Music Cognition Unit 1: Part 1
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Brain Anatomy + Research Methods
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
sensation
the mechanisms that gather raw information from our environment and translate those external stimuli into neural signals
perception
the awareness and basic interpretation of the sensory signals
Neurons
made up of the cell body, axons, axon terminals, 86 billion of them in the human brain
dendrites
branching extensions of a neuron that play crucial roles in receiving, integrating, and transmitting neural signals.
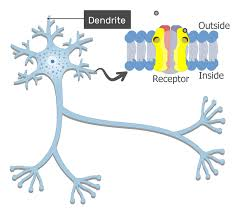
neurotransmitters
a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse
dopamine
supports learning mechanisms, scanning for and remembering smell, sight, cravings that get you back to the
endorphins
opioids made in our body and when they release they give you a pain release
for example) you eat a fry. ___ will release with the salt and oil that is so delicious whereas dopamine works with predictions.
How do neurons communicate?
within a neuron, information travels as an electrical signal.
between neurons, information travels via a chemical signal.
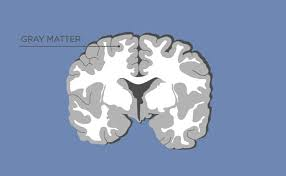
Gray matter
super delicate matter where the cell bodies have more water, and show up as gray in X-rays
white matter
axons that have very dense tissue and reflect white in an X-ray
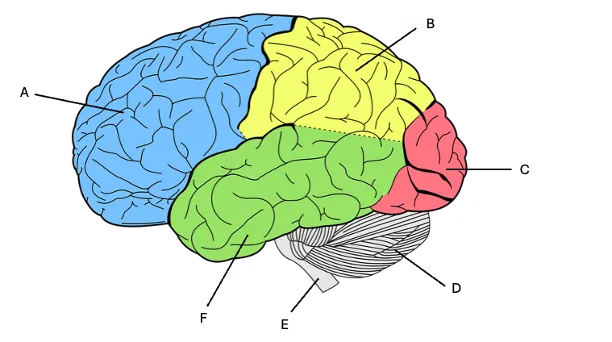
frontal cortex
A) decision making, planning, problem solving, personality, working memory, motor cortex, speech production
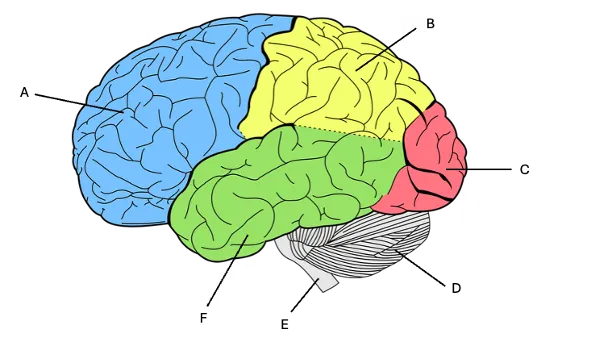
parietal lobe
B) sense of touch, sensory integration (combining multiple senses together)
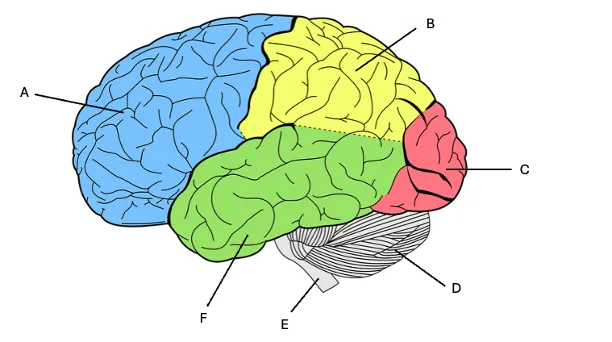
occipital lobe
D) only one function = vision
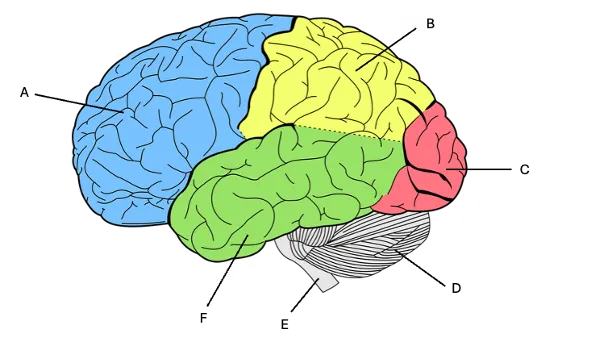
cerebellum
D) motor skill learning and motor coordination, beat prediction, gets signals from motor cortex and then puts it into a fluid movement, (suppressed with alcohol)
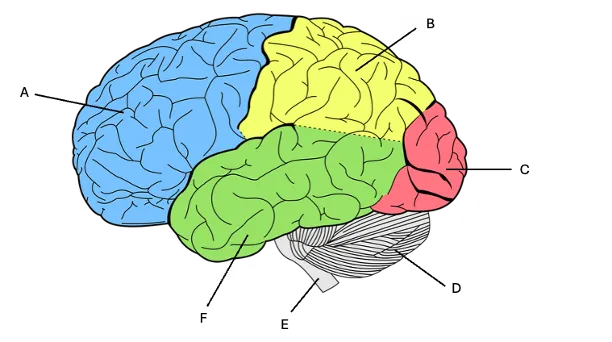
brainstem
E) connects the brain to the spinal cord, carrying signals that regulate body functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion as well as sending sensory information from the body to the brain. Has to do with auditory signal flow
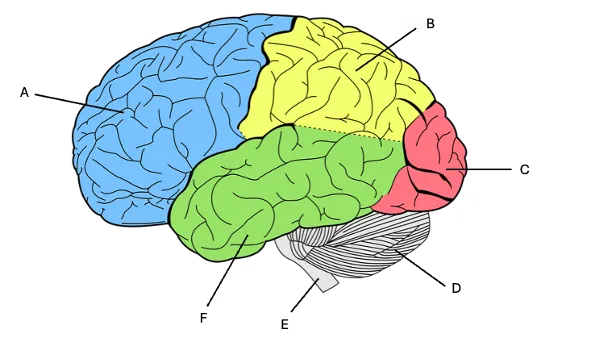
temporal lobe
F) memory, auditory cortex
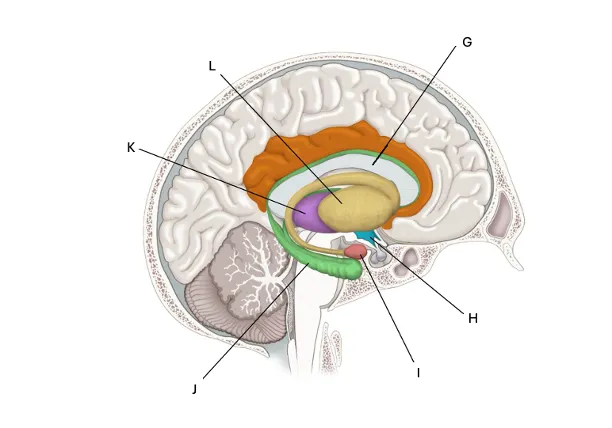
corpus callosum
G) makes sure both sides of the brain communicate for problem solving, motor control (why rubbing your stomach and patting your head is so hard) left hemisphere is dominant in speech and language
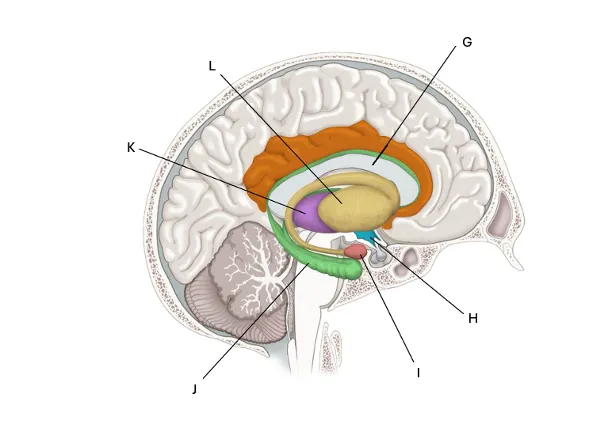
Hypothalamus
H) has control of all our internal states (ex. regulating temp, heart rate, sweat — regulation stuff), supports the fight or flight mechanism, part of our autonomous stuff that happens behind the scenes
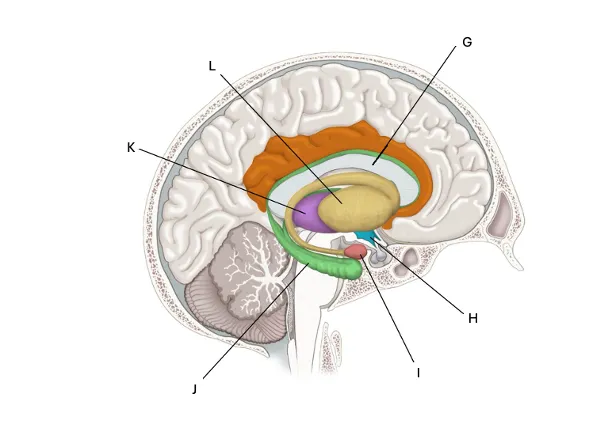
Amygdala
I) connected to fear + anxiety responses. important for threat detection. anxiety disorders usually are due to an overactive amygdala - creating more threats and over responding.
super survival oriented — its good to have varying ___ responses. it’s kind of like the first alarm system
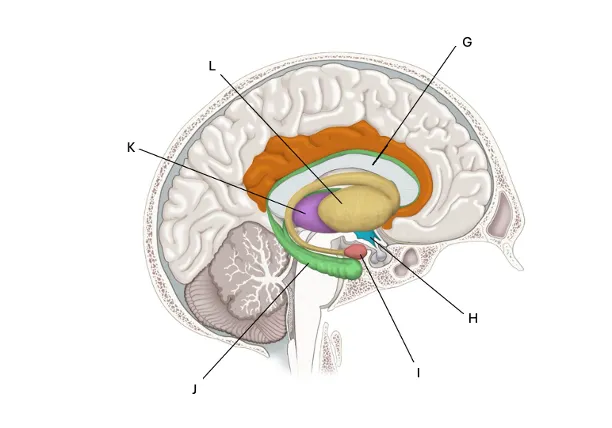
Hippocampus
J) Memory, especially emotional memory! highly connected to the amygdala so you can remember threats or things with an emotional component. (why you don’t remember what you ate for breakfast last tuesday, but can remember if you ate out and it was especially good — because your brain wants to recall it)
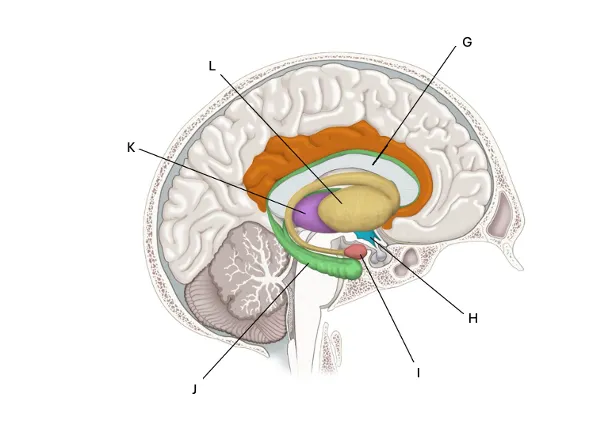
Thalamus
K) Auditory and visual signals come through here. Gets signals and sends them to where they need to go.
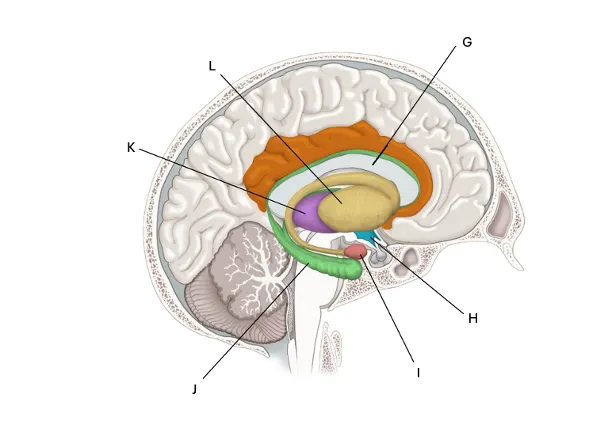
Basal Ganglia
L) vital for proper motor control, cognitive function, and reward processing.
sends signals to the motor cortex to facilitate movement, and can also send inhibitory signals which will then inhibit the motor cortex. Deals with learning, procedural memory
Gyrus
neuro term for bump
Suculus
neuro term for valley
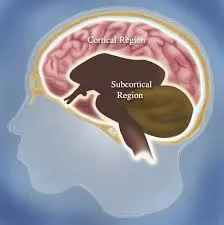
cerebrum (cerebral cortex)
the wrinkly part of the brain
CT (computed tomography) Scan
A series of x-rays to create 2D slices of the brain
it is a little limiting because you can not use radiation very often in a period of time
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
way more detailed images of structure, the stronger the magnets, the more detailed picture
a big magnet and the electrical components of hydrogen atoms. subjects them to magnetic field and the resonance recorded shows the density of the matter
safer than CT scan, no long term effects but you can’t wear any metal at all
you can get any slice you could want
fMRI (Functional MRI)
detects changes in blood flow and identifies regions of the brain that are active during a given task
it is useful to see what is lighting up but it is not time locked
this means the brain will react slower after the different stimuli
PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography
Uses radioactive glucose to show level of activity in brain regions based on metabolic activity
Glucose is the main sugar the brain uses as its energy source, so it can tell a lot about metabolic function. Essentially that the part of the brain using the most glucose is the most active… which is true-ish
more expensive because you have to hire people dedicated to just the radioactive material and this scan isn’t necessary too often
DTI (Diffusion Tensor Imaging)
Variant of MRI; Measures the movement of water molecules along the length of axons.
a way to confirm and network functioning and flow direction of connections and information
a way to map white matter without dissections
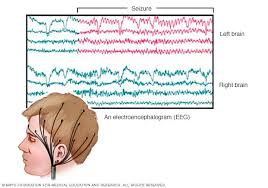
EEG (electroencephalogram)
Measuring the Electronic Signal across a collection of Neurons
uses scalp electrodes to record neuron activity
can distinguish rapidly changing events in the brain
attach gel and put on scalp/hair
more difficult to do it properly if you have curly or thick hair
schema
Implicit rules for how the world works; an internal model to help process incoming information.
ex. We don’t need to relearn how to open doors. We have encountered different types so many times that our system has an internal command network that queues up motor controls to open it and we don’t need to think about it.
Statistical Learning
The ability to track consistent patterns (i.e. statistical relationships) in the input to discover units and structures.
Top-down processing
A process of perception in which previous experiences (schema) are used to shape sensory information to fit the model
If you have a conscious expectation then you can hear things differently
Prediction Error
The difference between expected and actual input, also called mismatched Negativity
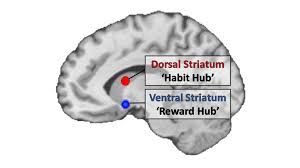
Dorsal Striatum
“habit hub”
Dopamine! marking the cueing devices almost like its remembering how to get the endorphins
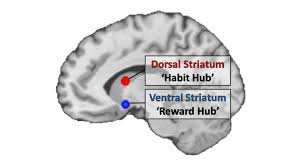
Ventral Striatum
Reward hub
Endorphins! The pleasureful reaction we feel.