Topic 1 - SACE Biology Stage 2
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
Nucleotide
a monomer of nucleic acids; contains a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Nucleoside
nitrogenous base + sugar
deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar present in DNA
ribose
A five-carbon sugar present in RNA
complementary base pairing
In DNA, T pairs with A; G pairs with C;
RNA, U pairs with A and G pairs with C
semi-conservative replication
in each new DNA double helix, one strand is from the original molecule, and one strand is new
helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks.
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
Hydrogen bonds
Type of bonding found between complementary bases
3
The number of hydrogen bonds found between the complementary nitrogenous bases G and C
2
The number of hydrogen bonds found between the complementary nitrogenous bases A and T
histone
Protein around which DNA wraps in eukaryotic cells in chromosomes
gene locus
specific location of a gene on a chromosome
chromatin
DNA in its normal uncondensed state in the nucleus.
gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a single functional protein or a single polypeptide or RNA molecule
chromosome
an independent section of the entire DNA genome that appears as a threadlike structure carrying genetic information in the form of genes
strand of DNA
single string of nucleotides connected to each other via the sugar phosphate backbone
5' to 3'
direction DNA is read
molecule of DNA
two strands of DNA joined together by complementary base pairing between nitrogenous bases
single circular chromosome
DNA is found in this form in prokaryotic (bacterial) cells
nucleus and mitochondria
DNA is found in these two locations in eukaryotic cells
nucleic acid
macromolecule made of a chain of nucleotides eg DNA, RNA
nucleosome
Bead-like structure in eukaryotic chromatin, composed of a short length of DNA wrapped around a core of 8 histone proteins
endonuclease
another name for a restriction enzyme
restriction enzyme
Enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides (4-8 nucleotides)
sticky ends
Single stranded ends of DNA left after cutting with restriction enzymes
primer
short sequence of single stranded DNA that is complementary in sequence to the start and end of a sequence of DNA to be copied
5' to 3'
Direction DNA is read
Oligonucleotide
a short polymer of nucleotides (usually fewer than 50) eg 10-30. Often used as primers.
Taq polymerase
Heat stable DNA polymerase from heat resistant bacteria Thermus aquaticus used in PCR
short tandem repeats
STR stands for......
non-coding
STRs are found in the........................regions of DNA
Negative
DNA has a ..............................charge due to the presence of phosphate groups
positively
DNA moves towards the .........................charged end of the polyacrylamide gel during gel electrophoresis
polyacrylamide gel
type of gel used to separate DNA fragments in gel electrophoresis
smallest
The...................DNA fragments travel the furthest along the gel in gel electrophoresis
Dideoxynucleotide
nucleotide that has hydroxyl groups removed which is used during DNA sequencing to terminate synthesis by blocking DNA polymerase
gene probe
Fluorescently or radioactively tagged DNA or RNA sequence that is complementary in sequence to a target DNA sequence. Used to locate the DNA sequence.
Transgenesis
transfer of genetic material from one species to another
recombinant DNA
DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources
bacterial plasmids
a tiny ring of DNA in the cytoplasm of bacteria that can replicate independently
recombinant plasmid
Plasmid that has an extra gene from another source inserted into it
Cluster Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat
CRISPR stands for..........
gRNA (guideRNA)
Sequence of RNA used in CRISPR that is complementary in sequence to the target gene (DNA). Part of the Cas9 complex which guides where Cas9 cuts the DNA.
Cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence
Function of the enzyme in the Cas9 complex
guideRNA and enzyme
Cas9 complex consists of......
thermal cycler
An instrument that automatically cycles through different temperatures used to complete PCR reactions
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
A technique for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers, DNA polymerase molecules, and nucleotides.
forward, reverse
Two types of primers required in PCR
Denaturation
First stage of PCR that involves heating mixture to 95-98˚C to break hydrogen bonds and separate DNA strands
Annealing
Second stage of PCR that involves cooling mixture to 56˚C so complementary DNA primers bind to the DNA
Polymerisation
Final stage of PCR that involves heating mixture to 72˚C to activate the Taq polymerase so free nucleotides bind by complementary base pairing to form the new complementary DNA strand
doubles
The number of copies of DNA ................. with every cycle of PCR
Probe or dye
Possible methods used to visualise DNA fragments on gel electrophoresis
capillary electrophoresis
A method of separating DNA samples based on the rate of movement of each component through a gel-filled capillary while under the influence of an electric field
Sanger method of DNA sequencing
A method used to determine the nucleotide sequence of a piece of DNA by selective incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication
DNA replication stops
Effect of tagged dideoxynucleotides (dATP, dGTP etc) on DNA replication when using the Sanger method
Electropherogram
data output from capillary electrophoresis where fluorescent signals are recorded as graphical peaks
Introns can be removed
Advantage of using recombinant yeast plasmids instead of recombinant bacterial plasmids
micro-injection
foreign DNA is inserted directly into a cell's nucleus using a glass micropipette
electroporation
Electrical current forms pores in cell membranes
homology directed repair
a mechanism in cells to repair double strand DNA breaks that relies on using the homologous chromosome as a repair template. This mechanism is used in genome engineering to incorporate precise genetic changes.
Non-homologous end joining
A mechanism for repairing double-strand breaks in DNA that involves quickly bringing together, trimming, and rejoining the two broken ends; results in a loss of information at the site of repair.
CRISPR-associated proteins
Cas stands for ..........
Vectors
Bacterial and yeast plasmids and viruses can be used as ......................... for transgenesis
Longest
The first peak seen on an electropherogram corresponds to the shortest/longest DNA fragment
DNA ligase
an enzyme that joins the sugar-phosphate backbones of DNA strands back together
Metabolism
◦ All chemical processes within an organism that sustain life
Anabolism
◦ The "building up" reactions
Eg synthesising DNA from free nucleotides
Eg photosynthesis
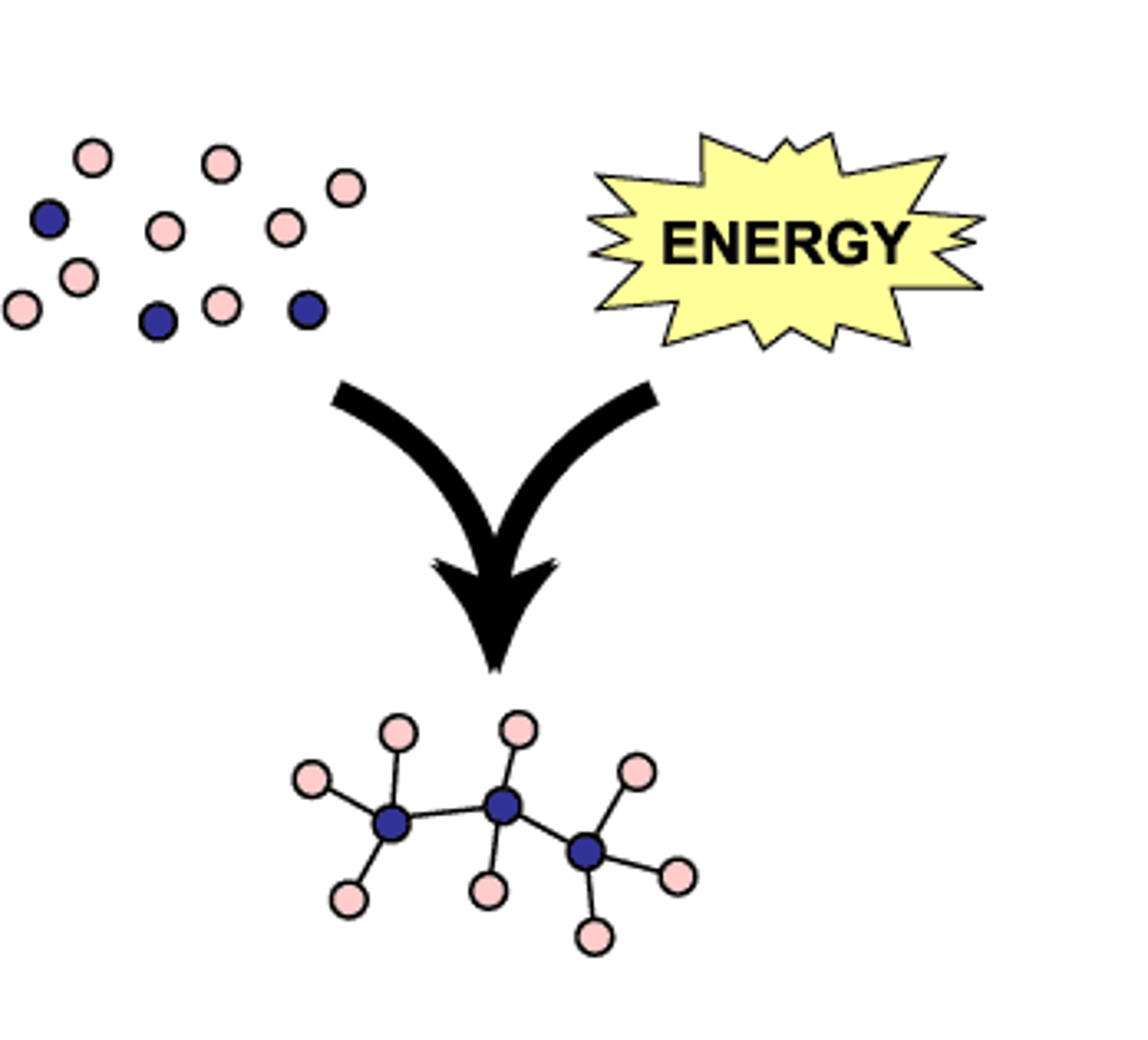
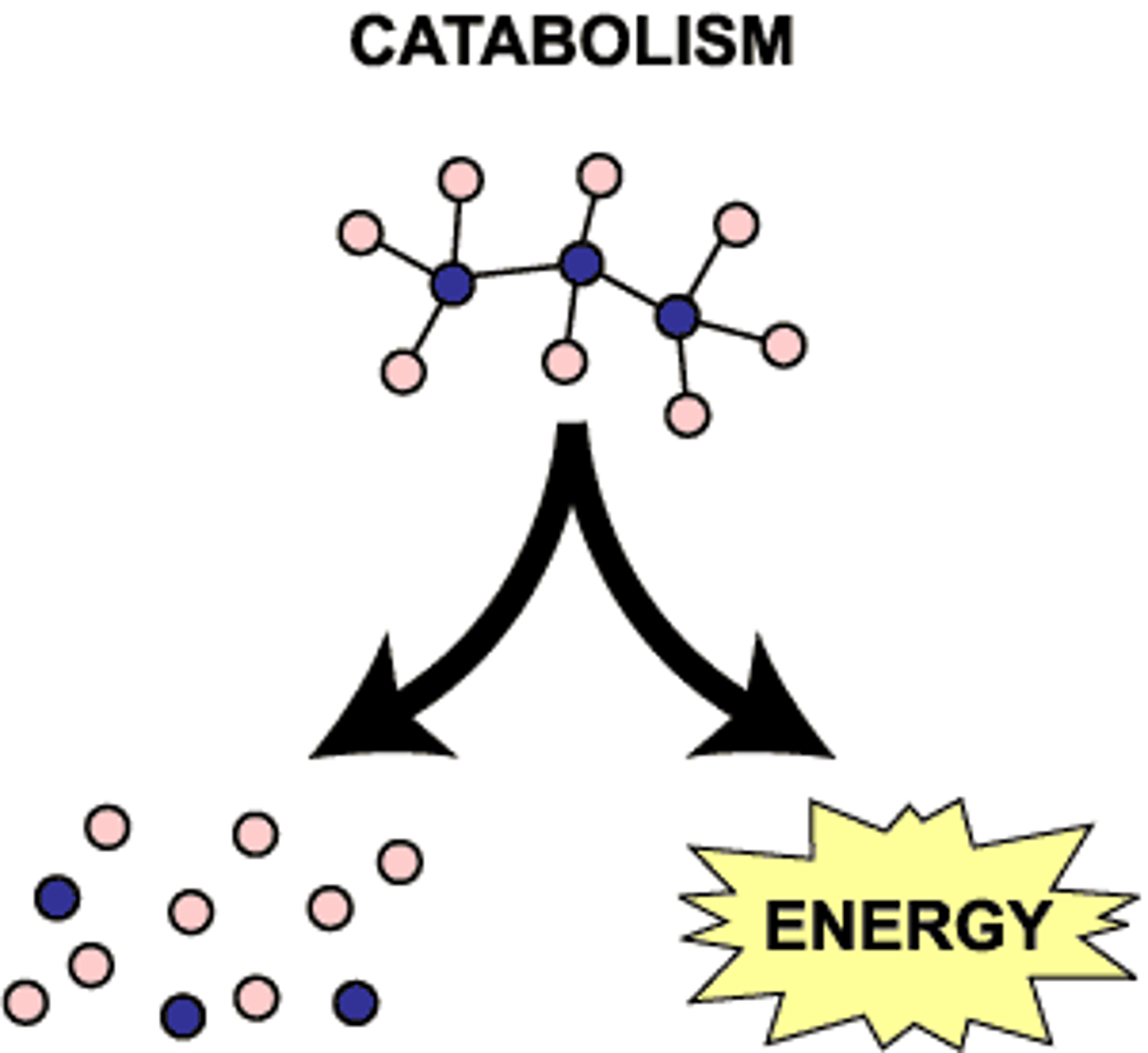
Catabolism
◦ The "breaking down" reactions
◦ Eg digesting proteins to amino acids
lower activation energy
Impact of enzymes on activation energy of reactions
Enzymes
Biological catalysts for chemical reactions in living organisms
protein
Enzymes are made of ................................
Substrate
reactant in an enzyme-catalysed reaction
active site
a region on an enzyme that binds to a substrate (protein or other substance) during a reaction
Conformational change
Term given to the slight change in shape to the enzyme's active site when substrate binds
Induced Fit Model
Model which explains that the enzyme active site undergoes conformational change as substrate binds
cofactor, temperature, pH
Factors that Effect Enzyme activity
cofactor
An inorganic compound or ion that binds to the enzyme (not the active site) which causes the active site to change shape and better bind the substrate. The enzyme is activated.
denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein caused by heat or other factor due to breaking of bonds between localised portions of the polypeptide chain
Denatured protein
◦When a proteins secondary, tertiary, or
quaternary structure is disrupted
◦ Peptide bonds are not broken
◦ Often irreversible
primary structure/peptide bond
These bonds are not broken when proteins are denatured
secondary, tertiary, or quaternary
These levels of structure are disrupted when proteins are denatured
primary structure
Protein folding is determined by the ________________
competitive inhibitors
molecules that compete with the substrate for binding at the active site
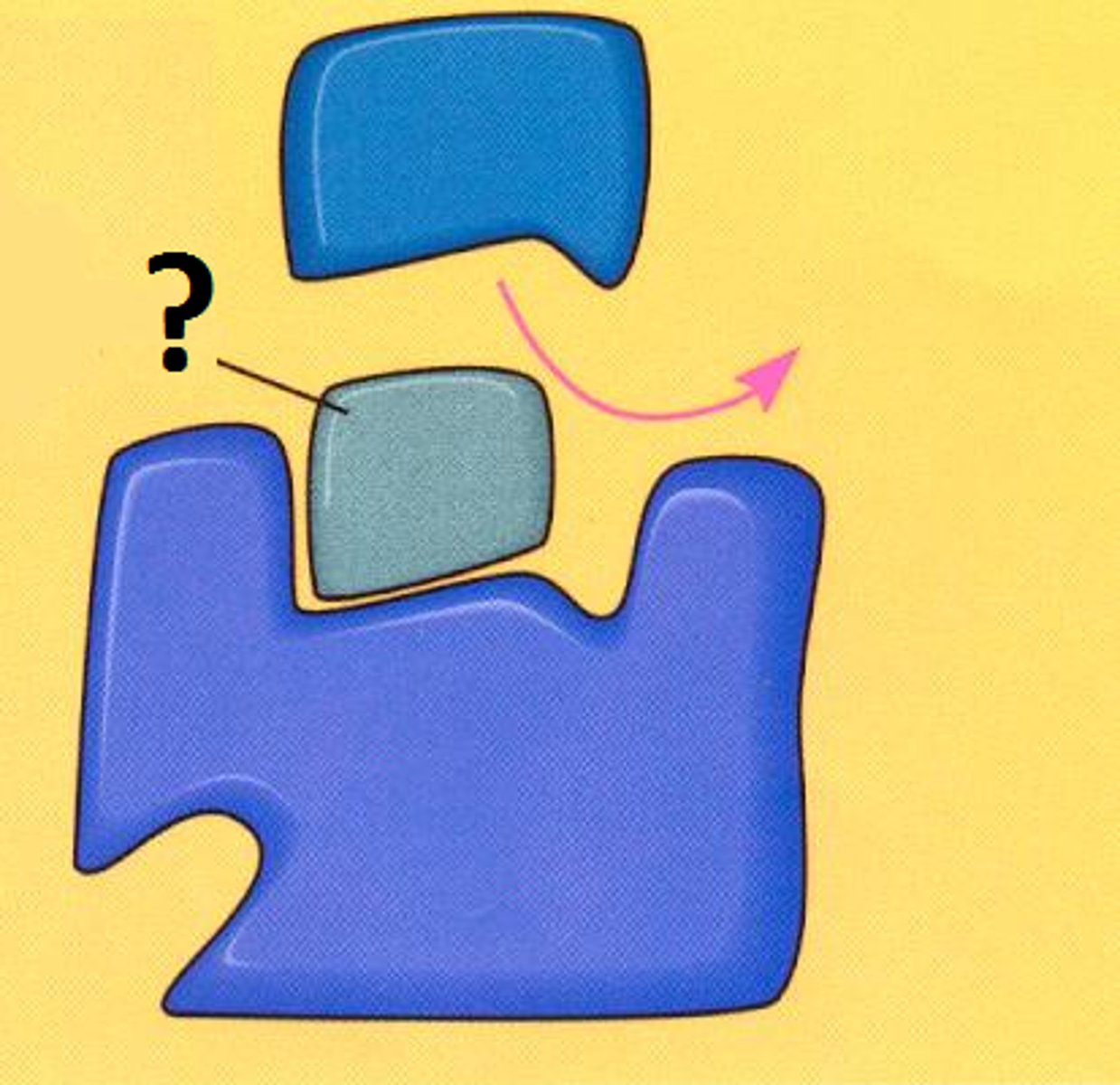
non-competitive inhibitors
Bind to an allosteric site (not the active site) and deform the enzyme and its active site (conformational change), stop the substrate from binding indirectly
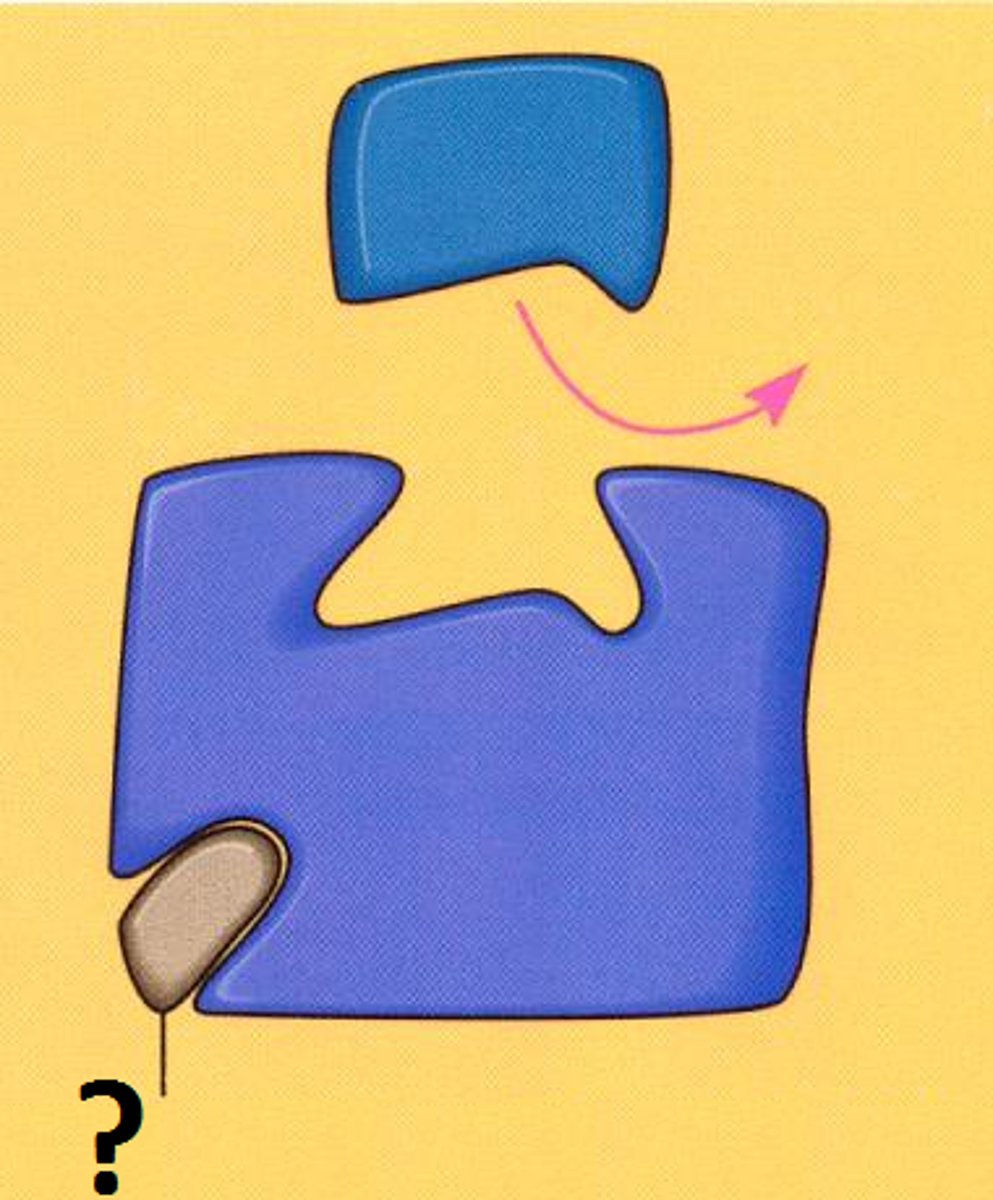
non-competitive inhibitors
In the presence of a lot of substrate, which type of inhibitor would be most effective?
allosteric site
A specific receptor site on some part of an enzyme molecule remote from the active site.
allosteric inhibition
the mechanism for inhibiting enzyme action in which a regulatory molecule binds to a second site (not the active site) and initiates a conformation change in the active site, preventing binding with the substrate
enzyme
Biological catalyst that speeds up a specific chemical reaction in a living system but is not used up in the reaction
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
active site
a region on an enzyme that is complementary in shape to a substrate or substrates
substrate
reactant in an enzyme-catalysed reaction
anabolic
any chemical reaction that builds up complex molecules from simpler molecules
catabolic reaction
any chemical reaction that breaks down complex molecules into simpler molecules
induced fit hypothesis
Theory of enzyme catalysis which states that the partial binding of a substrate to an enzyme alters the structure of the enzyme so that its active site becomes complementary to the structure of the substrate, enabling tighter binding
competitive inhibitor
Molecule that competes with the substrate for the enzyme active site
non-competitive inhibitor
a molecule that binds to an enzyme at a location outside the active site and inhibits the enzyme's function
slows down
effect of presence of competitive and/or non-competitive inhibitors on enzyme catalysed reaction rate
speeds up
effect of presence of co-factors on enzyme catalysed reaction rate