Usmle step 2 Hematology
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
G6PD deficiency
PX
Recurrent Hemolytic Crises
Sudden Onset
Jaundice, Dark Urine
transient Splenomegaly
Recurrent severe Infections
African-American pts.
Heniz bodies—small inclusions w/in erythrocytes
Bite Cells
↑ Reticulocyte count
Thalasemmia
Labs
Microcytic, Hypochromic Anemia, ↓ MCV, MCH
Hemoglobin A2
Target cells
Teardrop cells
Mixed Cryoglobulinemia syndrome
Fatigue
papable Purpura
Arthragias
Renal disease
Cryoglobulins
↓ complement
(+) rheumatoid factor
↑ transminases
Kidney injury
Anemia
Lymphoproliferative disorder
Fatigue
Lymphadenopathy
Splenomegaly
↓ RBC production
Sickle Cell Disease
Hemoglobin Eletrophoresis
⦸ Hemoglobin A
Hemoglobin A2—near normal
↑↑ Hemoglobin F
↑↑ Hemoglobin S
Sickle Cell trait
Hemoglobin Eletrophorosis
↓↓ Hemoglobin A
Hemoglobin A2—near normal
Hemoglobin F—near normal
↑ Hemoglobin S
a-Thalassemia minor
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
↓ Hemoglobin A
↑ Hemoglobin A2
Hemoglobin F—normal
⦸ Hemoglobin S
a-Thalassemia major
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
⦸ Hemoglobin A
↑↑ Hemoglobin A2
↑↑ Hemoglobin F
⦸ Hemoglobin S
Vitamin B 12 deficiency
Methylmalnoic acid develops Macrocytic anemia
Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)
_______metabolizes homocysteine into cystathionine(vitamin for hyperhomocysteinemia)
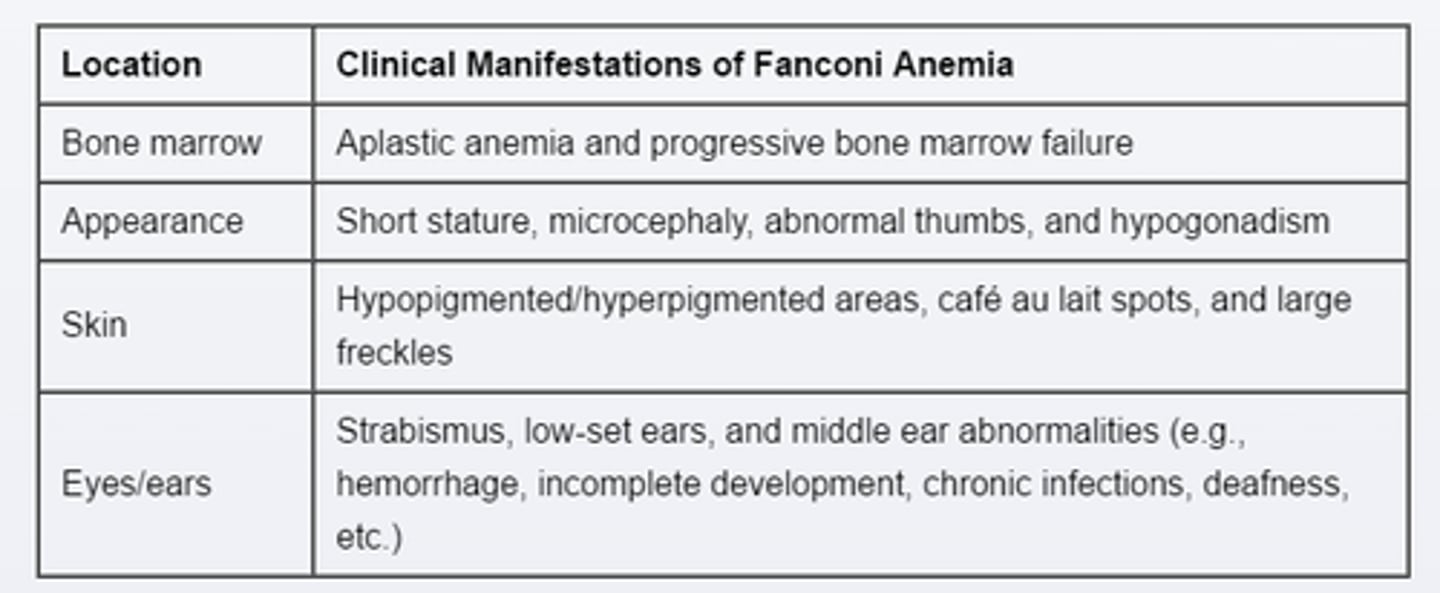
Fanconi anemia
PX
Autosomal recessive disorder
congenital marrow failure
poor growth
Short Statures, abnormal Thumbs & Forearm
Low set ears
Cafe-au-lait spots
macrocytic, Aplastic Anemia
CD40 ligand deficiency
hyper-Ig M syndrome
Immunoglobulins
B cell—normal (Total lymphocytes-T cell)
↓ IgG
↓ IgA
↑ IgM
↓ IgE
Common variable immunodeficiency
Immunoglobulins
B cell—Normal
↓ IgG
↓ IgA
↓ IgM
↓ IgE
Job syndrome
Hyper-IgE syndrome
Immunoglobulins
B cell—normal
IgG—normal
IgA—normal
IgM—normal
↑ IgE
Selective IgA deficiency
Immunoglobulins
B cell—Normal
IgG—normal
↓ IgA
IgM—normal
IgE—normal
Bruton (X-linked) agammaglobulinemia
Immunoglobulins
↓ B cell
↓ IgG
↓ IgA
↓ IgM
↓ IgE
DiGerorge syndrome (22q 11.2 deletion syndrome)
congenital heart disease
T cell deficiency
↓ Ca2+
susceptible to viral and fungal infections
Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy
Immunoglobulins
B-Cell—normal
↓ IgG
IgA—normal
variable Ig M
Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy
↑ sinopulmonary & GI infections
usually mild
Immunoglobulin levels generally normalize by age 9-15 months
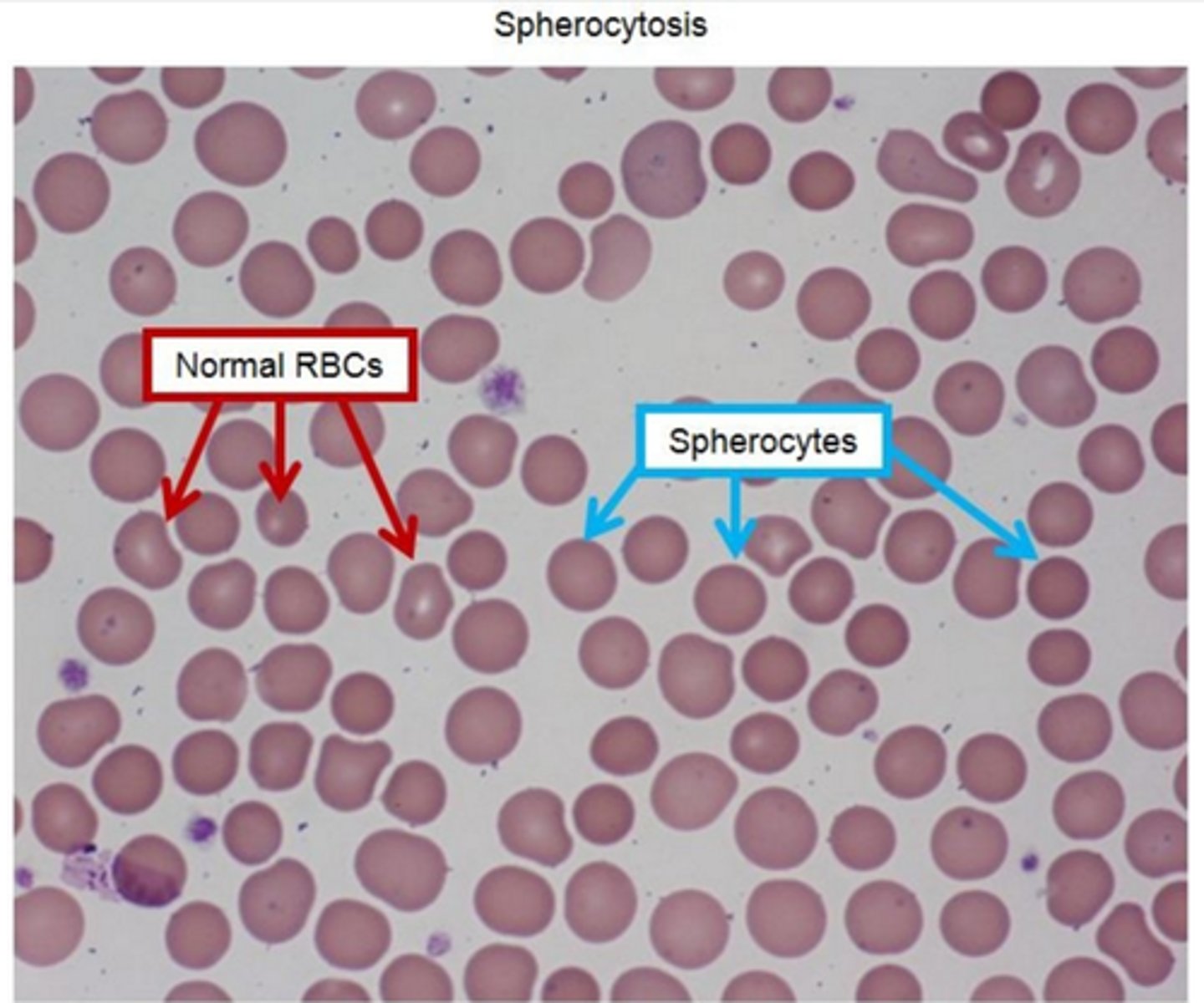
Hereditary spherocytosis peripheral blood smear present with ____
-multiple small, round, dense and hyperchromic red blood cells without central pallor
-classic triad: hemolytic anemia, jaundice, splenomegly
-↑ MCHC
-↑osmofragility on acidified glycerol lysis test, abnormal eosin-5-maleimide binding test, negative coombs test
-Supportive treatment (folic acid supplementation, blood transfusions, splenectomy)
-complications include pigment gallstones, aplastic crises from parvovirus B19 infection
Thalassemia
mild anemia with profound Microcytosis
-RDW is normal in all forms because all of the cells are of the same size
Sick cell trait + Hematuria
complication
Papillary necrosis
____would be elevated in vitamin B 12 deficiency anemia
-peripheral blood smear show large red blood cells and hypersegmented neutrophil
-Both folate and cobalamin are invovled in the conversion of Homo-cysteine to methionine
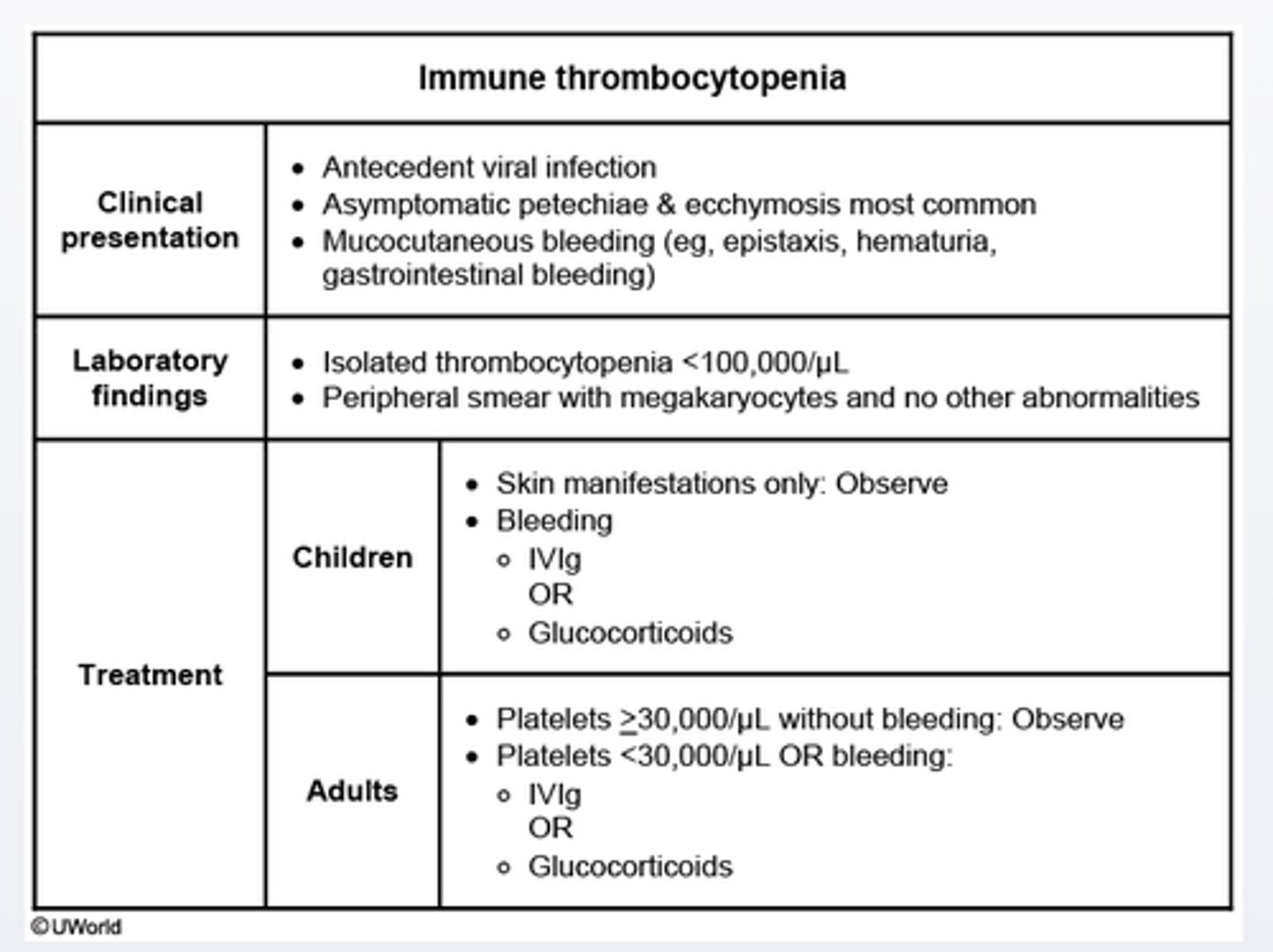
Immune thrombocytopenia treatment start when platelet_______
platelet< 30,000/ul
-children with bleeding should receive intravenous immunoglobulin or glucocorticoids
Mutiple myeloma clinical presentation_____
pts with multiple myeloma at increasesd risk for infection due to______
constituitional symptoms (weight loss, fatigue), bone pain, fractures(osteolytic lesions with factures at the 7th.8th ribs), renal insuffiency due to excessive production of monoclonal protein.
-increased risks for infection due to impaired effective antibody production
G6PD peripheral blood smear show___bodies
-an X lined hereditary cause of hemolytic anemia in which hemolytic episodes may be triggered by medications (e.g sulfa drugs)
-Peripheral blood smear may show cell with Heinz bodies
Hereditary spherocytosis usually a ___Coombs test
-usually has a strong family history (most cases are autosomal dominant), positive osmotic fragility test and a negative Coombs test
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria usually present with a ____ Coombs test
-caused by a defect in the cell membrane anchor that leads to complement-mediated hemolysis with a negative Coombs test but evidence of venous thrombosis and sometimes episodic intravascular hemolysis
Sickle cell anemia
-usually associated with a strong family history and sickle shaped cell on peripheral blood smear.
-Splenmegly may be seen in childhood, but autoslpenectomy is a more common finding by adulthood
Both hereditary spherocytosis and Autoimuune hemolytic anemia cause___vascular hemolytic anemia. A negitive family history and ____Coombs test suggest AIHA; a positive family history and a_____Coombs test suggst HS. The peripheral blood smear in both conditions may show_____
-cause extravasucular hemolytic anemia.
-A negative family history and positive Coombs test suggest AIHA; a positive family history and a negative Coombs test suggest HS
-The periphera blood smear in both conditions may show spherocytes without central pallor

Schistocytes
-seen Disseminated intravascular coagulation with fragmented red blood cells (schistocytes) and thrombocytopenia
-Sclerderma renal crisis present with acute renal failture and malignant hpyertension. Peripheral blood smear can show microangiopathic hymolytic anemia with schistocytes and thrombocytopenia
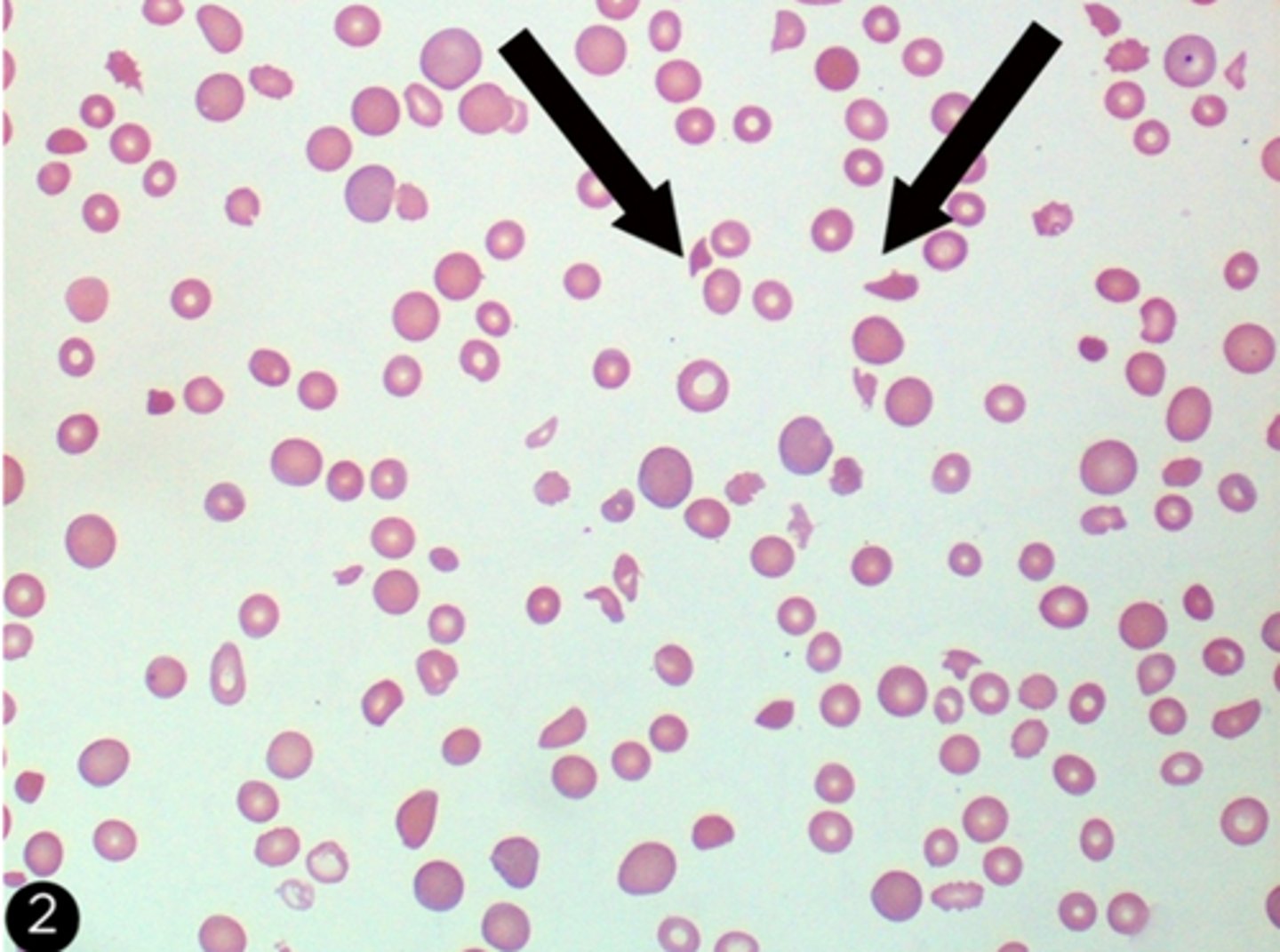
Burr cells
-also known as echinocytes are spiculated appearing red blood cells with serrated edges that can be seen in liver disease and end stage renal disease.
-However burr cells are less common in the acute kidney injury seen in sclerderma
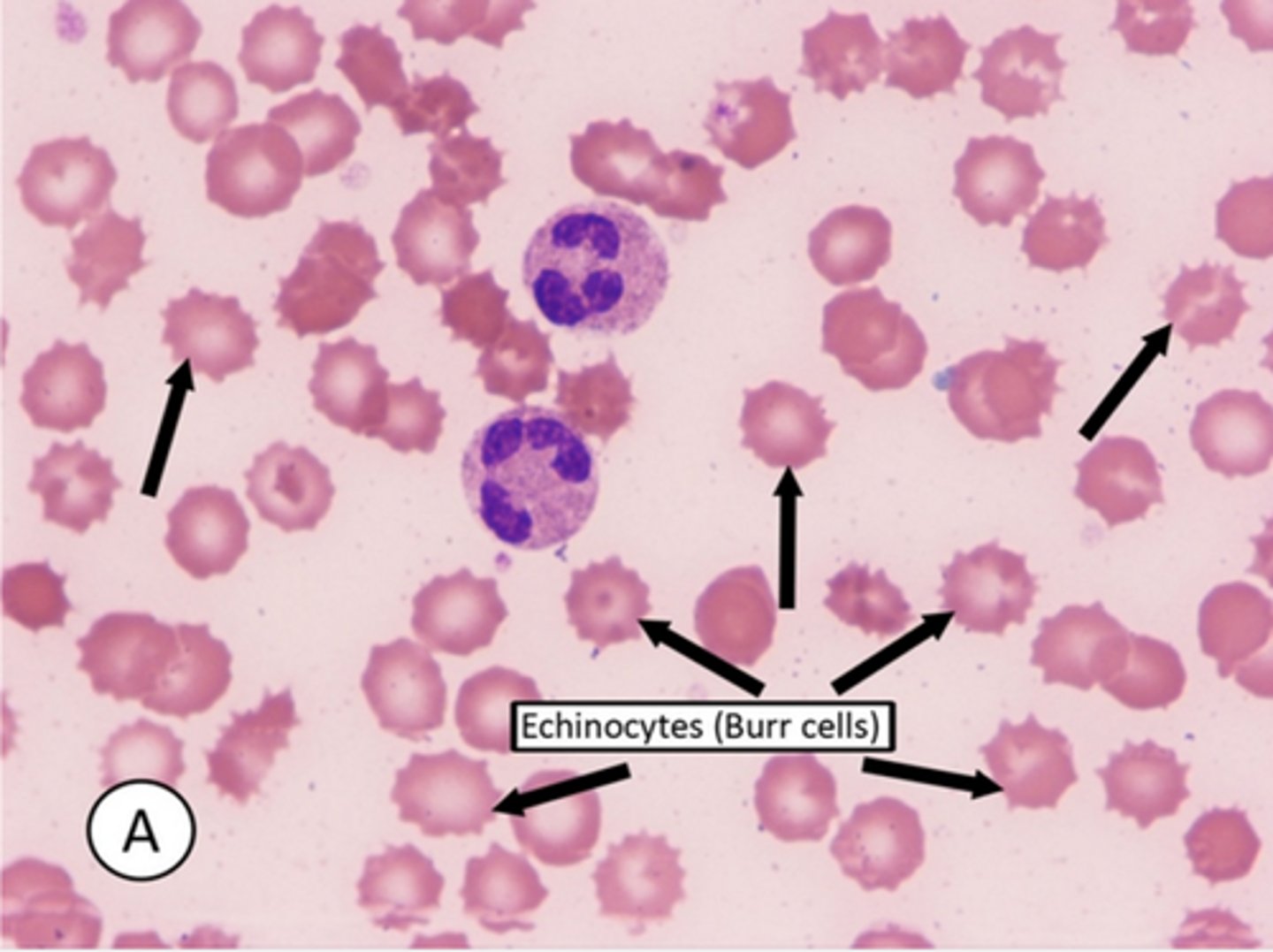
Howell-Jolly bodies
-are basophilic remnants of the nucleus that appear as small black pellets in RBCs. They are seen in pts with a history of spenectomy or functional asplenia
-HJ bodies are not seen in healthy individuals as normal spleen efficiently removes them
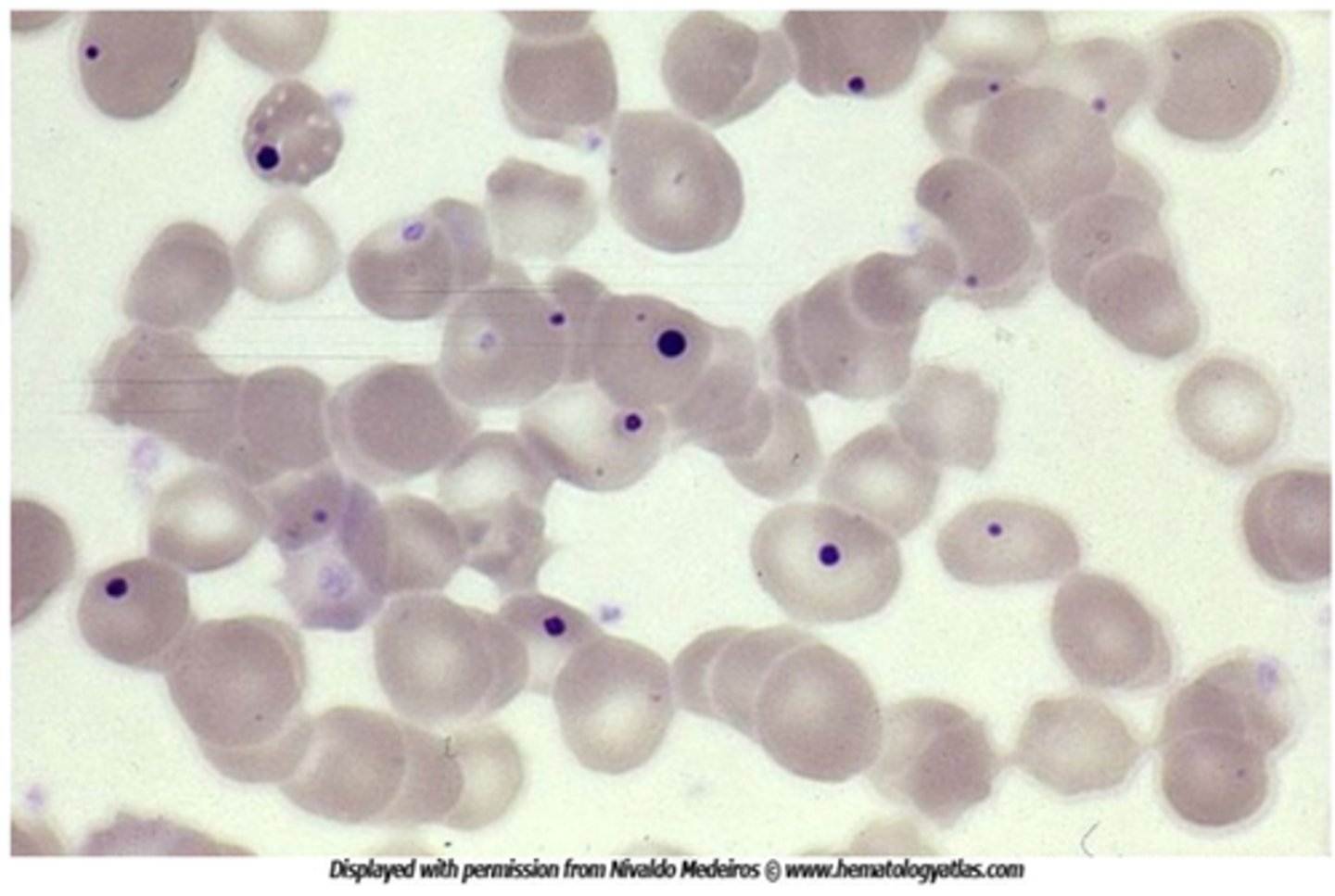
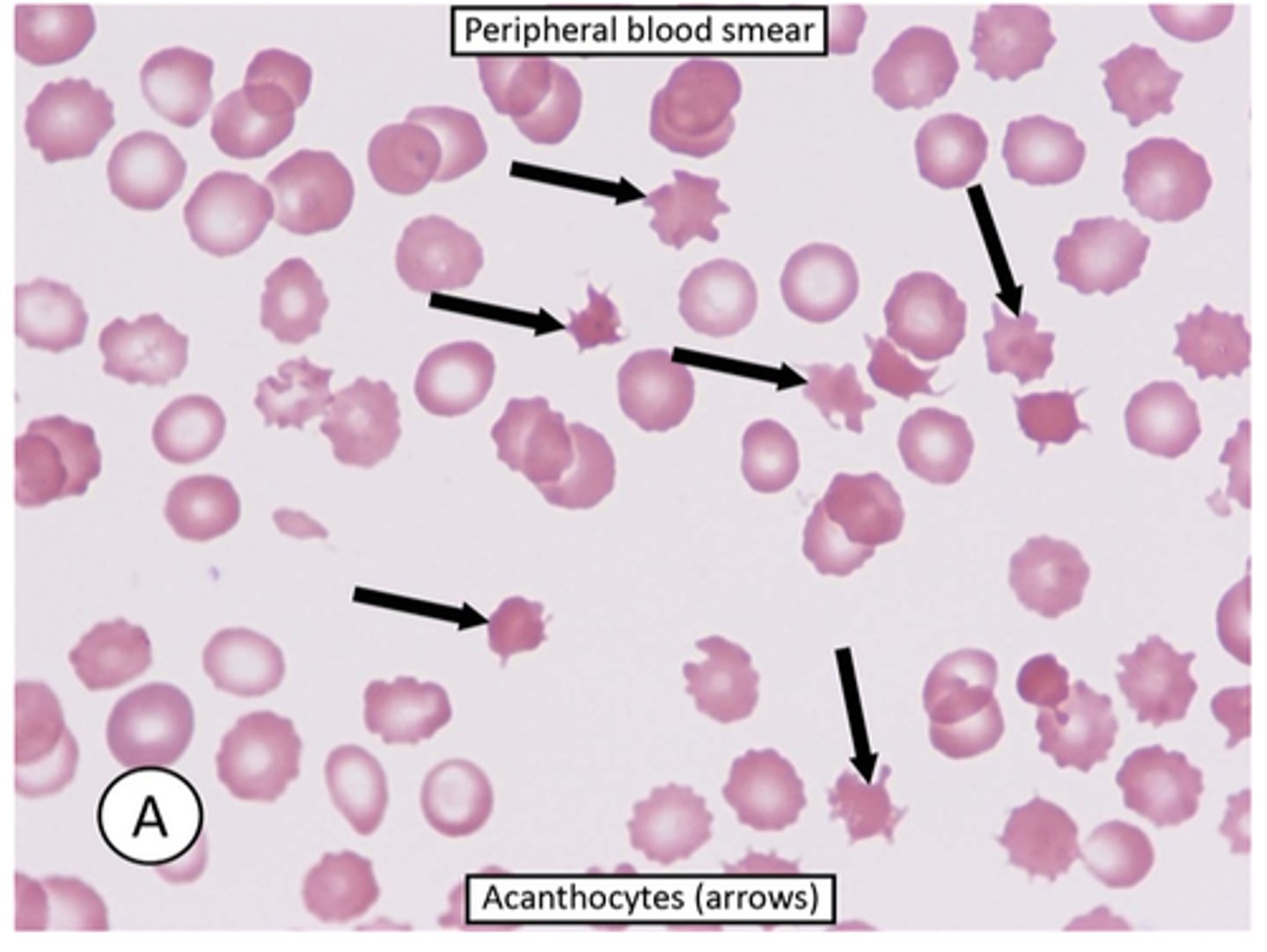
Spur cells
-acanthocytes are RBCs with irregularly sized and spaced projections that are most commonly seens in liver disease
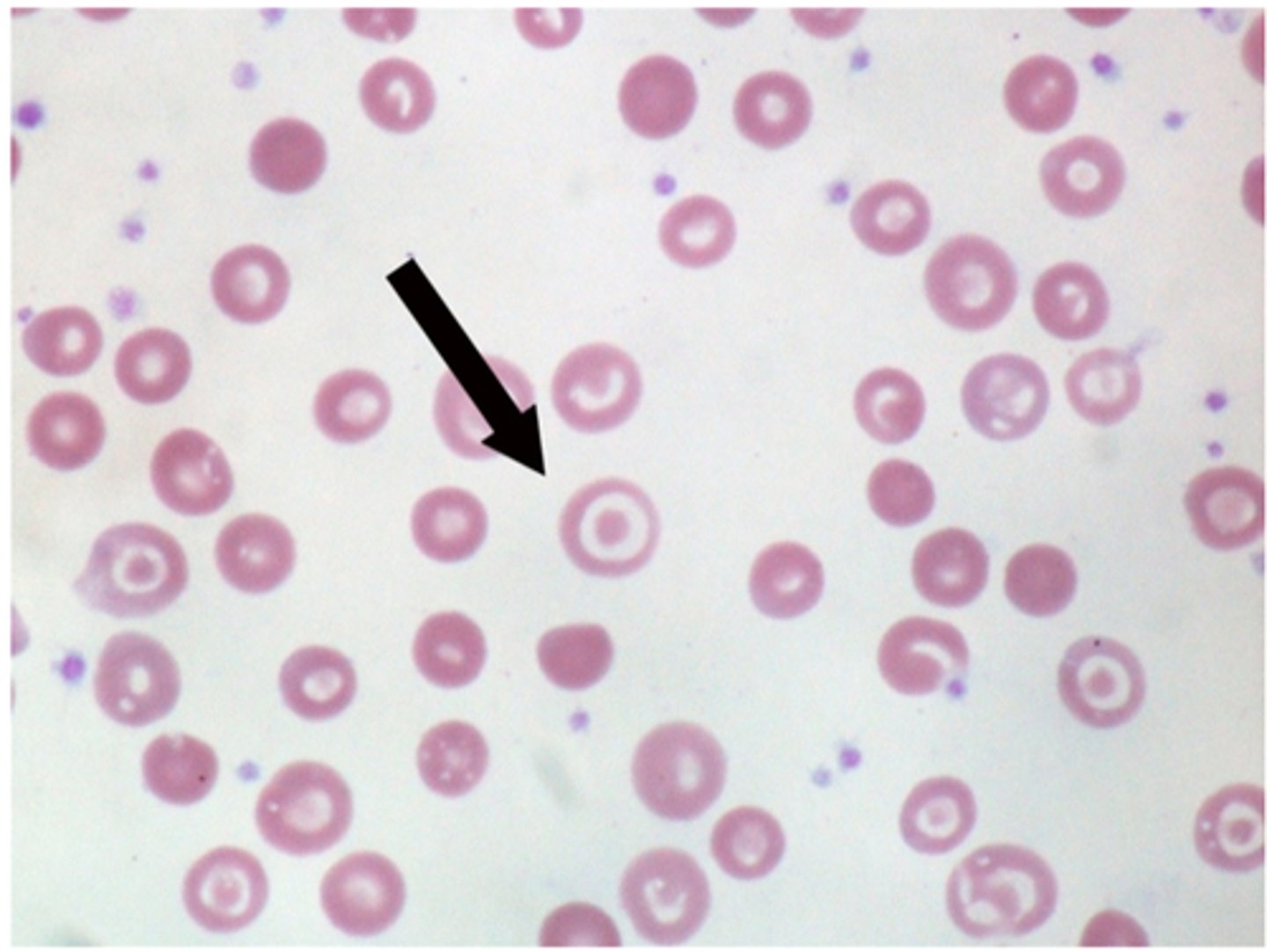
Target cells
-are red blood cells with a central density surrounded by pallor (bull's eye appearance). They are usually seen in pts with hemoglobinopathies (e.g thelassemia) or chronic liver disease (especially obstructive liver disease)
27 year old man present to ED with unremitting nose bleeding. He reports having a similar bleeding episode one year ago. On physical exam, there are several ruby-colored plapules on his lips that blanch partially with pressure. Digital clubbing is also present. Th liver span is 8 cm and the spleen is not palpable.
Lab show hematocrit 60%
WBC 8,000/mm3
platelets 180,000/mm3
_____cause for the pts's increased hematocrit
- Arterovenous shunting

Differential
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome (hereditary telangiectasia) Vs.
Polycythemia vera
OWR—Telangiectasias + Digital clubbing
PCV— ~60 y.o. + ↑ RBCs + Splenomegaly

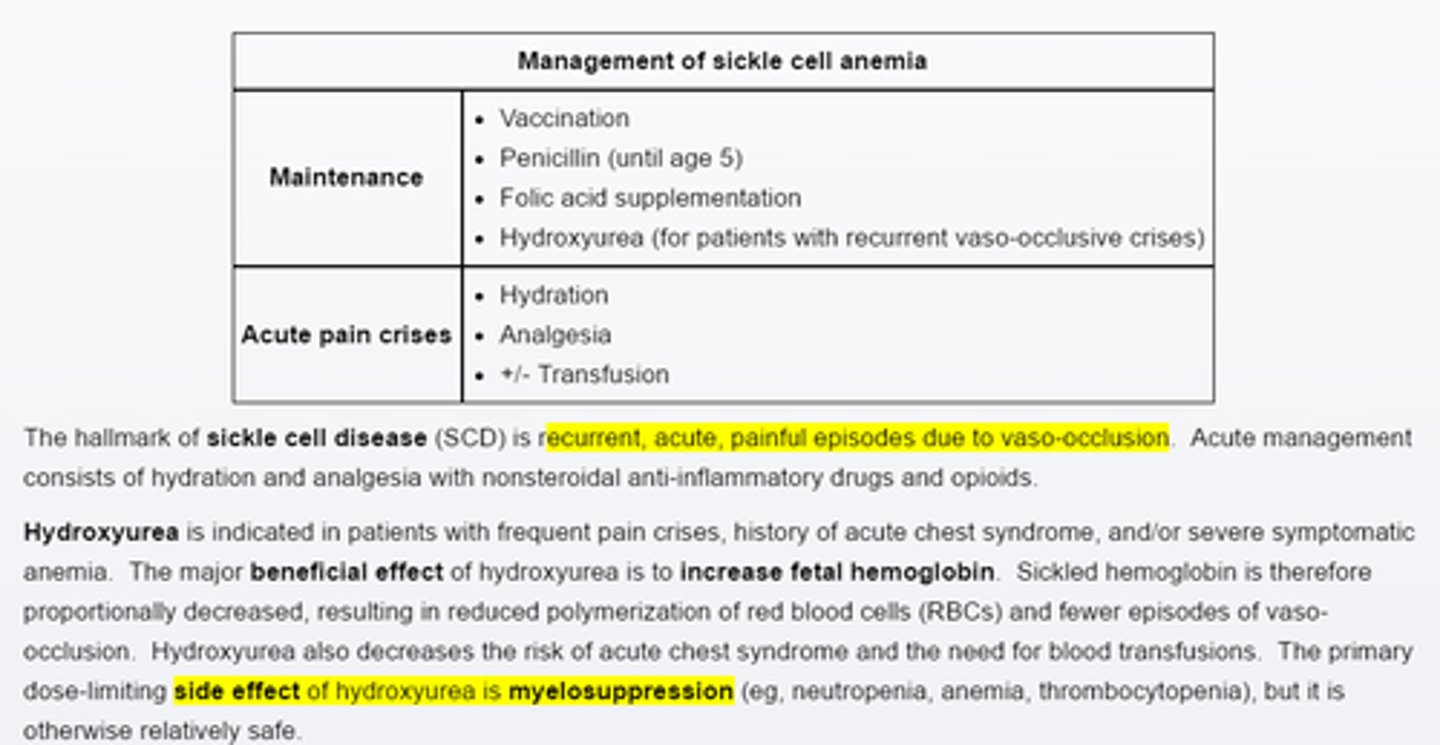
Management of sickle cell anemia, _____ is for pts with frequent pain crises. Main side effect is_____
Hydroxyurea
Myelosupression—Neutropenia, Anemia
high risk complication of pagets disease___
hearing loss due to enlargement of the temporal bone and encroachment on cochlea
Potential complications of multiple myeloma___
can cause bone pain and focal lytic lesions
acute and chronic kidney injury
Hypercalcemia
systemic symptoms.

Severe Combine Immunodeficiency (SCID)
pts present in infancy with severe infections, failture to thrive and chronic diarrhea, CD19 low, CD3 abscent,
Ig G 220 mg/dl (650-1500)
Ig A 45mg/dl (76-390)
Ig M 18 mg/dl (40-345)
Pernicious anemia most common cause of _____in ______
- common cause of vitamin B 12 deficiency in whites of northern european ancestry
-suspected in pts with megloblastic anemia, atrophic glossitis (shiny toungue), viertiligo, thyroid disease, and neurologic abnomalities
Isoiazid cause_____anemia
-isoniazid use is associated with 2 major side effects, peripheral neuropathy and hepatotoxicity
-can cause sideroblastic anemia
carcinoid syndrome present with_____(cardiac valvular disease)
-tricuspid regurgitation

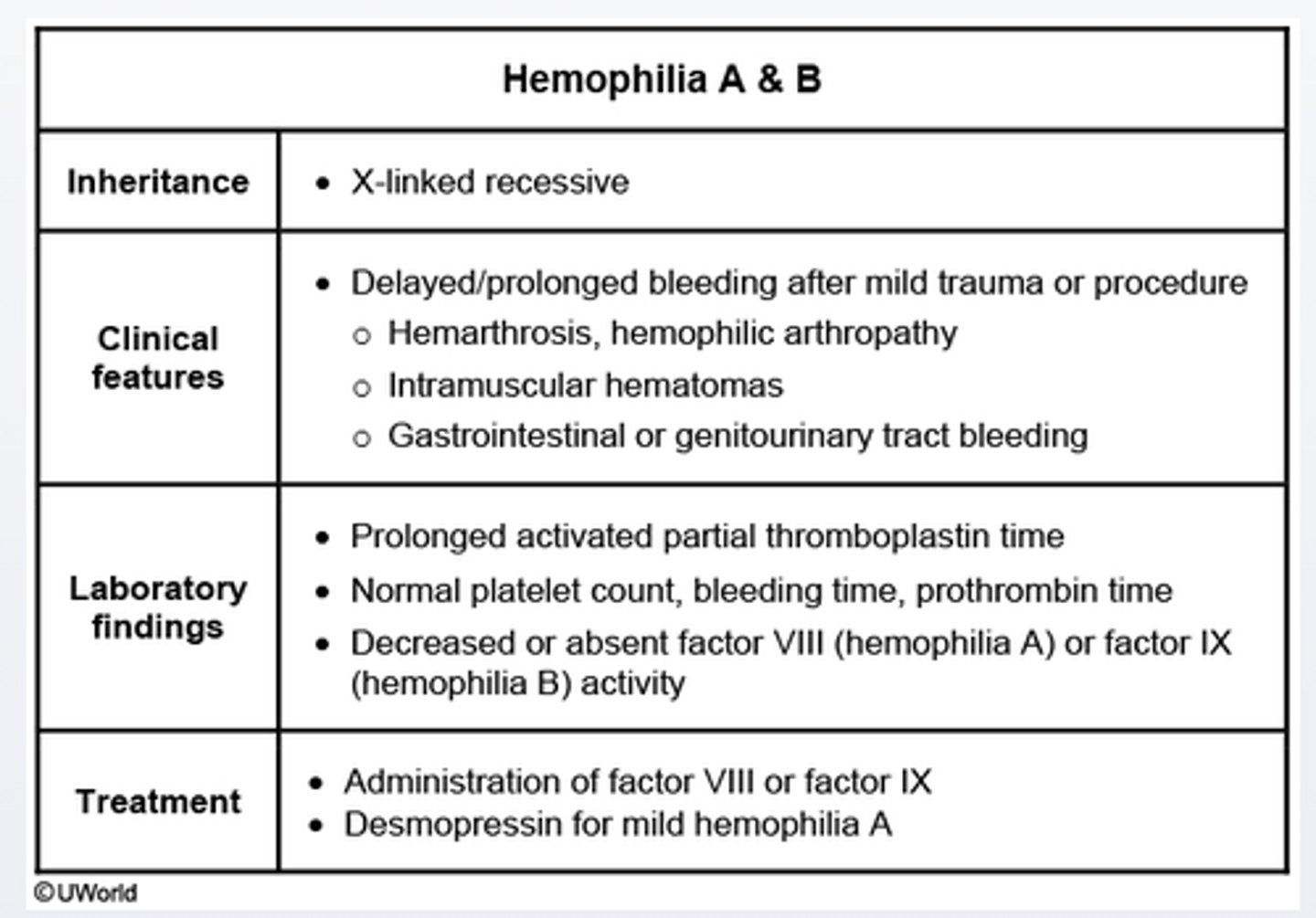
Hemophilia A & B
Recurrent hemarthrosis and skeletal muscle hemorrhage after mild trauma are the common manifestations of this disorder
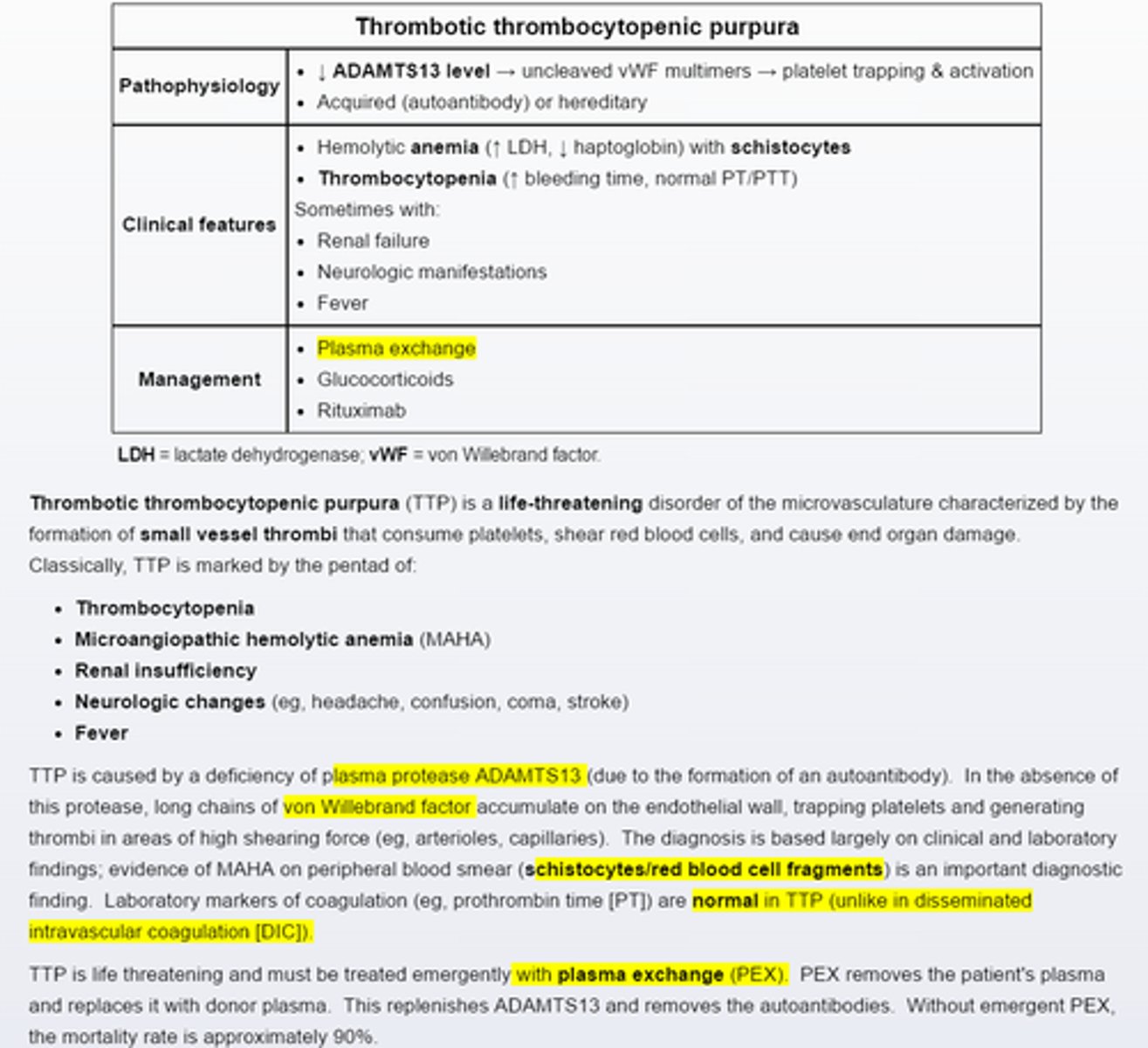
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
-caused by autoantibodies to plasma protease ADAMTS 13 and is marked by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia
-TTP is life threatening and requires emergent treatment with plasma exchange
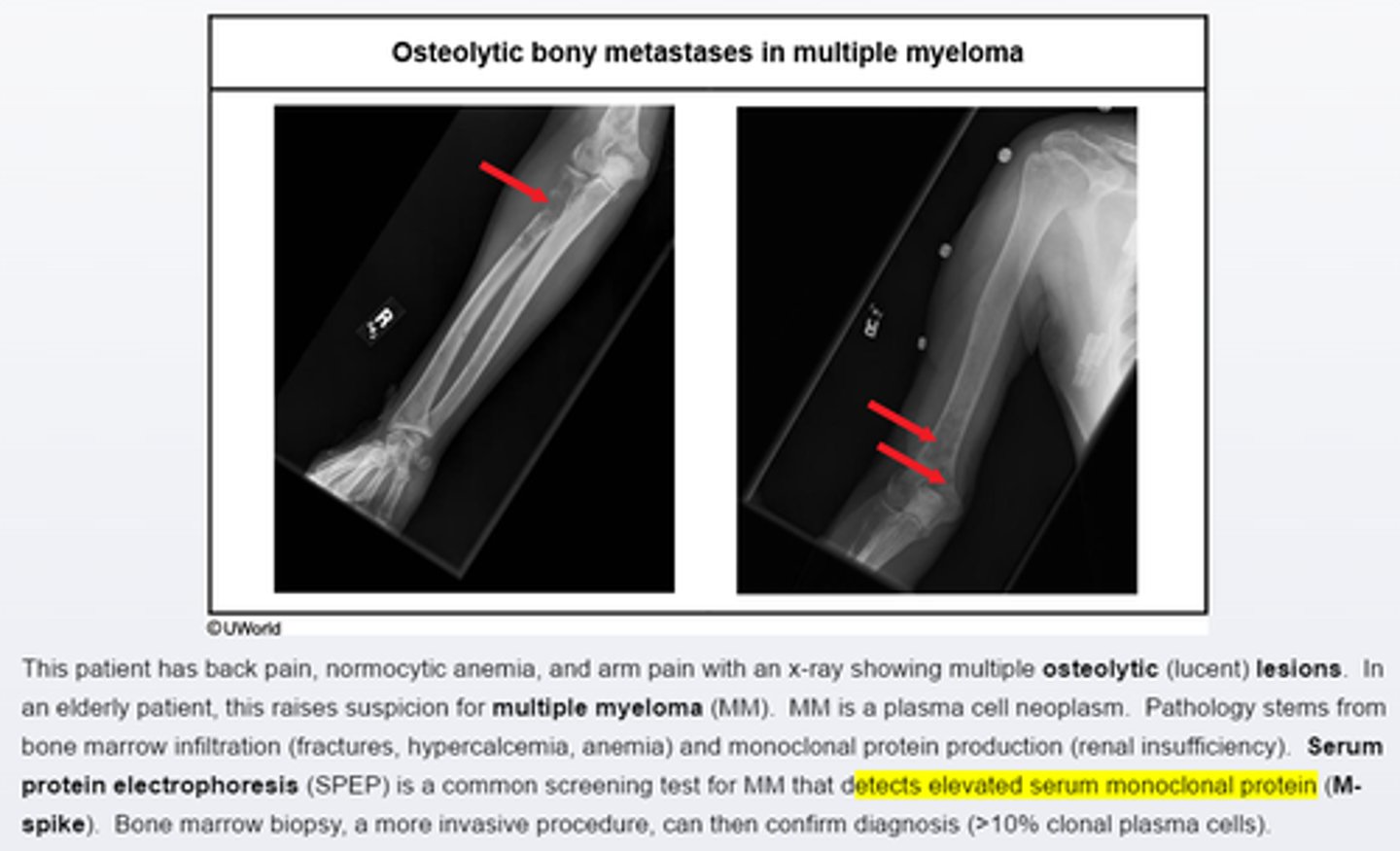
Multiple myeloma present with__ and ___on x ray
-bone pain is common presenting syndrome in multiple myeloma
-elderly pts wtih evidence of osteolytic lesions on X ray should suspect MM
-screening test is serum/urine protein electrophoresis
-diagnosis can be confirmed with bone marrow biopsy
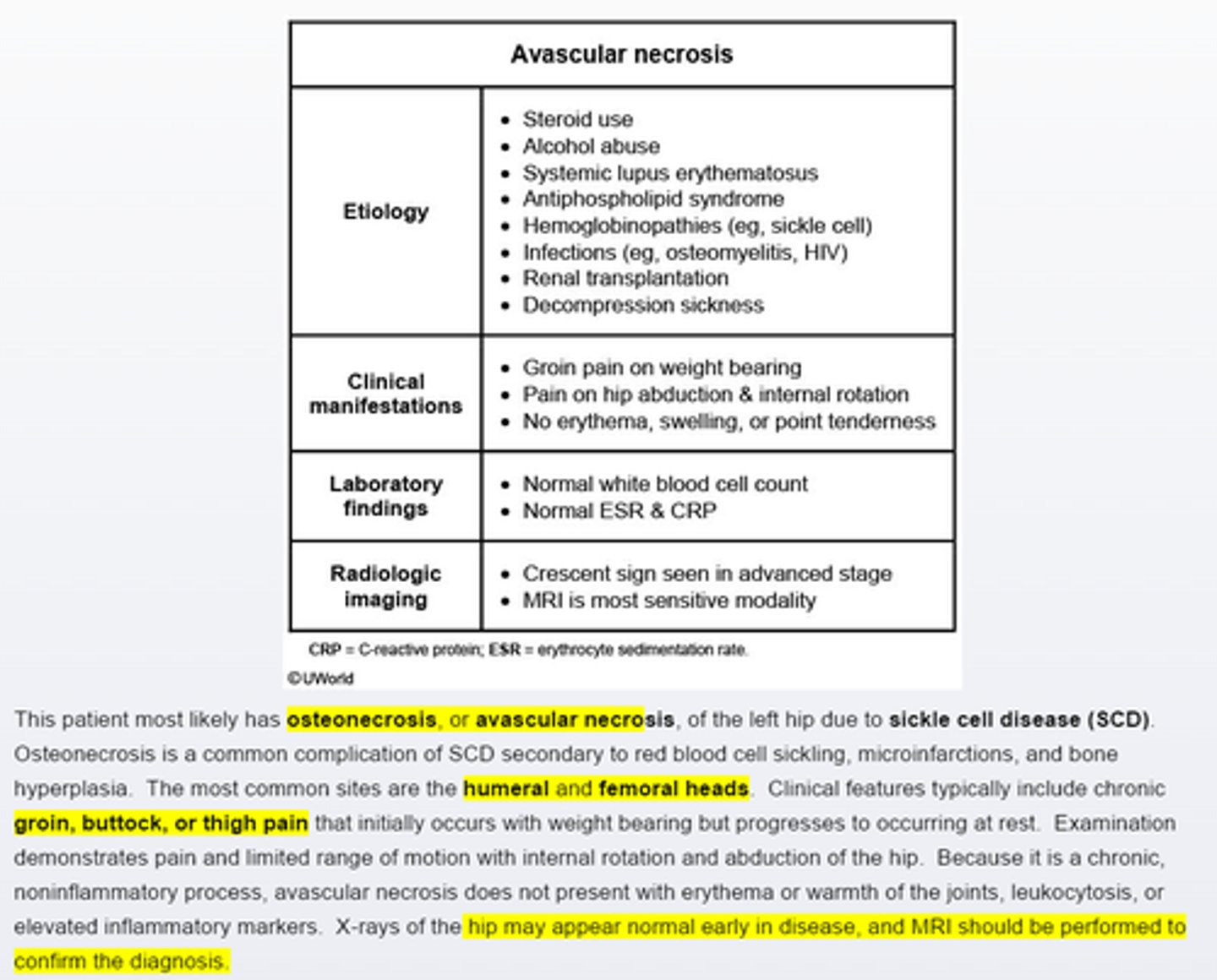
sickle cell disease develop left thigh pain on flexion, extension, and rotation of the left hip, with restricted range with motion is due to___
avasuclar necrosis
Osteoid osteoma
appears as sclerotic ,cortical lesion on imaging with a central nidus of lucency. Typpically causes pain that is worse at night and unrelated to activity. However, the pain is quickly relieved by Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medications
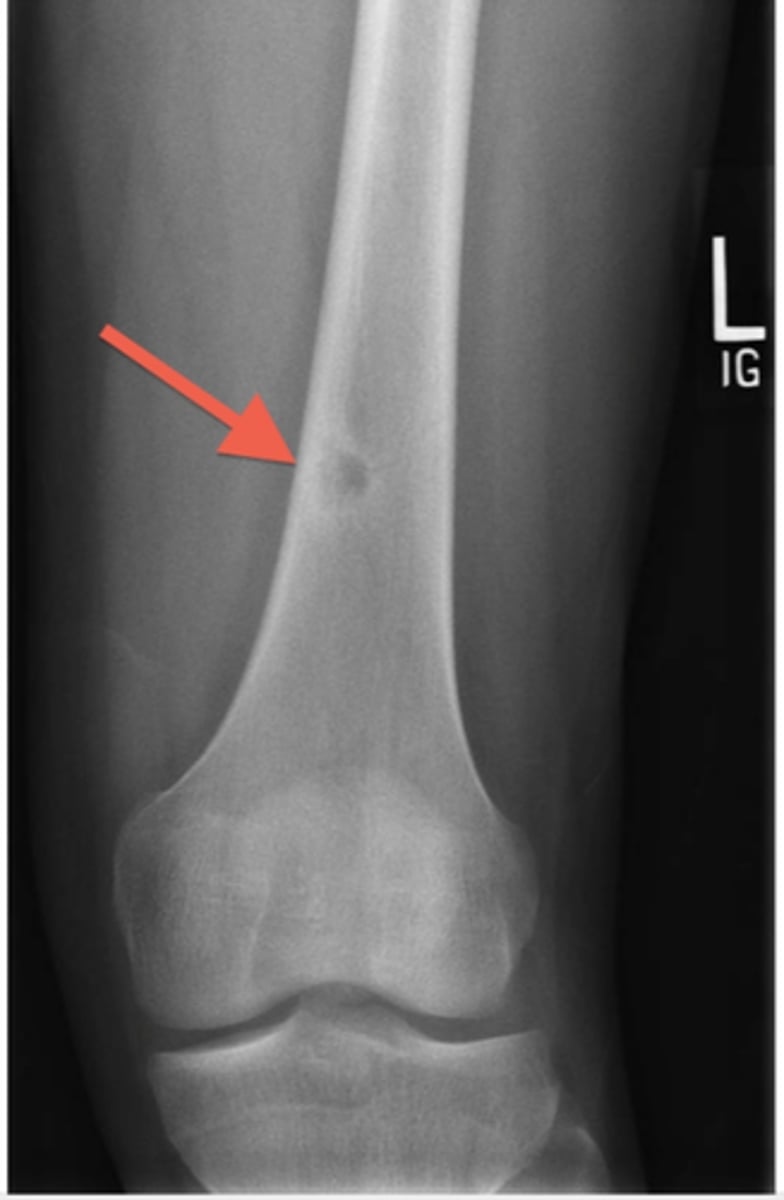
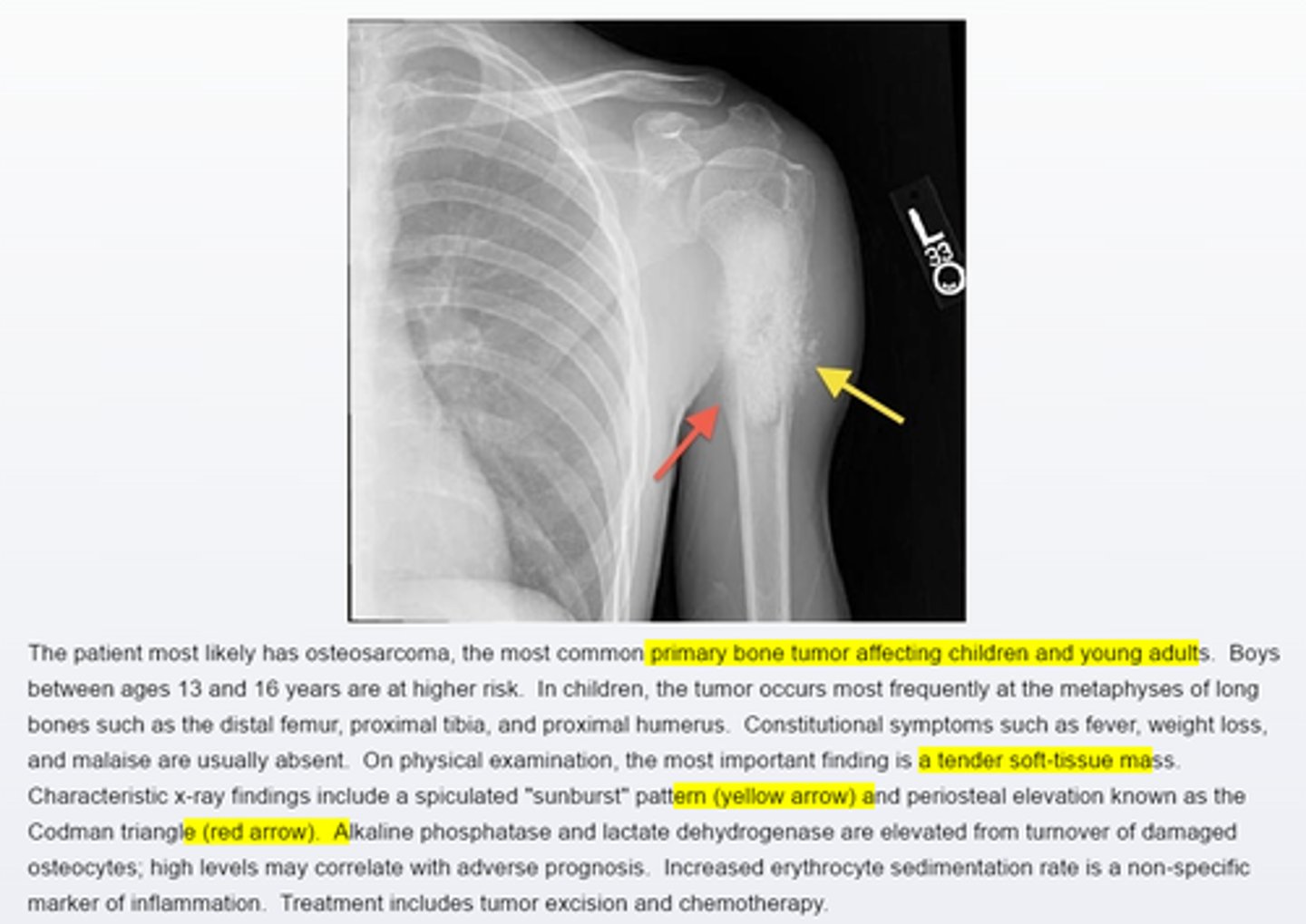
Osteosarcoma
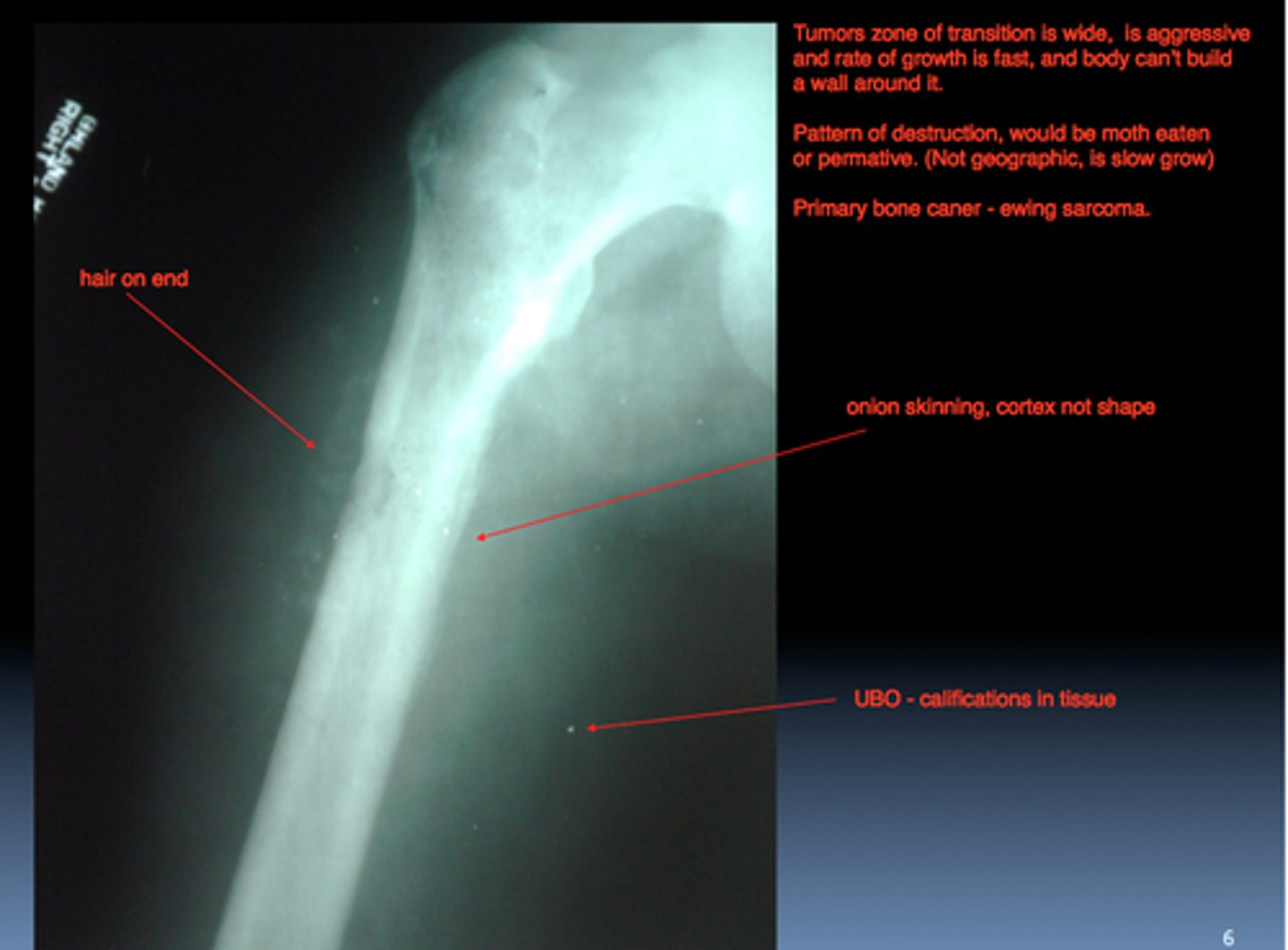
Ewing sarcoma
X ray shows an osteolytic lesion with a periosteal reaction that produces layers of reactive bone, giving the classic onion skin appearance
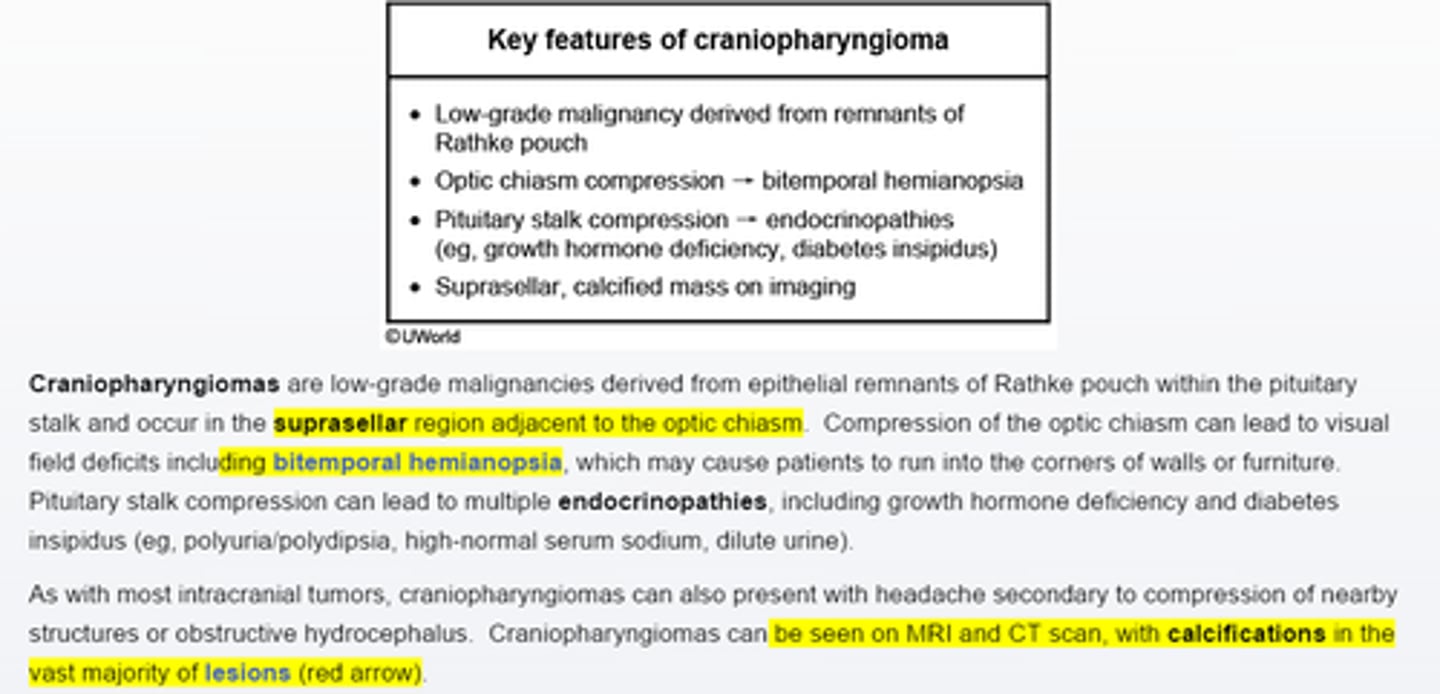
craniopharyngioma
craniopharyngioma differentiate diagnosis

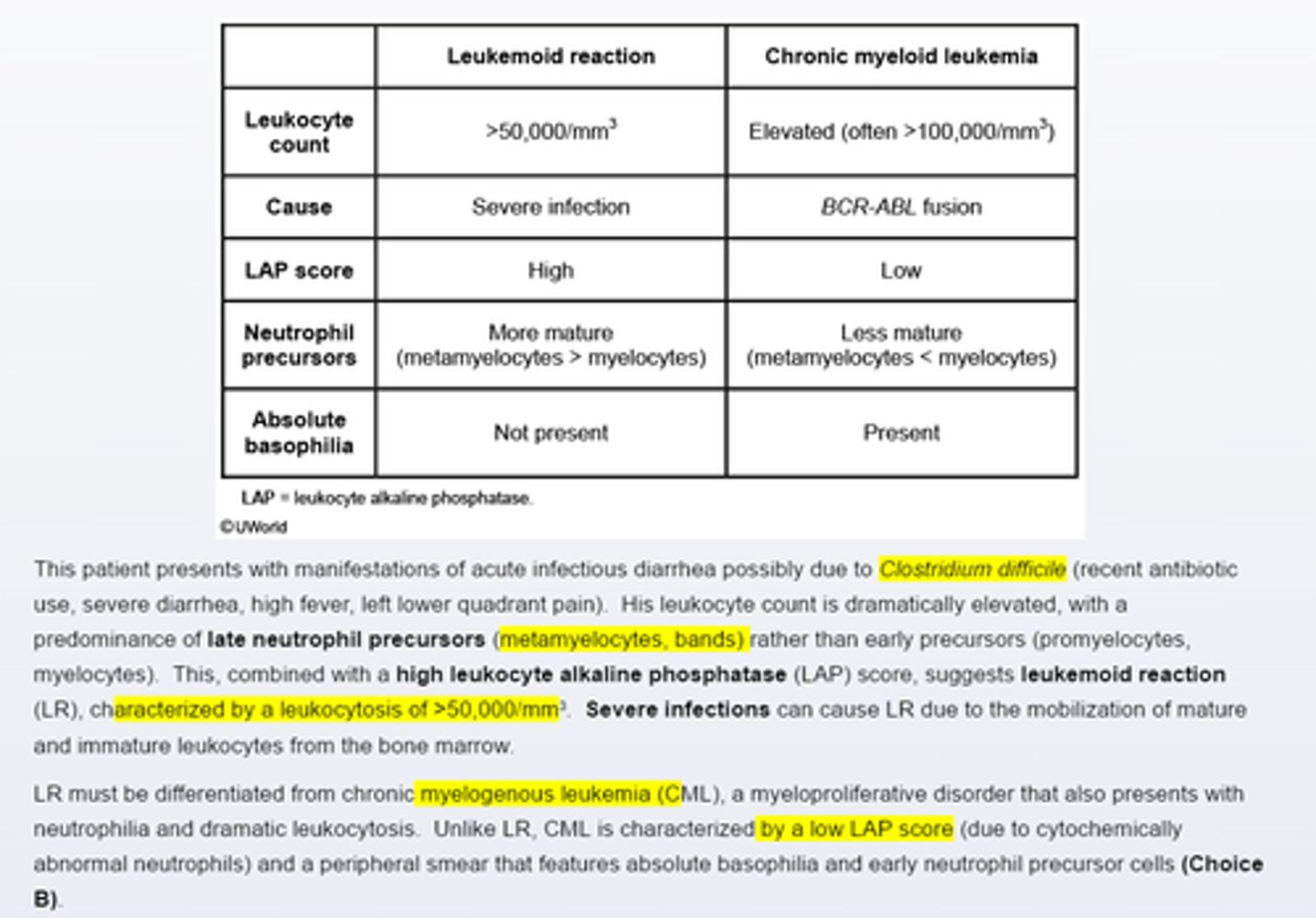
Leukemoid reaction
Leukemoid reaction must be differentiated from chronic myelogenous leukemia. CML is characterized by a low LAP and a peripheral smear that features absolute basophilia and early neutrophil precursor cells
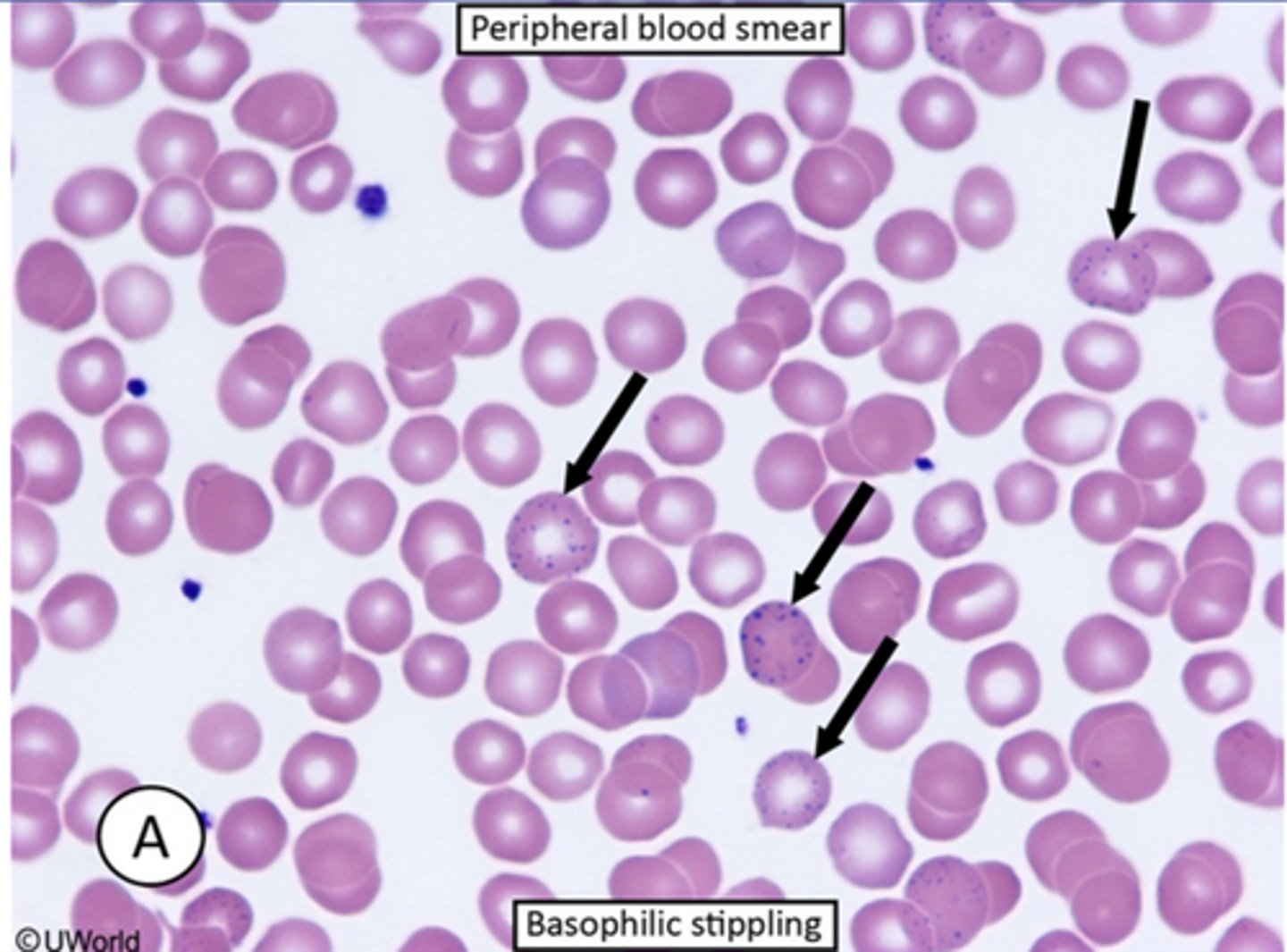
Basophilic stippling
-represents ribosomal precipitates that appear as blue granules of various sizes dispersed throughout the cytoplasm of red blood cells. It is seen with thalaseemias as well as lead or heavy metal poisoning
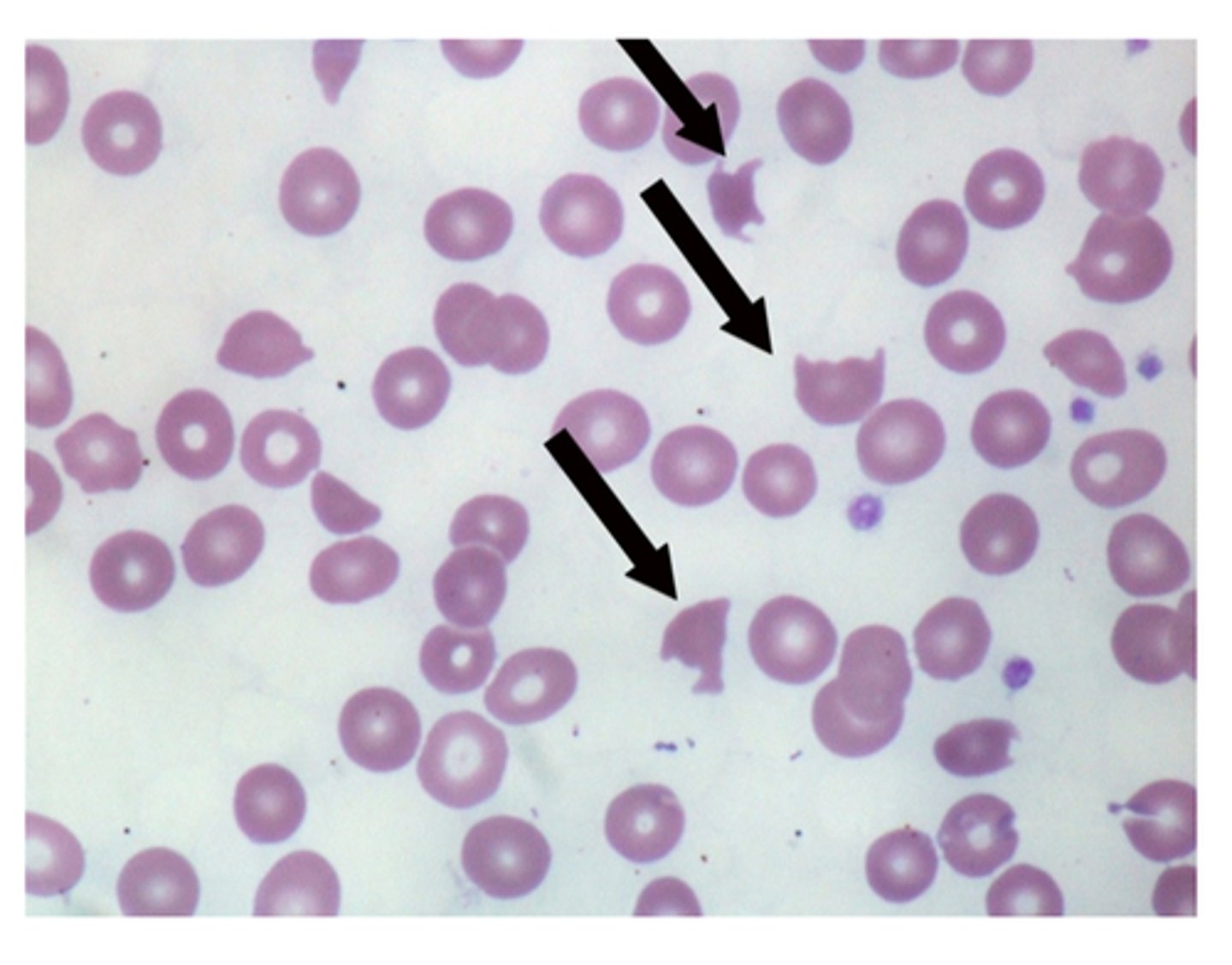
Helmet cells
or schistocytes (black arrow), are framented red blood cells. Their presence suggests traumatic microangiopathic hemolytic condition such as DIC, hemolytic uremic syndrome and throbotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Helmet cells are not typically seens in SCD as this hemolysis is intrinsic, not traumatic
Peripheral blood smear show rouleuax formation, a finding sees with______
a finding seen with elevated serum protein
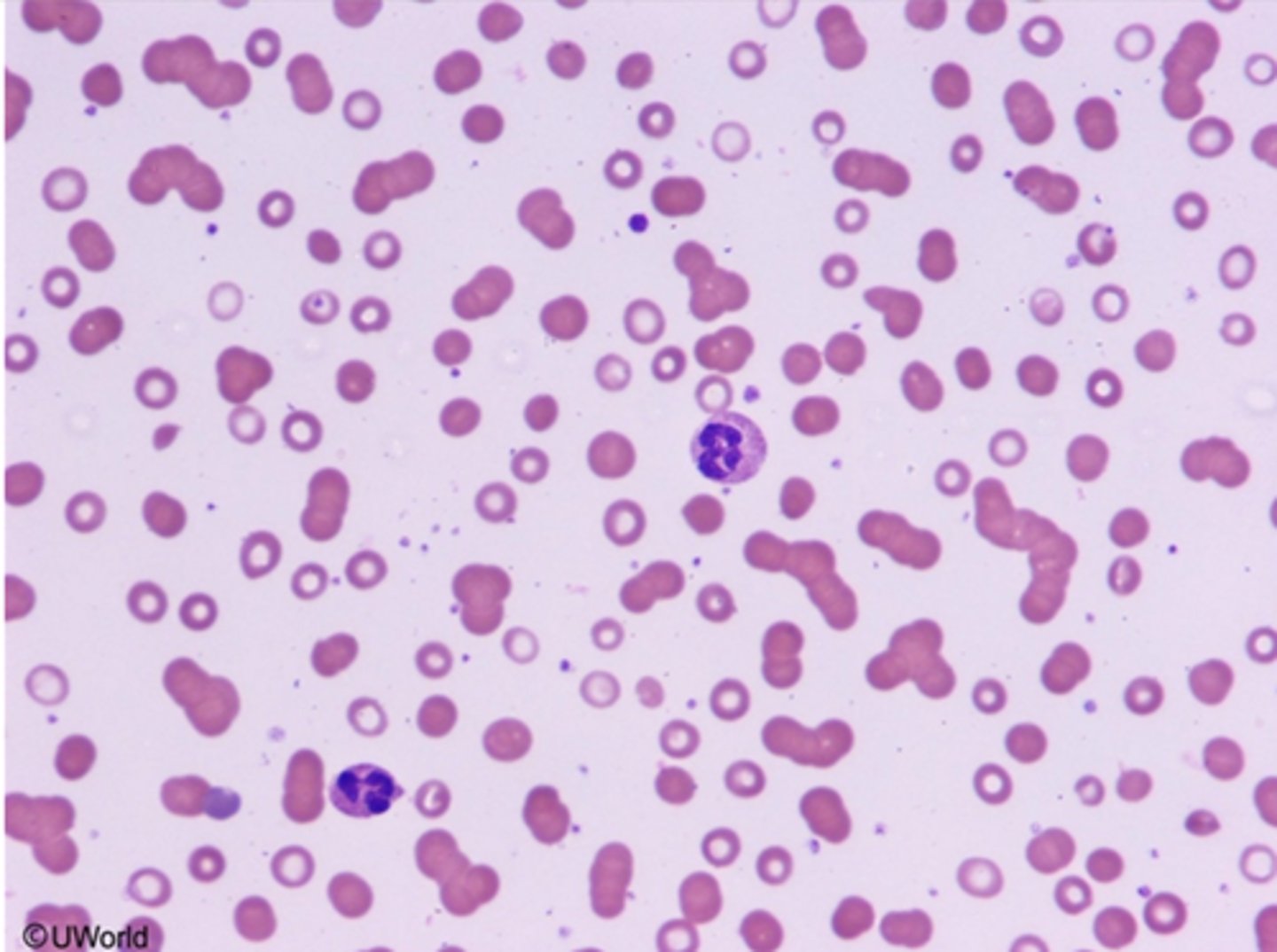
Multiple myeloma present with____, and a protein gap(_______)

DIamond-blackfan syndrome
-macrocytic pure aplasia associated with several congenital anomalies such as short stature, webbed neck, cleft lip, shielded chest and triphalangeal thumbs
Wiskott-aldrich syndrome and Fanconi's anemia

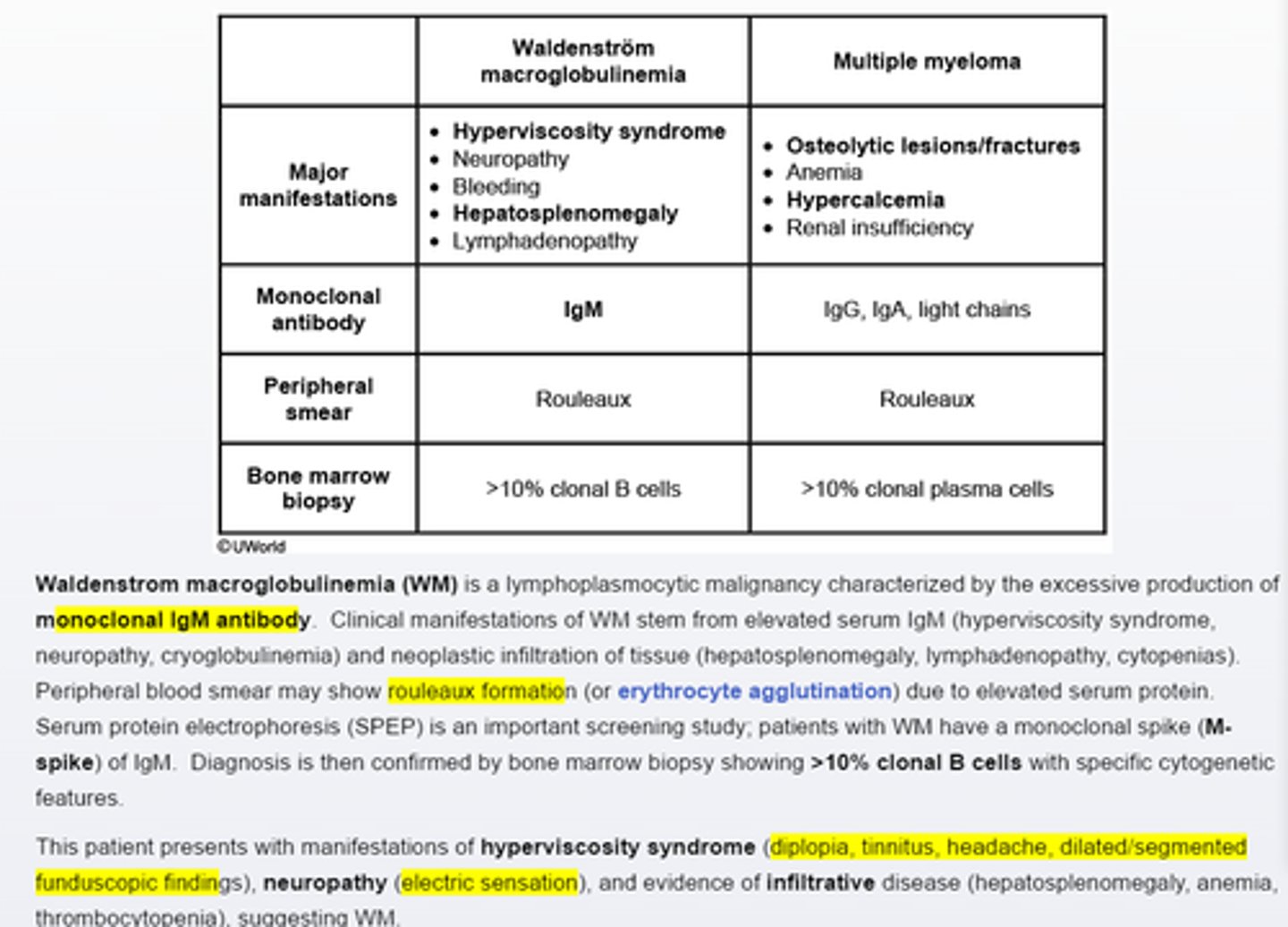
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
characterized by excessive monoclonal IgM, end organ damage and > 10% clonal lymphocytes by bone marrow biopsy-hyperviscosity syndrome (diplopia, tinnitus, headache, dialated/segmented funduscopic findings), neuropathy (electric sensations) and evidency of infiltrative disease(hepatosplenomegly, anemia, thrombocytopenia), suggesting WM
Anemia of chronic disease

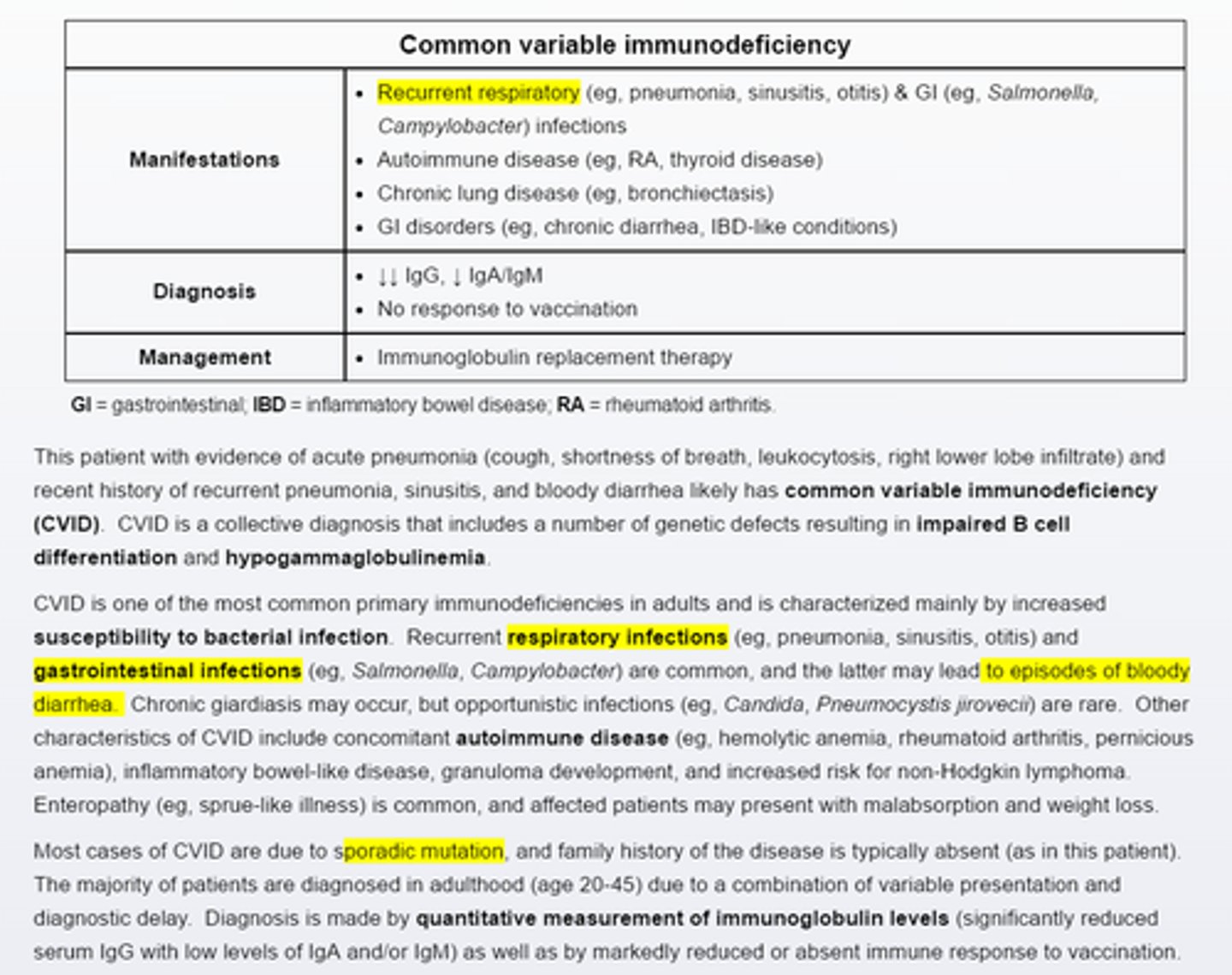
Common variable immunodeficiency
Recurrent bacterial infections in an adult should raise suspicious for common variable immuodeficiency.
-Quantitative measurement of serum immunoglobulin levels is needed to establish the diagnosis.
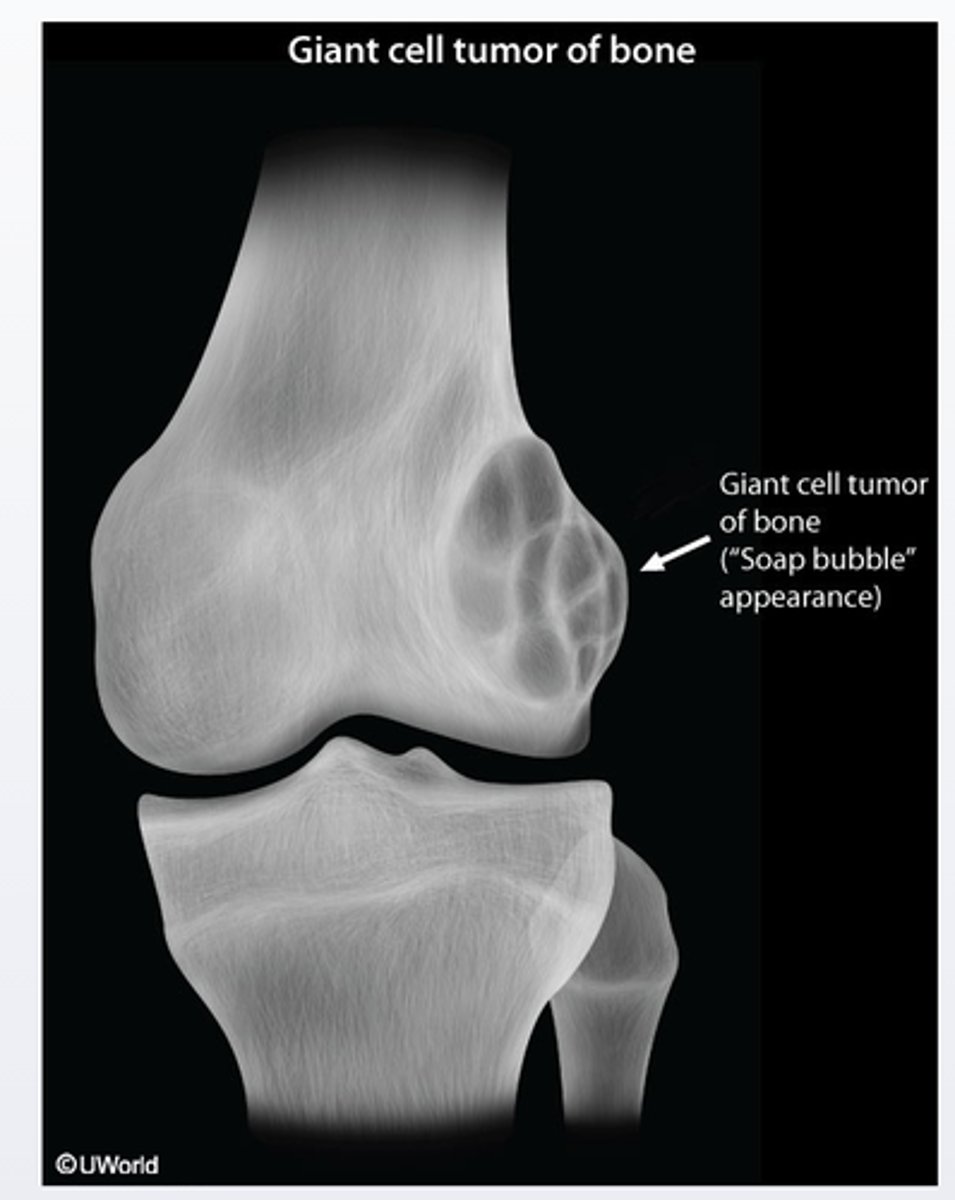
Giant cell tumor
Giant cell tumor of bone is a benign and locally aggressive skeletal neoplasm that usually presents with pain, swelling and decreased range of joint motion at the involve site. It typically presents as osteolytic (with a soap-bubble appearence on radiographs) in the epiphyseal regions of the long bones and most commonly involves the distal femur and proximal tibia around the knee joint
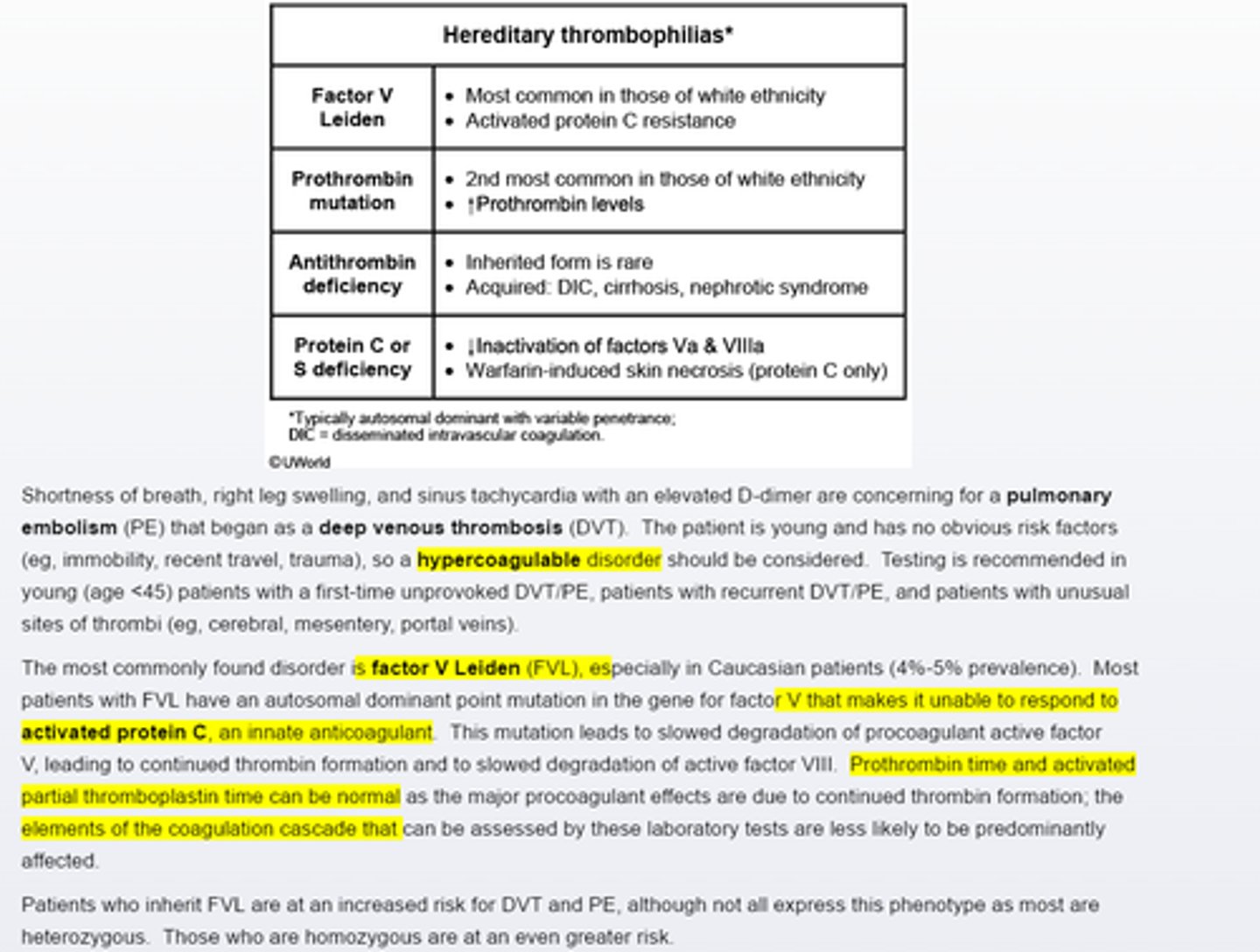
Hereditary thrombophilia
Factor V leiden is the most commonly inherited hypercoagulable disorder in the caucasian population, leading to increased risk of thrombosis.
Testing should be considered for an unprovoked first time thrombus in young age<45 pts or those with an unusual site of throbus
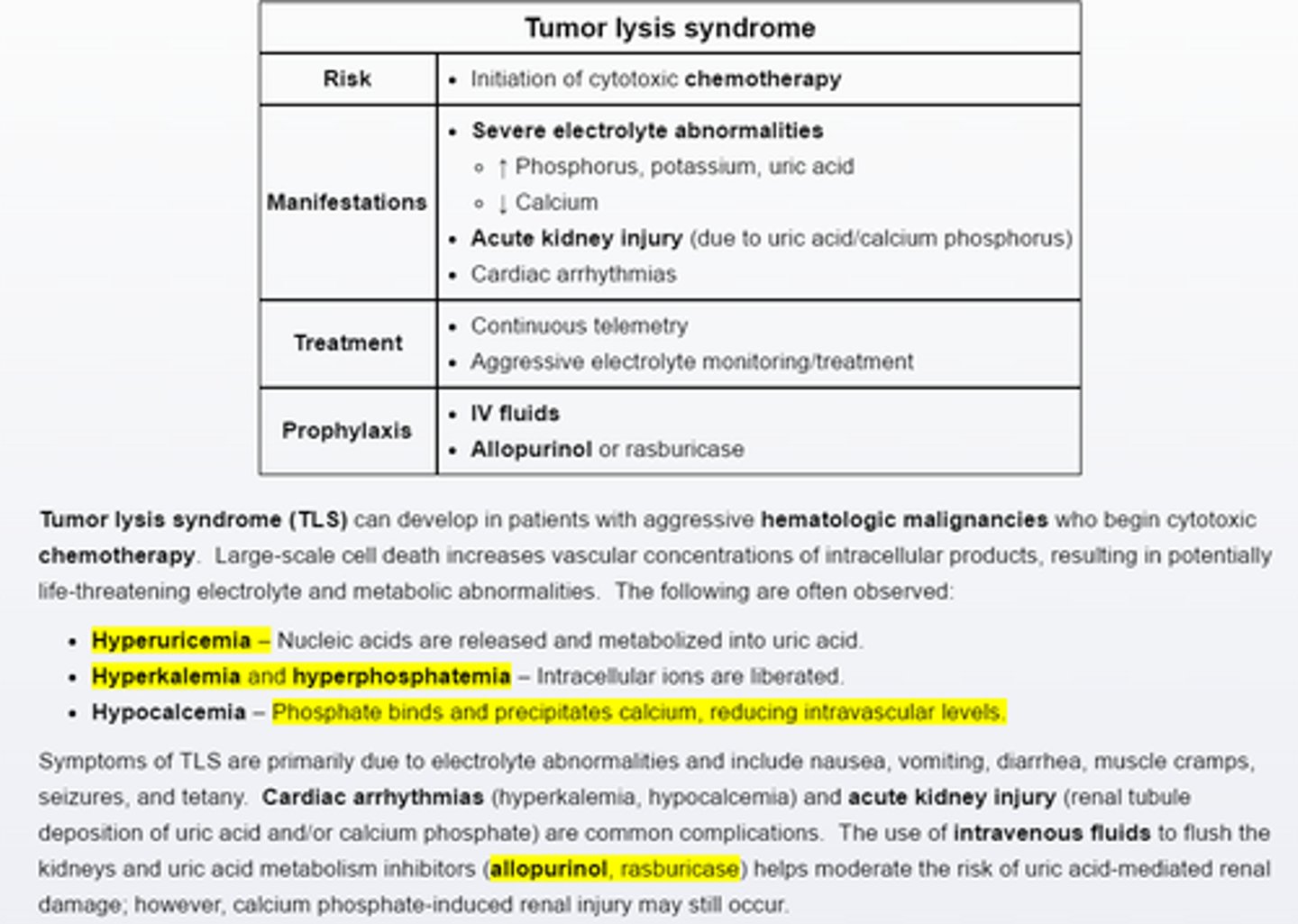
Tumor lysis syndrome
Pts with aggressive hematologica malignancies are at risk for tumor lysis syndrome when initiated on cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Intracellular contents are released, resulting in hyperuricemia, hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, and hypocalcemia due to calcium phosphate binding. Major complications include acute renal injury (uric acid/calcium phophate tubular injury) and cardiac arrthymias. Pretreatment with intravenous fluids and allopurinol reduces the risk of uric acid induced kidney injury.
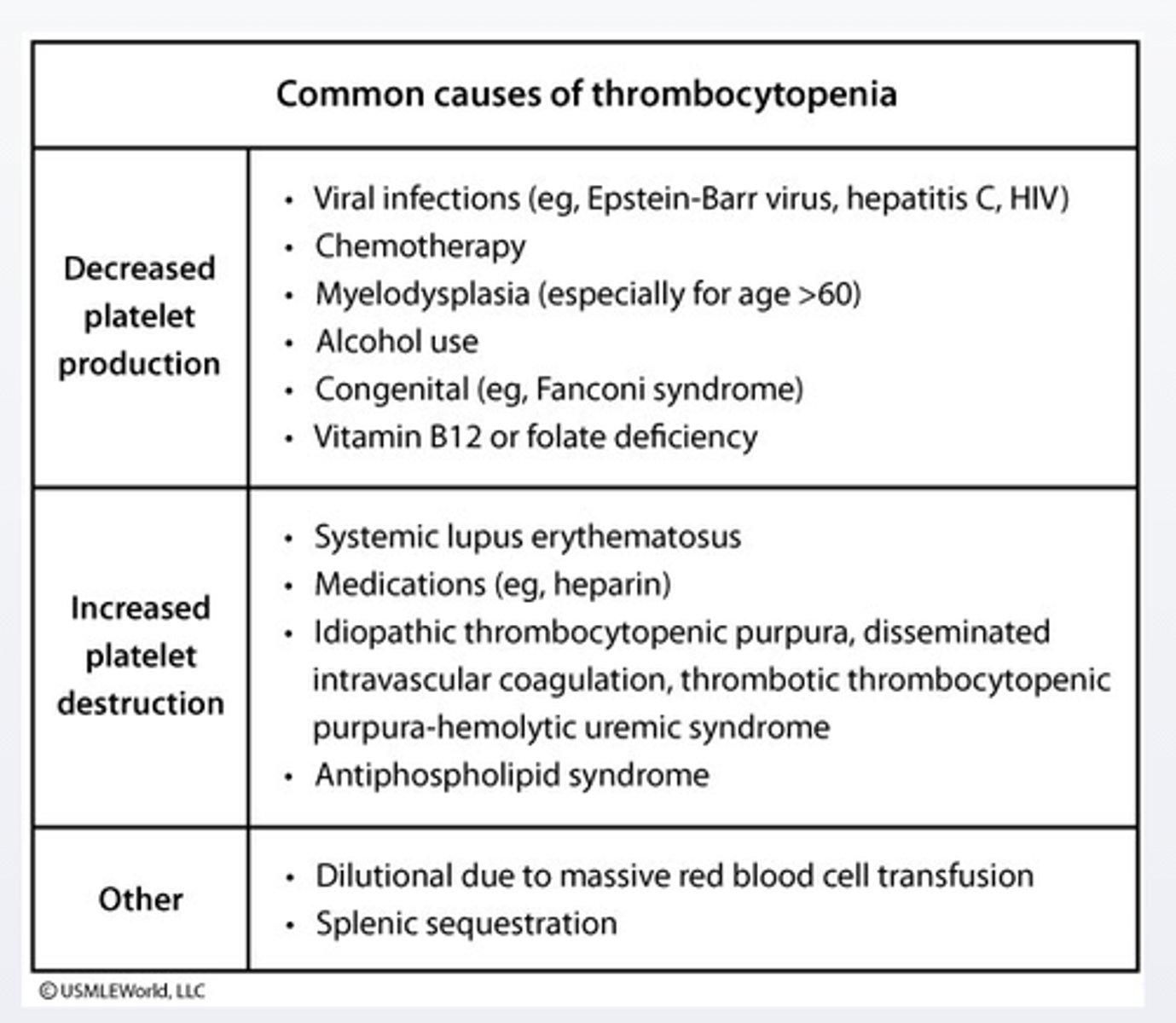
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura is usually diagnosed after excluding other possible causes of thrombocytopenia. These pts should be tested for hepatitis C and HIV as thrombocytopenia may be the intial presentation of HIV infection (up to 5%10% of pts)
treatment of the underlying infection can affect the platelet count
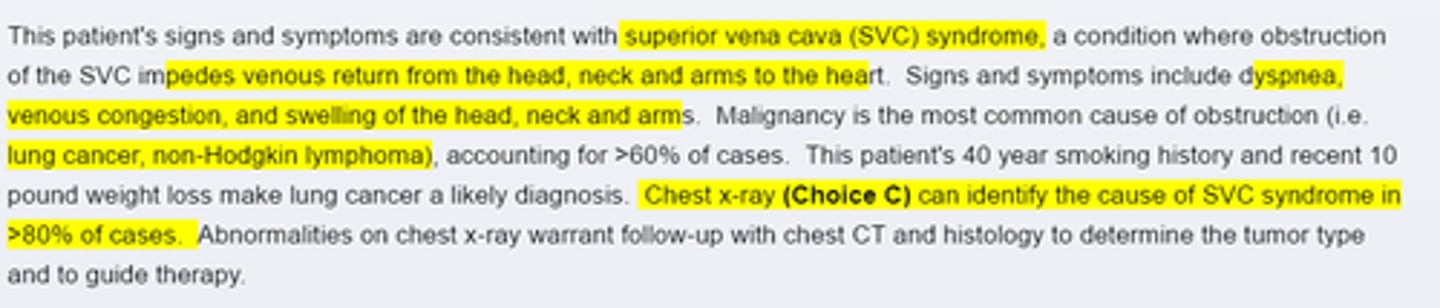
Superior vena cava syndrome
Malignancy is the most common cause of SVC syndrome. Lung cancer(particularly small cell lung cancer) and NHL are often implicated. Other possible causes include fibrosing mediastinitis (secondary to histoplamosis or Tb infection) or thrombosis secondary to indwelling central venous devices. When the history and physical exam are suggestive, chest X ray is warranted.
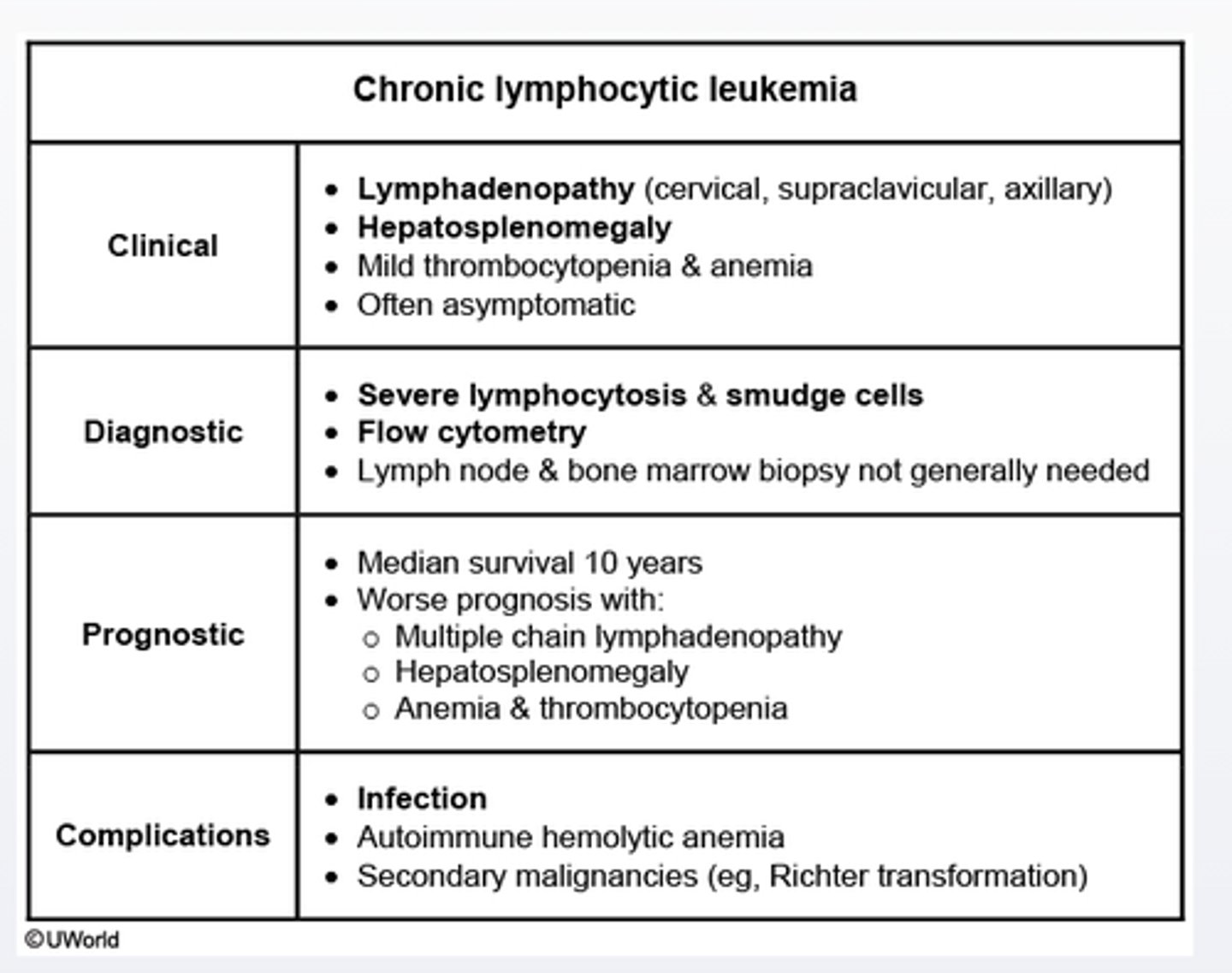
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is seen almost exclusively in elderly pts.
Peripheral smear is characterized by a marked leukocytosis with mature lymphocytes and smudge cells.
Acute myeloid leukemia
AML is the most common acute leukemia in adults and is typically associated with fatigue and symptoms related to >=1 cytopenias. Acute promyelocytic leukemia is a unique from of AML that often presents with life threatening coagulopathy due to disseminated intravascular coagulation.(prolonged PT/active PTT, hypofibrinogenemia)
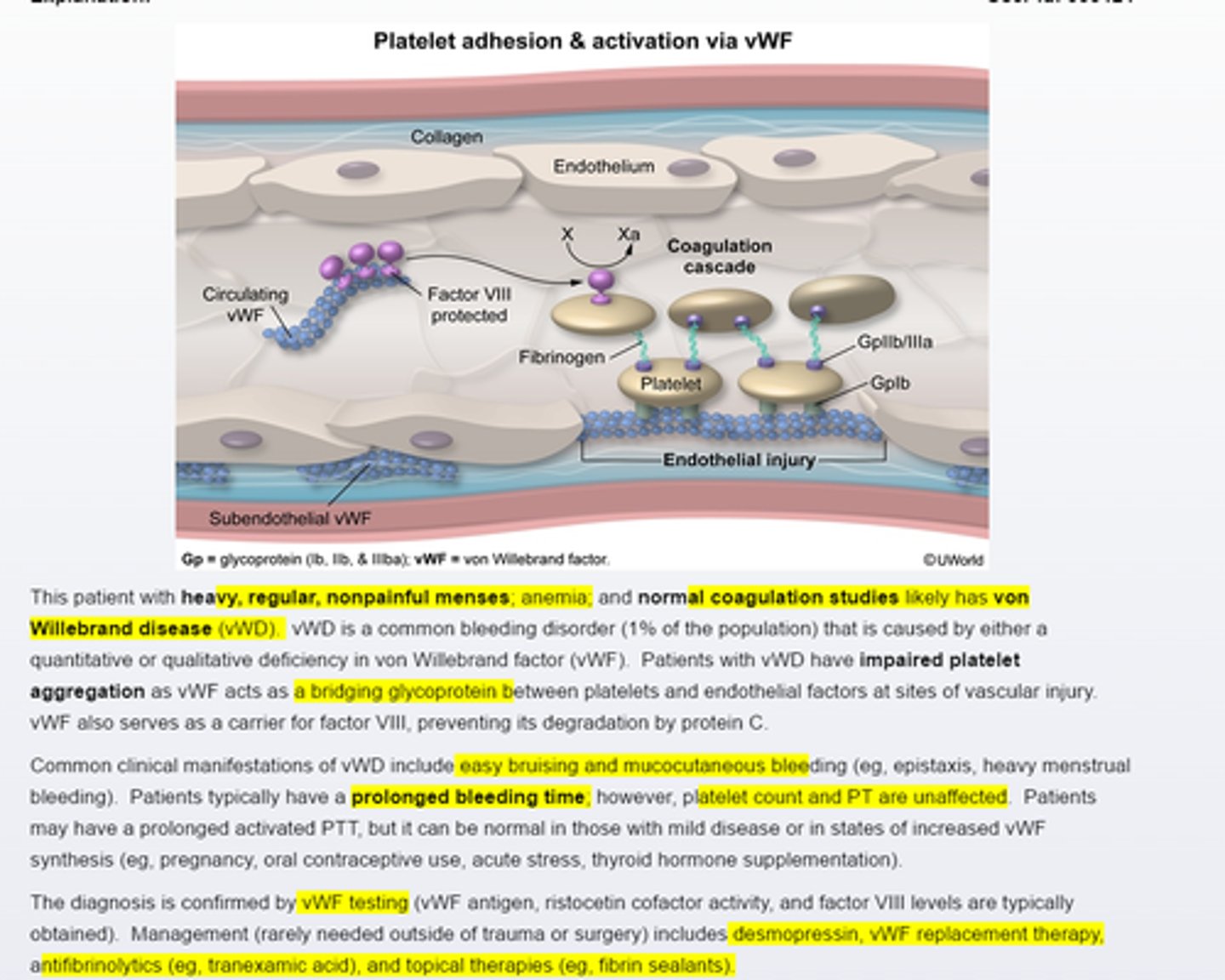
von Willebran disease
Von willebrand disease is a common bleeding disorder that causes impired platelet aggregation. Typical manfestations include easy brusing and mucocutaneous bleeding (regular, heavy menses). Platelet counts and coagulation studies are often normal, although activated PTT (25~40 seconds )and bleeding time (2-7 mins) may be prolonged
Hereditary hemochromatosis
is commonly associated with calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition in joints, leading to chondrocalcinosis, pseudogout and chronic anthropathy. Pts commonly also have diabetes and liver disease. Diagnosis is suggested by iron overload on serum iron studies and can be confirmed by genetics tests.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
PX
Most common adult acute leukemia
~ 65 y.o.
Cytopenia—Fatigue, Weakness, Bleeding, Bruising
↓ HgB, platelet
↑ Lactate dehydrogenase
Myeloblasts w/ Auer Rods
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
DX
Bone Marrow Biopsy
hypercellular
myeloid blasts
Microcytic Anemias
↓ MCV + ↓ HgB
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Lead toxicity
Thalassemia
Sideroblastic Anemia
Normocytic Anemias
↓ Reticulocytes + ↓ HgB
Leukemia
Aplastic anemia
Anemia of Chronic disease
Normocytic Anemia
↑ Reticulocytes + ↓ HgB
Hemorrhage
Hemolysis
Spherocytosis
G6PD deficiency
Autoimmune
Microangiopathic
Macrocystic Anemia
↓ MCV + ↓ HgB
Vit. B12 deficiency—neuro sx
Folate Deficiency
Alpha Thalassemia
Associated Condition
Hydrops fetalis—↑ abdominal circumference
Aplastic Anemia
DX
Bone Marrow Biopsy
hypocellular marrow
↑↑ stromal & fat cells
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Surgical Repair Indications
Growth > 5 mm/ 6 mos.
Growth > 10 mm/ 1 year
AAA > 55 mm in males
AAA > 50 mm in females
Phenytoin
Side Effects
Folic Acid Deficiency
impairs folic acid absorption in the jejunum
Because folate (tetrahydrofolate) is required for purine and thymidine synthesis, deficiency impairs DNA synthesis,
megaloblastic anemia
Gingival Overgrowth/ Hyperplasia
↓ folic acid → impaired collagenase activity and a subsequent buildup of gingival matrix