M - biodiversity + classification
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What are the three main domains of life?
The three main domains of life are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. They are distinguished by their cellular structures and genetics:
Archaea: Single-celled organisms that often thrive in extreme environments, such as hot springs and salt lakes. Their cell membranes contain unique lipids, and their genetic material is more similar to that of eukaryotes than bacteria.
Bacteria: Another group of single-celled organisms, bacteria have diverse shapes and can be found in various environments. They reproduce asexually through binary fission and have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan.
Eukarya: This domain includes all organisms with eukaryotic cells, which have membrane-bound organelles and a defined nucleus. Eukarya encompasses a wide variety of life forms, including animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
what is taxonomy
Taxonomy is the science of classifying and naming organisms based on shared characteristics and relationships. It provides a hierarchical system to organize biological diversity.
what are the taxonomic groups used in classification
The taxonomic groups used in classification are
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
These groups help categorize organisms based on their evolutionary relationships.
Daddy Karl Played Class On Friday Gowan Spurs
what is phylogeny
Phylogeny is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among species or groups of organisms. It traces lineage and how different species are related through common ancestors.
what is courtship behaviour
Courtship behaviour refers to the set of actions, displays, or rituals performed by animals to attract mates and engage in reproductive activities. These behaviours can include vocalizations, visual displays, and elaborate movements.
simple;
releasing hormones
using sound
visual displays
complex;
dancing
building displays/structures
how do you write the scientific name of an animal
The scientific name of an animal is written using the binomial nomenclature system, consisting of two parts: the genus name (capitalized) and the species name (lowercase), both italicized or underlined.
What are the positives and negatives of courtship behaviors?
Courtship behaviors have several advantages and disadvantages.
Positives:
Facilitate Mate Selection: Courtship behaviors help individuals to choose suitable mates based on compatibility, characteristics, and mutual attraction.
Strengthen Bonds: Engaging in courtship rituals can build emotional connections and promote social bonding between partners.
Promote Genetic Diversity: Courtship mechanisms can facilitate mating between genetically diverse individuals, leading to healthier offspring.
Increase Reproductive Success: Effective courtship increases the chances of reproductive success by ensuring that mates are more likely to produce viable offspring.
Negatives:
Time-Consuming: Courtship may require significant time and energy, potentially diverting attention from other important activities or responsibilities.
Risk of Rejection: Individuals may face emotional distress or lowered self-esteem if they experience rejection during the courtship process.
Misinterpretation: Courtship signals can sometimes be misinterpreted, leading to misunderstandings and conflict between individuals.
Resource Investment: Courtship often involves substantial investment in terms of gifts, displays, or rituals, which can be detrimental if the investment does not lead to successful mating.
what is a species
A species is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring, sharing common characteristics and a genetic makeup. They are often defined by similarities in morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche.
what is a taxa or taxon
A taxa, or taxon, is a group of one or more populations of organisms that form a unit in the biological classification system. It can refer to any rank in the hierarchy of classification, such as species, genus, family, or order.
what is phylogenetic classification
Phylogenetic classification is a method of categorizing organisms based on their evolutionary relationships, considering their common ancestry and development through evolutionary time. This approach uses phylogenetic trees to illustrate the connections between different species.
what is artificial classification
Artificial classification is a method of categorizing organisms based on arbitrary characteristics or traits, NOT their evolutionary relationships. This approach often focuses on superficial similarities and can disregard the organisms' genetic or ancestral connections.
what is biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or on the entire planet, including the diversity of species, genetic variations, and ecological communities. It plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting ecosystem services.
how is an environment broken down
environment - continent/earth
ecosystems - communities of organisms that interact with their habitat
habitat - non living component of an ecosystem (abiotic)
community - living components of an ecosystem (biotic)
collection of population - total of one species in a community
what are the three components of biodiversity
species diversity, genetic diversity, and ecosystem diversity.
what is species diversity
the number of different species, and number of individuals of one species within a community.
what is genetic diversity
the variety of different genes possessed by individuals within a population or species, influencing traits and adaptability.
what is ecosystem diversity
the range of different habitats present in a given area, from local habitats to the planet.
what is species richness
the total number of different species present in a given area, regardless of their abundance, at any given time.
what is the index of diversity
a mathematical formula that quantifies the diversity of species in a community, taking into account both the number of species and their relative abundance.
d = index of diversity
N = total number of organisms of all species
n = number of individuals of each species
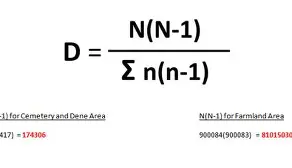
how can farming effect diversity
Farming can significantly reduce biodiversity by
altering natural habitats
introducing monocultures
using pesticides
filling in ponds or draining marsh land
removal of hedgerows
over-grazing land
These practices can lead to habitat destruction, species extinction, and disruptions in ecosystem functions.
how can the effects of farming on biodiversity be countered
Implementing sustainable farming practices such as
crop rotation (includes a nitrogen fixing crop)
intercropping (reducing pesticide use)
organic farming
leaving the cutting edge on fields
A shaped hedges
natural meadows
leaving wet corners
maintaining existing ponds /creating new ones
can help counteract the negative effects of farming on biodiversity.
what two methods can quadrats be used to measure species abundance
Random sampling to estimate species density in large areas.
Systematic sampling along transects to assess distribution patterns.
what des MRR stand for and what is it used for
mark
release
recapture
methods used in ecology to estimate population size of species by marking individuals, releasing them, and later recapturing them to assess the proportion of marked to unmarked individuals.
what equation for estimated population size uses the data from MRR

assumptions needed for MRR
proportion of marked to unmarked in the sample is representative
marked individuals are distributed evenly
no immigration or emigration
few/no births or deaths
marking doesn’t effect survival chances
mark is not rubbed off or lost so individuals are incorrectly identified
what factors need to be considered when using quadrats for sampling
size of quadrat
placement of the quadrat
the number of quadrats in an area
the type of habitat
the species being studied
the time of year
the sampling method used
what is the method for random sampling with quadrats
Randomly place quadrats in the study area, ensuring that their locations are determined mathematically or using a random generator, to reduce bias and obtain a representative sample of the habitat.
what is the method for systematic sampling with quadrats
Systematic sampling with quadrats involves placing quadrats at fixed intervals along a transect line, allowing for a structured approach to sample the habitat systematically and compare different areas accurately.
what are the disadvantages in having low genetic diversity, compared with a high genetic diversity
Low genetic diversity can lead to
increased susceptibility to diseases
reduced adaptability to environmental changes
a higher risk of extinction
whereas high genetic diversity enhances resilience against predators or disease and survival in changing conditions.
is a form of preparation for the unexpected
how can genetic diversity be investigated
full DNA sequencing
each base is tagged with a florescent dye
how many bases can a gene have
few 100 - 2 million
how is mRNA useful in investigating genetic diversity
you can compare the mRNA between individuals
evaluate comparing mRNA as a method for investigating genetic diversity
+
easier to obtain samples
smaller samples so fast to compare
free in cytoplasm
-
due to splicing it doesn’t give ‘the whole picture’
what else can be used to compare genetic diversity other than mRNA
Amino acid sequence
what are the limitations for comparing AA sequences
many bases code for the same amino acid so organisms could have the same AA sequence but have different base sequence.
why can’t genetic diversity be determined by observable characteristics
most phenotypic traits are polygenic and influenced by environmental factors
what is genetic diversity
number of different alleles of genes within the same species
what does Polygenic mean
trait controlled by multiple genes, contributing to a range of phenotypes.
it may also be influenced by environmental factors.
what are the types of transects
line - string or tape stretched across the ground in a straight line. Recording any organism that passes over
continuous belt - a strip about a metre wide made of two parallel lines. Species within the strip are recorded
interrupted belt - similar to a continuous belt but species are recorded in quadrats in intervals along the transect.
what are the three advantages of using standard deviation
provides a measure of variability within a dataset.
useful in comparison across different data sets.(overlaps) so whether it’s significant
reduces the effect of anomalies
when would you use spearman rank
correlation coefficient to assess the strength and direction of association between two ranked variables.
what are the four different statistical tests
Spearmen’s rank
t-test
Pearson’s correlation
chi-square test
what is the formula for spearman’s rank
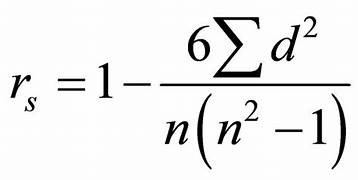
what is succession
how an ecosystem and changes and over time.
what is meant by succession stages
the series of ecological changes that occur in an ecosystem, leading from initial colonization by pioneer species to a mature, stable community.
usually biotic changes
usually makes the environment less hostile - so new communities are formed, so biodiversity will fluctuate over time
what are possible changes the occur during succession
area made less suitable to the existing species, so new species better suited may outcompete these species.
make the area more suitable, so the species there will be better adapted and outcompete other species in the community
stage 1 of succession
colonisation by the PIONEER SPECIES
common qualities of pioneer species
asexual reproduction (fast so population grows rapidly)
usually photosynthetic, so they don’t rely on other organisms
tolerance to extreme conditions
ability to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere (limited nutrition)
stage 2 of succession
as the pioneering species dies and decomposes, this produces more accessible nutrients, making it suitable for more organisms.
(layer of soil will thicken as plants decompose) - thicker soil can hold more water, changing the abiotic factors
and breaks down rock
during this the following species may outcompete the earlier ones, as the environment becomes more suitable for them
This process repeats, and more and more nutrients are available to more complex organisms and the biodiversity changes within the ecosystem.
stage 3 of succession
climax community
that emerges after a series of ecological changes. It represents a stable ecosystem in which the species composition remains relatively unchanged over time, until disrupted by an external event.
what is detritus
organic matter produced by the decay of dead plants and animals.
secondary succession