Government macroeconomic objectives and policies
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Expansionary fiscal policy
increase in Government spending and a fall in Taxation
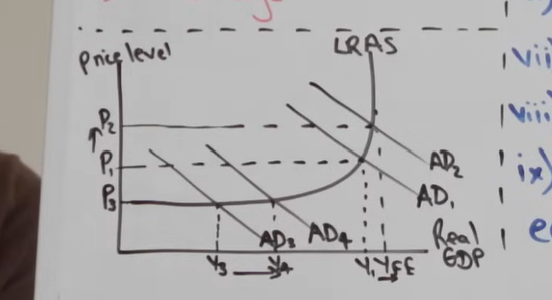
cons of expansionary fiscal policy
Demand pull inflation and current account deficit —> tradeoffs
worsening of gov finances - may rack up more debt
crowding out - typically happens when the government borrows money to finance its spending, which can raise interest rates, making it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money
time lags
evaluation of fiscal policy
Size of the output gap
Size of the multiplier
Consumer/Business Confidence
State of Gov Finances
LR returns to the GOV
Laffer curve ideas
Role of automatic stabilisers
Crowding out vs Crowding in
Classical view of self-correcting economy in a recession
What is an automatic stabiliser
Automatic stabilisers are automatic fiscal changes as the economy moves through stages of the business cycle – e.g. a fall in tax revenues from the circular flow during a recession or an increase in state welfare benefits when unemployment is rising.
Quantitative easing
Central bank may use to increase the supply of money in the banking system designed to encourage commercial banks to lend at cheaper interest rate
Monetary policy
Involves changes in interest rates, the supply of money and credit and exchange rate by the central bank to influence the macro-economy and achieve target outcomes
Interest rates
The amount you’re charged to borrow money
Central Bank can set official monetary policy interest rates, which then affect the interest rates offered by banks to borrowers and savers.
Lowering IR can stimulate borrowing and spending, while raising them can reduce borrowing and spending to control inflation
What are government securities and what does selling them mean.
Government securities are debt instruments issued by the government to raise money. These could be things like bonds or Treasury bills, where the government borrows money from investors with a promise to pay it back with interest after a certain period.
When a central bank sells government securities, it is essentially offering these bonds or Treasury bills to private banks or investors. The central bank receives money from the buyers in exchange for these securities.
Open Market Operating
Central banks buy and sell government securities in the open market to influence the money supply Purchases inject money into the economy, while sales withdraw money
Central Banks
Monetary authority and major regulatory bank in a country. A central bank is responsible for operating monetary policy and maintaining financial stability