T Lymphocyte Development
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
T cell development
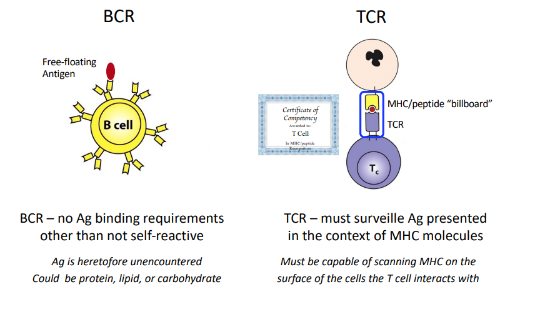
thymic stroma cells provide
-microenvironment for T-cell development
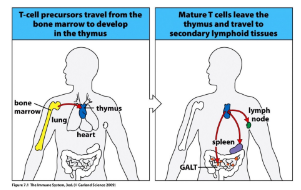
-T cells develop in the thymus from progenitors that are derived from pluripotent stem cells located in the bone marrow
-T cell development takes 3 weeks and generates mature T cells that populate the peripheral lymphoid organs
-thymus absolutely required
bone marrow to thymus process
thymus anatomy and architecture
-lobules separated by trabeculae
-peripheral cortex: densely packed lymphoid cells around epithelial stroma
-central medulla: less lymphocyte rich, contains dendritic cells and macrophages
-thymic classroom
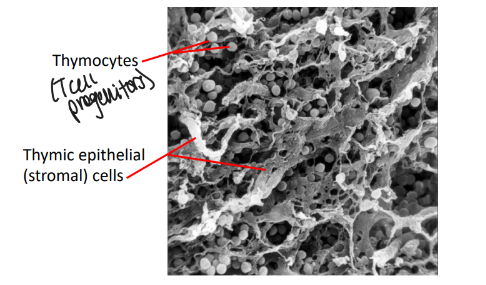
no thymus = no T lymphocytes
-lymphoid progenitors enter the thymus in the cortico-medullary region
-signals from the thymic stroma promote T-lineage commitment, and differentiation
-key signal driving T-cell fate specification is activation of the NOTCH1 receptor
DiGeorge syndrome
-failure during embryogenesis of development of the 3rd and 4th branchial arches results in absence of the thymus (also heart defects and hypoparathyroid state)
-DiGeorge children develop normal numbers of naive B lymphocytes but no T lymphocytes despite having completely normal hematopoietic stem cells
-due to lack of critical signals normally delivered by thymic stroma
-result is severe immunodeficiency with no helper or cytotoxic T cells, and hence no T cell-dependent B cell maturation
summary
parallels with B cell development in the bone marrow
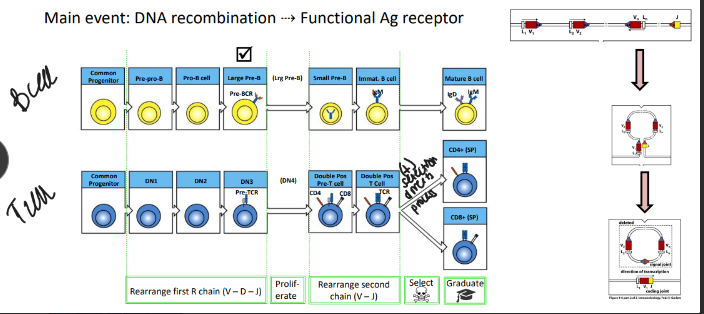
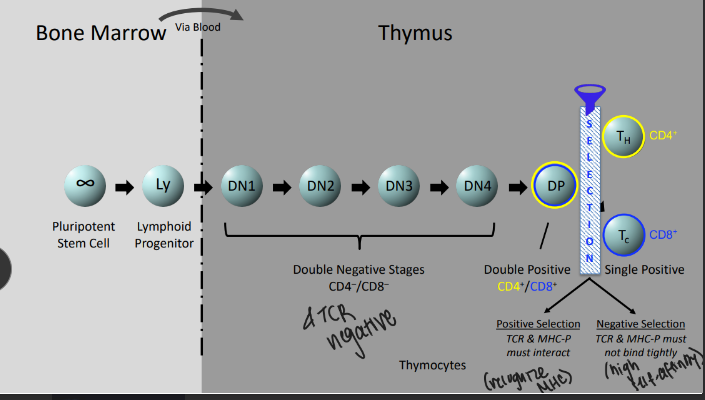
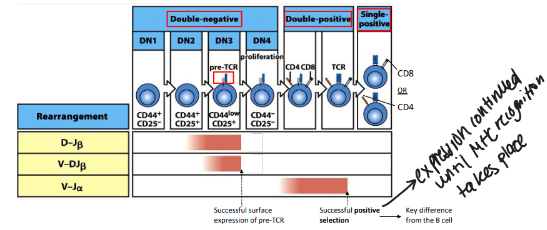
stages of alpha-beta T cell development
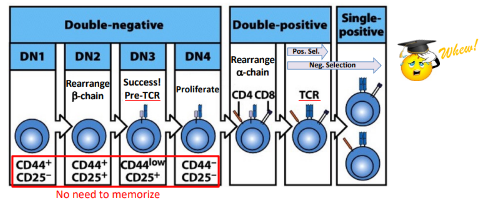
-DN stages are distinguished by surface “markers” like CD25 (IL-2Ralpha chain)
-until the first DNA break DN thymocytes are not committed to the T-cell lineage
TCR-beta rearrangement
-structure of TCRbeta with 2 DJ clusters and constant (C)-region exons allows 2 full rounds of recombination
T-cell development is coupled with
-rearrangement of the T-cell receptor genes
-TCRbeta rearrangement starts with D→J in DN2 cells and is shut down by successful surface expression of the pre-TCR (like B cells)
-TCRalpha rearrangement occurs in DP thymocytes→ends with successful positive selection (unlike B cells)
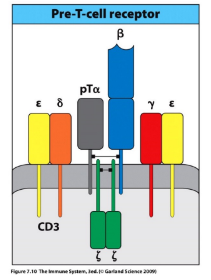
pre-TCR signaling
-pre-TCR receptor: beta-chain plus invariable pre-T(alpha) chain
-associates with CD3 signaling complex (analogous to the pre-BCR’s Igalpha/Igbeta complex)
-tonic ligand-independent signaling
-key effects: ends all beta-locus rearrangement (degrade RAG), induces proliferation to generate a pool of cells that share the new beta-chain and will subsequently rearrange their alpha-chain loci, induces expression of both CD4 & CD8 → double-positive stage of development
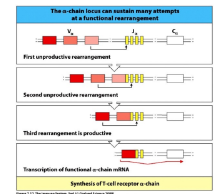
TCR-alpha rearrangement
-only one joint (V-to-J)
-60 J segments and 70-80 V segments allow multiple rounds of recombination
-successful TCR-alpha expression does NOT end recombination (key difference from B cells)
-TCR-alpha recombination terminated only when the new TCR shows the ability to interact with self-MHC/peptide complexes (positive selection)
-DP cells survive only ~4 days unless rescued by successful TCR-MHC/peptide interaction
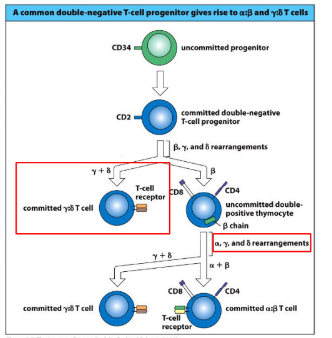
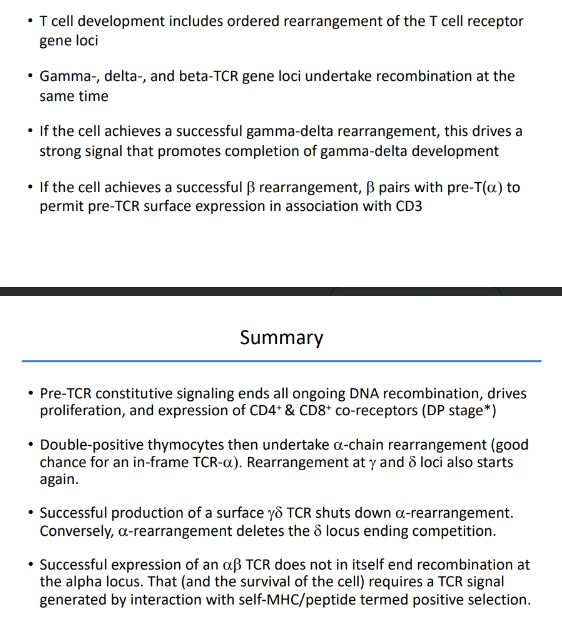
gamma-delta and alpha-beta T-cells develop in
-competition
-alpha-beta T cells: most abundant, either CD4+ or CD8+, responsible for adaptive immune response, alpha-beta TCR in the surface
-gamma-delta T cells: gamma-delta TCR on surface, minor population (1-5% of T cells)- most are CD4-/CD8-, recognize non-protein antigens, can function without MHC presentation, one of a subset of lymphocytes termed “innate-like:”; limited TCR diversity
lineage choice: gamma-delta v alpha-beta
-gamma, delta, and beta TCR loci are all undergoing rearrangement at the same time
-success at the gamma and delta loci drives a strong signal and promotes gamma-delta T cell development
-in a twist of genomic fate, the alpha-locus is housed entirely within the alpha-locus (between Valpha and Jalpha gene segments); once the alpha locus rearranges V to J, the delta locus is deleted
overview of alpha-beta TCR generation
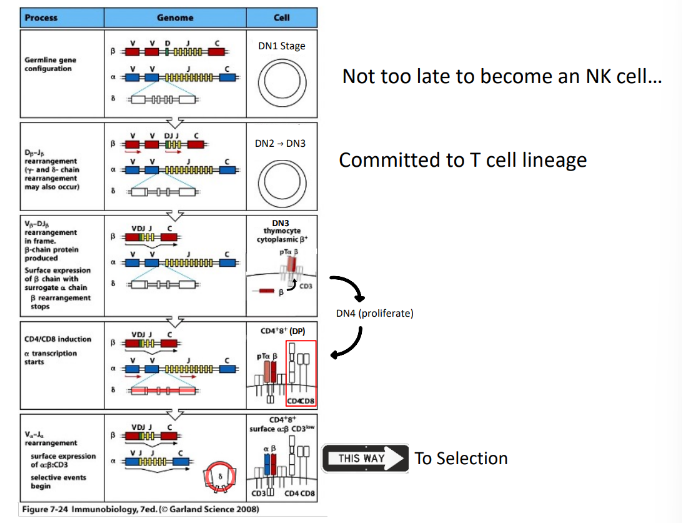
summary
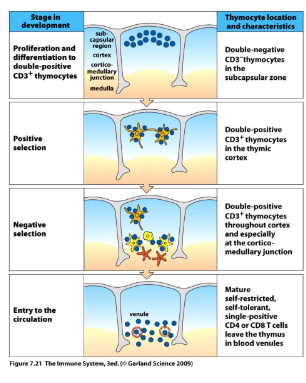
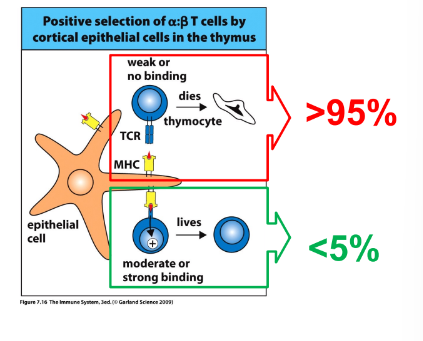
T-cell selection
-positive selection: process of rescue from cell death and maturation to SP CD4 or SP CD8 cells upon recognition of MHC-self peptides; signal is modest and sustained
-negative selection: TCR receptors that respond too strongly to self peptide are eliminated as potentially self reaction; signal is strong
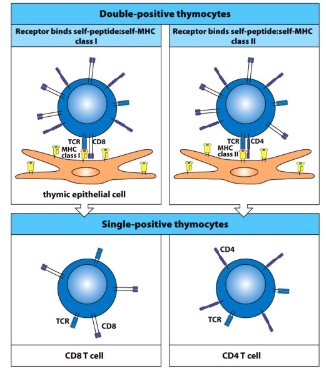
positive selection is coupled with
-CD4 or CD8 cell fate specification
-if the new TCR interacts with MHC I, the DP cell will maintain CD8 co-receptor expression and cease expression of CD4
-if the new TCR interacts with MHC II, the DP cell will maintain CD4 co-receptor expression and cease expression of CD8
-if no TCR-MHC interaction, alpha-chain V-J rearrangement continues, generating new TCR’s in hope of rescue
most DP cells fail positive selection and die by
-apoptosis
-if after multiple encounters there is no TCR interaction with self-MHC/peptide complexes and the alpha-chain runs out of recombination options, cell dies by apoptosis
-more than 95% of DP cells fail to be positively selected and undergo programmed cell death
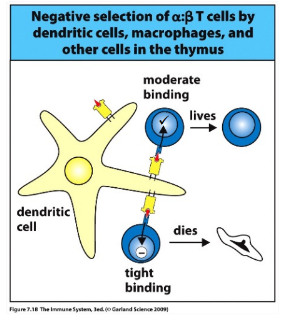
negative selection
-strong affinity of the new TCR for self-MHC/peptide complexes triggers cell death
-ongoing both in the cortex (epithelial cells) and the medulla (thymic epithelial cells plus macrophages and DCs)- incomplete in the absence of medullary macrophages and DCs → autoimmune disease
-~2% of the original DP thymocytes graduate (survive negative selection)
thymic representation of self
-AIRE (autoimmune regulator): gene highly expressed in thymic medullary epithelial cells and DCs, encodes a transcriptional activator, induces expression of “ectopic” or “tissue-restricted” proteins
-AIRE dysfunction → autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome (APECED): inflammatory glandular destruction (thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, beta-islets), ovarian/testicular failure, vitiligo (melanocyte loss) and alopecia