Mechanotransduction in Disease and Microenvironment Effects
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Disease
Any harmful deviation from the normal structural or functional state of an organism, generally associated with certain signs and symptoms and differing in nature from physical injury.
Microenvironment
A small, specialized area that surrounds and supports cells and tissues.
Aberrant
Deviating from the usual or natural type: atypical, abnormal.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Cause: Autoimmune attack on synovial joints. ECM Destruction: Chronic inflammation leads to excessive MMP activity, breaking down collagen, fibronectin, and hyaluronic acid in the joint ECM.
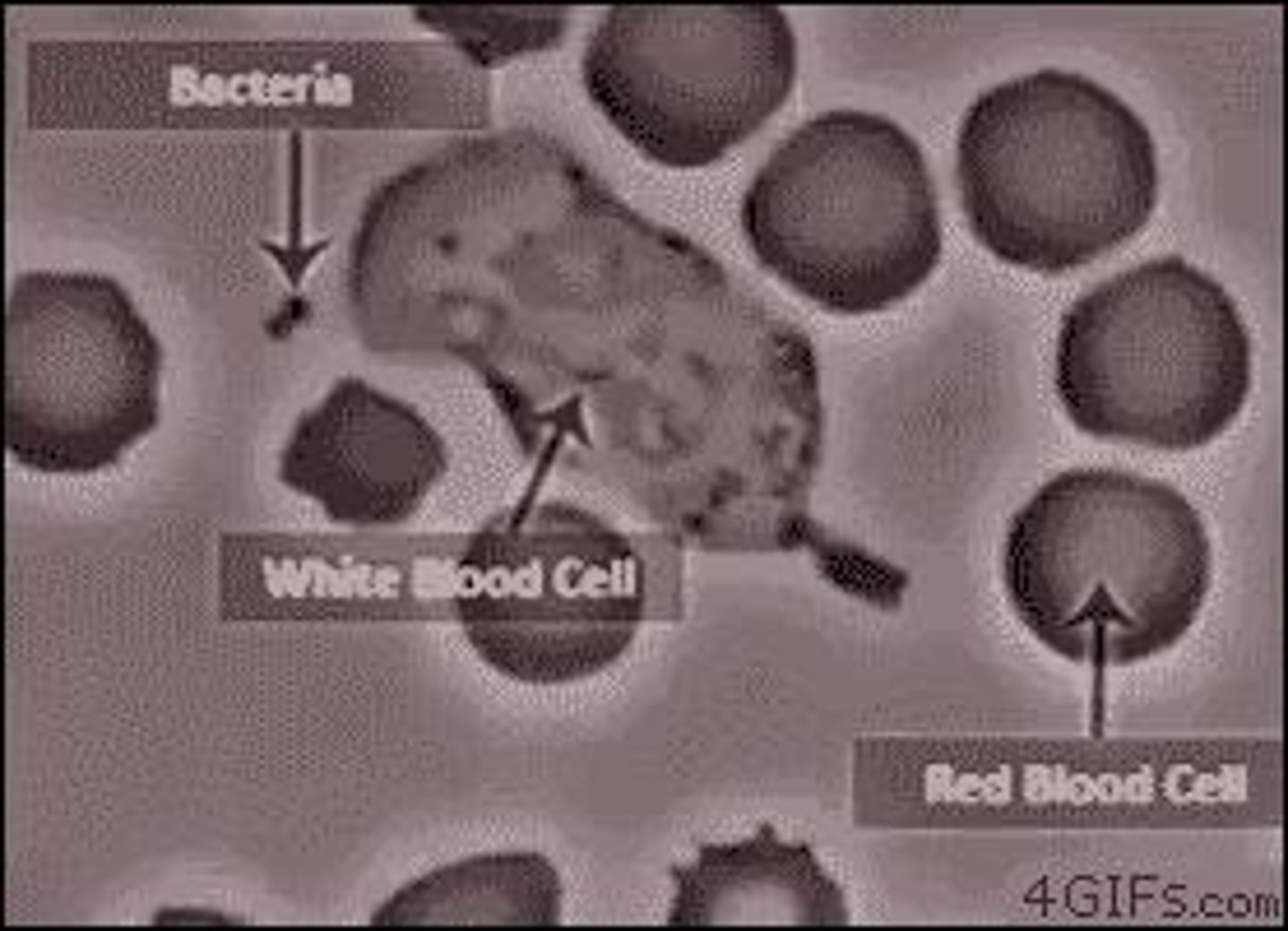
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Cause: Long-term smoking, air pollution, genetic factors (e.g., α1-antitrypsin deficiency). ECM Destruction: Elastin and collagen degradation in alveolar walls due to elastase overactivity, leading to emphysema and airway collapse.
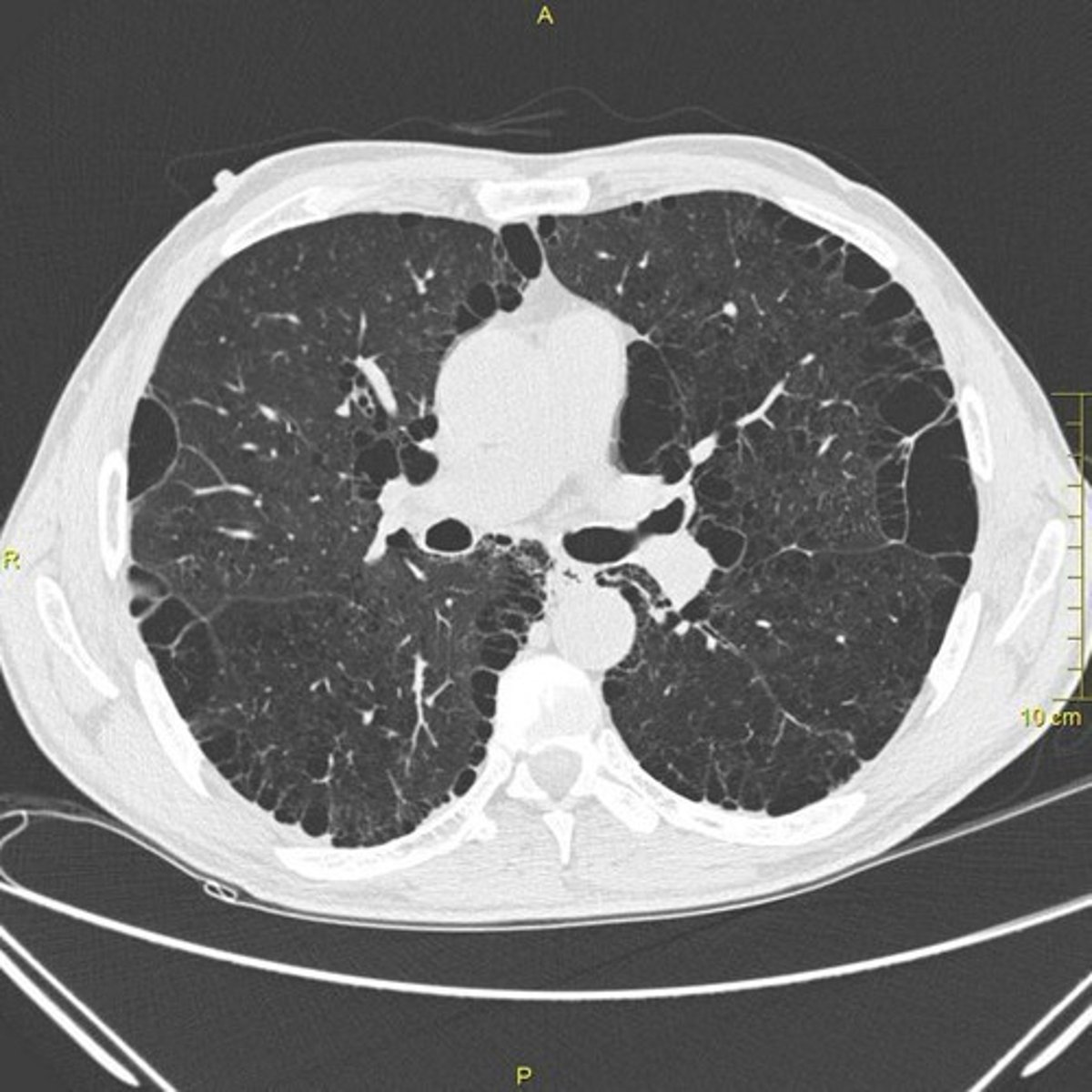
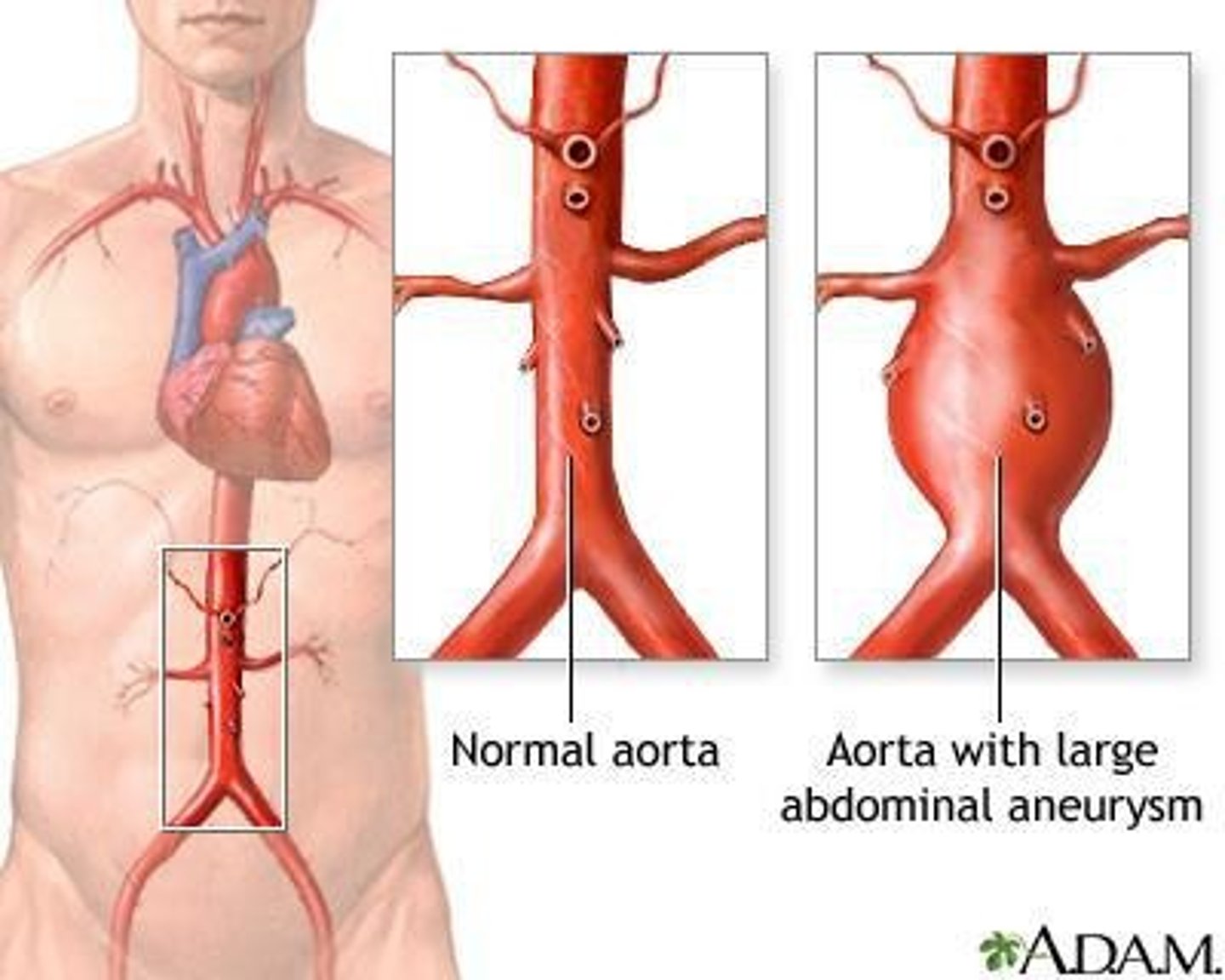
Aortic Aneurysm
Cause: Chronic hypertension, genetic disorders (Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome). ECM Destruction: Weakening of elastin and collagen fibers in the arterial wall due to increased MMPs and inflammatory cytokines.
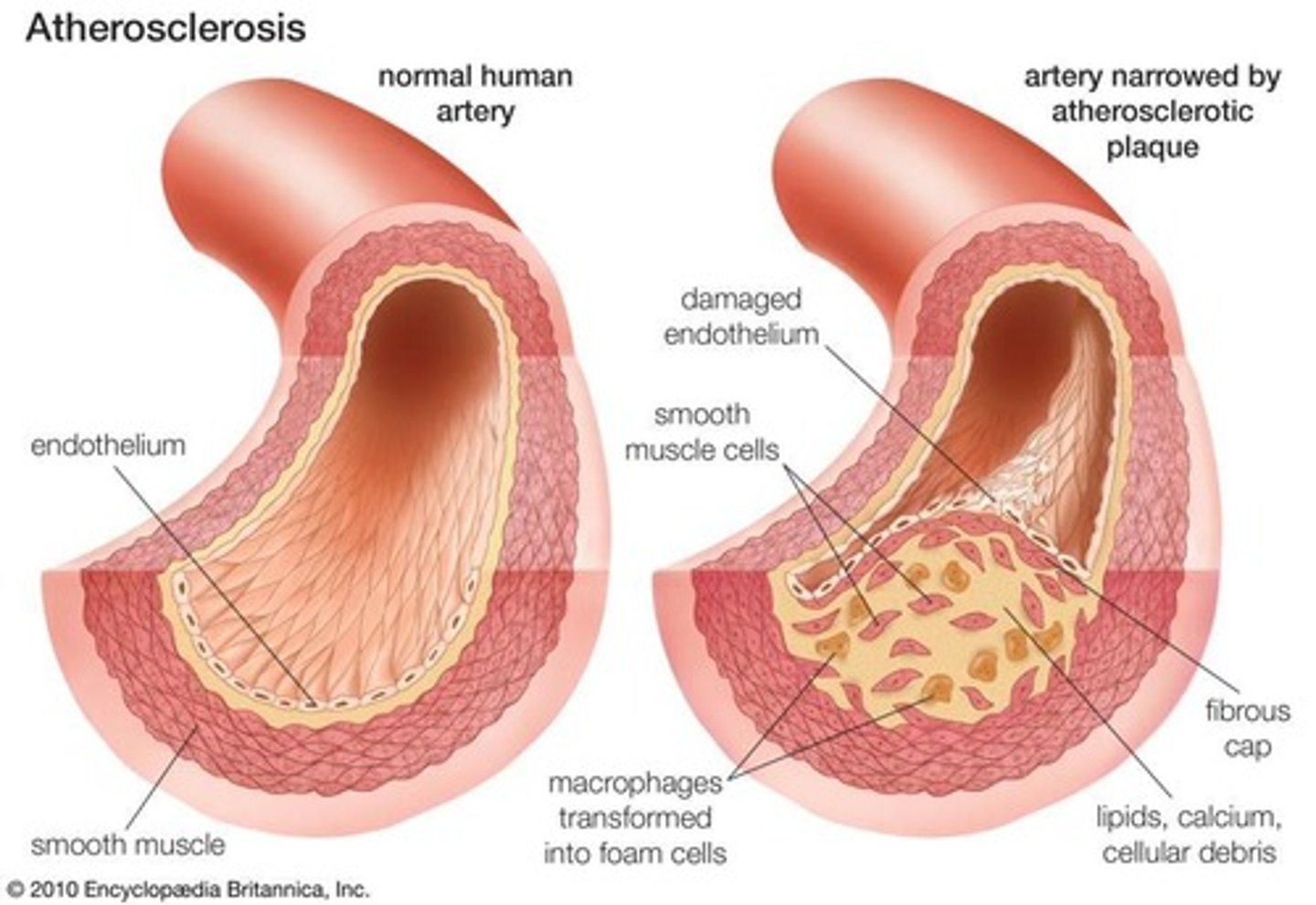
Atherosclerosis
Cause: High cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, diabetes. ECM Overproduction: Plaques contain excessive ECM proteins (collagen, elastin, proteoglycans) deposited by vascular smooth muscle cells. Calcification further stiffens arteries.
Pulmonary Fibrosis (Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, IPF)
Cause: Chronic lung injury (environmental toxins, infections, acid reflux). ECM Overproduction: Excessive deposition of collagen (Type I and III) and fibronectin by activated fibroblasts (myofibroblasts), leading to stiffened lung tissue.
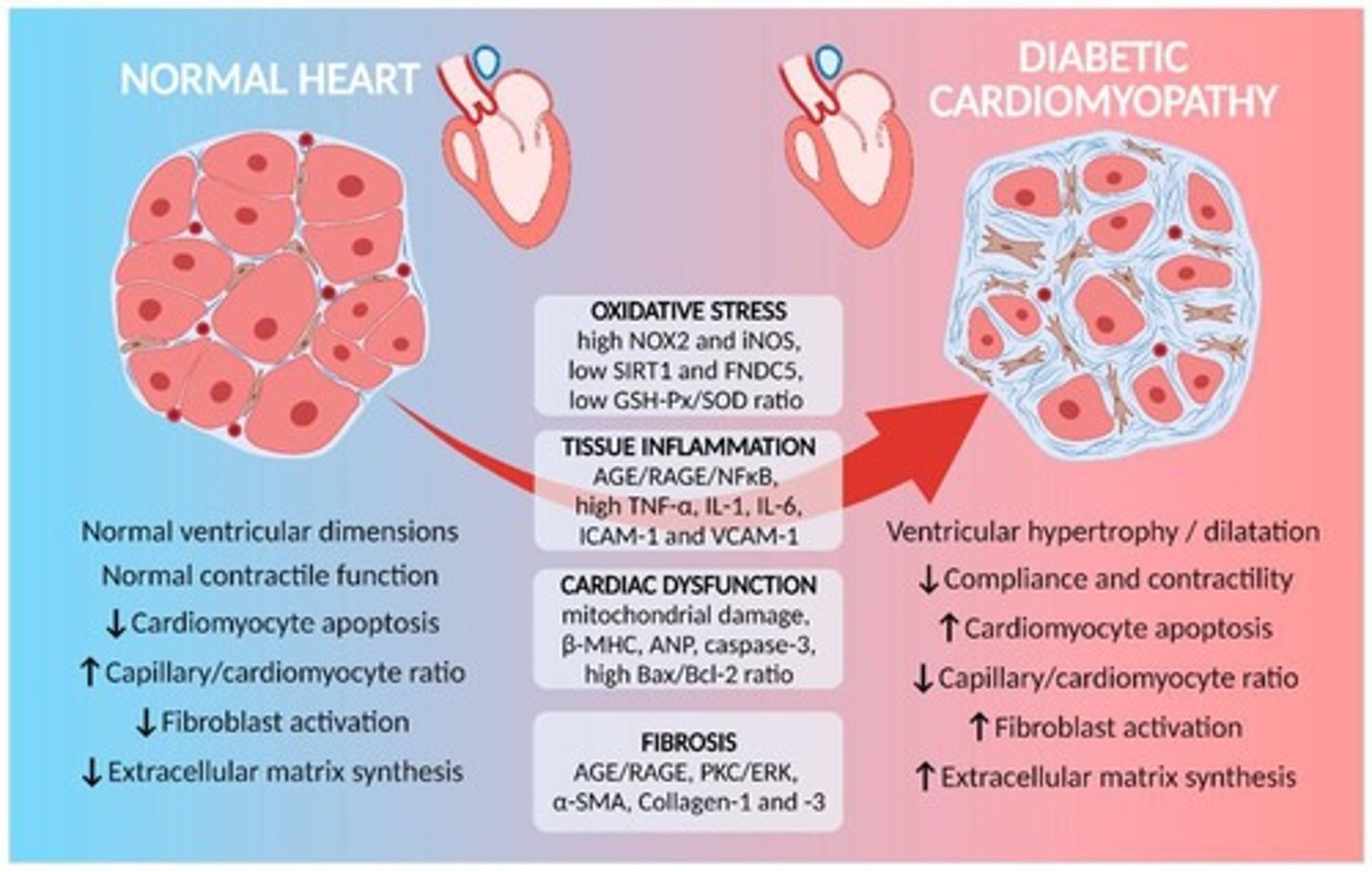
Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Cause: High blood sugar increases oxidative stress and inflammation in the heart. ECM Changes: Excessive collagen I and III deposition → myocardial fibrosis. Reduced elastin → loss of flexibility, leading to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Cause: Hyperglycemia damages small blood vessels and reduces fibroblast function. ECM Changes: Reduced collagen I and fibronectin synthesis → slow wound healing. Excessive MMP activity degrades ECM too quickly, preventing proper tissue repair.
Mechanotransduction Connection
Increased ECM stiffness activates fibroblasts via YAP/TAZ. TGF-β signaling drives fibroblast differentiation into myofibroblasts, worsening fibrosis.
ECM Destruction
Destruction of the ECM is present in nearly all diseases.
ECM Overproduction
Some diseases alter the ECM in different ways in different areas of the body.
Impact of Mechanotransduction
How disease can impact the microenvironment (ECM, Cell function) and how these all translate into mechanotransduction.
Prevalence and Incidence Rate
The frequency of a disease in a population, often expressed as a percentage or ratio.
Sex Based Differences
Variations in disease prevalence, incidence, and outcomes based on biological sex.
Treatment Outcomes
The outcomes/success rates with current treatment methods.
Patient Outcomes Improvement
How could we better study/treat/test/improve patient outcomes.
Homework Goals
Understanding the disease, its causes, prevalence, progression, impact of mechanotransduction, and treatment options.
Diabetes
Affects multiple organ systems through dysregulated ECM remodeling, with stiffening (fibrosis) in some tissues and degradation (poor wound healing, vascular damage) in others.
ECM Remodeling
The process by which the extracellular matrix is altered, impacting various cellular behaviors and disease progression.
Cancer
Involves ECM remodeling for tumor growth and metastasis.
Pancreatic Cancer
Characterized by desmoplasia and ECM stiffening.
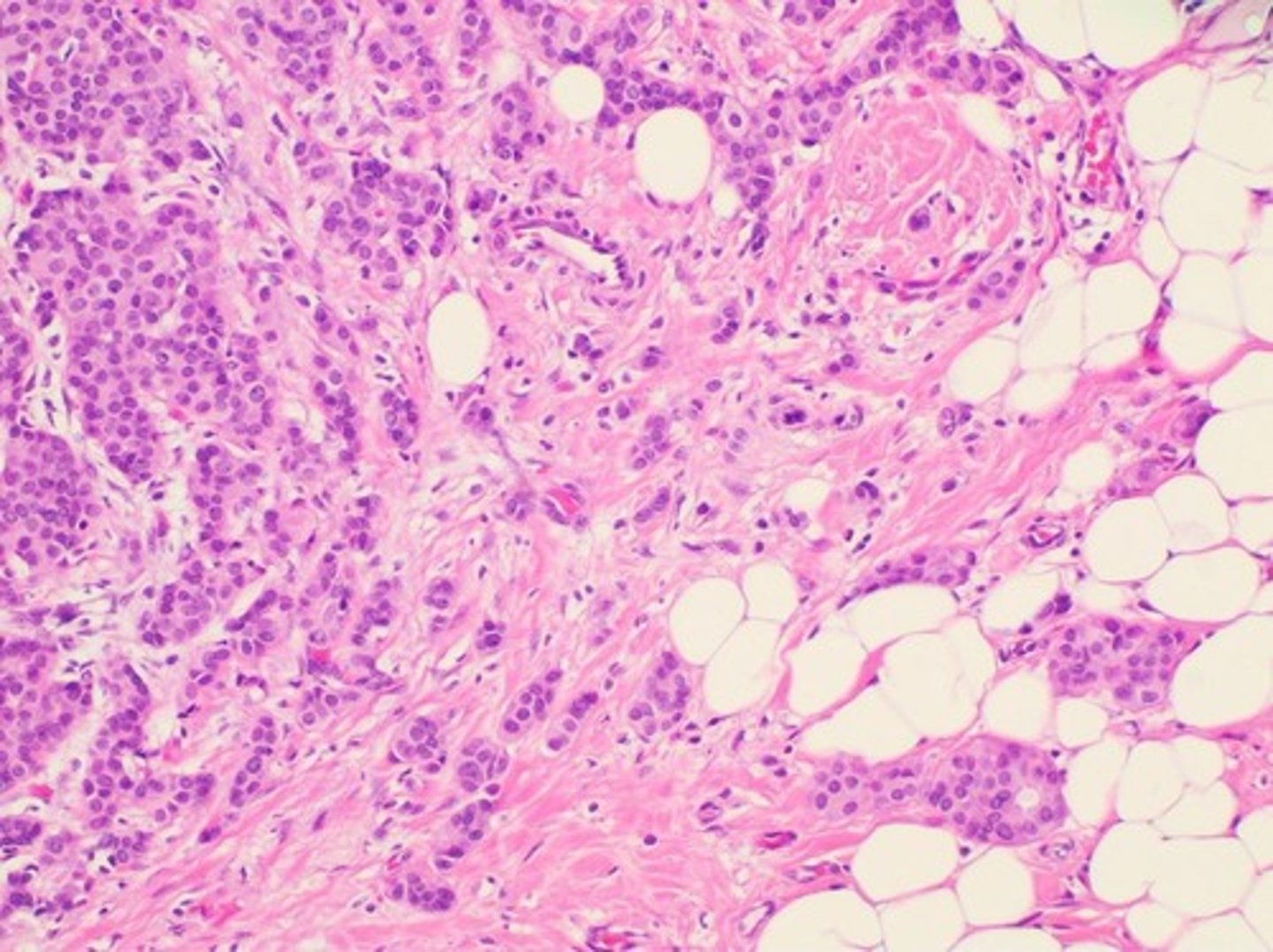
Desmoplasia
Excessive ECM deposition (fibronectin, collagen I/III) creates a dense, fibrotic barrier around the tumor.
MMPs
High levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) degrade ECM locally, allowing tumor invasion.
Mechanotransduction
Stiff ECM activates integrins and FAK signaling, promoting tumor growth.
ECM Topography
Altered ECM topography enhances cell migration and metastasis.
Dense ECM
Limits drug delivery, reducing chemotherapy effectiveness.
Cell Proliferation
Normal function involves controlled cell division to maintain tissue homeostasis, but disease can lead to uncontrolled proliferation.
Breast Cancer
An example of disease impacting cell proliferation through loss of cell cycle regulation due to mutations.
Cell Death & Apoptosis
Normal function involves programmed cell death to remove damaged or unneeded cells; disease can alter this process.
Neurodegenerative Disease
Example: Alzheimer's, where misfolded proteins trigger excessive neuronal apoptosis.
Cell Migration & Invasion
Normal function involves movement for wound healing and immune response; disease can impair or enhance this migration.
Metastatic Cancer
Example: Pancreatic Cancer, where tumor cells hijack MMPs to enhance migration.
Cell Adhesion & Communication
Normal function involves attachment to ECM and neighboring cells; disease can alter this function.
Atherosclerosis
Example of endothelial dysfunction where chronic inflammation reduces endothelial adhesion, increasing permeability.
Cellular Mechanosensing
Normal function involves responding to mechanical cues to regulate behavior; disease can misregulate this function.
Pulmonary Fibrosis
Example where excessive collagen deposition stiffens lung ECM, leading to respiratory failure.
Cellular Metabolism
Normal function involves energy production through metabolic pathways; disease can lead to dysfunction.
Type 2 Diabetes
Example of beta-cell dysfunction due to chronic hyperglycemia impairing insulin secretion.
Mechanotransduction
Increased ECM stiffness disrupts glucose-stimulated insulin release.
Pathology
Systemic metabolic failure, hyperglycemia, organ damage.
Normal Function (Immune Cell Function)
The immune system defends against pathogens and removes damaged cells.
Disease Impact (Immune Cell Function)
Hyperactive or suppressed immune response drives pathology.
Example (Immune Cell Function)
Autoimmune Disease (Rheumatoid Arthritis)
Disruption (Immune Cell Function)
Overactive T cells and macrophages trigger chronic inflammation.
Mechanotransduction (Immune Cell Function)
Increased ECM degradation (MMPs) damages joints, worsening inflammation.
Pathology (Immune Cell Function)
Joint destruction, pain, loss of function.
Normal Function (Differentiation & Stem Cell Fate)
Stem cells differentiate into specialized cell types based on environmental signals.
Disease Impact (Differentiation & Stem Cell Fate)
Impaired differentiation disrupts tissue maintenance.
Example (Differentiation & Stem Cell Fate)
Osteoporosis (Bone Loss)
Disruption (Differentiation & Stem Cell Fate)
Aging and hormonal changes shift mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) away from osteoblast differentiation.
Mechanotransduction (Differentiation & Stem Cell Fate)
Reduced ECM stiffness prevents MSCs from sensing mechanical cues needed for bone formation.
Pathology (Differentiation & Stem Cell Fate)
Weakened bones, fracture risk.
Proliferation
Rate at which cells divide and multiply.
Dysregulation of cell cycle
Altered signaling pathways (e.g., p53, Rb, Wnt).
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death.
Altered caspase activity
Mitochondrial dysfunction, loss of pro-apoptotic signaling (e.g., BAX, BCL-2).
Senescence
Irreversible cell cycle arrest with secretory phenotype (SASP).
Migration
Directed movement of cells.
Differentiation
Specialization of stem/progenitor cells.
Metabolism
Energy production and nutrient utilization.
ECM Remodeling
Degradation, deposition, or stiffening of the extracellular matrix.
Autophagy
Cellular self-digestion of damaged components.
Adhesion
Cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions.
Secretion
Release of cytokines, growth factors, or ECM components.
Chronic inflammation
excess pro-inflammatory cytokines
Cancer
paracrine signaling for tumor growth
Autoimmune diseases
hyperactive immune cell secretion
Endocytosis/Exocytosis
Cellular uptake or release of molecules
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis alterations
changes in endocytosis processes involving clathrin
Exosomal cargo changes
modifications in the contents of exosomes
Neurodegenerative diseases
defective synaptic vesicle cycling
Infectious diseases
pathogen entry
Extracellular Fluid
pH, Ion Balance, Nutrients
pH shifts
altered ion gradients, metabolic waste accumulation
Vascularization & Blood Flow
Abnormal angiogenesis, hypoxia, vascular leakage
Oxygen Tension
Altered oxygen availability, oxidative stress
Cell Presence & Activity
Chronic inflammation, immune suppression or hyperactivation
Lymphatic Drainage & Fluid Homeostasis
Impaired clearance of interstitial fluid, leading to swelling and toxin buildup
Metabolite Availability & Nutrient Competition
Depletion of key metabolites, competition between host cells and pathogens/tumor cells
Exosome & Extracellular Vesicle Dynamics
Increased or altered EV secretion, influencing signaling
Neuronal Signaling & Innervation
Changes in nerve density, neurotransmitter levels, and pain signaling
Hormonal & Endocrine Factors
Dysregulated hormone levels altering tissue responses
Epigenetic Landscape
Changes in DNA methylation and histone modifications affecting gene expression
Ocular Shingles
a viral infection affecting the eye and surrounding structures caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
Prevalence
the proportion of individuals who have a disease or condition at a specific point in time, including both new and existing cases
Incidence
the number of new cases of a disease that develop within a specific time period in a population at risk
Overall shingles incidence
~4 per 1,000 people per year
HZO incidence
~0.3 to 0.7 per 1,000 people per year
Recurrent Cases
About 10% of patients may experience recurrence
Sex-based differences
Slightly higher incidence in women, possibly due to differences in immune function
Prodromal phase
1-5 days before rash with pain, burning, tingling in affected dermatome
Acute eruptive phase
1-2 weeks with a red, blistering rash along the ophthalmic nerve distribution
Acute eruptive phase
1-2 weeks duration where a red, blistering rash appears along the ophthalmic nerve distribution.
Ocular involvement
Includes conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis, and scleritis.
Chronic/Postherpetic Phase
Weeks to months, or longer, characterized by persistent nerve pain known as postherpetic neuralgia (PHN).
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN)
Persistent nerve pain that can last months to years.
Corneal scarring
Can lead to vision loss and secondary glaucoma in severe cases.
Neurotrophic keratopathy
Corneal desensitization leading to ulceration and perforation.