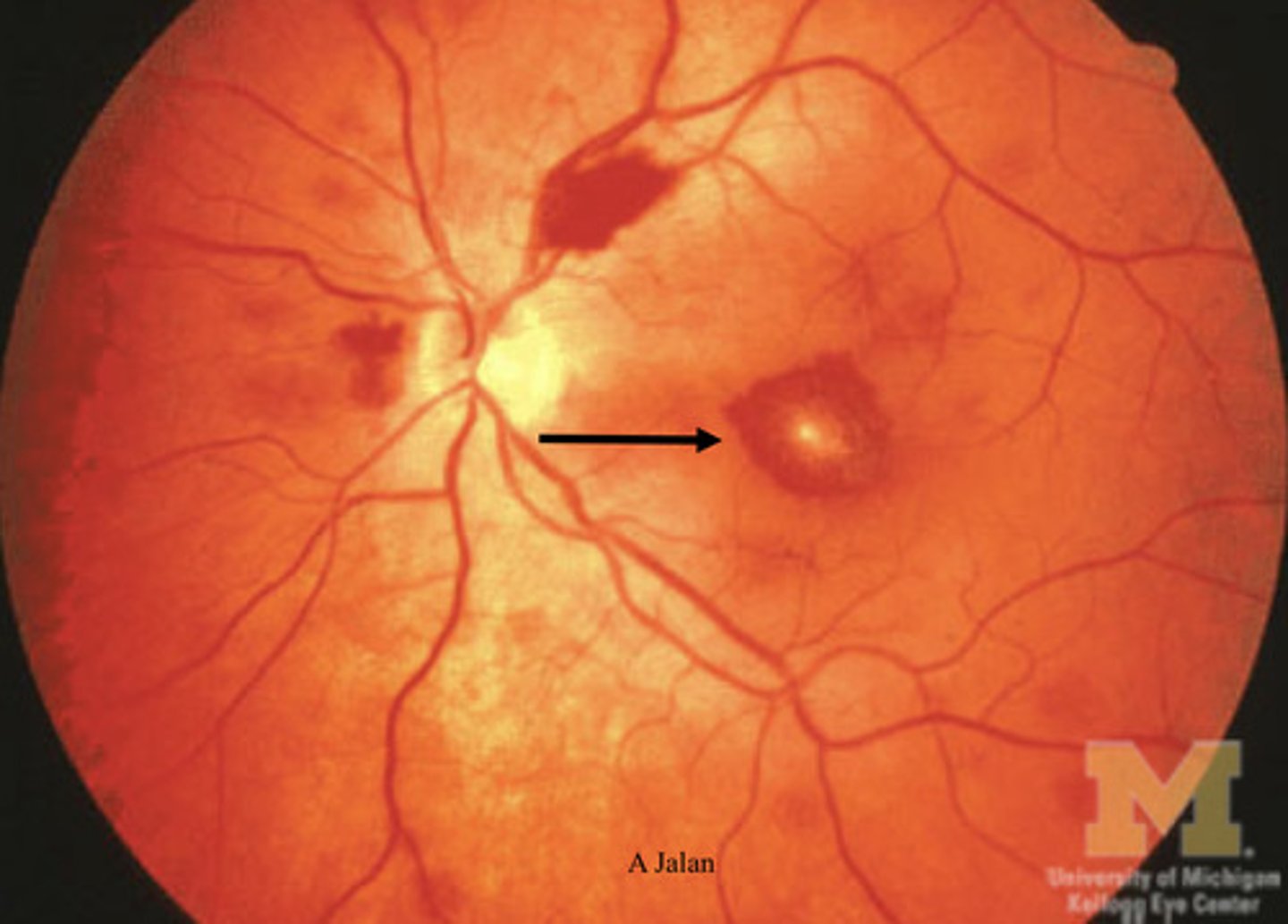
2 ways to classify anemia
underlying mechanism
- impaired erythrocyte production
- increased rate of destruction
- blood loss
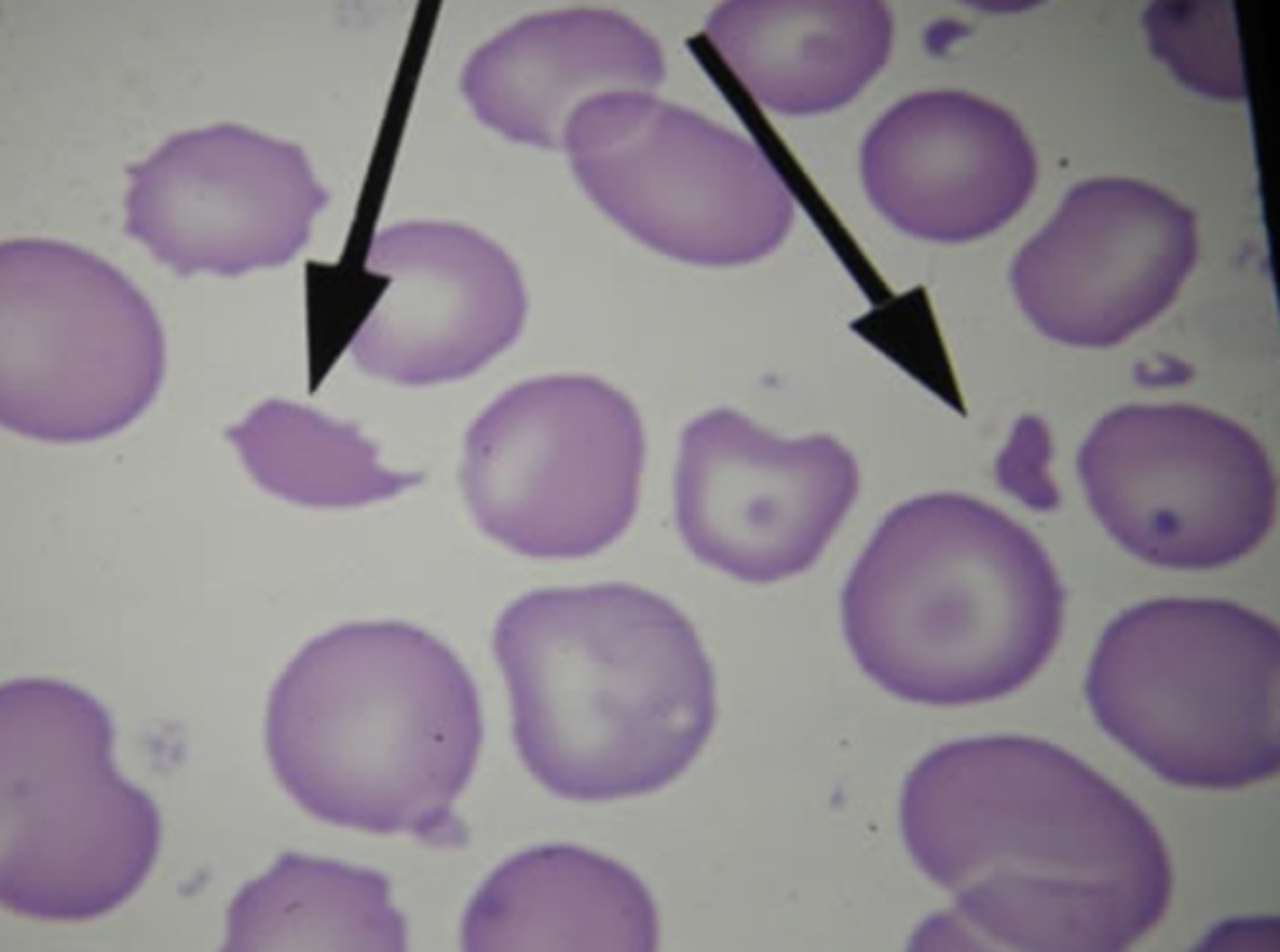
appearance of RBCs:
- size (normocytic, microcytic, macrocytic)
- color/hemoglobin content (normochronic, hypochronic)
- shape (round, sickle)
anemia caused by impaired erythrocyte production
- aplastic anemia (bone marrow failure)
- megaloblastic anemia (maturation failure) -> pernicious, folate deficiency anemia
- iron deficiency anemia
anemia caused by increased rate of destruction
- hemolytic anemia (intravascular + extravascular)
- sickle cell anemia (intravascular)
aplastic anemia
impaired erythrocyte production -> disturb stem cell differentiation
- hypocellular
- creates empty marrow spaces -> filled by fat cells and fibrous stroma
- pancytopenia -> reduction of RBCs, platelets, WBCs
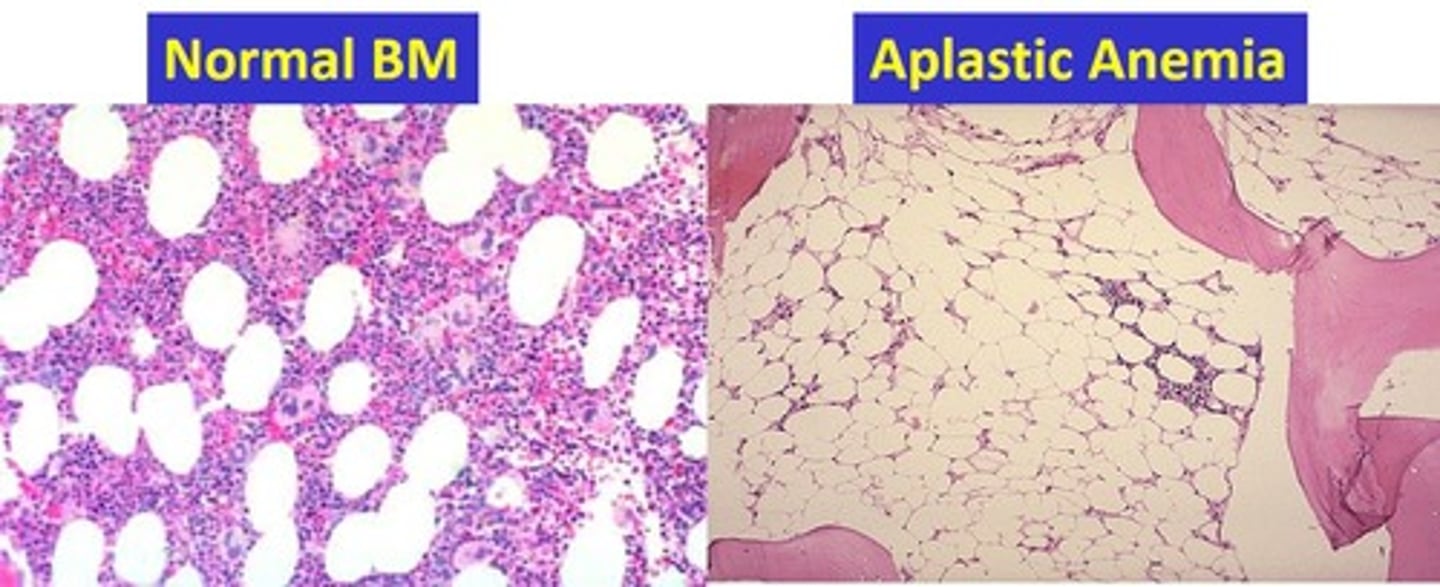
megaloblastic anemia
impaired erythrocyte production -> disturb maturation of erythroblasts
- caused by impaired DNA + defective nuclear maturation
- cytoplasmic maturation not in sync w nuclear maturation
- defective cell maturation + division
- major types: vitamin B12 deficiency, folic acid deficiency (both coenzymes for DNA synthesis)
pernicious anemia description
caused by vitamin B12 deficiency
- macrocytic
- mean cell volume greater than 100
- hypersegmented neutrophils (4+ lobes)
- causes neurologic change: posterolateral spinal tract
- folate can improve hematologic signs but not neurologic ones
pernicious anemia ocular findings
- gradual vision loss
- can be cecocentral scotoma (skewed to side)
- pallor of optic disc
- dec color vision
folate deficiency anemia
caused by dec intake, increased requirements (pregnancy), malabsorption
- NO neurologic changes
- macrocytic
- normal serum vitamin B12
iron deficiency anemia
most common; caused by dietary lack, impaired absorption, increased requirements, chronic blood loss
- microcytic, hypochromic
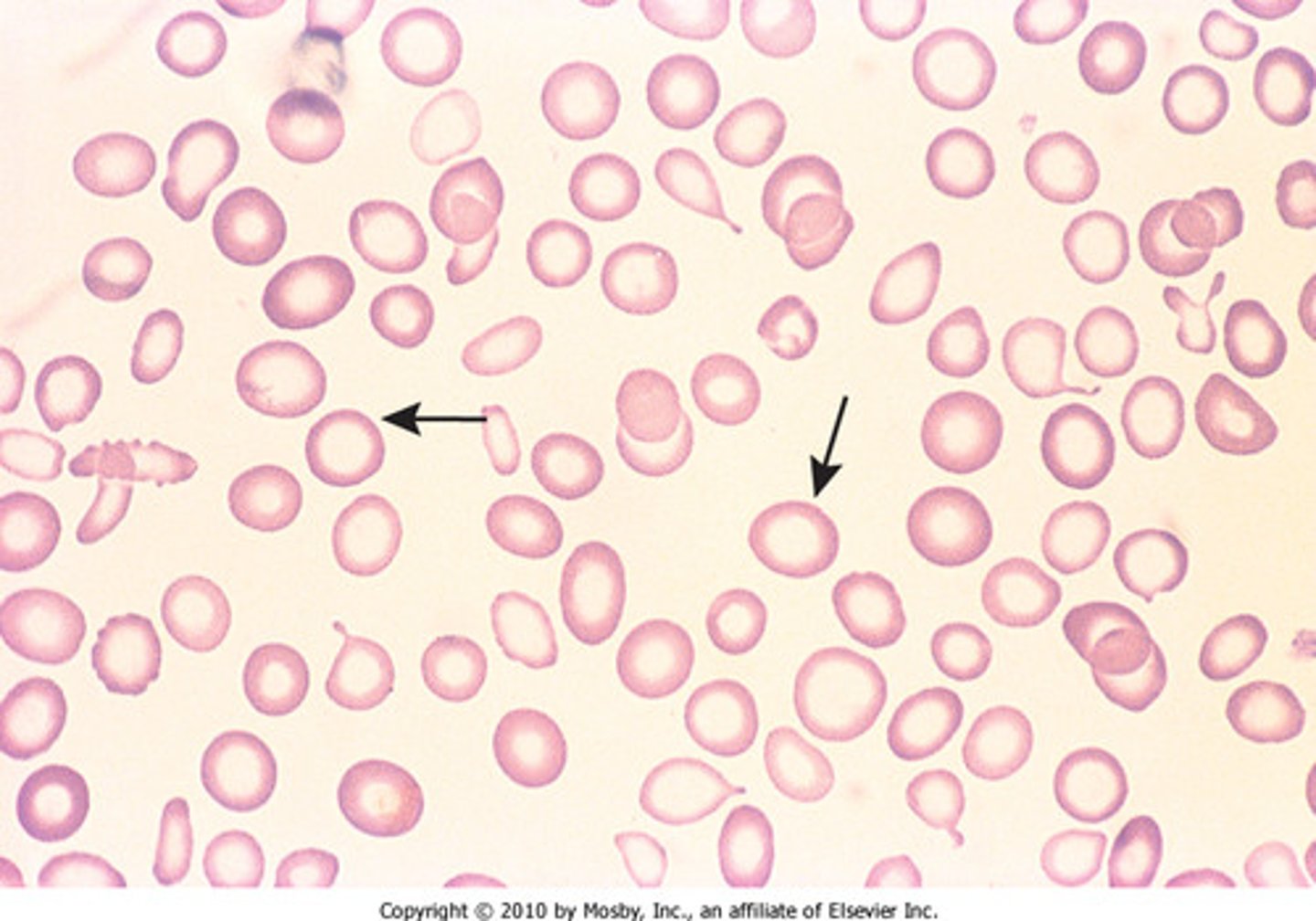
pathway of iron deficiency anemia
1. initial blood loss/deficiency
2. ferrtin and transferrin (storage forms) loss in bloodstream
3. ferritin and transferrin lose ability to make Hgb
4. low serum iron
** progressive deficiency
hemolytic anemia
premature destruction
- short survival of RBCs
- accumulate hemoglobin breakdown products
- see inc erythropoiesis in bone marrow
-