Chemical Reactions of Copper and Percent Yield Quiz
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
First Reaction
solid copper reacts with aqueous nitric acid to produce aqueous copper nitrate, nitrite gas, and water
solid copper reacts with aqueous nitric acid to produce aqueous copper nitrate, nitrite gas, and water
Cu(s) + 4HNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
What is the first reaction clasify as?
Redox
Second Reaction
aqueous copper nitrate reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to form solid copper hydroxide and aqueous sodium nitrate
aqueous copper nitrate reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to form solid copper hydroxide and aqueous sodium nitrate
Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NaOH (aq) → Cu(OH)2 (aq) + 2NaNO3(aq)
What does the second reaction classify as?
metathesis
Third Reaction
aqueous copper hydroxide heats into solid copper oxide and gaseous water
Cu(OH)2 (aq) → CuO (s) + H2O (g)
What is the third reaction classified as?
dehydration (decomposition)
Fourth Reaction
solid copper oxide reacts with aqueous sulfuric acid to produce aqueous copper sulfate and water
solid copper oxide reacts with aqueous sulfuric acid to produce aqueous copper sulfate and water
CuO(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CuSO4(aq) + H2O(l)
What is the fourth reaction classified as?
metathesis
Fifth Reaction
aqueous copper sulfate reacts solid zinc to produce aqueous zinc sulfate and solid copper
aqueous copper sulfate reacts solid zinc to produce aqueous zinc sulfate and solid copper
CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
What is the fifth reaction classified as?
Redox
Why was the copper washed at the end of the experiment?
to remove any excess salt of ZnSO4
In the reaction, Cu(s) + 4HNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2H2O(l), what is oxidized, reduced, the oxidizing agent, and the reducing agent?
oxidized- copper
reduced- nitrogen
oxidizing agent- nitrogen
reducing agent- copper
In the reaction, CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s), what is oxidized, reduced, the oxidizing agent, and the reducing agent?
oxidized- zinc
reduced- copper
oxidizing agent- copper
reducing agent- zinc
Does oxidation occur in metathesis reactions?
no because there is no change in oxidation number of metathesis’ atoms
Does oxidation occur in dehydration reactions?
no because the addition or removal of water does not involve an oxidation or reduction reaction
What is the net ionic equation of the first reaction?
Cu(s) + 4H+(aq) + 4NO3- (aq)→ Cu+2 (aq) + (NO3)2- (aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2H2O (l)
What is the net ionic equation of the second reaction?
Cu+2 (aq) + OH- (aq) →Cu(OH)2 (s)
What is the net ionic equation of the third reaction?
Cu(OH)2 (s) → CuO(s) + H2O(s)
What is the net ionic equation of the fourth reaction?
CuO(s) + 2H+(aq) → Cu+2 (aq) + H2O(l)
What is the net ionic equation of the fifth equation?
Cu+2 (aq) + Zn(s) → Zn+2 (aq) + Cu(s)
Decantation
separating insoluble solids from liquids by pouring out the liquid while keeping the solids inside the container
Filtration
the solution passes through hte filter paper and is collected in a flask; solid collected in filter paper
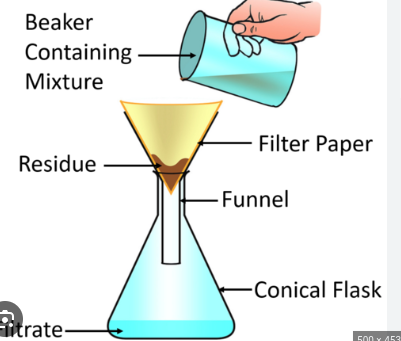
extraction
transference of compound (s) from a solid or liquid into a different solvent or phase
First reaction, Cu(s) + 4HNO3(aq)
added HNO3 to the beaker containing copper
it reacted to produce nitrate gas which was captured by the fume hood
turned green, sizzled, orange smoke
then added 100mL of water to dilute the copper nitrate
ended up bluish green
Second reaction, Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NaOH (aq)
sodium hydroxide is added to copper nitrate
turns clear blue into foggy lighter blue
top layer is clear, bottom layer is cloudish looking texture (cloudish, dark grey)
produces solid copper hydroxide (grey cloudy stuff)
produces sodium nitrate (blue liquid)
Third Reaction, Cu(OH)2 (aq)
let black copper hydroxide settle before decanting
add 200mL of hot water to produce copper oxide
decant again to remove the water
black cloudy stuff is left
Fourth Reaction, CuO(s) + H2SO4(aq)
sulfuric acid is added to copper oxide
turns blue and clear
produces copper sulfate and water in a solution
Fifth Reaction, CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s)
zinc is added to the solution of water and copper sulfate under the fume hood
bubbles; copper turns red
zinc is added and mixed until the solution is colorless with red copper at the bottom
then once here is no gas anymore, decant the solution
wash the copper with water and decant
repeat twice to ensure that only copper is left
then let the copper air dry or heat the copper until it is dry
solid copper and zinc sulfate is produced
Reactants
solid copper, aqueous nitric acid, aqueous copper nitrate, aqueous sodium hydroxide, solid copper hydroxide, solid copper oxide, aqueous sulfuric acid, aqueous copper sulfate, solid zinc
Products
aqueous copper nitrate, gaseous nitrite, liquid water, solid copper hydroxide, aqueous sodium nitrate, solid copper oxide, gaseous water, aqueous copper sulfate, aqueous zinc sulfate, solid copper
Limiting Reactant
calculate the amount of product produced from each reaction; the reactant that produces the least amount is the limiting reactant; use grams, moles, and mole ratio to calculate; copper is the limiting reactant
% Yield
actual yield/ theoretical yield x 100%
What is the difference between filtration and decantation? Use technical terminology in your response.
When filtration is used, liquid flows into a medium through which solids are unable to pass; decantation separates liquids from solids by slowly and carefully pouring the liquid from the container
Give two classifications for the HNO3 used in the lab.
a strong acid
reactant
Give two classifications for the NaOH used in the lab.
strong base
reactant
Copper
Cu (s); red solid; insoluble; reactant and product
Copper nitrate
Cu(NO3)2 (aq); blue-green clear liquid; soluble; product and reactant
copper hydroxide
Cu(OH)2; solid; black cloudy, fluffy; insoluble; product and reactant
copper oxide
CuO; solid; black cloudy stuff; insoluble; product and reactant
copper sulfate
CuSO4; aqueous; blue and clear; soluble reactant and product
How did you know that the metathesis reactions went to completion?
there was a component that was removed from the solution; a solid (Cu(OH)2) from the 2 second reaction and water from the fourth reaction
What salts could remain on the copper retrieved in the last step if proper washing was not done in each of the previous steps that required washing the precipitate?
sodium nitrate and zinc sulfate
Which salt should have been removed in each of the steps that required you to wash the product?
sodium nitrate should be removed in reaction 3 if not already removed; zinc sulfate would have been removed after reaction 5
What effect, if any, would adding less than 2.00 g of Zn have on the copper produced by the final reaction of the lab, CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)?
there would be less copper removed from the copper sulfate compound if there was less grams of zinc added
Why are measurements of a liquid more accurate when made using a graduated cylinder that when they are made using a beaker?
graduated cylinders are designed for accurate measurements of liquids with a much smaller error than beakers; has permanently marked incremental graduatins incorporated in the clear cylinder
What is the limiting reactant in the final reaction of the lab, CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s), when 2.00 g of Zn reacts with 20mL of 2.0 M CuSO4(aq)? Show all math to support your answer.
Zinc is the limiting regeant
Explain how to prepare 1.00L of a 3.0M H2SO4(aq) from a concentrated solution of the acid that is 18.0 M.
add .16667 L of 18.0 M H2SO4 to a beaker
then add water until there is 1L of solution