Lab 8: Urinary System Anatomy, Histology, and Physiology
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What are the basic functions of the urinary system?
Maintenance of homeostasis, most directly performed by the kidneys which also function in:
Removal of metabolic wastes
Maintenance of fluid balance, electrolyte balance, acid-base balance, and blood pressure
Regulation of erythropoiesis
Detoxification
Activation of vitamin D
Gluconeogenesis
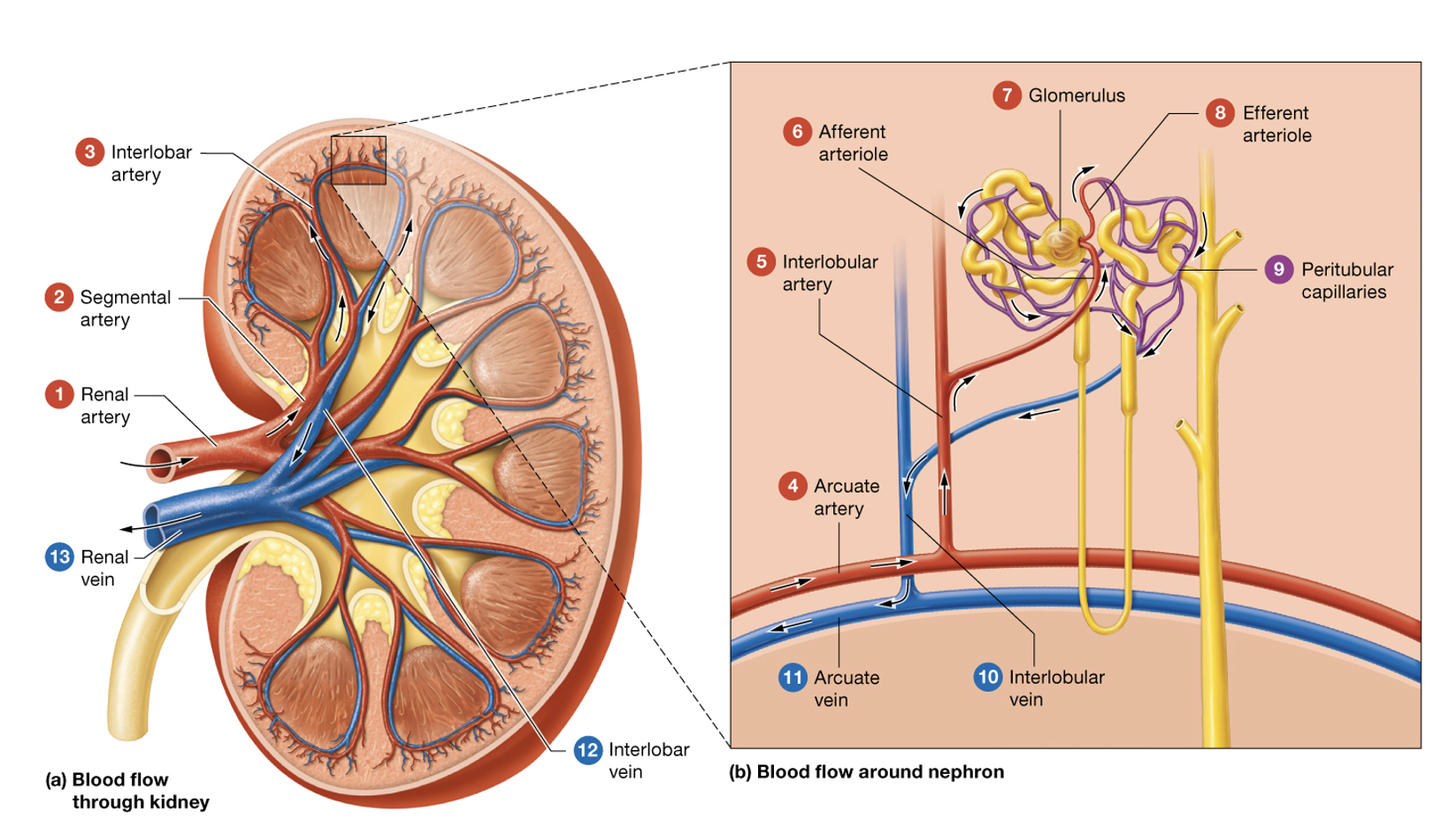
What is the pathway by which blood flows through the kidneys.
Renal artery → segmental artery → interlobar artery → arcuate artery → interlobular artery → afferent arteriole → glomerulus → efferent arteriole → peritubular capillaries → interlobular vein → arcuate vein → interlobar vein → renal vein
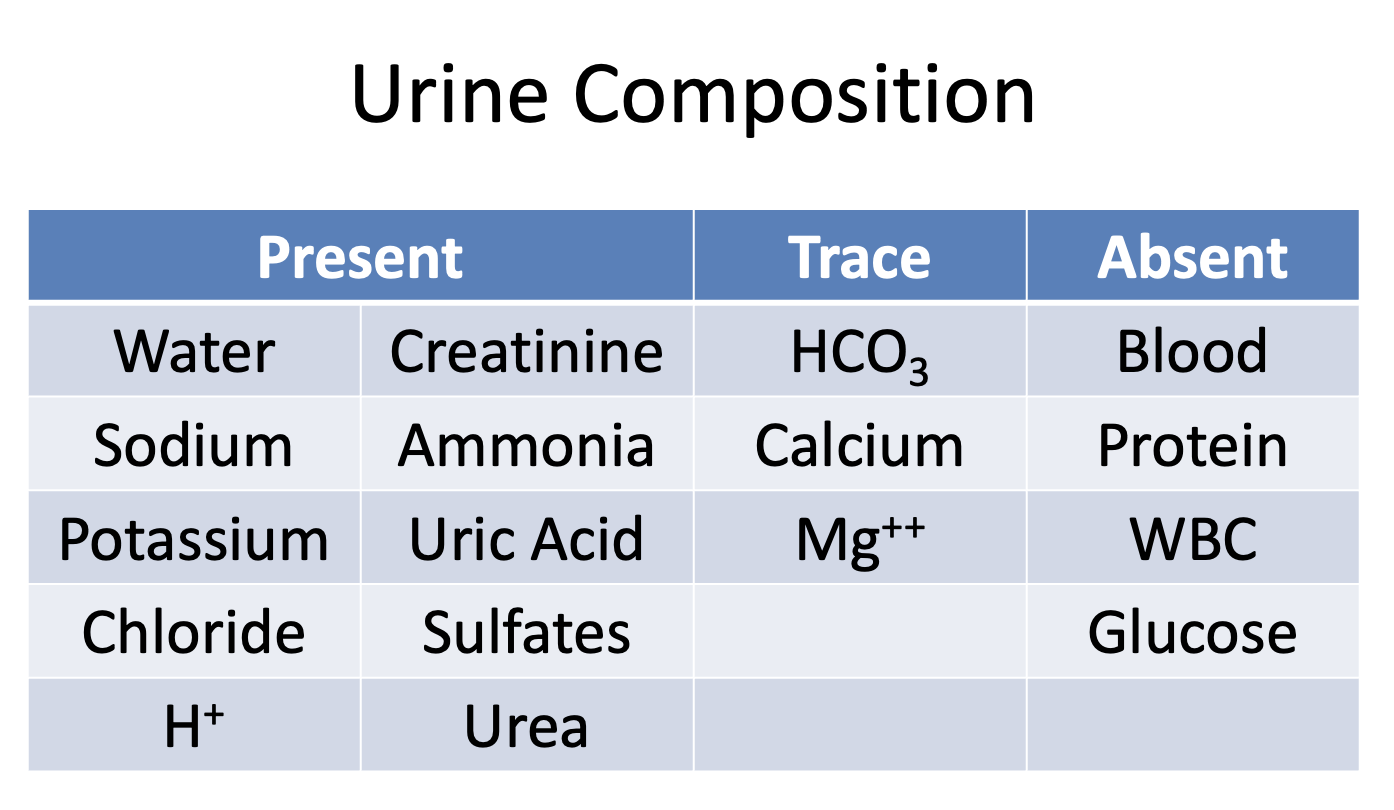
What substances are present in the urine?
Wise Cats Sing About Pretty Unique Chants Secretly, Hiding Undercover
Water
Creatinine
Sodium
Ammonia
Potassium
Uric Acid
Chloride
Sulfates
H+
Urea
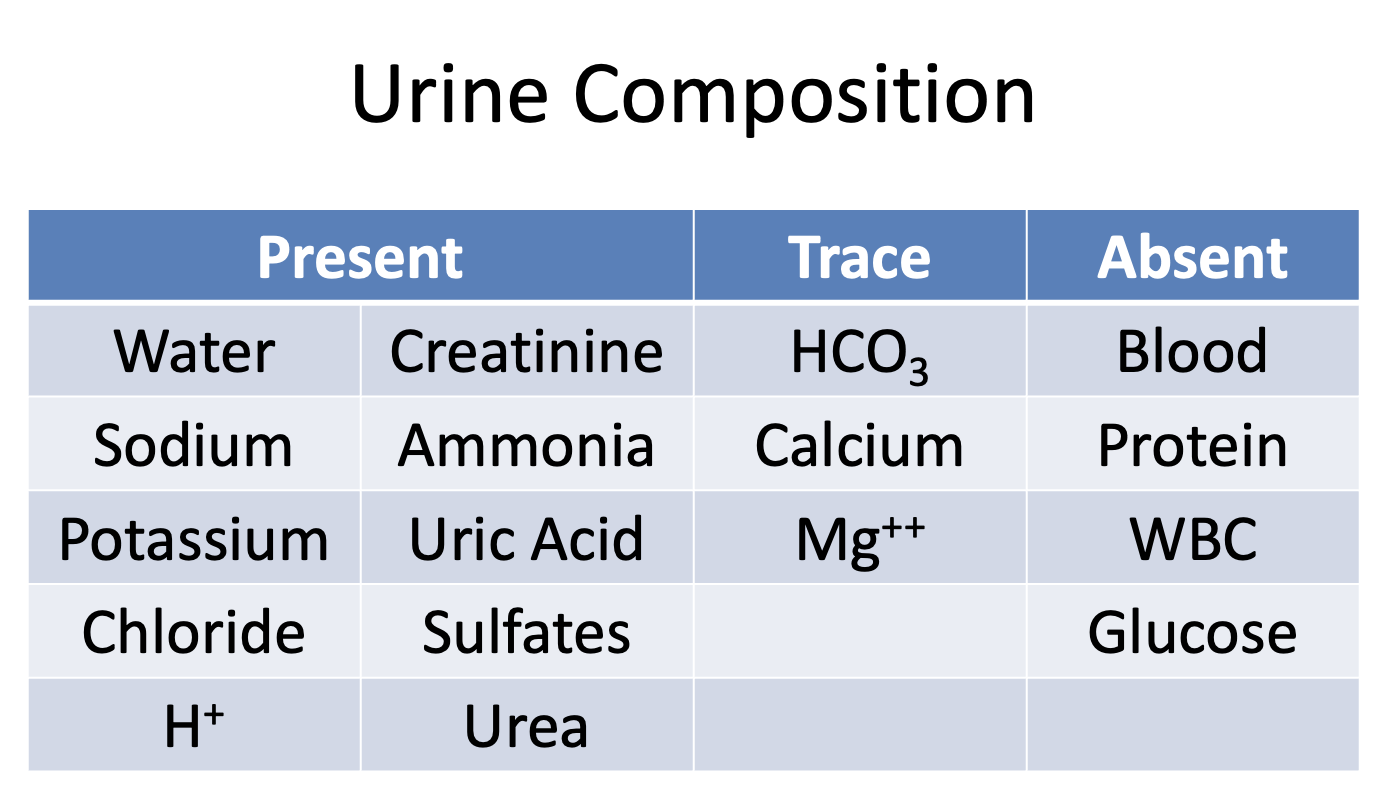
What substances are there only traces of in the urine?
HCO3
Calcium
Mg++
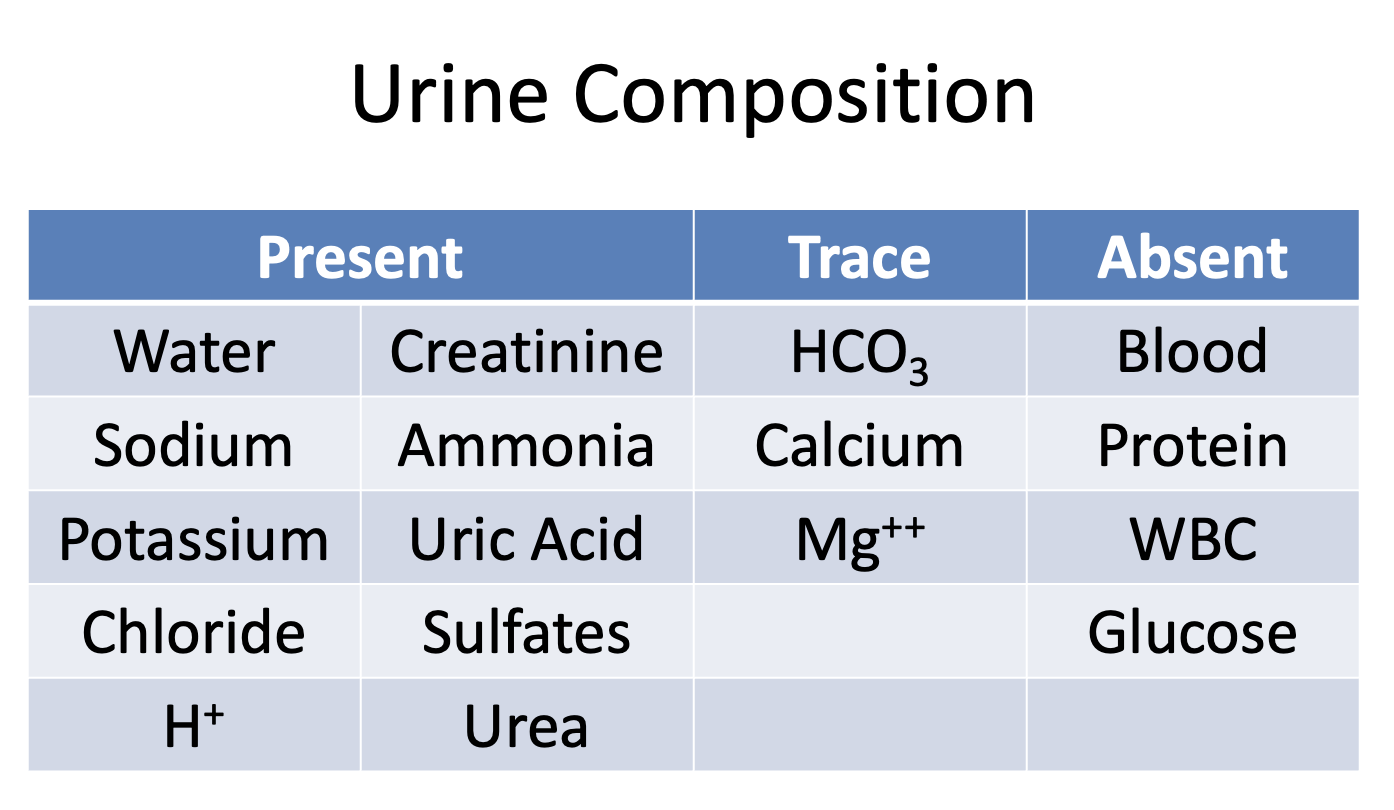
What substances are absent in the urine?
Blood
Protein
WBCs
Glucose
Which characteristics of the urine are assessed in a urinalysis?
Color
Translucency
Odor
pH
Specific gravity
What is considered normal for the color of urine in a urinalysis?
Yellow due to urochrome (a hemoglobin breakdown product)
May be altered by foods, vitamins, drugs, dyes, and blood
What is considered normal and abnormal for the translucency of urine in a urinalysis?
Normal - transluscent
Abnormal - cloudy, may indicate an infection or large amounts of protein
What is considered normal for the odor of urine in a urinalysis?
Mild odor
May be altered by diseased states (ex: diabetes mellitus), infection, and foods
What is considered normal and for the pH of urine in a urinalysis?
6.0
May range from 4.5-8.0
What is considered normal and abnormal for the specific gravity of urine in a urinalysis?
1.001-1.035
What does specific gravity measure in a urinalysis?
The concentration of dissolved solids in urine
Indicates hydration levels and kidney function
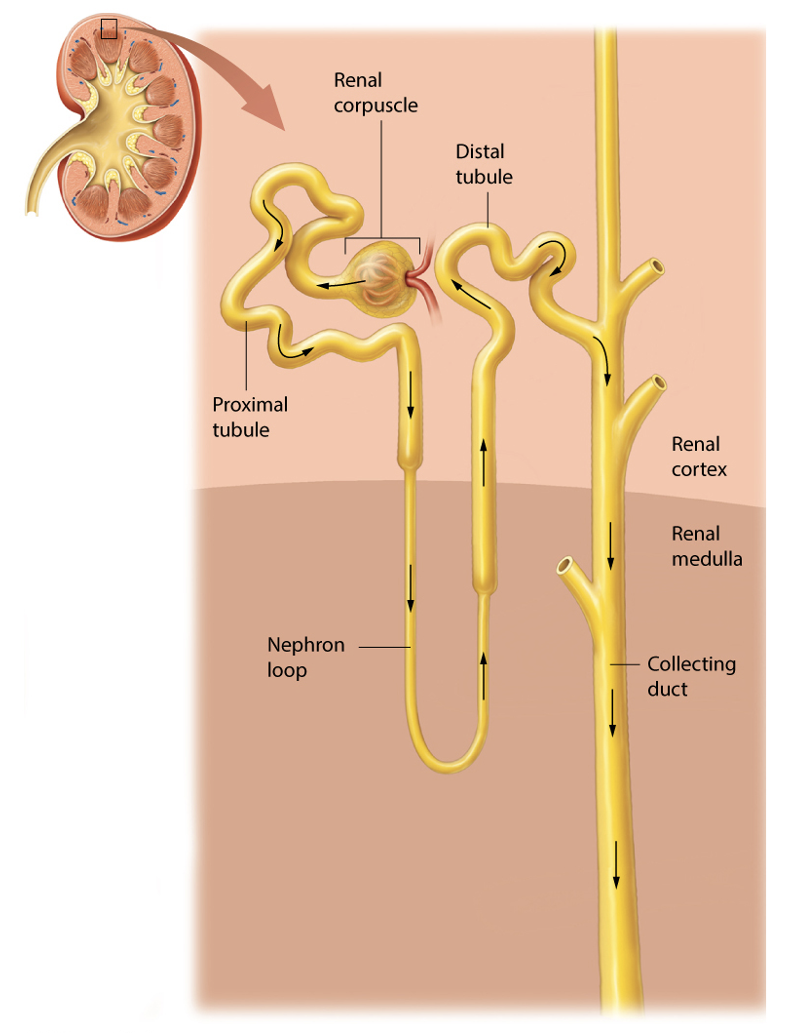
List and draw the structures of a nephron.
Renal corpuscle
Glomerulus
Glomerular capsule
Renal tubule
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Loop of Henle
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
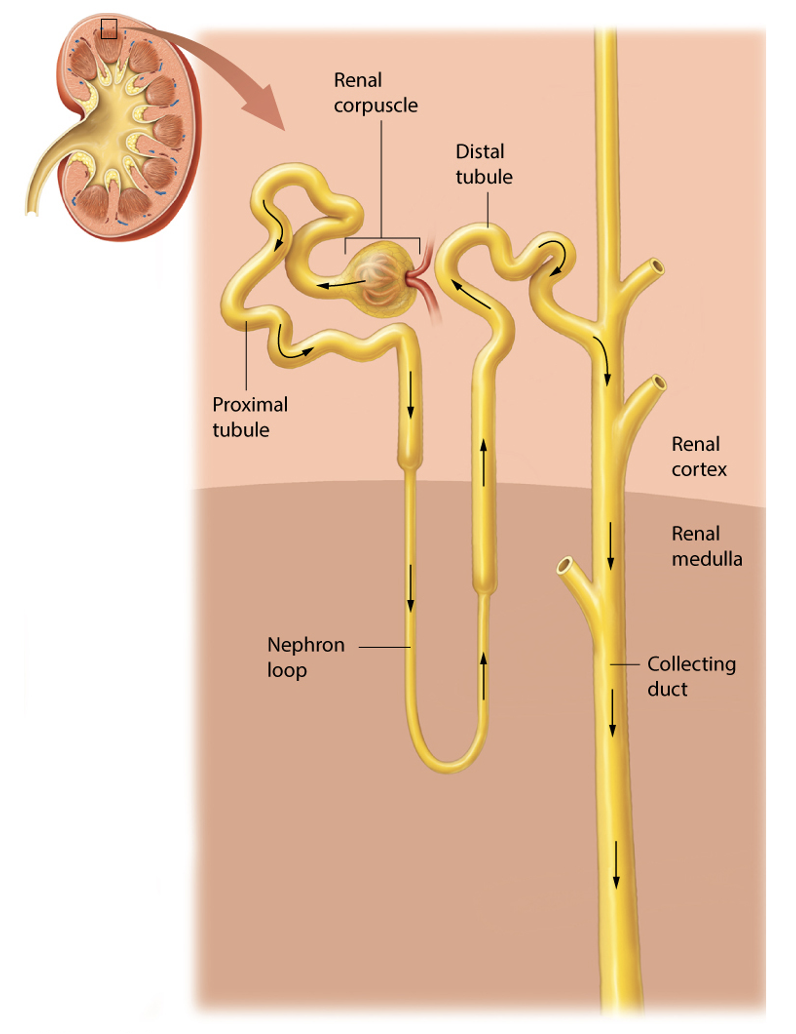
What are the functions of a nephron (and it’s divisions)?
Blood filtering
Reabsorption of nutrients, water, and ions
Secretion of H+ and waste products into the filtrate
Transportation of salts out of the filtrate