IBDP Biology 2025 Topic 1 Nature of Biology and Stats
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Binomial nomenclature
the system of nomenclature in which two terms are used to denote a species of living organism, the first one indicating the genus and the second the specific epithet.
Box-and-whisker
• A diagram that summarizes data using the median, the upper and lower quartiles, and the values. Used when the
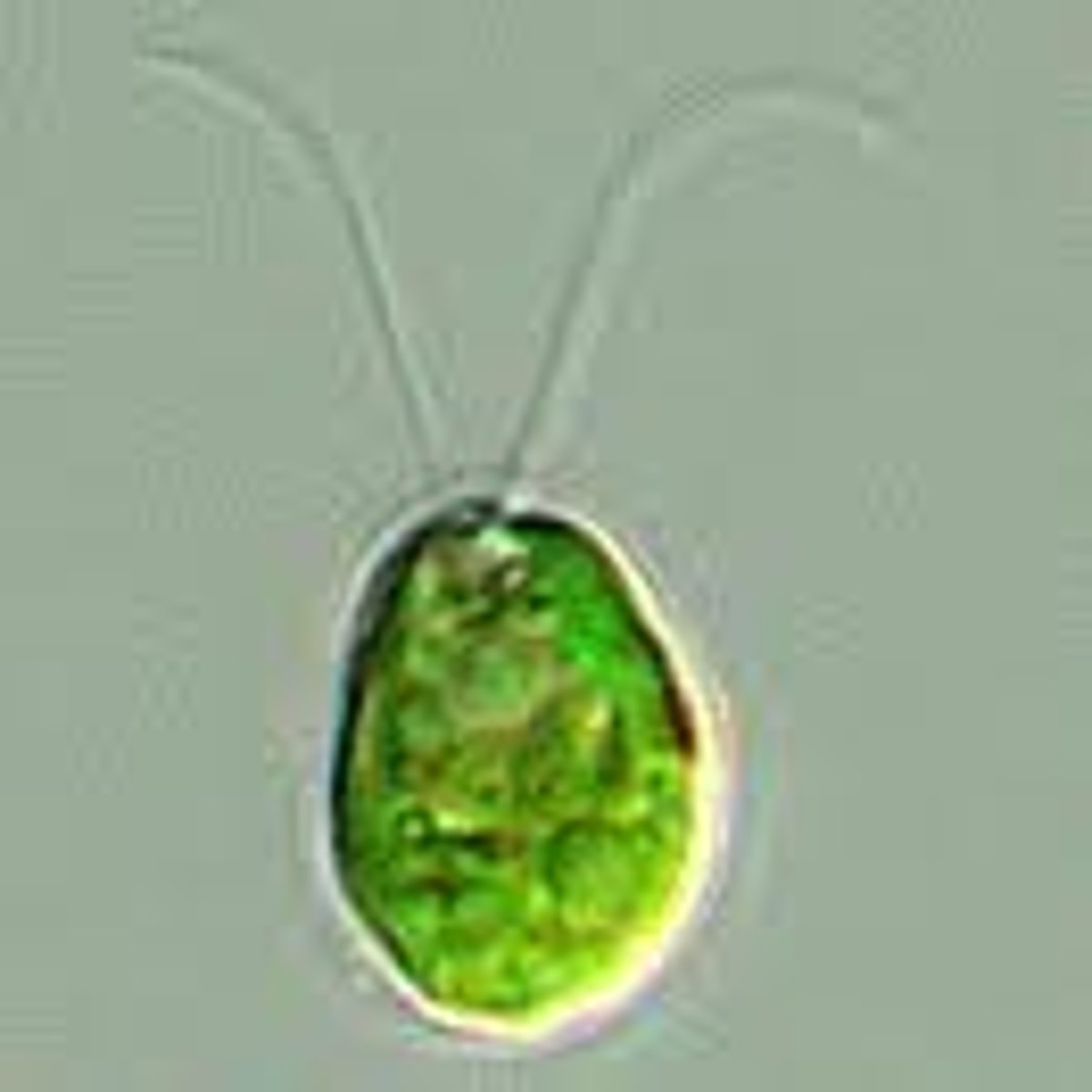
Chlamydomonas
unicellular green algae
Class
in classification, a group of closely related orders
Continuous variation
variation in a population showing an unbroken range of phenotypes rather than discrete categories
Descriptive statistic
a statistic that quantifies or characterizes a dataset without drawing inferences about some larger population
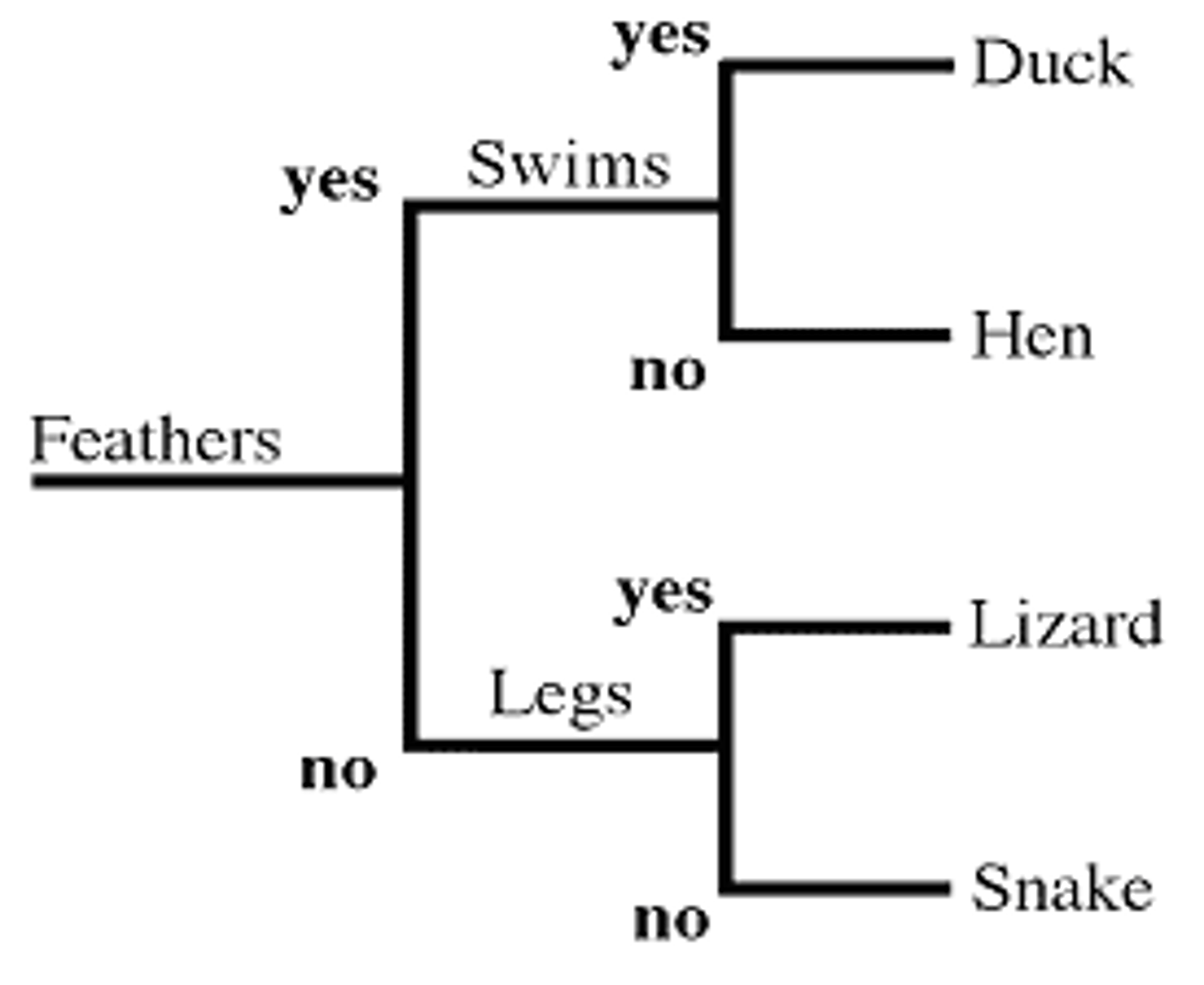
Dichotomous key
step by step approach to identify an organism using a series of paired descriptions
Discrete variation
variation in a heritable characteristic that has an either/or form, such as either being albino or not being albino
Domain
A taxonomic category above the kingdom level. The three domains are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.
Emergence
when 2 or more items are combined together a different property comes into existence
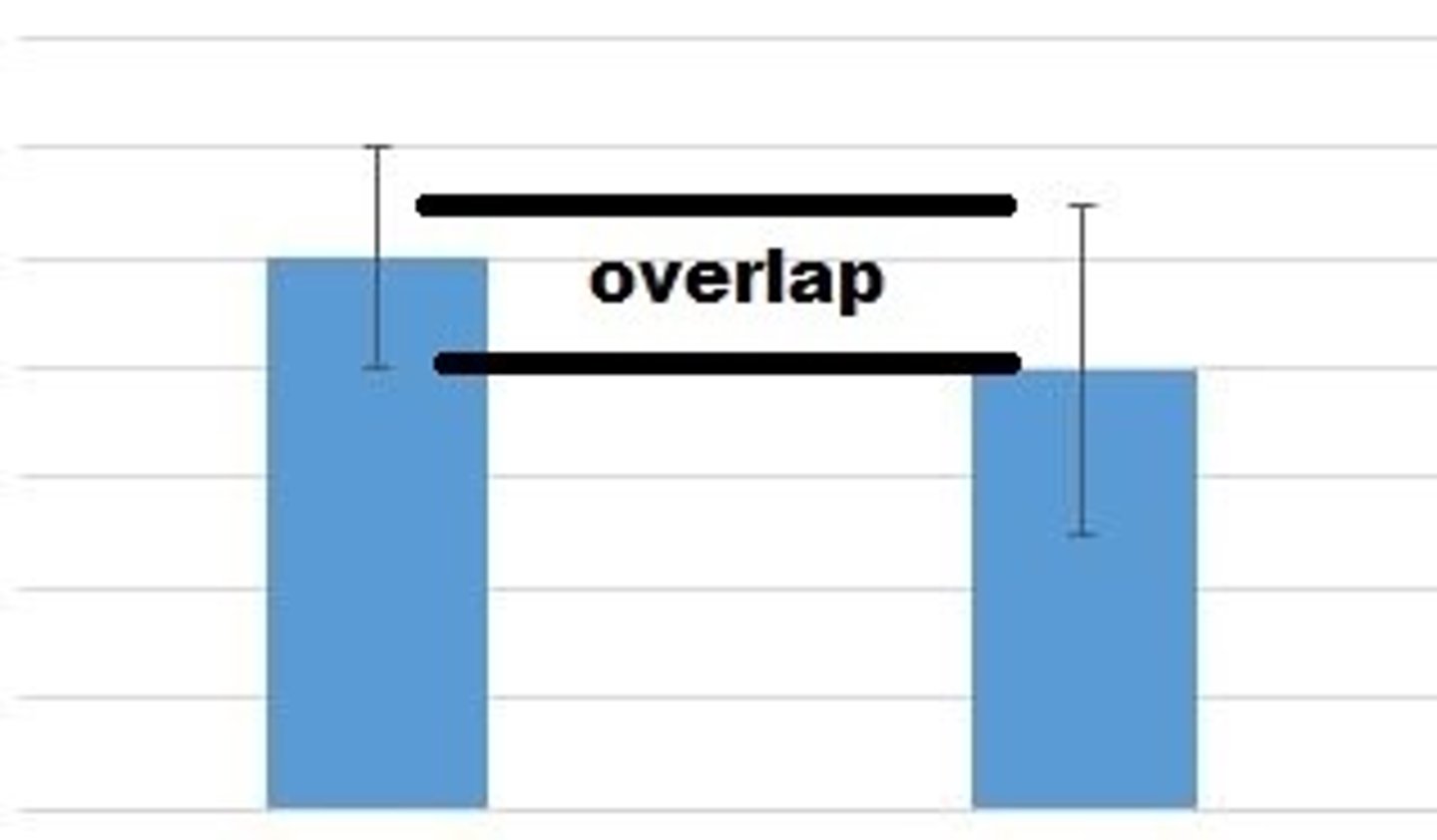
Error bar
Representation of uncertainty displayed on a graph.
Excretion
Process by which metabolic wastes are eliminated from the body
Growth
increase in size or number of cells
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
Interquartile range
The difference between the upper quartile and the lower quartile.
Interspecies
arising or occurring between species
Intraspecies
within the same species
Kingdom
large taxonomic group, consisting of closely related phyla
Mean
the arithmetic average of a distribution, obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
Median
the middle score in a distribution; half the scores are above it and half are below it
Metabolism
the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life.
Mode
The value that occurs most frequently in a given data set.

Movement
Change in position of the body or of a body part; motion of an internal organ
Nutrition
the process of providing or obtaining the food necessary for health and growth.
Order
(biology) taxonomic group containing one or more families
Organism
An individual living thing
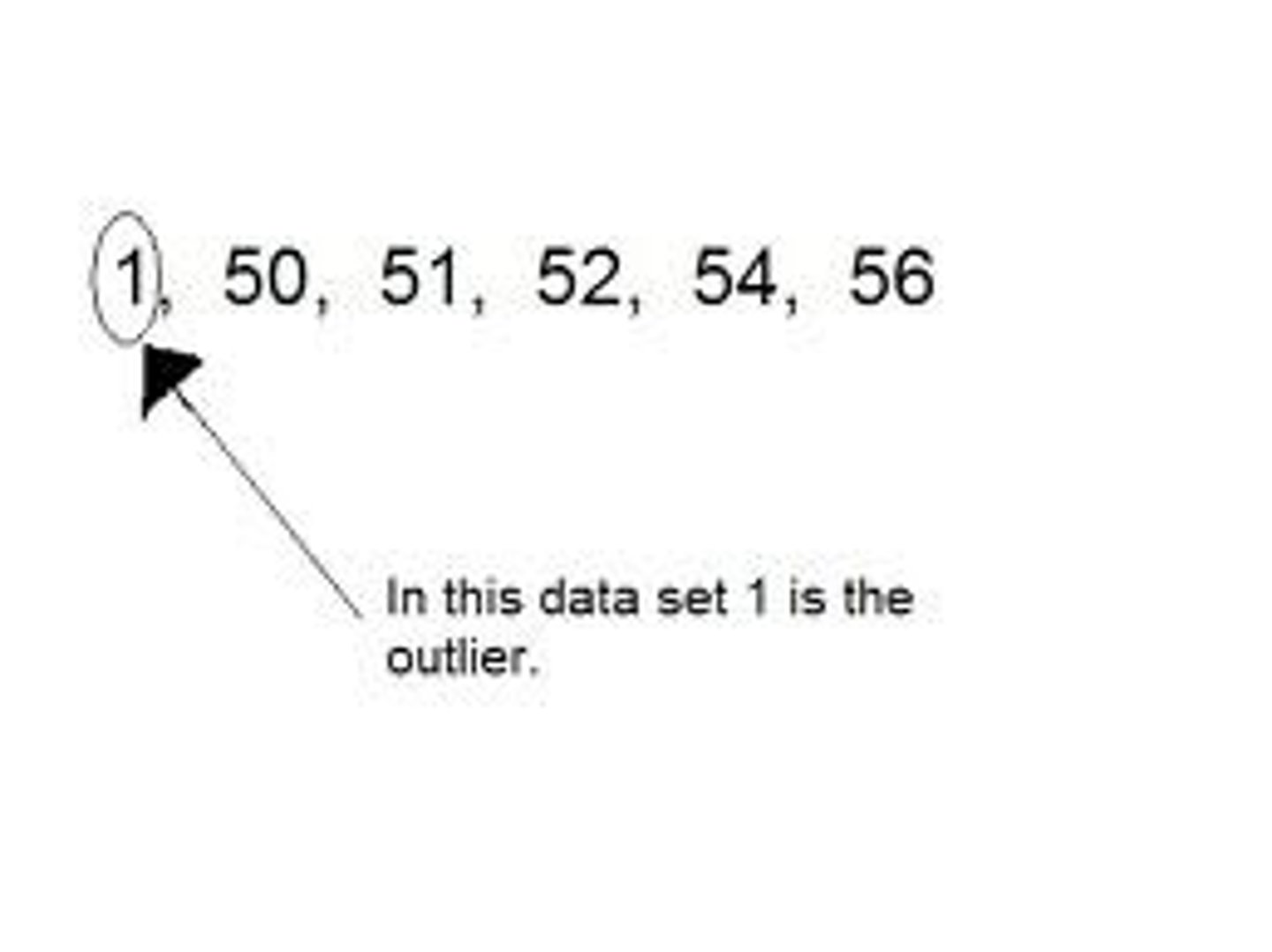
Outlier
A value that "lies outside" (is much smaller or larger than) most of the other values in a set of data.
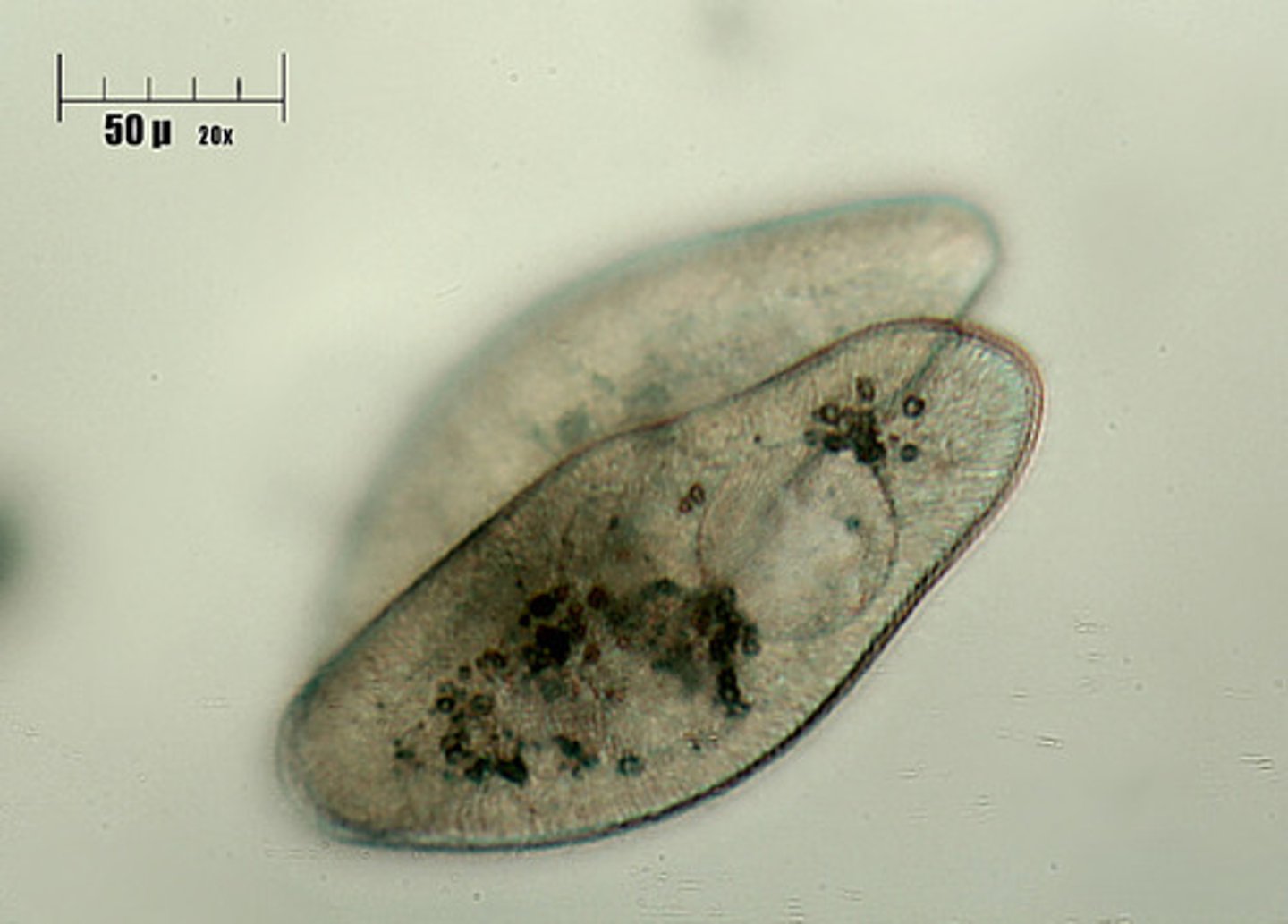
Paramecium
a single-celled freshwater animal that has a characteristic slipperlike shape and is covered with cilia.

Phylum
in classification, a group of closely related classes
Qualitative
Data in the form of words
Quantitative
Data that is in numbers
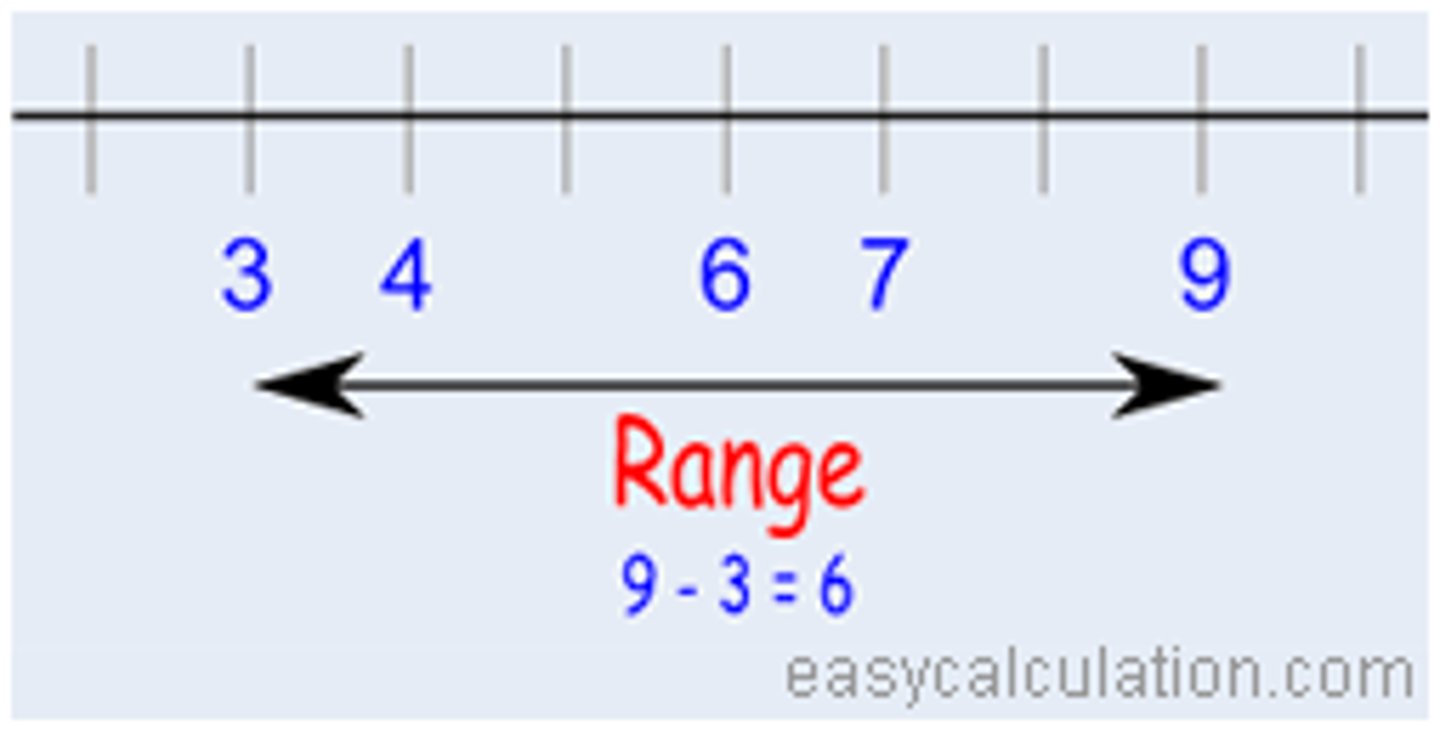
Range
Distance between highest and lowest scores in a set of data.
Reproduction
Ability to generate offspring
Response
An action or change in behavior that occurs as a result of a stimulus.
Species
A group of organisms that are closely related and can mate to produce fertile offspring
Standard deviation
a measure of variability that describes an average distance of every score from the mean
Taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified
Unicellular
A single celled organism
Variation
differences in physical traits of an individual from the group to which it belongs

genus and species
Two parts of the Scientific names of organisms.
Genus
A classification grouping that consists of a number of similar, closely related species
Family
(biology) a taxonomic group containing one or more genera
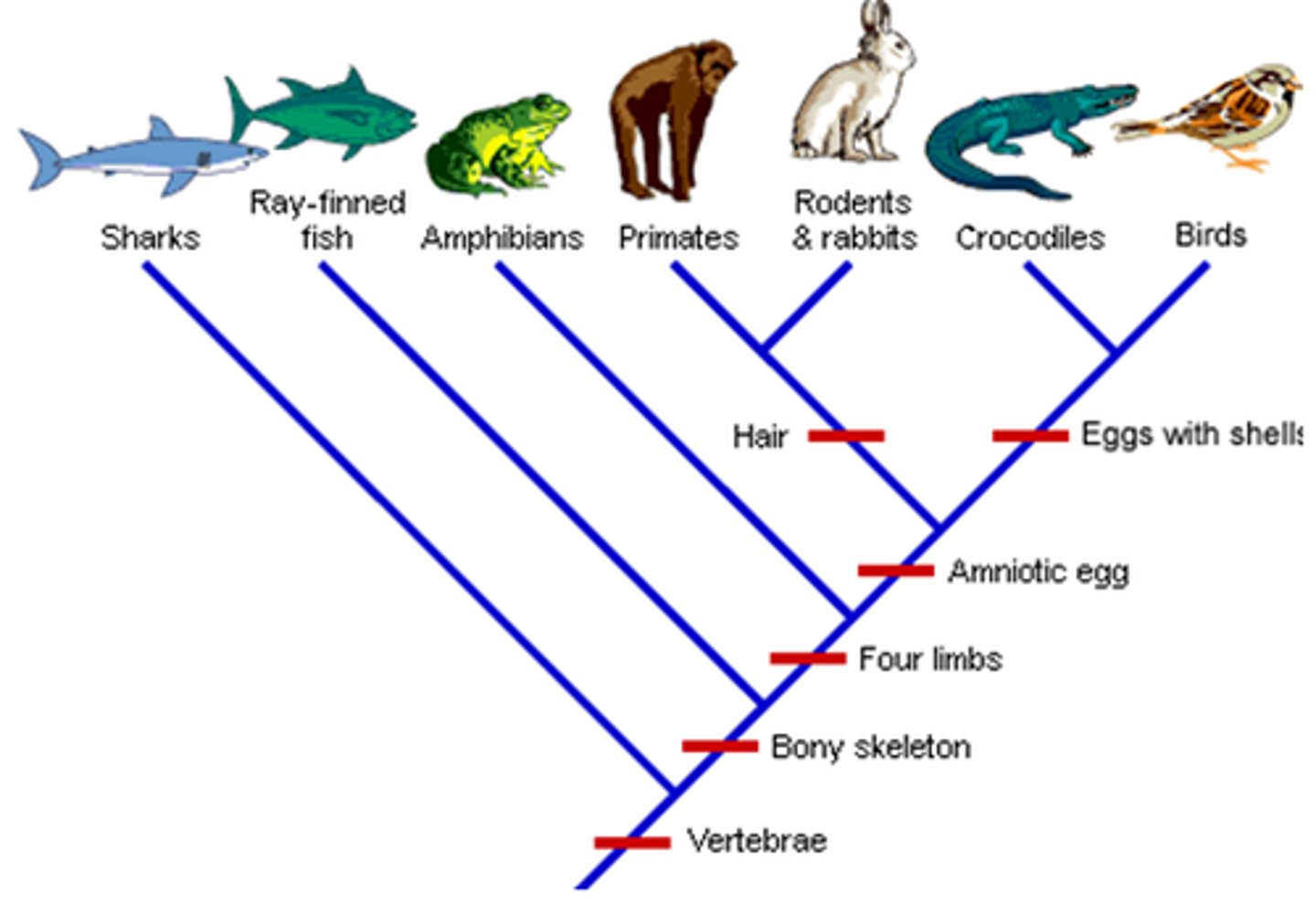
Cladogram
a branching diagram showing the cladistic relationship between a number of species.
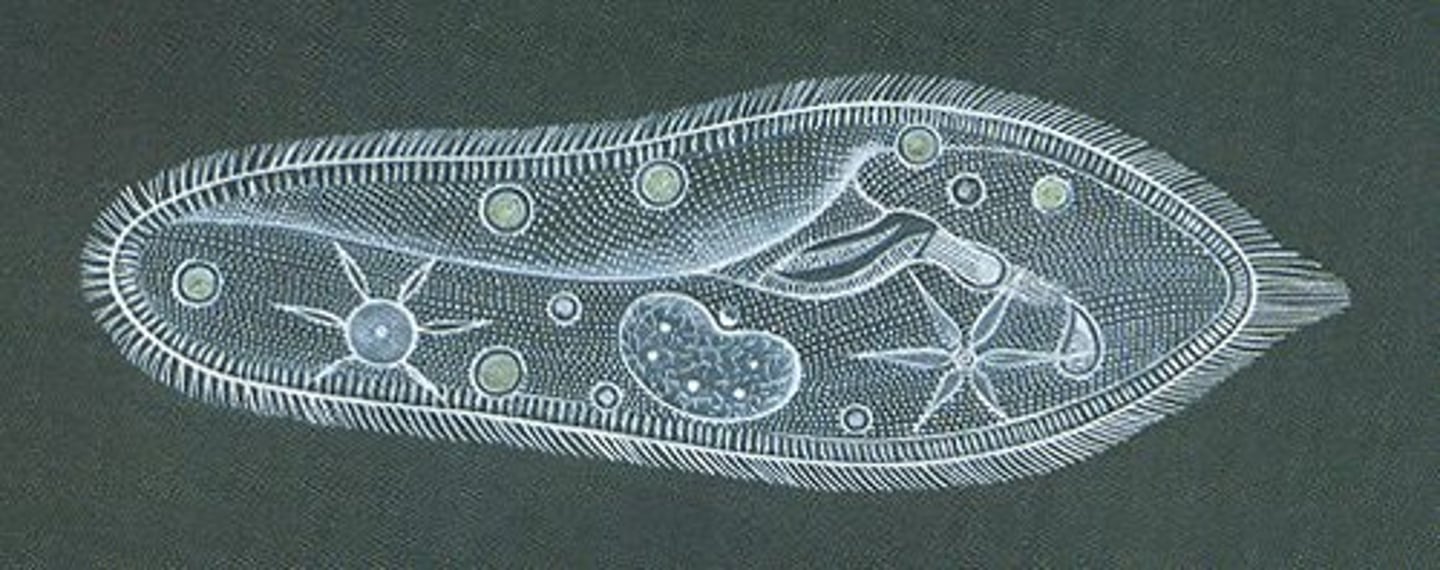
Paramecium
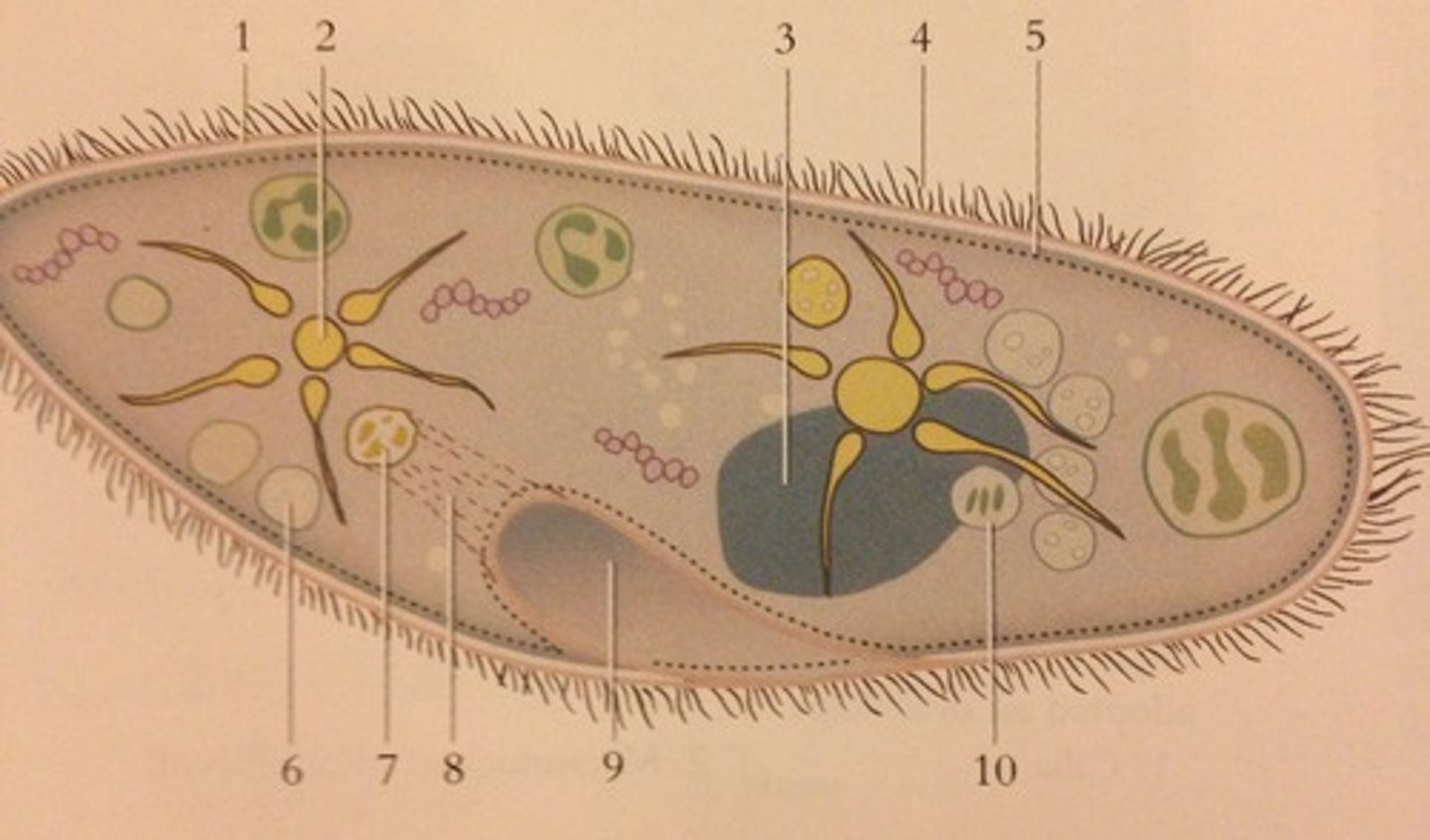
contractile vacuole (paramecium)
The cell structure that collects extra water from the cytoplasm and then expels it from the cell
Oral grove
where the food enters in the paramecium then is broken down and distributed
Anal Pore (Paramecium)
region of the cell membrane of a ciliate where waste-containing food vacuoles fuse and are then emptied into the environment
food vacuole
Stores nutrients for the cell
Cilia
The hairlike projections on the outside of cells that move in a wavelike manner
Cell plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer that protects and encloses the cell; controls transport into and out of the cell; maintains homeostasis
cytoplasm
the material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus. Site of metabolic reactions
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
gene flow
Movement of alleles into or out of a population due to the migration of individuals to or from the population
crossing over
the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics in offspring.
random orientation
the random position of each pair of chromosomes in the nucleus when the spindle microtubules become attached. Their random orientation will eventually result in which chromosomes end up where.
Mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information
Genetic Variation Sources
Mutations, gene flow, meiosis, and sexual reproduction.
random fertilization
source of genetic variation caused by the unlimited number of possible sperm & egg combinations
nomenclature
technical names or naming system in an art or science