Lecture 4 Polymers - Physics
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What Are some unique traits of Polymers?
• Chain entanglement
• Summation of intermolecular forces
• Time scale of motion
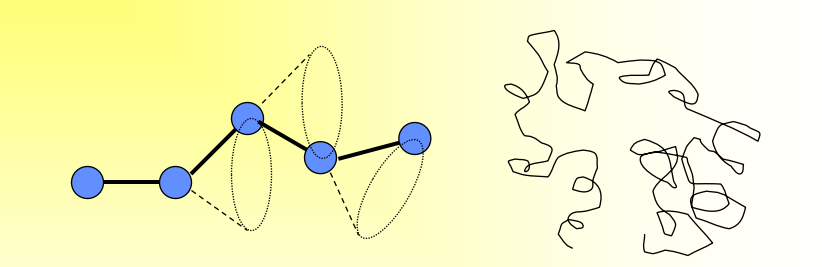
How does the shape of a polymer chain affect if it is in an amorphous state?
• Rotation of the bond → chain bending and twisting → random coil → end to end distance is much smaller than the total chain length
• Entanglement of the neighboring chain
• Amorphous polymer is like a pot of spaghetti, but with much higher ratio of length/diameter
• Different bonds have different rotational property C-C C=C C≡C benzene ring
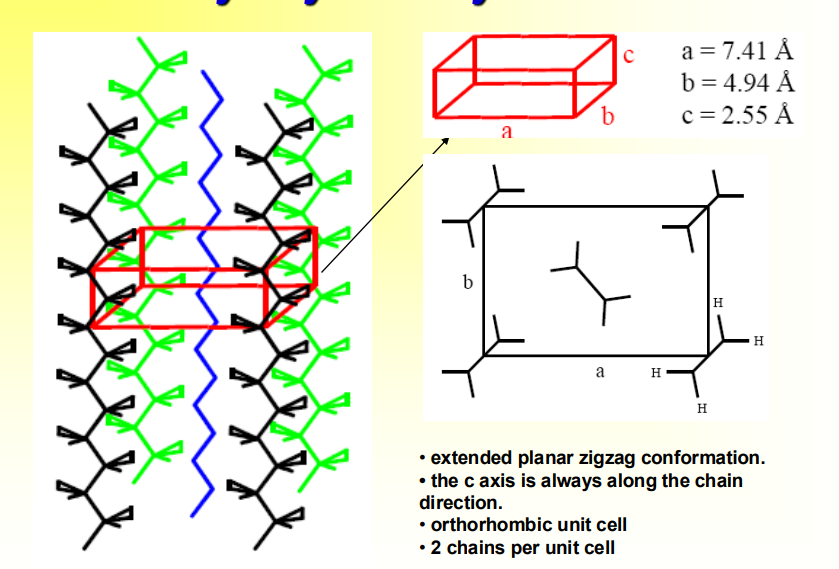
How does a polyethylene Crystal Unit Cell look?
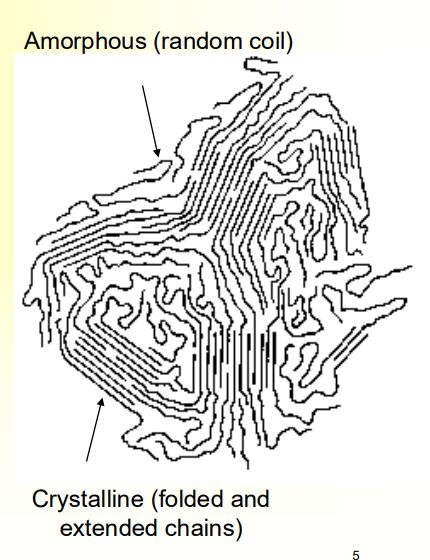
Describe the Crystallinity of Polymers
• Long-chain molecules can not be
crystallized completely
• Most polymers are either semi-
crystalline or amorphous
• Anything that prevents chain
alignment or discourages inter-
chain bonding will decrease
crystallinity (C%).
• Factors affecting C% include
– molecular structure
– intermolecular force
– processing conditions
• Increasing C% results in higher
mechanical strength
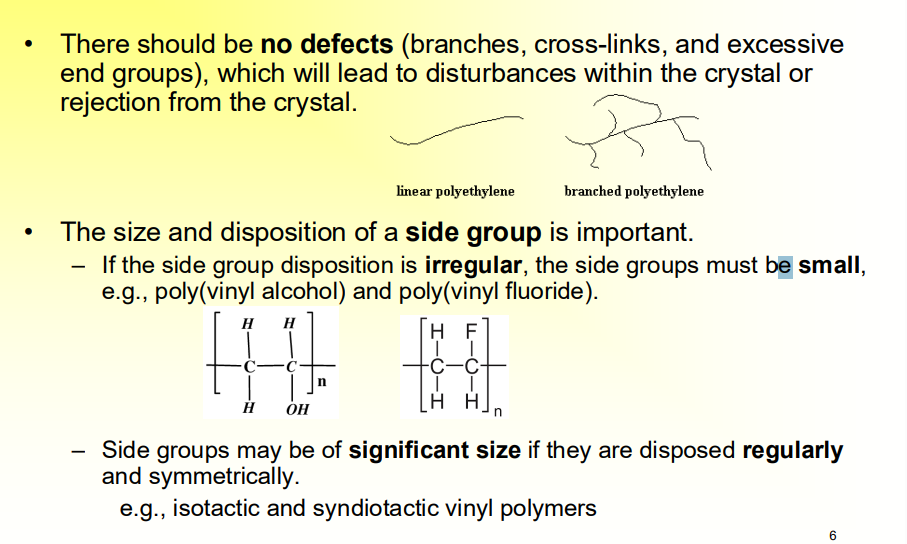
What are some Structural requirements for Crystallization?
There should be no defects (branches, cross-links, and excessive end groups), which will lead to disturbances within the crystal or rejection from the crystal.
The size and disposition of a side group is important.
If the side group disposition is irregular, the side groups must be small, e.g., poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(vinyl fluoride).
Side groups may be of significant size if they are disposed regularly and symmetrically.
e.g., isotactic and syndiotactic vinyl polymers
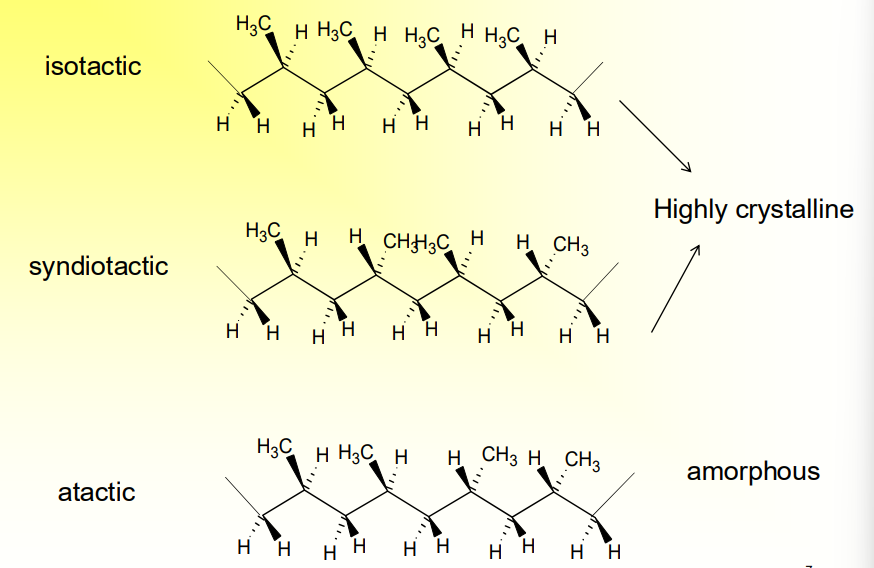
What is Tacticity related to polymers and crystal structure?
It relates to the stereoisomerism of a polymer chain
Isotactic - repeated pattern of stereoisomerism: Highly Crystalline
Syndiotactic - Alternating Patter of Stereoisomerism: Highly Crystalline
Atactic - No Pattern: Amorphous
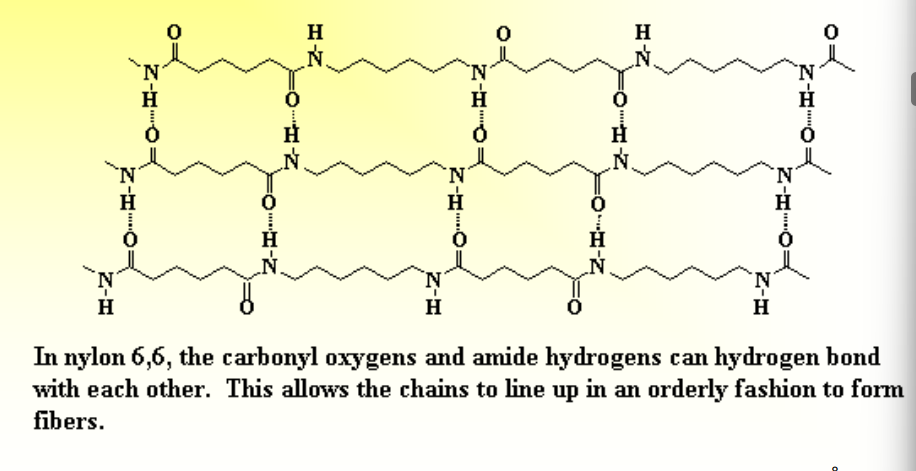
How do Intermolecular Forces Affect Crystallinity?
Attractions/Repulsions between molecules can affect how they line up, and how crystalline their structure can become
What is Quenching?
It is a type of heat treatment, when you habe a mount, and every molecule is in an amorphous state, and quickly lower the temperature. It does not give the polymer chains enough time to move around and align themselves, and reduces crystallinity.
What is Annealing
Caps the Polymer at a higher temperature, for a while, so the polymer has enough time to move around and align with itself, it increases crystallinity.

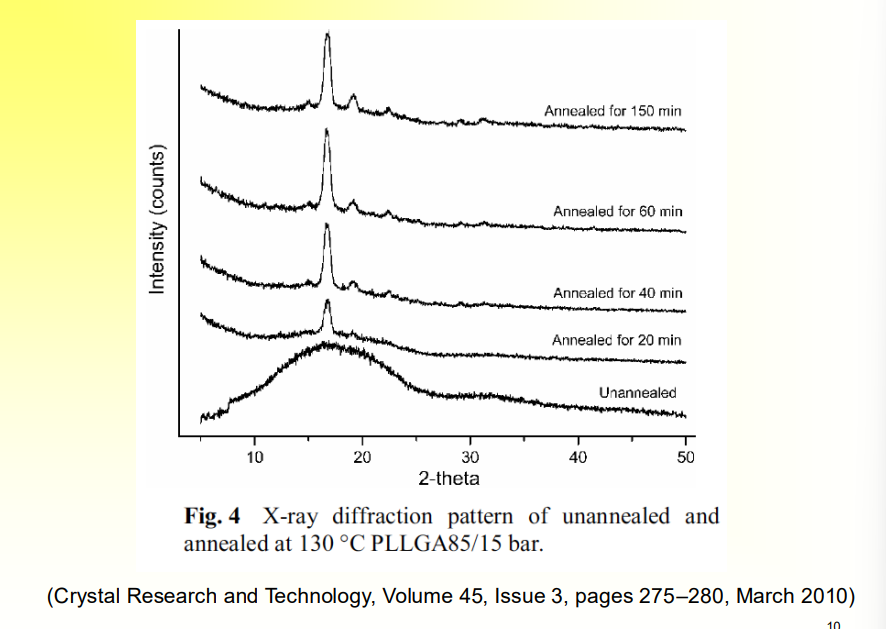
How can we know that annealing is helping to increase crystallinity?
Xray Diffraction
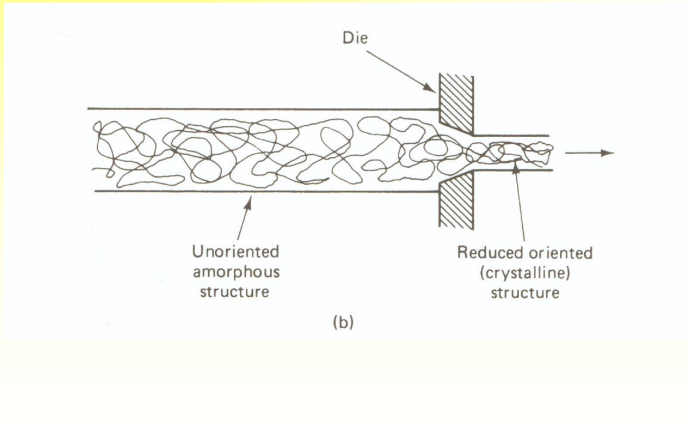
What is Drawing?
Draw a polymer through a die, using mechanical force. It increases crystallinity.
What is Melting?
Melting: occurs when there is enough energy for overall translational chain motion to overcome secondary bonds, disrupting long range orders,
It is unique to crystalline material.
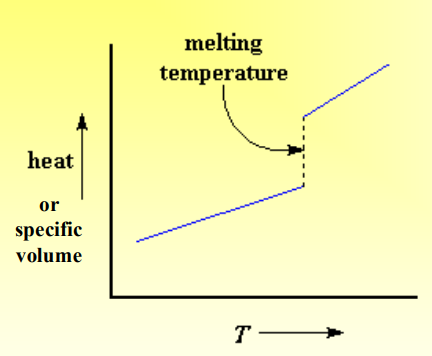
What is Glass Transition?
Occurs when there is enough enery to cause molecular motion around the polymer backbone. It goes from solid to viscous liquid. It is special to amorphous materials
What is the Glass Transition Temperature
• Glass transition temperature: the temperature at which a glassy polymer softens into a viscous liquid or rubbery phase. On the molecular level, it is the temperature at which chains in amorphous (i.e., disordered) regions of the polymer gain enough thermal energy to cause molecular motion around the backbone.
• Tg above room temperature, glassy materials
• Tg below room temperature, rubbery materials
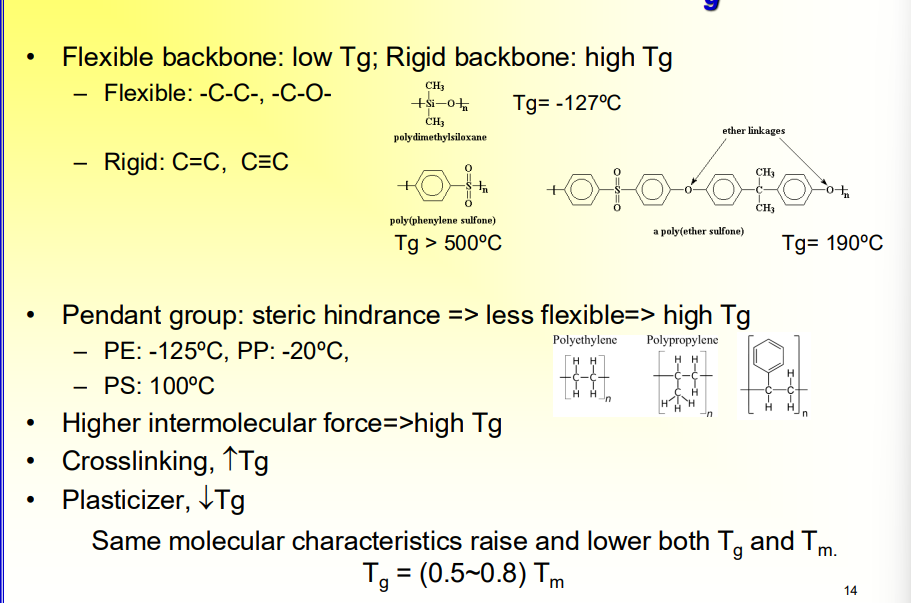
What are some factors that influence Tg
Flexible backbone: low Tg; Rigid backbone: high Tg
Flexible: -C-C-, -C-O-
Rigid: C=C, C≡C
Pendant group: steric hindrance => less flexible=> high Tg
PE: -125ºC, PP: -20ºC,
PS: 100ºC
Higher intermolecular force=>high Tg
Crosslinking, increase Tg
Plasticizer, decrease Tg
Same molecular characteristics raise and lower both Tg and Tm.
Tg = (0.5~0.8) T
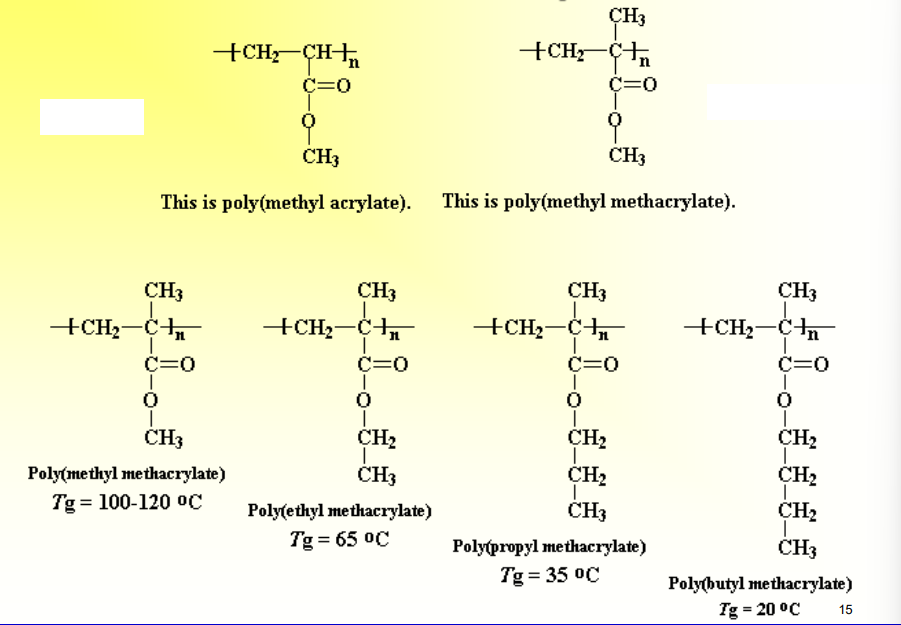
Do Side Groups Affect Tg
Yes, typically larger side groups increase Tg, but if the side groups increase flexibility of the overall chain, then they can decrease Tg
Tg=18ºC for poly(methyl acrylate)
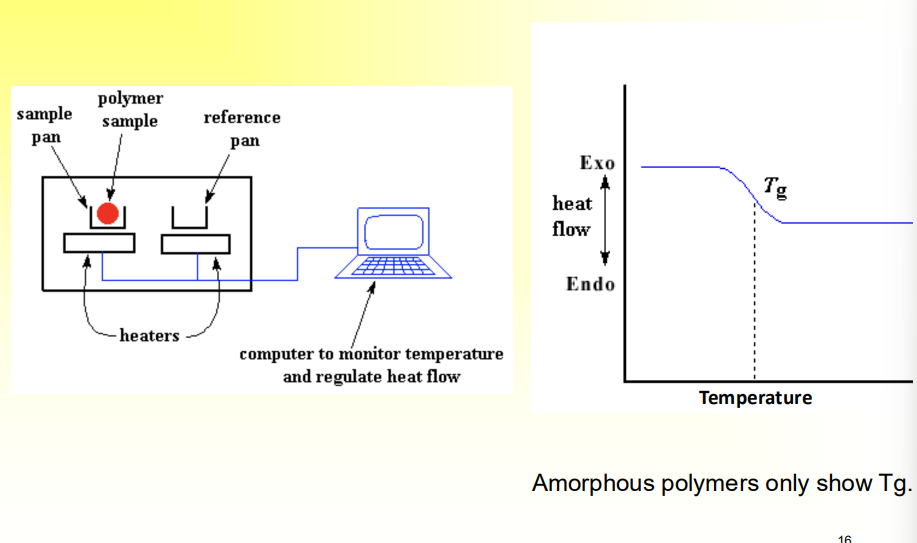
How to know the Tg?
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Have two pans, sample pan with polymer and reference pan with nothing
Provide heat to both pans and increase, and measure heat exchange differences.
How would a semicrystalline polymer’s DSC look?
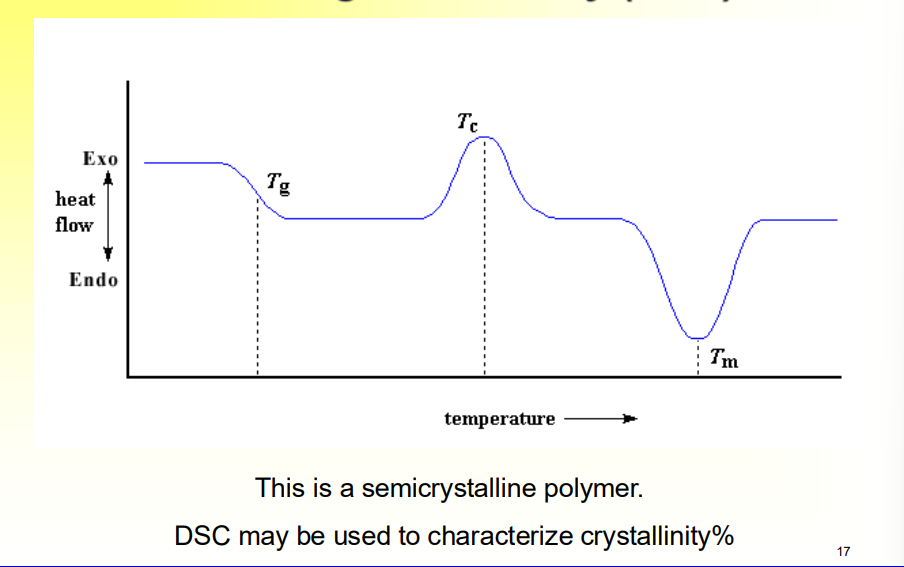
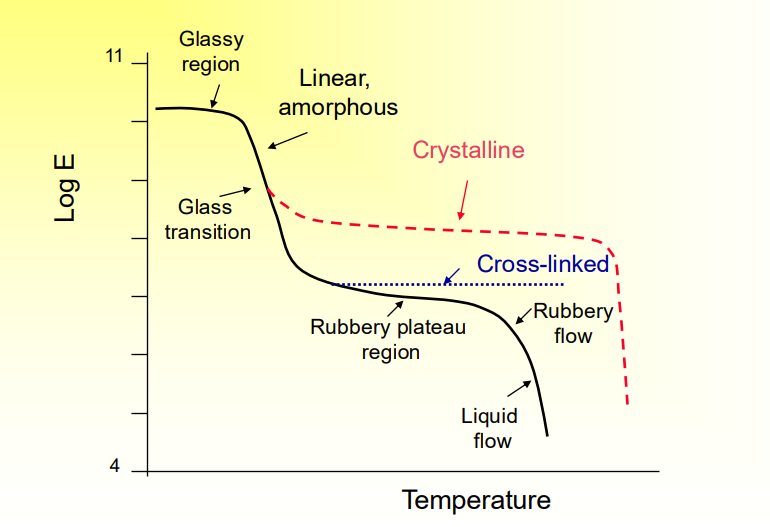
Temperature Dependence of Mechanical Properties
Black is Amorphous, red is when it is semicrystalline, blue is cross-linked amorphous
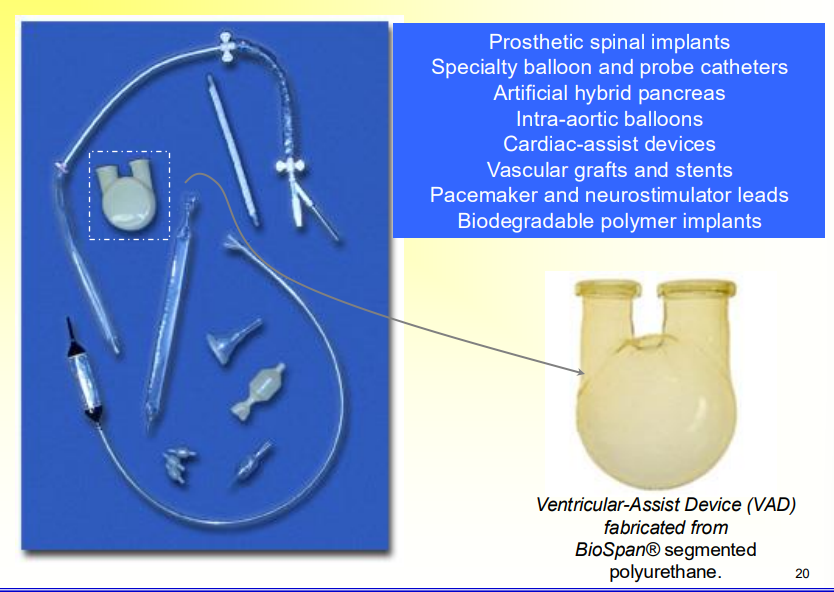
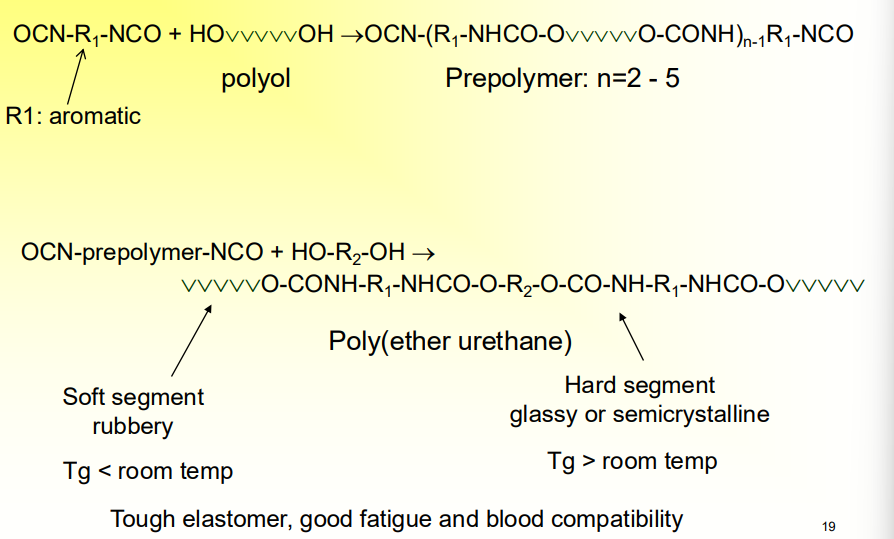
What is the specialty of Segmented Polyurethane
Many different types of temperature dependencies for the segments
It is a tough elastomer, good fatigue and blood compatibility
What do the different Types of Polymers’ Stress Strain Curves Look like?
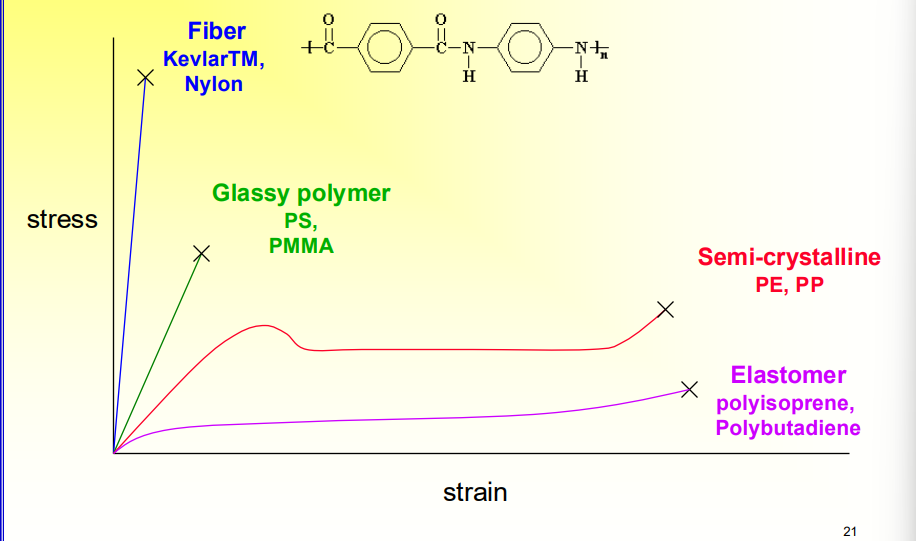
What is the Stress-Strain Behavior of a Ductile Polymer
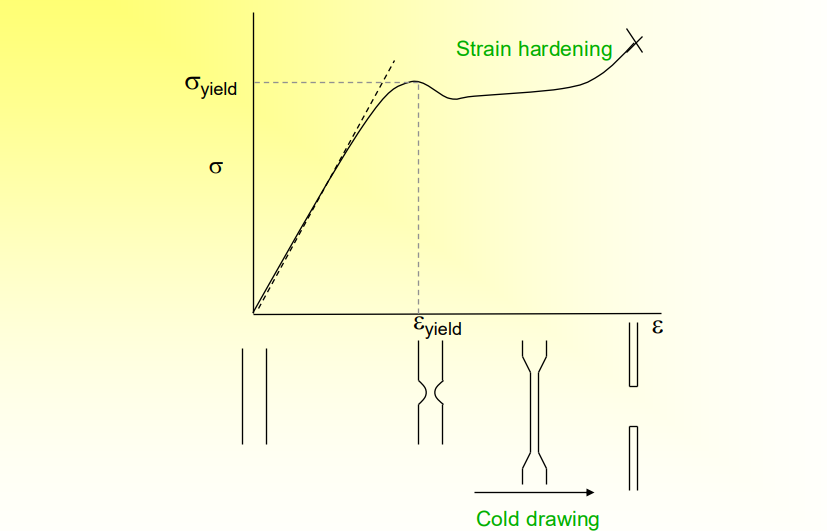
The yield point is the point of deformation where is cannot go back
For polymer materials, the maximum is defined as yield point. Yield strain for polymer is on the order of 5-10%, much higher than metal (0.2%)
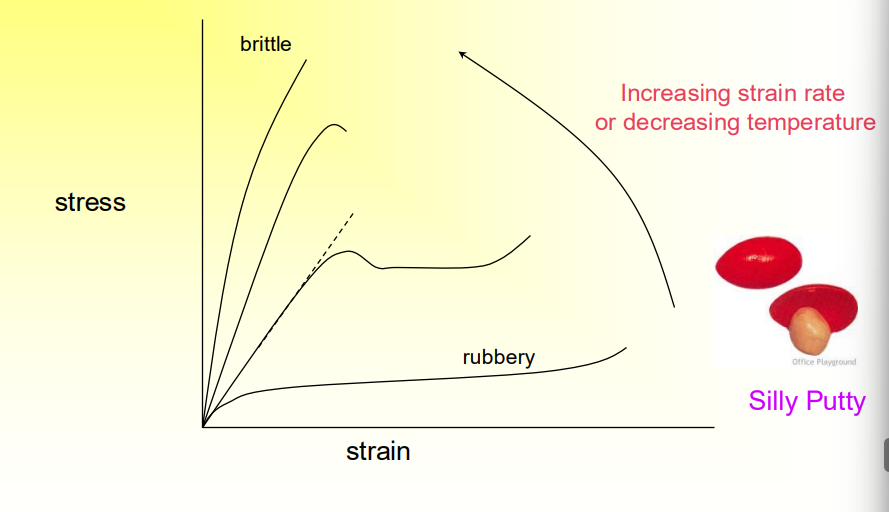
What is the Ductile-Brittle Transition?
When you have a typical polymer but change the temperature or strain rate.
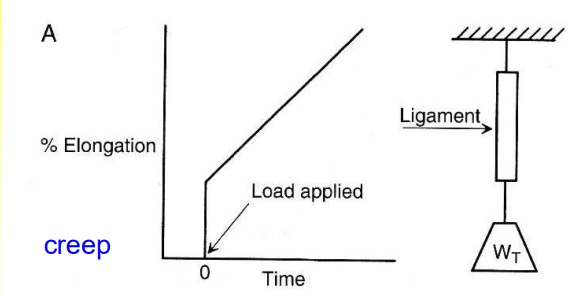
What is Creep?
A type of viscoelastic behavior: It is a time dependent extension under load
What is Stress Relaxation
A type of viscoelastic behavior:
A time dependent decrease in stress at fixed strain is called stress relaxation
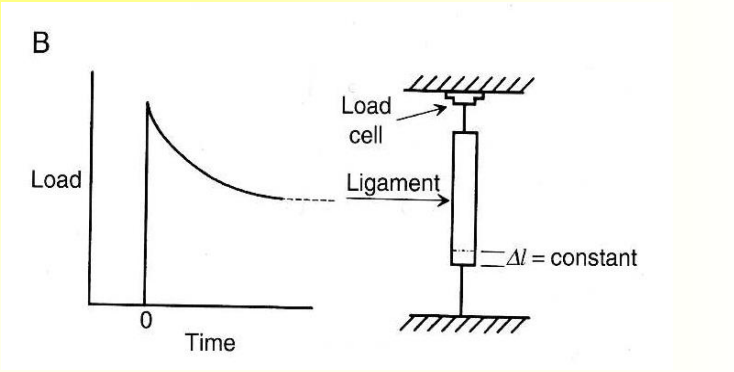
What are some viscoelastic properties of polymers?
• Both creep and stress relaxation are results of viscous flow. Viscoelastic behavior is a combination of elastic and viscous flow responses.
• Polymers and biological tissue materials are usually viscoelastic. Strain rate must be reported when reporting measured mechanical moduli.