A&P II Lab practical 1
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/148
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:45 PM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
1
New cards
\#1 posterior pituitary
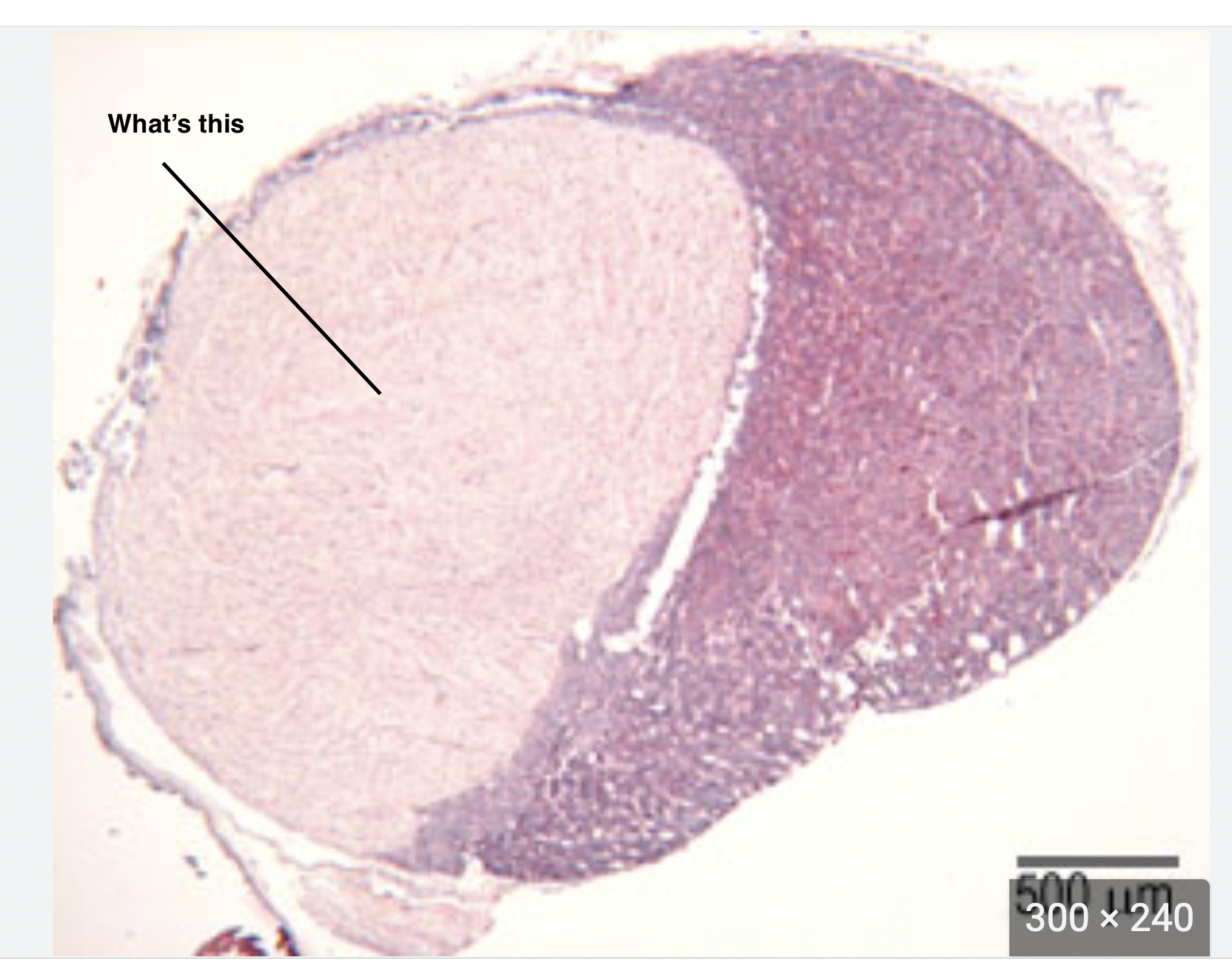
2
New cards
\#2 anterior pituitary
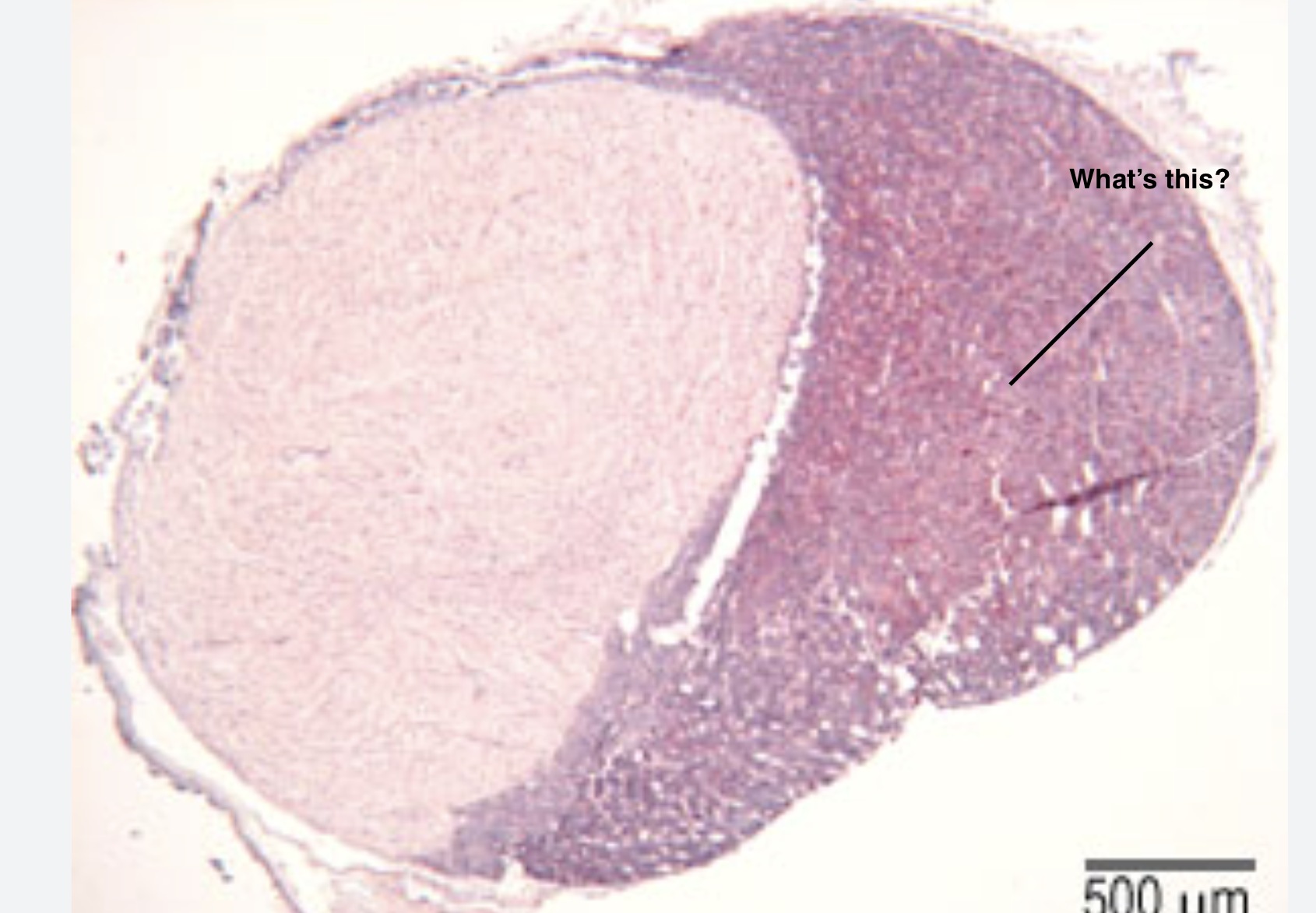
3
New cards
What does the GH target
- Liver
- Skeletal muscle
- bones
- Skeletal muscle
- bones
4
New cards
What is the action of the GH
promotes growth of body tissues, cell growth and division
5
New cards
What does the PRL hormone target
Mammary glands
6
New cards
What is the PRL hormone actions
To PROMOTE/STIMULATE milk production from mammary glands
7
New cards
What does the TSH target?
Thyroid gland
8
New cards
What is the TSH action?
to stimulate thyroid hormone release from thyroid that those help to increase metabolism and promote nervous and skeletal system growth
9
New cards
What does the ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic) target
Adrenal cortex
10
New cards
What is the ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic) action?
to stimulate hormone release by adrenal cortex meaning induces to produce glucocorticoids
11
New cards
What does FSH target?
ovaries/testes
12
New cards
What is the FSH action?
STIMULATE gamete production in gonads (eggs, and sperm)
13
New cards
What does the LH target?
ovaries/ testes
14
New cards
What is the LH action?
STIMULATE androgen production by gonads
male- testosterone by testes
Female- stimulates ovulation
male- testosterone by testes
Female- stimulates ovulation
15
New cards
What does the ADH target?
kidney tubules
16
New cards
What is the ADH action
stimulate reabsorption by kidneys
17
New cards
What does oxytocin target?
uterine smooth muscle & mammary glands
18
New cards
What is the oxytocin action
stimulate uterine contraction during birth & inject milk into mammary glands
19
New cards
What does Thyroxine and Triiodothyronin target?
most tissues
20
New cards
What is the action of thyroxine?
metabolic rate
21
New cards
What is the action of triiodothyronin?
Growth and development
22
New cards
What is does calcitonin target?
bone
23
New cards
what is the action of calcitonin?
to reduce blood calcium levels
24
New cards
What does parathyroid hormone target?
bone, kidneys, and intestines
25
New cards
What is the action of PTH?
increase blood calcium levels
26
New cards
Cell population that create the hormones of thyroid gland (what is thyroid gland made out of)?
Follicular cells/parafollicular cells(C cells)
27
New cards
Follicular cells
* Thyroglobulin
* Triiodothyronine
* Tetraiodothyronine/Thyroxine
* Triiodothyronine
* Tetraiodothyronine/Thyroxine
28
New cards
Parafollicular cells (C cells)
Calcitionin
29
New cards
Adrenal cortex zones
1) Zona Glomerulosa
2) Zona Fasciculata
3) Zons Reticularis
2) Zona Fasciculata
3) Zons Reticularis
30
New cards
Hormone released by zona glomerulosa
mineralocorticoids(regulate mineral balance) example→aldosterone
31
New cards
Hormone released by zona Fasiculata
Glucocoticoids( regulate glucose metabolism) example→ crotisol, corticosterone, cortisone(stress hormones to increase glucose levels)
32
New cards
Hormone released by Zona Reticularis
Androgens (stimulates masculination) examples → dehydroepian-drosterone
33
New cards
Hormones released by adrenal medulla
Stress hormones example → epinephrine, norepinephrine
34
New cards
What do adrenal glands target?
regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions.
35
New cards
Pancreas cell population that create the hormones?
Islets of langerhans/ pancreatic islets
36
New cards
What are the pancreatic islet cells?
* Alpha (a) cells
* Beta (B) cells
* Delta cells
* PP cells/ F cells
\
* Beta (B) cells
* Delta cells
* PP cells/ F cells
\
37
New cards
What does alpha cells secrete?
Glucagon
38
New cards
What does Beta cells secrete?
Insulin
39
New cards
What does Delta cells secrete?
Somatosin (GHIH) inhibits the release of both glucagon & insulin
40
New cards
What does PP cells secrete?
Pancreatic polypeptide (regulates pancreatic secretion activities, and also impacts liver glycogen storage and gastrointestinal secretion)
41
New cards
Thymus gland cell population that create the hormones?
Thymopoetin
42
New cards
What hormone does thymus secrete
Thymopoetin
43
New cards
What is the action of thymus
Aids in the dev, of T lymphocytes of the immune system
44
New cards
What does the thymus targte?
T cells(T-lymphocyte)
45
New cards
Pineal gland secretes what hormone
melatonin
46
New cards
Pineal gland targets what?
various tissues
47
New cards
What is the action of the pineal gland?
To regulate biological clock
48
New cards
Parathyroid glands, cell pop that creates the hormones
chief cells(produce PTH) and oxyphil cells
49
New cards
What do testes target
reproductive male organs
50
New cards
Testes, cell pop that creates the hormones
leydig cells
51
New cards
What hormones do testes secrete
testosterone and inhibin
52
New cards
What action of testes
Stimulates dev of secondary sex characteristics and sperm production (testosterone)
Inhibits FSH release from pituitary (inhibin)
Inhibits FSH release from pituitary (inhibin)
53
New cards
Ovaries, cell pop that creates the hormones
Granulosa cells
54
New cards
What hormones do ovaries produce?
Estrogen and progesterone
55
New cards
What is the action of ovaries?
Stimulates dev of sex characteristics and prepares body for child birth (estrogen)
Contributes to reg of the menstrual cycle and crucial for pregnancy (progesterone)
Contributes to reg of the menstrual cycle and crucial for pregnancy (progesterone)
56
New cards
Thyroid gland
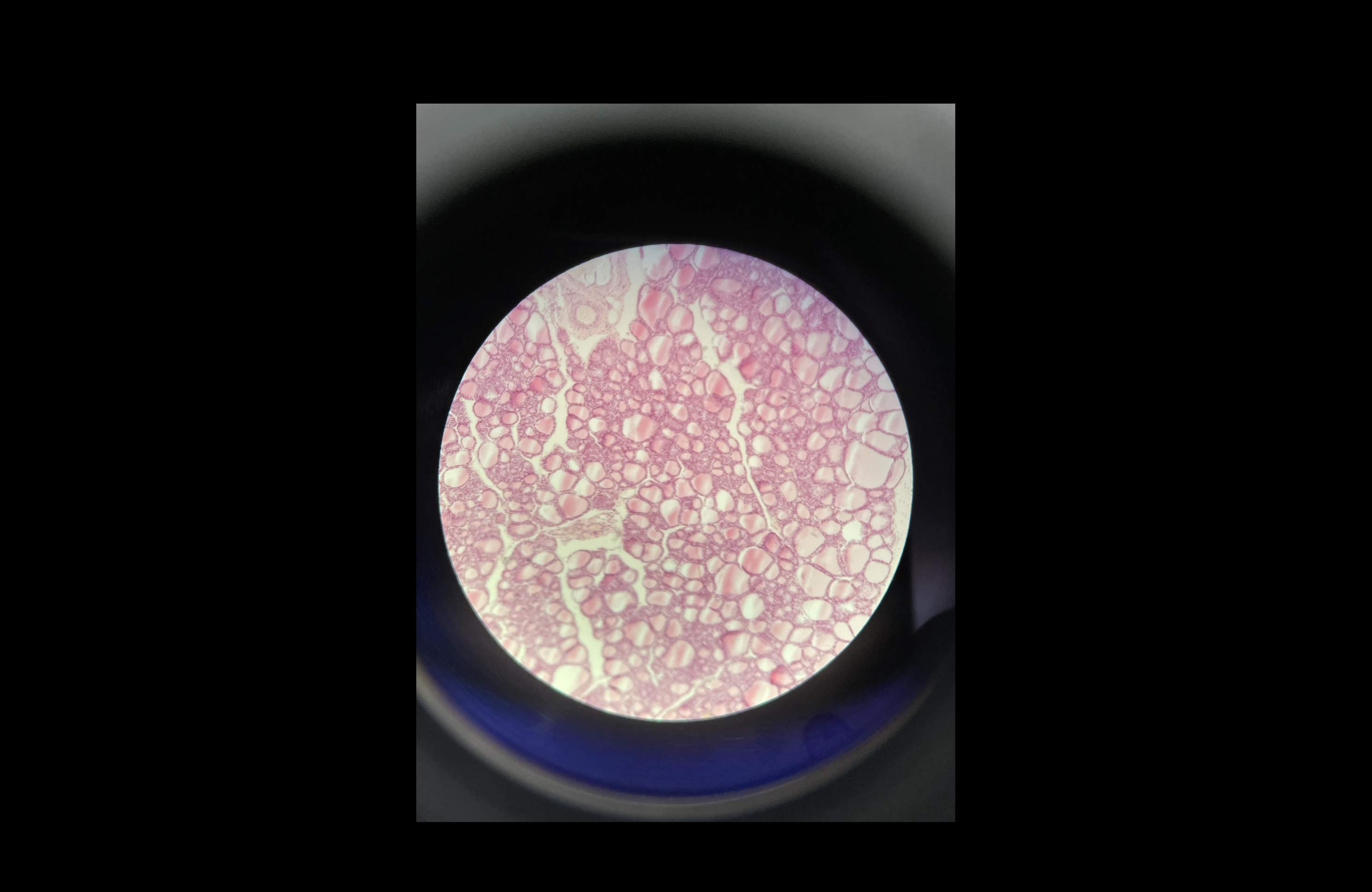
57
New cards
Adrenal gland
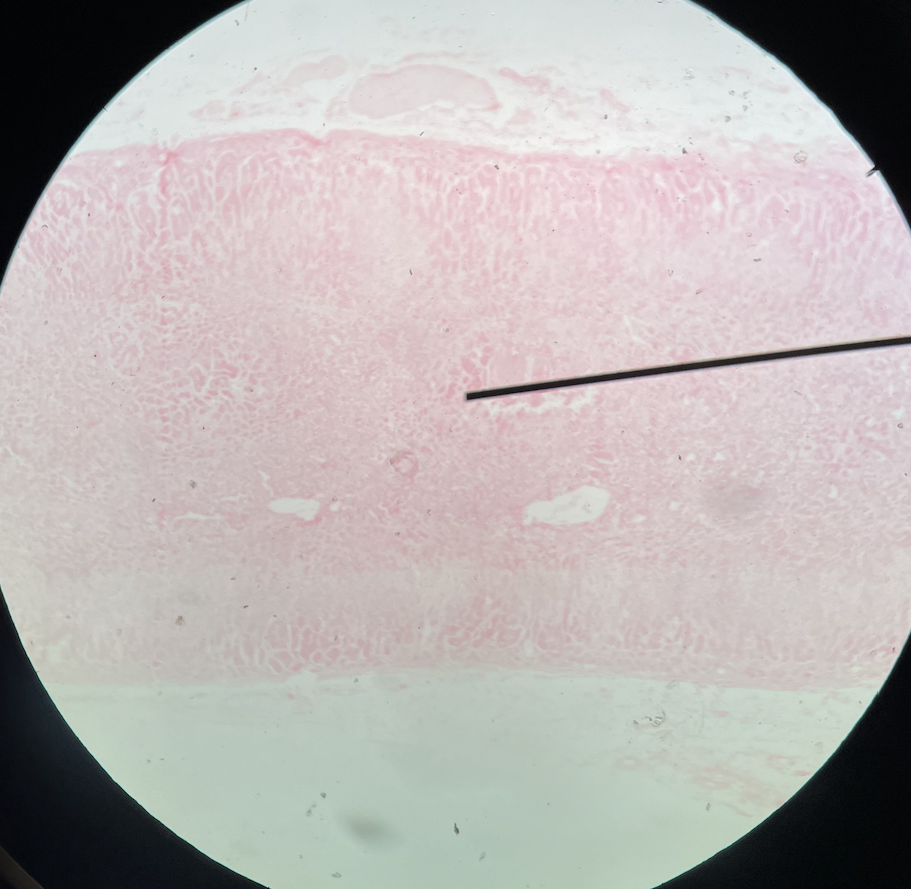
58
New cards
Pancreas
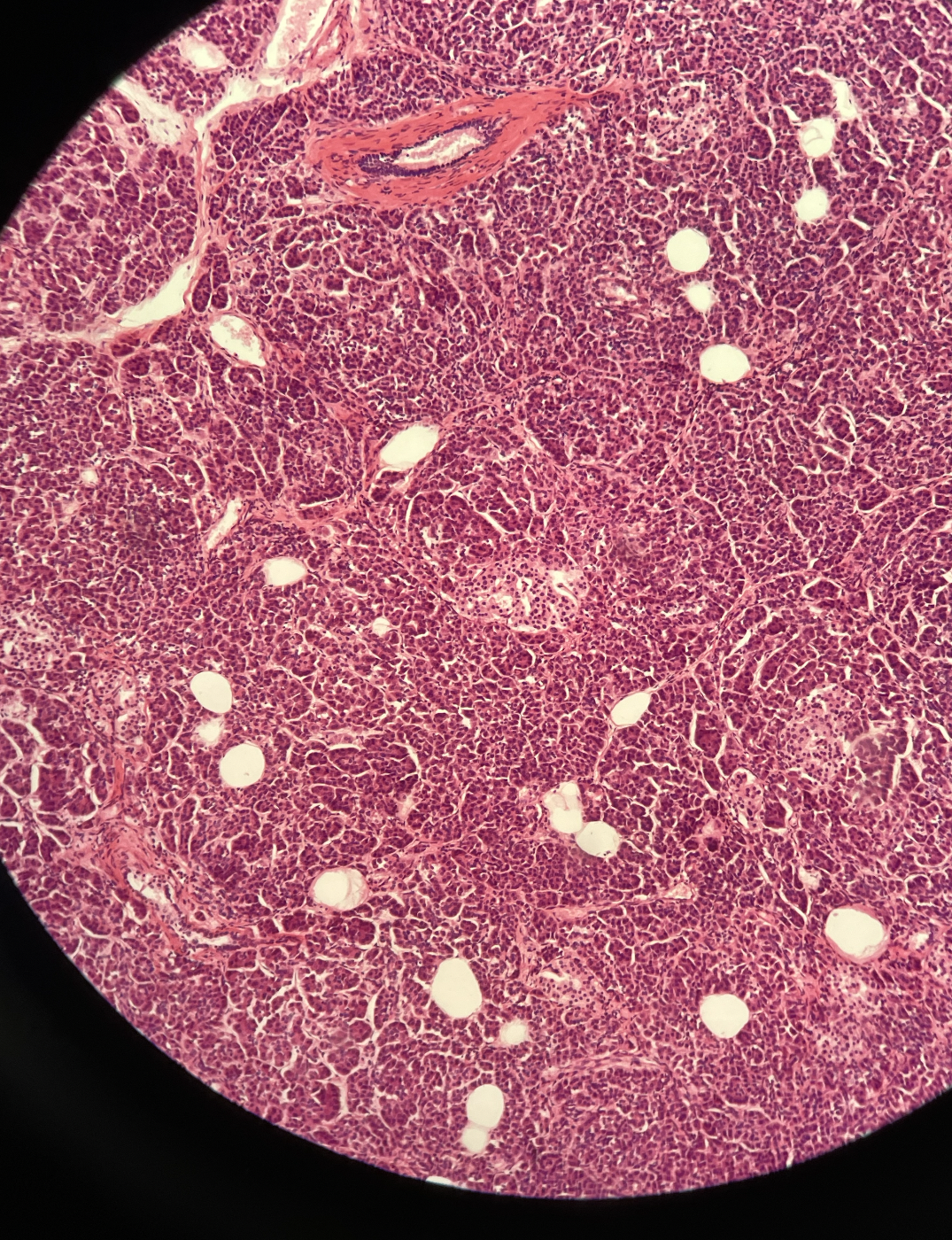
59
New cards
testes
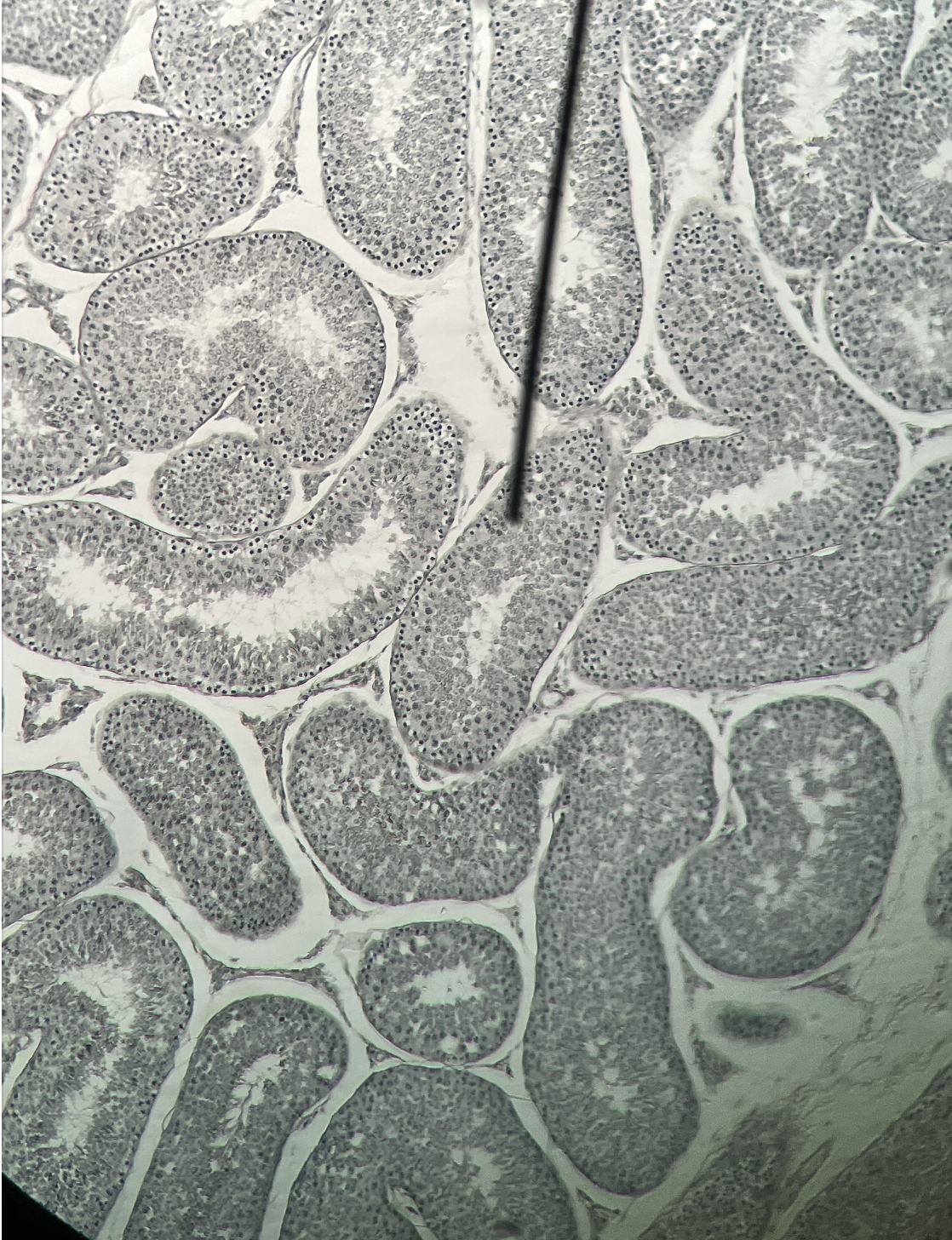
60
New cards
ovaries
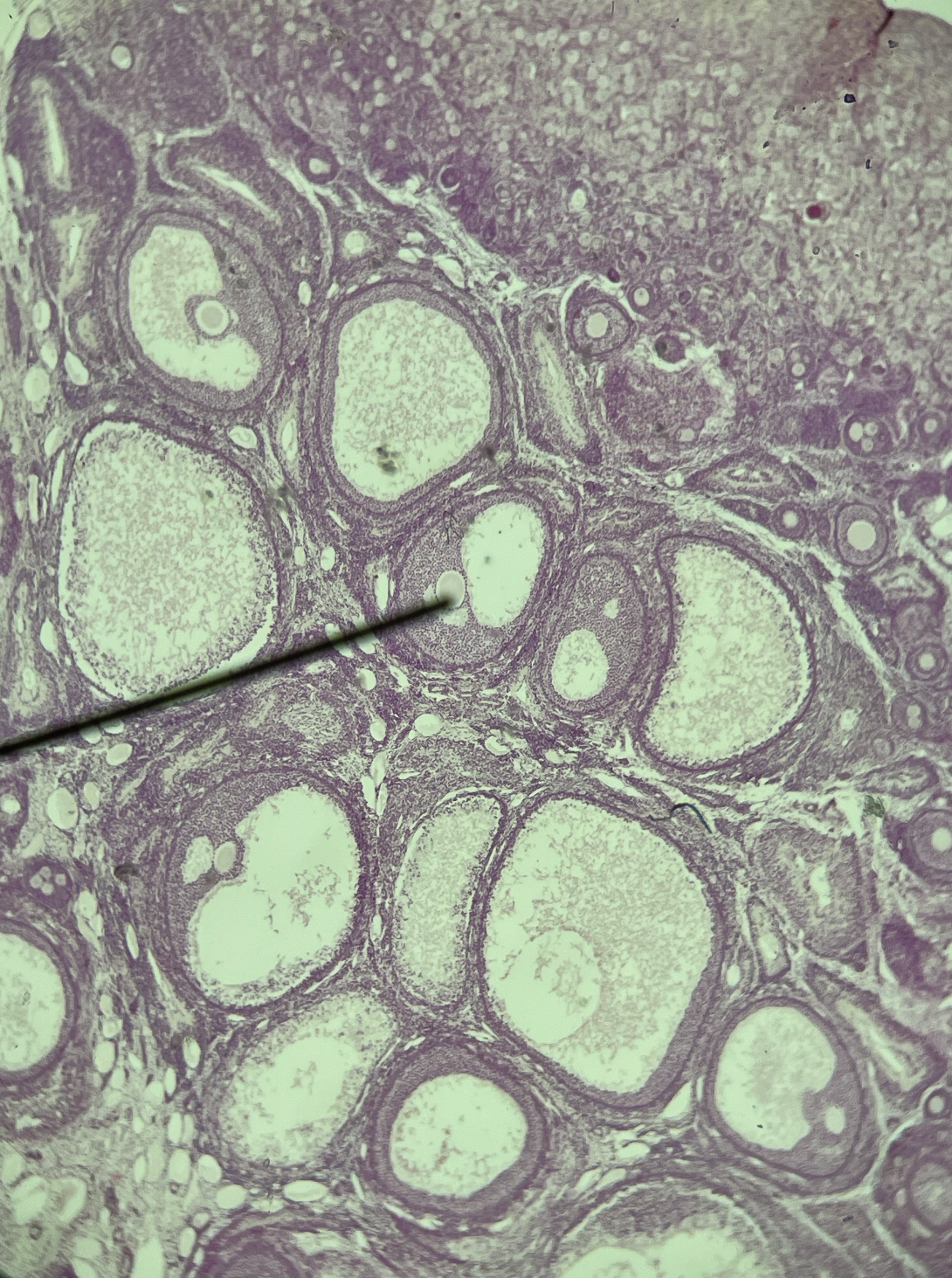
61
New cards
Thymus gland
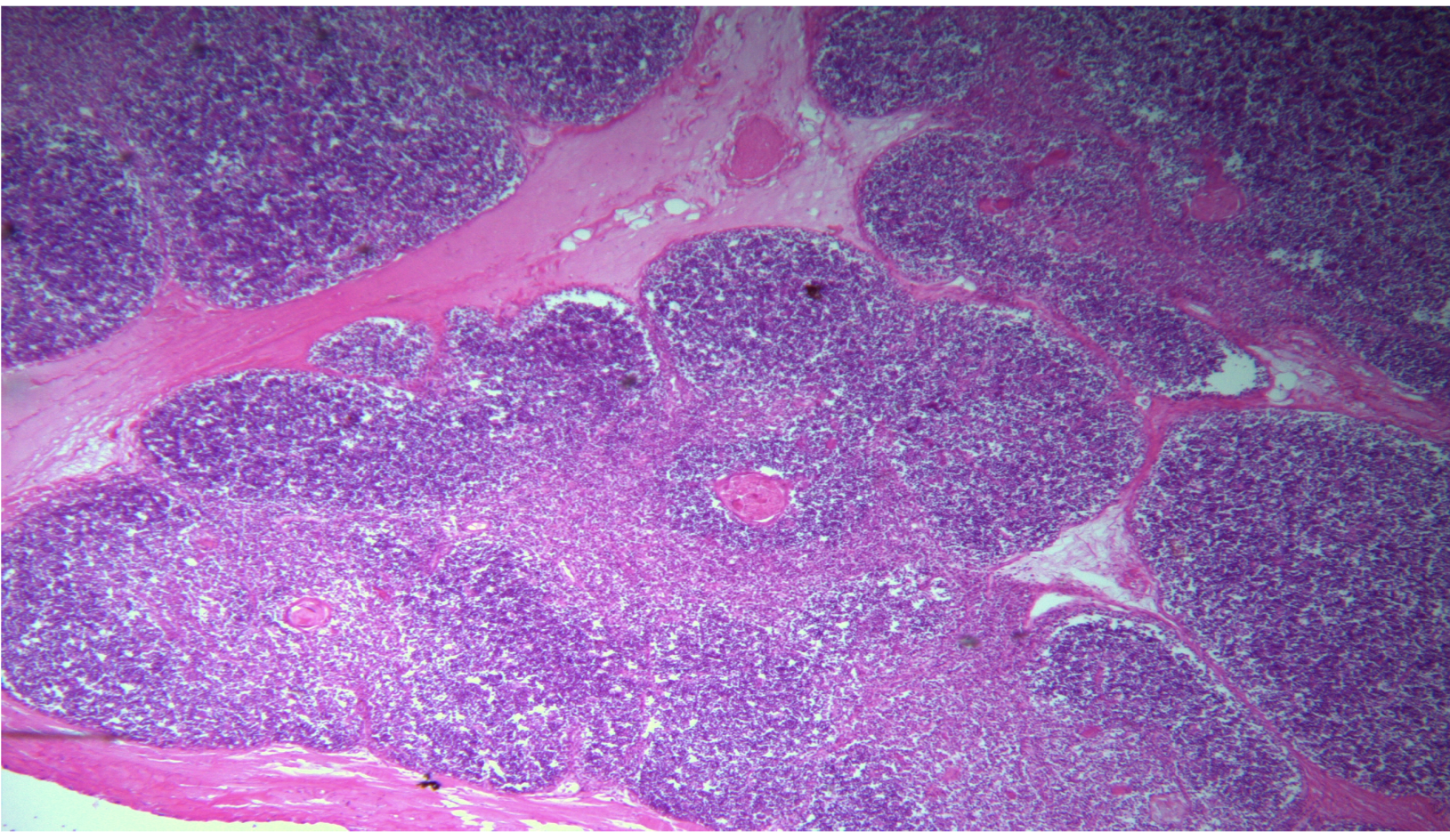
62
New cards
right auricle (flap)
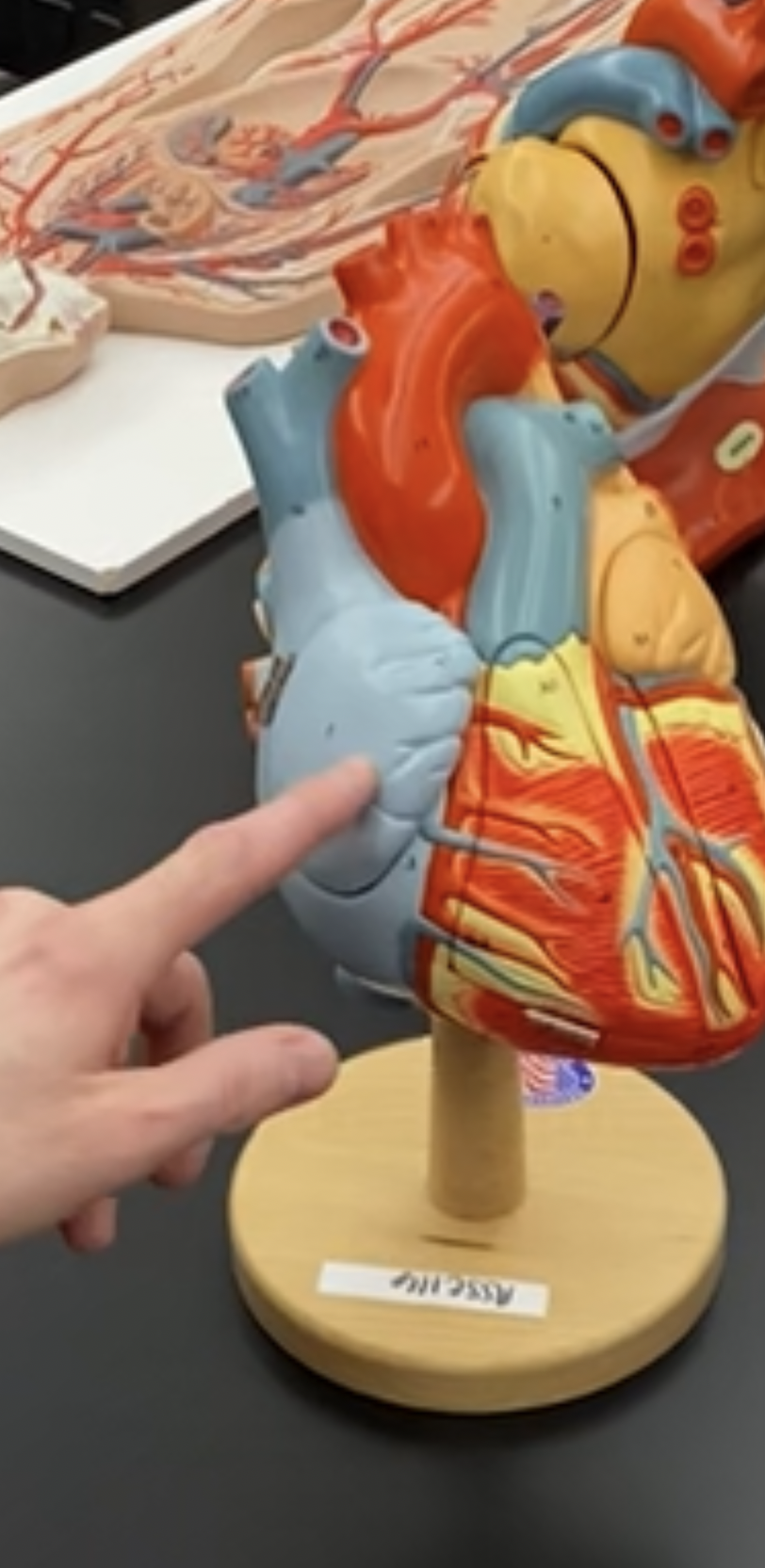
63
New cards
atrium (chamber)

64
New cards
superior vena cava
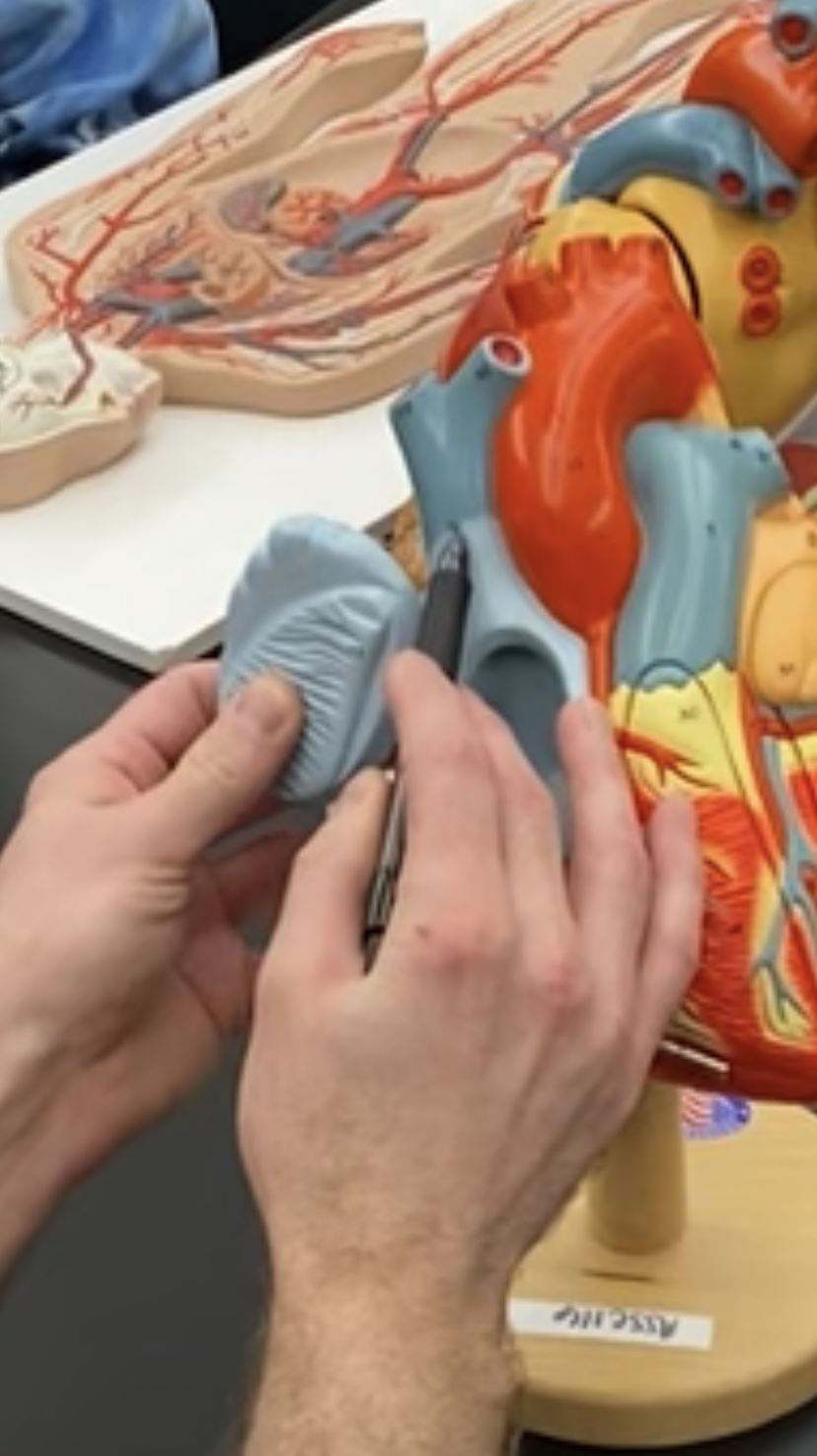
65
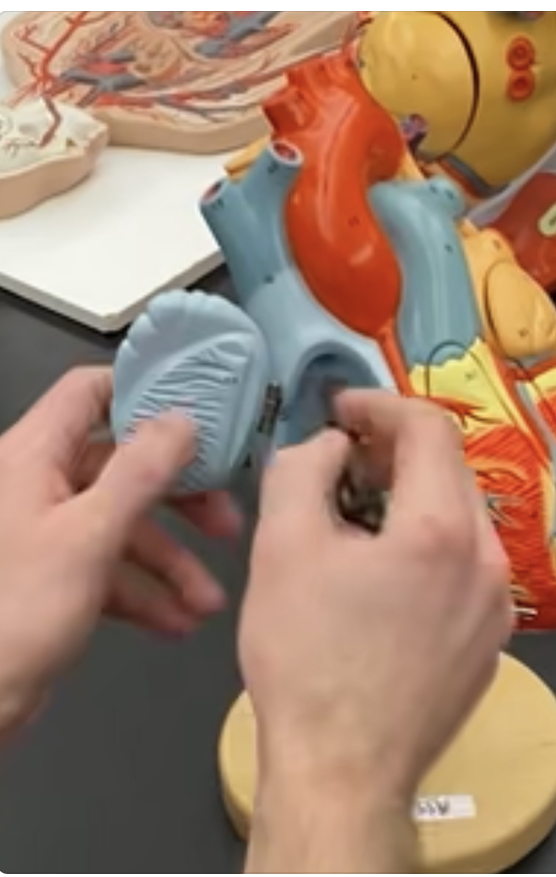
New cards
inferior vena cava

66
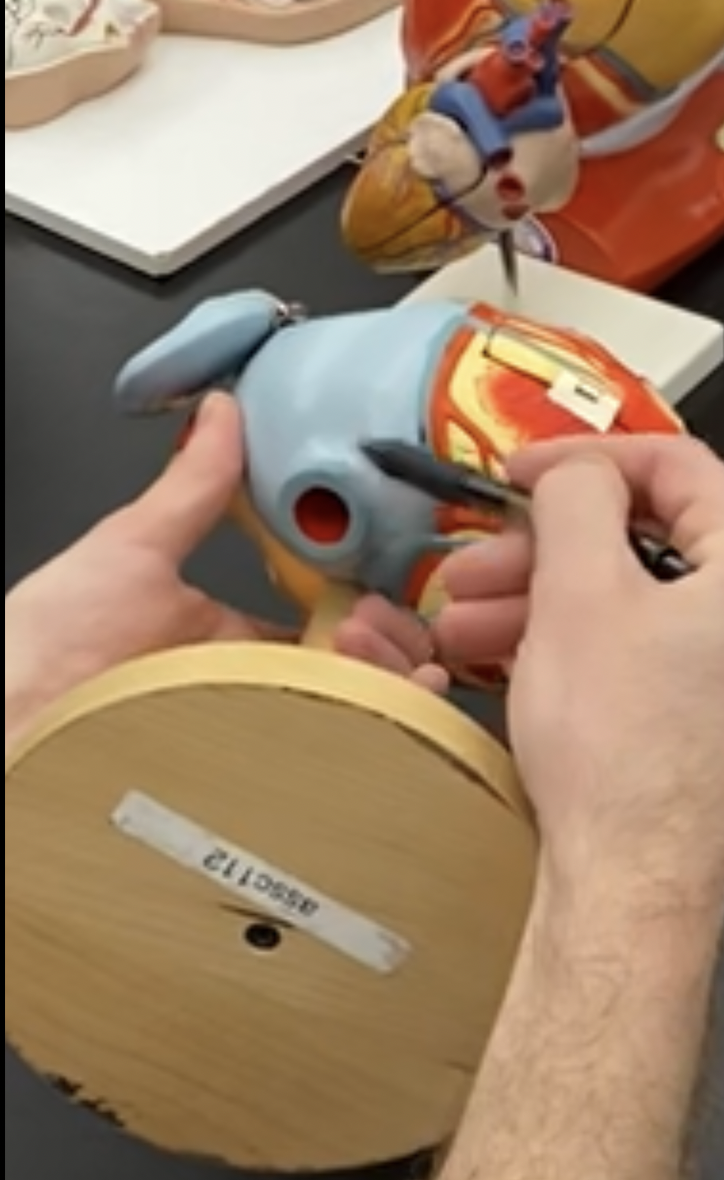
New cards
fosa ovalis
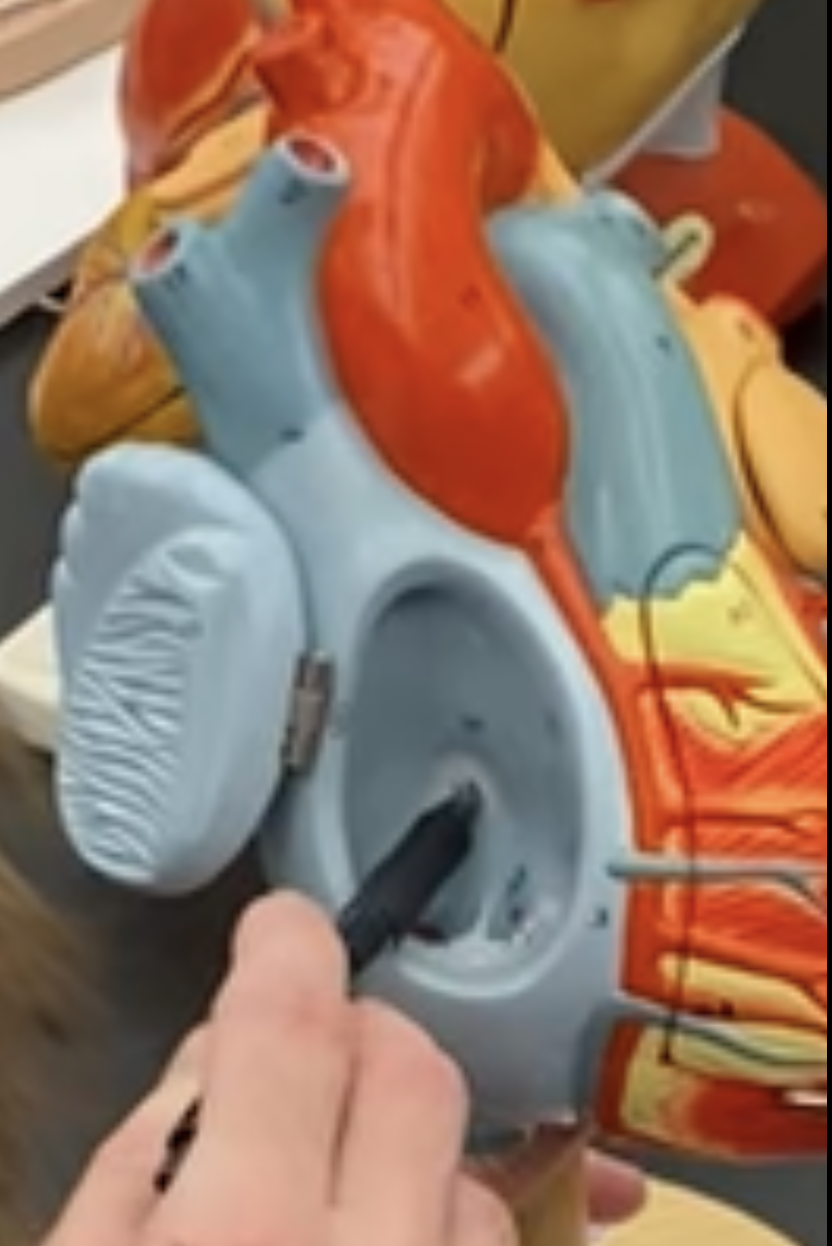

67
New cards
right ventricle
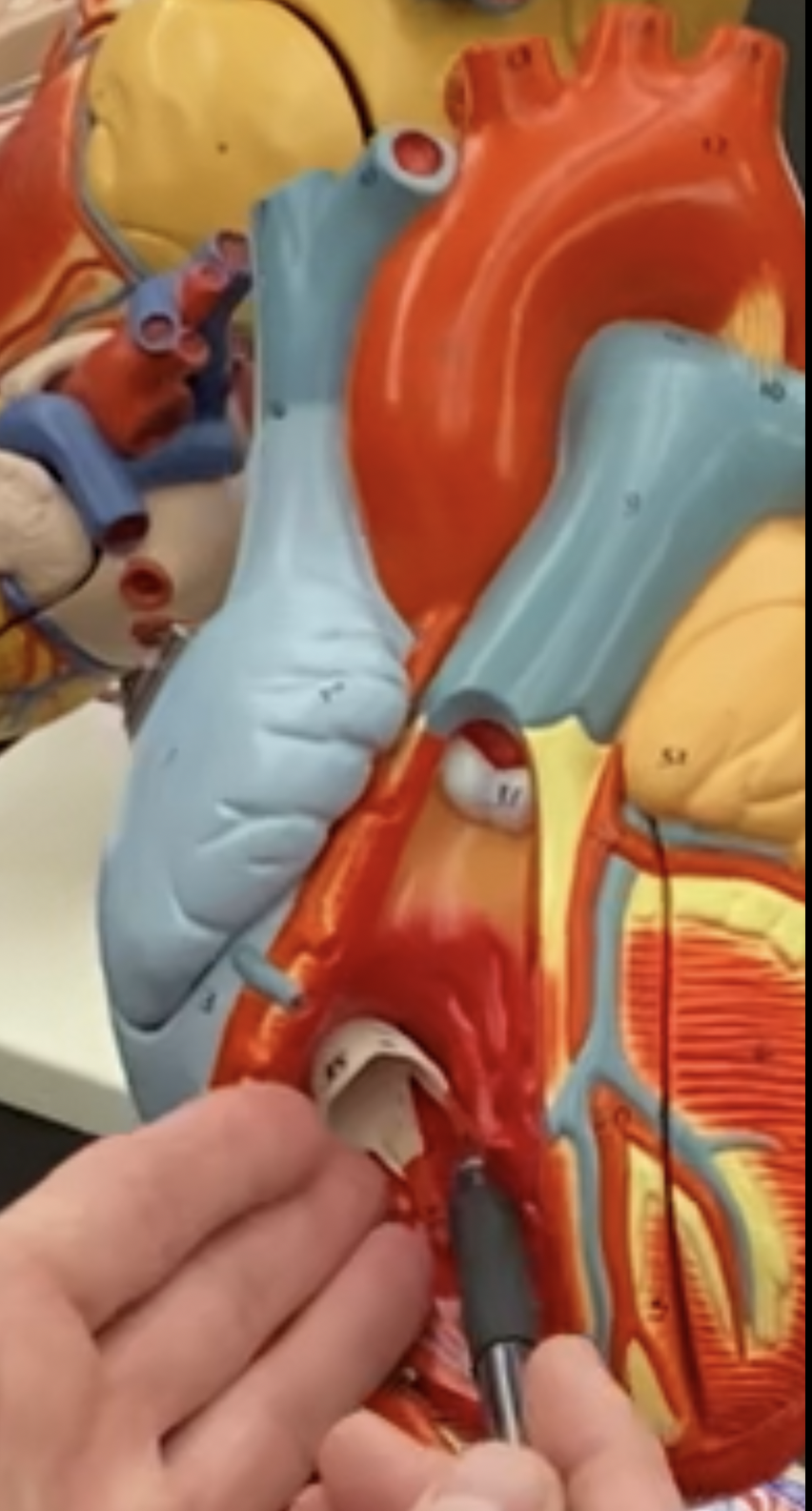
68
New cards
Right AV valve tricuspid
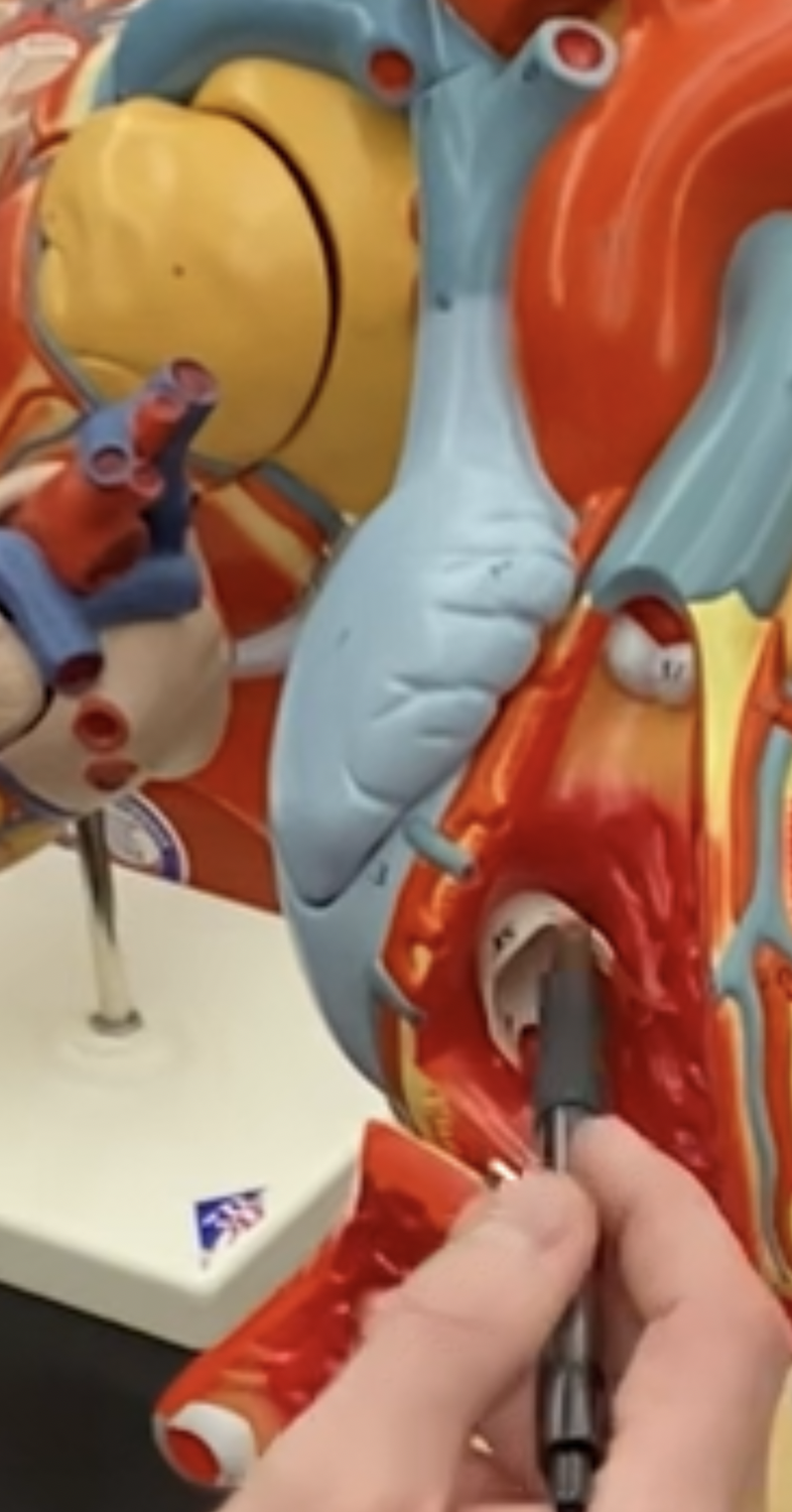
69
New cards
chorde tendene
70
New cards
papillary muscles
71
New cards
ridges, folds trabecule chorde
72
New cards
pulmonary trunk
73
New cards
pumlomary valve, pulmonary semilunar
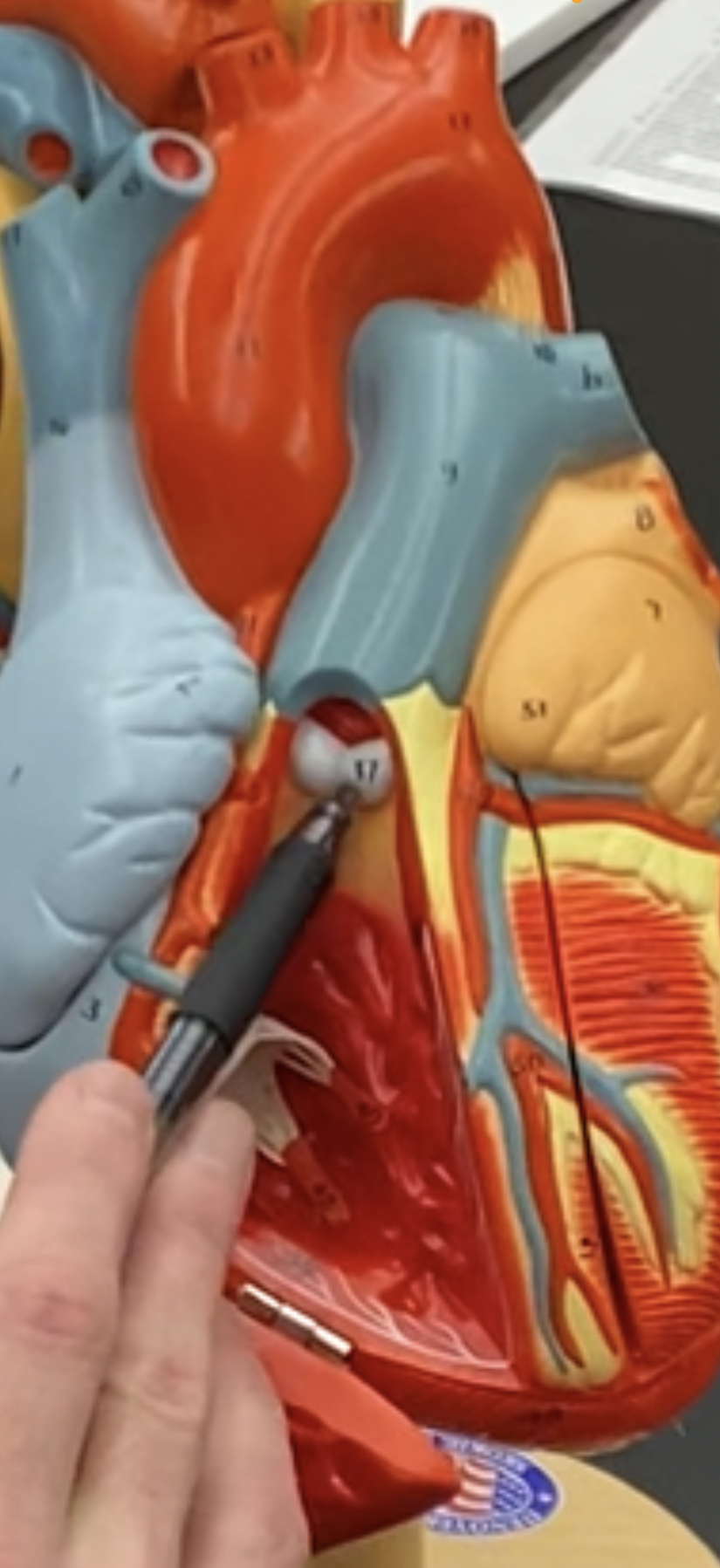
74
New cards
Right pulmonary artery(blue)
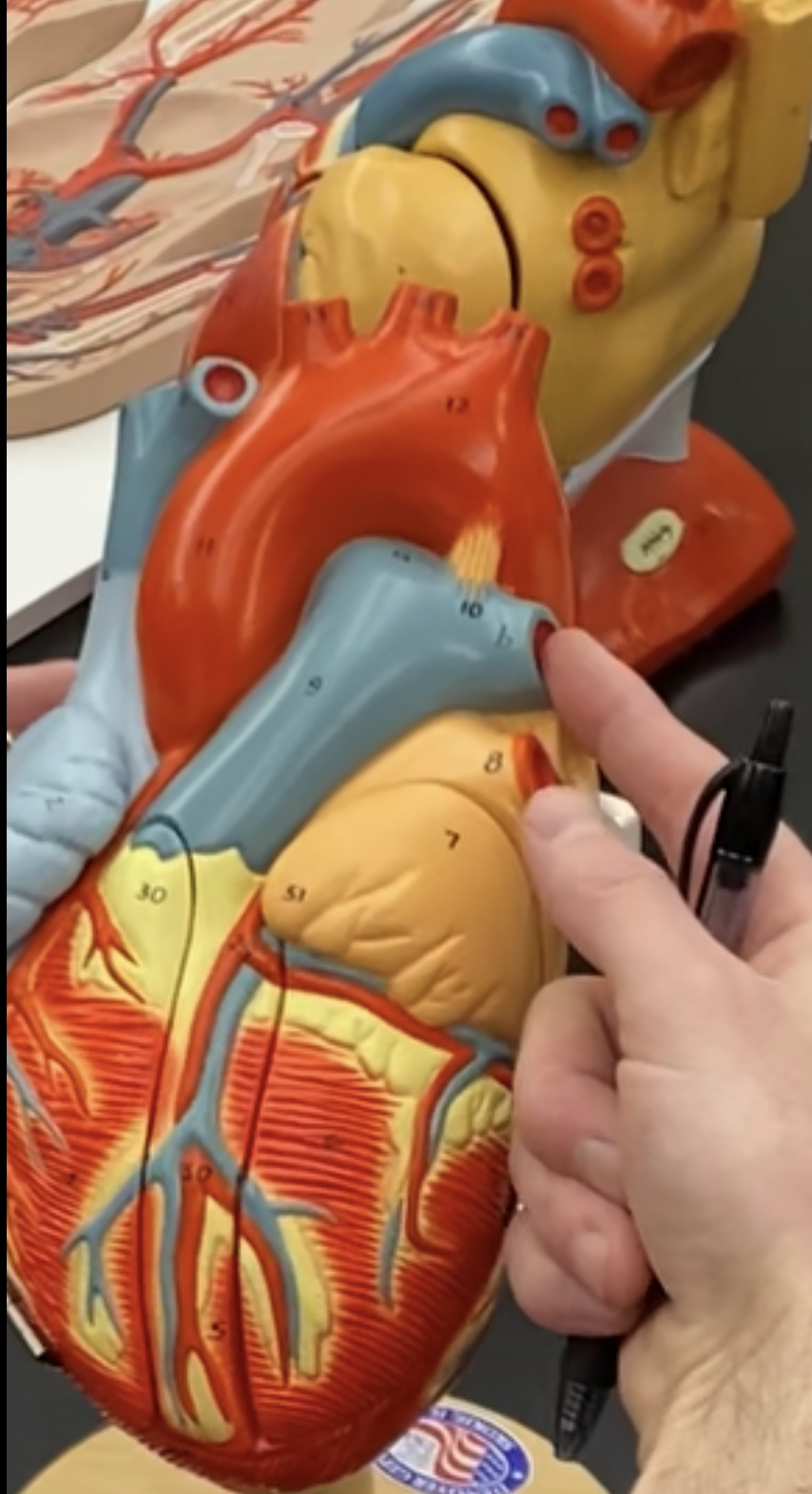
75
New cards
left atrium
76
New cards
pulmonary veins (red)
77
New cards
left auricle
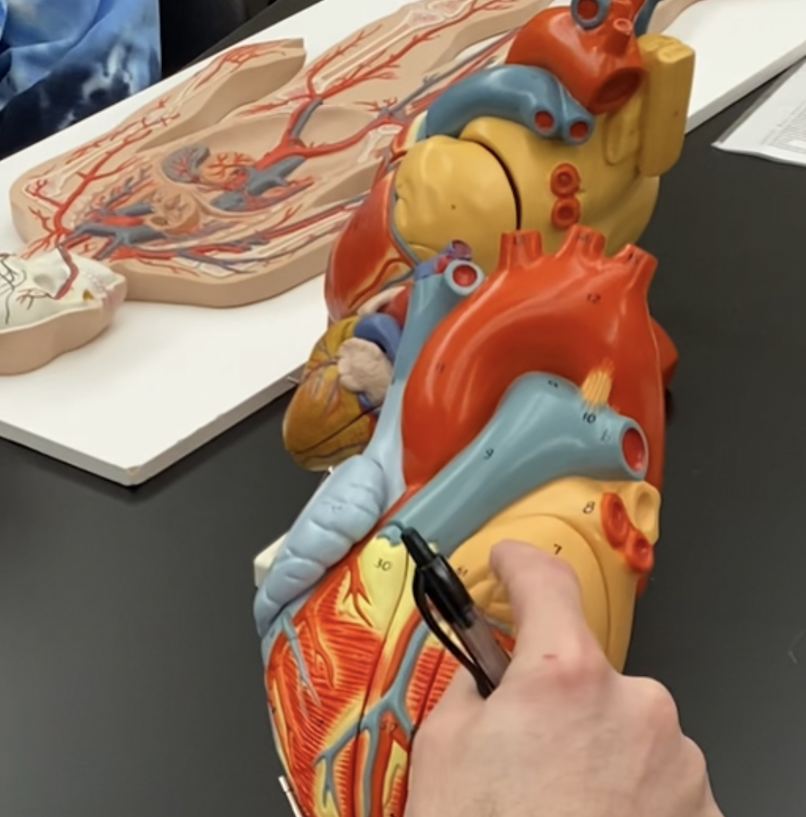
78
New cards
left atrium
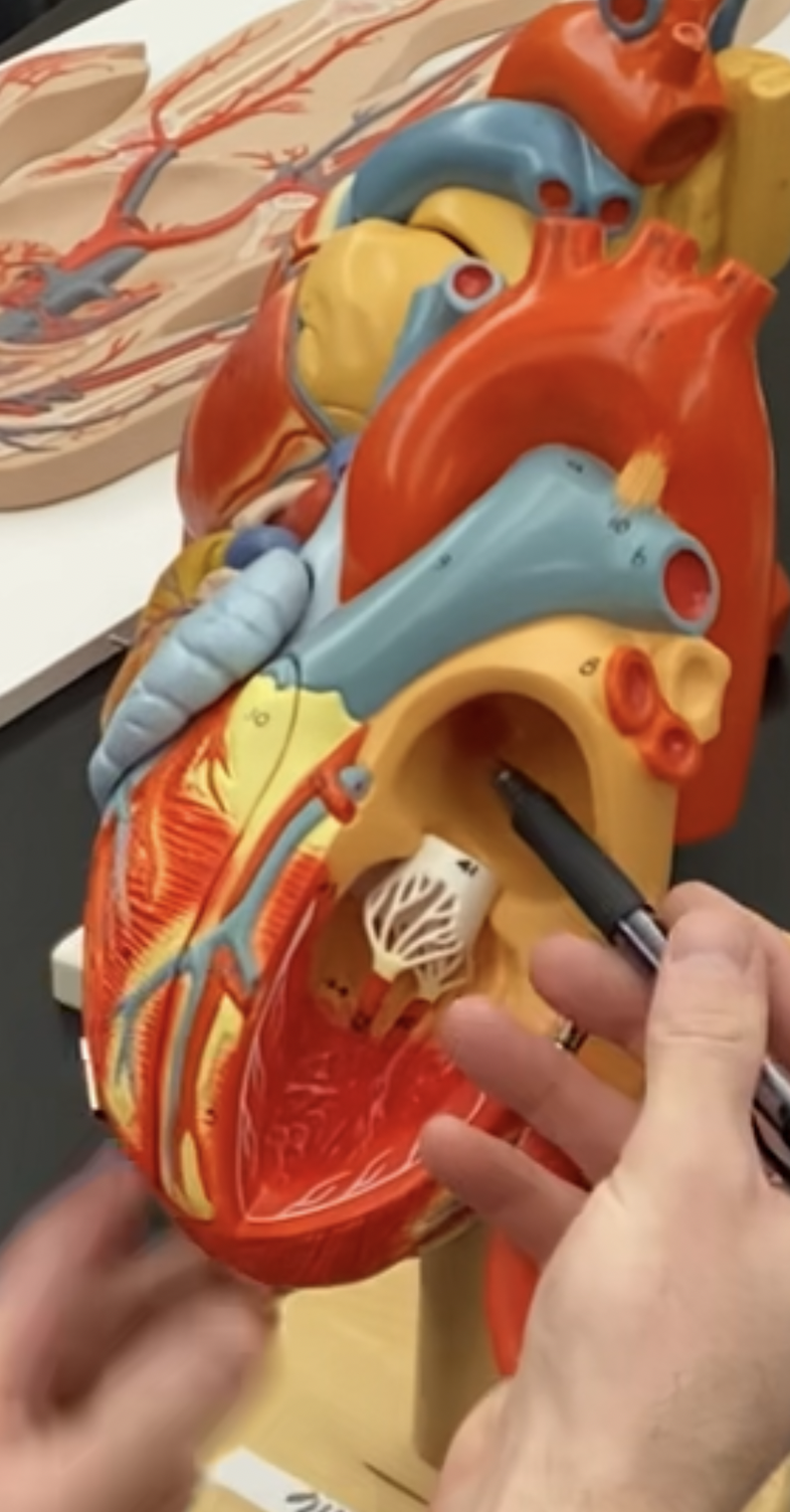
79
New cards
Left AV valve, Bicuspid/mitrial valve
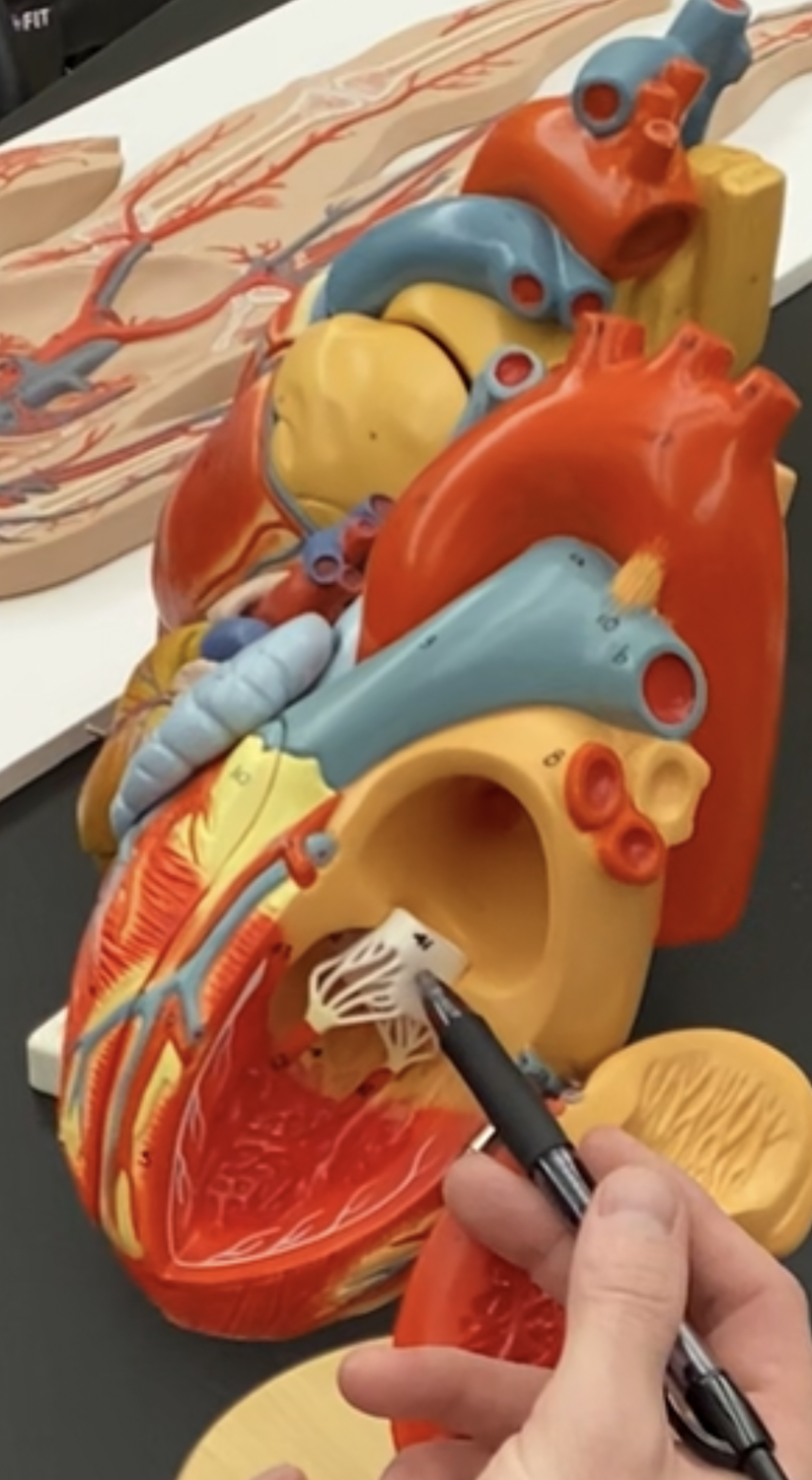
80
New cards
left chordea tendene
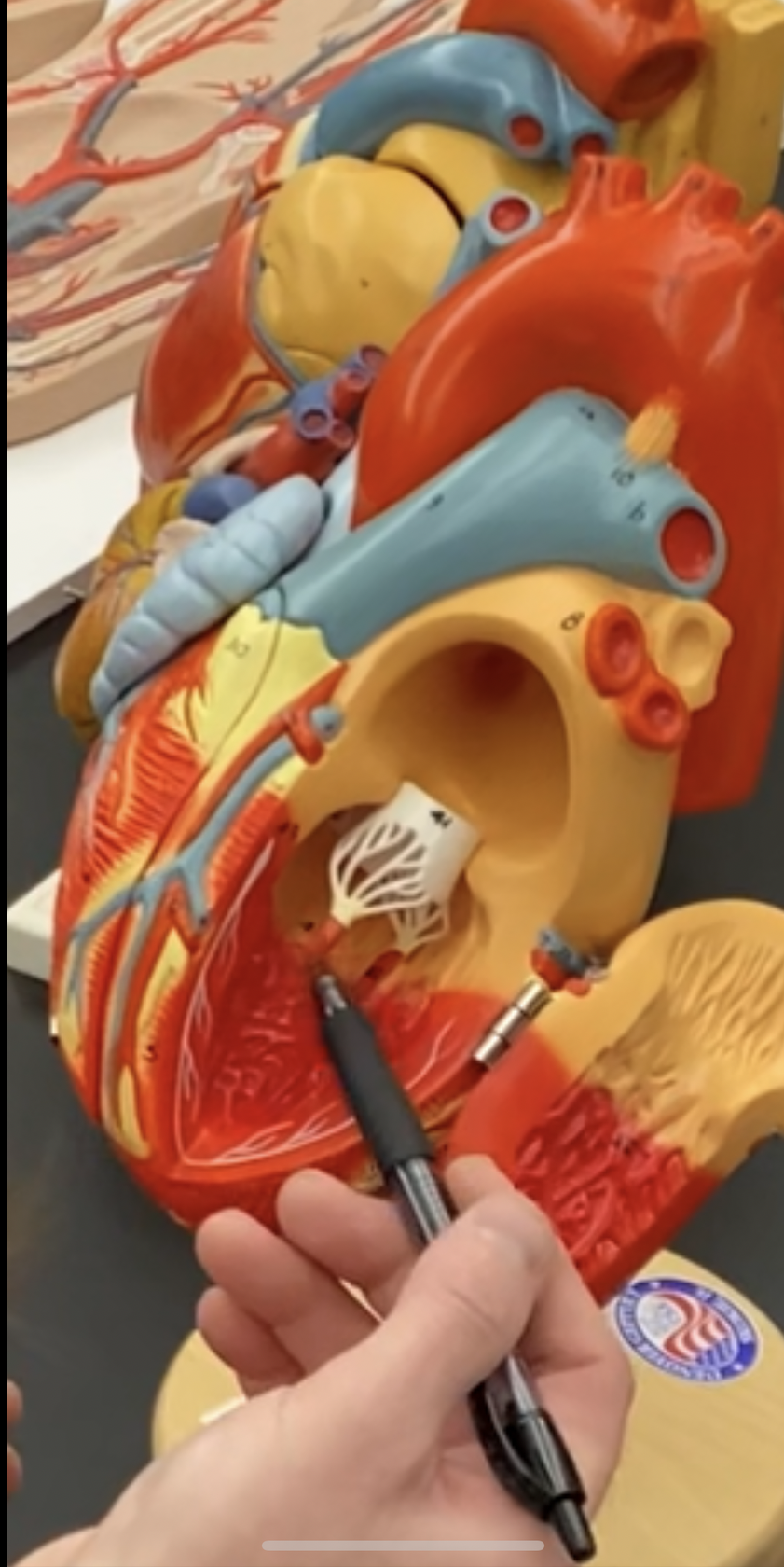
81
New cards
aortic arch
82
New cards
Aortic valve/ semilunar
83
New cards
Left common coratid
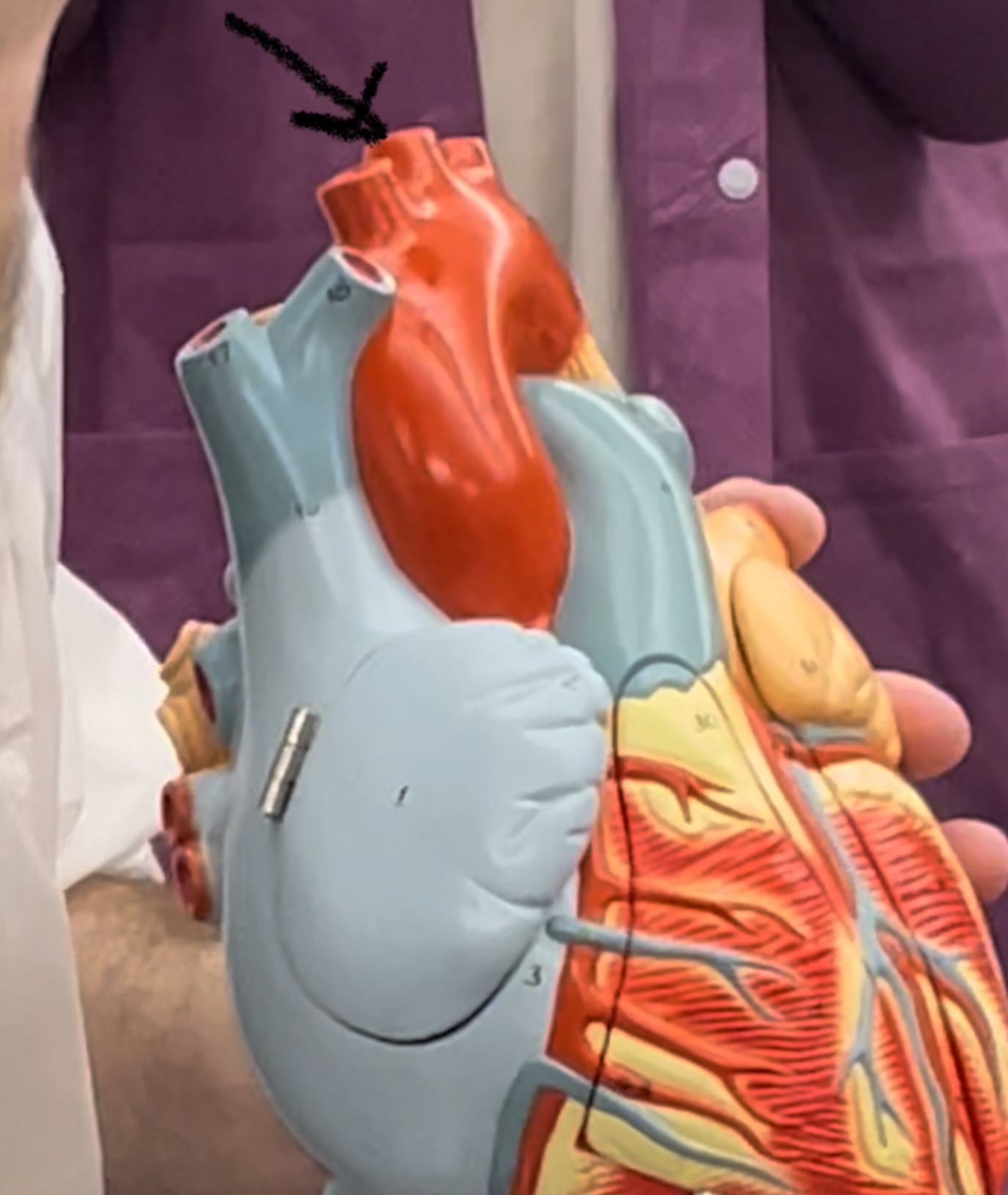
84
New cards
Left suplavian
85
New cards
Brachiosephalic trunk/ artery
86
New cards
7 major organs that will be covered in A&P II
1) Endocrine
2) Circulatory
3) Immune
4) Respiratory
5) Digestive
6) Urinary
7) Reproductive
2) Circulatory
3) Immune
4) Respiratory
5) Digestive
6) Urinary
7) Reproductive
87
New cards
What is pulmonary circulation?
a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again.
88
New cards
What is systemic circulation?
carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again.
89
New cards
What and where is the perdicardium
Located within the thoracic cavity, above myocardium and it’s a thin sac that protects heart from friction
90
New cards
Myocardium
responsible for heart’s pumping action
91
New cards
Left side of the heart
has to pump harder
92
New cards
Right atrium receives?
Oxygen-depleted(deoxygenated) blood from body
93
New cards
Left atrium receives?
Oxygenated blood from lungs
94
New cards
Tricuspid and Bicuspid do what?
help facilitate blood flow
95
New cards
What do semilunar valves do?
Help prevent the backflow of blood into the segment it just exited
96
New cards
Blood flow order
\- Superior and inferior vena cava
\- To the right atria
\- Through the AV valve tricuspid
\- To the right ventricle
\- Through the pulmonary valve
\- To the to the pulmonary arteries to the lungs
\- Through the pulmonary veins
\- To left atrium
\- Through the Bicuspid
\- To aortic valve
\- Through aorta and coronary arteries
\
\- To the right atria
\- Through the AV valve tricuspid
\- To the right ventricle
\- Through the pulmonary valve
\- To the to the pulmonary arteries to the lungs
\- Through the pulmonary veins
\- To left atrium
\- Through the Bicuspid
\- To aortic valve
\- Through aorta and coronary arteries
\
97
New cards
Coronary veins
Drain deoxygenated blood from cardicac muscle
98
New cards
Left/Right Coronary arteries
Supply cardiac muscle with oxygenated blood
99
New cards
Heart conduction
* Begins in bundle of nerve tissue Sinoatrial node(Makes atria contract & blood empties into ventricles
* Impulse then travels to the atrioventricular node
* To the bundle of HIS
* Thr bundle branches
* The purkinje fibers
* Impulse then travels to the atrioventricular node
* To the bundle of HIS
* Thr bundle branches
* The purkinje fibers
100
New cards
EKG- Electrocardiogram
Measures the waves of electrical activity of the heart as it beats
Explore top notes
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1344d ago0.0(0)
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1344d ago0.0(0)