Ch 22 respiratory system
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Gas exchange
Supplies body with O2 and removes CO2
Processes of Respiration
Pulmonary ventilation
External Respiration
Transport of Respiratory of Gases
Internal Respiration
. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing)
inspiration and expiration, movement of
air into and out of lungs-exchange of air b/w atmosphere and alveoli of
lungs.
and expiration, movement of
air i
. External Respiration
lungs (pulmonary capillaries)
Oxygen moves from the lungs into blood
Carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the lungs
Transport of respiratory gases
Transport of oxygen from the lungs to the tissue cells
Transport of carbon dioxide from the tissue cells to the lungs
. Internal Respiration-
body tissues- (systemic capillaries)
Oxygen moves from the blood to the body cells
Carbon dioxide moves from the body cells into the blood
larynx up
Upper respiratory system-
larynx down
Lower respiratory system
Functions of external nose:
1. provides an airway for respiration
2. warms, moistens, and filters incoming air
3. detects olfactory stimuli
4. speech chamber- modifies vibrations as they
pass through the resonating chambers
Two types of mucous membranes in nasal cavity
Respiratory mucosa
Olfactory mucosa
Respiratory mucosa
Nasal
Mucosa
– pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium w/ large amounts of globlet cells
Olfactory mucosa
Olfactory epithelium
- olfactory receptors for smell
What are the 3 regions of pharynx
3 Regions:
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
Lined with Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Nasopharynx
rises up to close of
nasopharynx and prevent food
from entering
Uvula-
nasopharynx contains
adenoids (pharyngeal tonsils)
-tubal tonsils
what are the 5 opening
-5 openings:
2 internal nares
2 openings to the auditory tube
1 opening into oropharynx
Lined with stratified squamous
epithelium
Oropharynx
respiratory and digestive function
food, drink and air passage
-contains tonsils
-palatine tonsils
lingual tonsils
Oropharynx
Lined with stratified squamous
epithelium
Laryngopharynx
respiratory and digestive function
air and food passage
Description of the Larynx
Short passageway connecting laryngopharynx with trachea
air passage, switching mechanism to route food and air into the
proper channels, and voice production.
Cilia in upper respiratory tract move mucous and trapped particles down toward pharynx
Cilia in lower respiratory tract move them up toward pharynx
prevents food from entering the trachea
Epiglottis

sound

pitch

speech:

Trachea
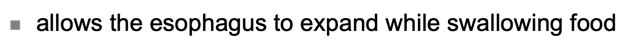
Posterior Tracheal Wall
Conducting Zone Structures
Trachea-(primary) bronchi-(secondary bronchi)-(tertiary Bronchi)- bronchioles-Terminal bronchioles-respiratory bronchioles-alveolar ducks
- last bronchiole before
alveoli
Terminal bronchiole
- exhibit alveoli
-wall consists entirely of
alveoli
Respiratory bronchioles
- terminate in sacs of alveoli
Alveolar duct
- consist of two or more
alveoli
=
Alveolar sac
– structure in lung where gas
exchange takes place
Alveoli
Respiratory Zone
Respiratory bronchioles-alveolar ducts (lead into alveolar sacs)
Overall Histological changes as respiratory passages branch:
1. loss of cartilage
2. proportional amount of smooth muscle increases (though it is absent in alveoli)
3. gradual thinning of epithelium
1° bronchi àtertiary bronchi- psuedostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
bronchioles - simple columnar epithelium (w/ globlet cells)
terminal bronchioles - simple cuboidal
ducts + sacs- simple squamous - smooth muscle
alveoli - very elastic - have elastic fibers
What are the three types of Aveolar
-Type I alveolar cells
macrophages
-Type II alveolar cells
-- form alveoli – site of gas
exchange
-Type I alveolar cells
("dust cells") remove
dirt and debris from alveolar space
macrophages
-secretes surfactant - prevents
alveolar collapse upon recoil
-secrete alveolar fluids-keeps air
moist
-secretes antimicrobial proteins
-Type II alveolar cells
-the barrier that respiratory gases must pass during external respiration
*Membrane made up of alveolar wall and capillary wall
The Respiratory Membrane (alveolar capillary membrane):
Paired organs in thoracic cavity
-Fissure divide the lungs into lobes
- Right lung 3 lobes
- Left lung 2 lobes
-Left lung about 10% smaller
than right lung
=
Lungs
Each lung enclosed by double-layered pleural membrane
Parietal pleura
Visceral pleura
most superficial
lines wall of thoracic cavity
Parietal pleura
covers lungs themselves
Visceral pleura
space between layers
Pleural cavity
reduces friction, produces surface tension
Pleural fluid
inflammation of pleural membrane-
causes pain due to friction between layers- if it
persists, excess fluid is produced and accumulates
in pleural space -pleural effusion
Pleurisy=pleuritis-
- lung collapse usually just part of lung;
rarely entire lung
Atelectosis
-is 760mmHg at sea level
external air pressure
atmospheric pressure (Patm)
(during quiet inhalation pressure
inside alveoli decreases to 758mmHg
-air pressure in alveoli
- Alveolar pressure (Palv)=
(always about 4 mmHg less
than alveolar pressure- this must be
maintained to prevent collapse of lungs
pressure exerted by pleural
fluid in pleural cavities
intrapleural pressure (Pip)
n involves changing volume of thoracic cavity to produce
pressure gradients (drives air into or out of lungs)
Pulmonary Ventilation
describes the relationship between the pressure and
volume of a gas.

Boyles law
In the lungs- when the lungs expand, lung volume increases,
and pressure inside the lungs falls below atmospheric pressure
and air moves into the lungs. what happens to the diaphragm
diaphragm contrast ( lungs inhale)
In the lungs- when lung volume decreases (expiration), pressure
inside the lungs is greater than the atmospheric pressure
(pressure increases) and air moves out of the lungs. What happens to the diaphragm
diaphragm relaxes lungs exhale
nInvolves muscle contraction.
*air moves into lungs when the air pressure inside the lungs is less than the air pressure in the
atmosphere.
Inspiration is active
– most important muscle of inhalation
Flattens, lowering dome when contracts, this increase in volume decreases the pressure inside the lungs below atmospheric pressure and allows air to enter
Responsible for 75% of air entering lungs during normal quiet breathing
Diaphragm
Contraction elevates ribs
this increases the volume by increasing the diameter of the thoracic cavity
25% of air entering lungs during normal quiet breathing
External intercostals
Accessory muscles for deep, forceful inhalation
sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis minor,and scalenes
Normally passive – muscle relax instead of contract
due to elastic recoil of lungs and chest wall
Exhalation
Forced expiration (active) involves contraction of abdominal muscles and internal intercostals -occurs during exercise and playing wind instruments.
Forced Expiration
What are the 3 nfactors affect rate of airflow and ease of pulmonary ventilation
Alveolar Surface Tension
Lung compliance
Airway resistance

Alveolar Surface Tension

Lung compliance

. Airway resistance
Ventilation can be measured using a
spirometer