Chapter 18.1.3-18.1.6: Balancing Nuclear Equations and Identity of Types of Radioactive Decay
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
To balance nuclear reactions, the sum of the ___________ of the ___________ must equal the sum of the ___________ of the _____________. Also, the sume of the number of ____________ must equal the sum of the number of ____________.
mass numbers , reactants , mass numbers , products , reactant protons (i.e. atomic number), product protons (i.e. atomic number)
The mass numbers of a proton, electron, and neutron are ________.
1, 0, and 1.
In nuclear notation, Z is ________, N is _________, and A is _________, where A = _________.
the atomic number (number of protons) , neutron number (nº) , mass number , Z + N
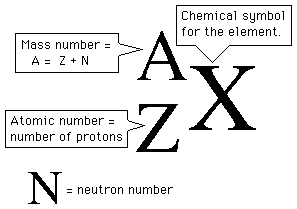
Radioactive nuclei are _________. The _________ is the nucleus that is undergoing radioactive decay and the product _________ is the new nucleus that’s made. All _________ with __________ are radioactive.
unstable , nuclide , nuclide , nuclides , 84 or more protons
The nuclear symbol for an electron (i.e. “negatron”) is ________.
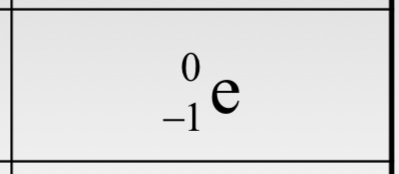
Alpha (α) particles are represented as _________ in nuclear notation and Rutherford found that α-particles are actually _________.
(see picture) , helium ions (+2 charge) with 2 protons and 2 neutrons
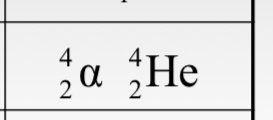
Alpha particles are the most _________, but the least _________. Losing an alpha particle means the atomic number (Z) _________ and the mass number (A) ________.
ionizing , penetrating , decreases by 2 , decreases by 4
Beta (ß) particles are represented as __________ in nuclear notation and is consistent with the emission of an electron from the nucleus.
(see image)
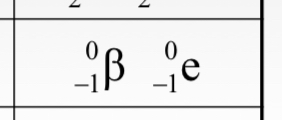
A beta particle is like an _________ (moving much faster, produced from the nucleus). When an atom loses a beta particle, its atomic number (Z) _________ and its mass number (A) __________. In beta decay, a neutron __________.
electron , increases by 1 , remains the same , changes into a proton
Positrons (ß+) have the same mass and charge magnitudes as regular electrons, but with opposite charge (i.e. antimatter). It’s nuclear notation is _________.
(see image)
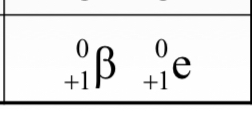
A positron has a charge of _________ and _________ mass. When an atom loses a positron, its mass number (A) __________ and its atomic number (Z) _________. Losing a positron means a proton has _________.
+1 , negligible , remains the same , decreases by 1 , turned into a neutron
In the process of __________, in order for one element to change into another, the __________ must change.
transmutation , number of protons
What is “electron capture”? Where does it occur?
The process by which an electron is captured by a nucleus and, with a proton, produces a neutron (i.e. atomic number decreases by 1). It occurs in radioactive nuclei where the decay is not energetic enough to produce the two gamma rays associated with positron decay.
Gamma emission is the _________ ionizing, but the _________ penetrating. There _________ loss of particles from the nucleus and _________ in the composition of the nucleus (i.e. same Z and A). It generally occurs _________.
least , most , is no , no change , after the nucleus undergoes another type of decay and the remaining particles rearrange
When a nucleus forms, some of the mass of the separate nucleons is converted into energy (_________). The difference in mass between the separate nucleons and the combined nucleus is called the _________.
binding energy , mass defect
__________ can be used to detect radioactive rays because they expose __________.
Film badges , light-protected photographic film
Radioactive rays cause the air to become _________. An _________ detects radiation by its ability to penetrate the flask and ionize the air inside. A __________ works by _________ generated when _________ are ionized by radioactive rays.
ionized , electroscope , Geiger-Muller counter , counting electrons , Ar gas atoms
Radioactive rays cause certain chemicals to __________ when they strike the chemical. A _________ is able to count the __________.
give off a flash of light , scintillation counter , number of flashes per minute
We know that processes with a constant half-life follow _________ kinetic rate laws. Since the rate of change is __________, we know that radioactivity is not a chemical reaction.
first-order , not affected by temperature
To calculate the age of super old stuff (e.g. radiocarbon dating), we can use the equation for the _________, which is _________.
first-order integrated rate law , ln(N0/N) = -kt OR N = N0e-kt
t1/2 = 0.693/k
k is the decay constant
The average lifetime of an atom is equivalent to _________.
1/k (comparing to the equation for t1/2, the half-life is 0.693 times the average lifetime of an atom)
The equation used in 14C dating to determine the age of a biological artifact is _________.
t = (8270)ln(15.3/dt) y