Geography - Population and settlement
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What is population
It means the number of people living in a certain area
What is a population pyramid
It shows the structure of a population
What is natural increase
It is when the birth rate is above the death rate
What is natural decrease
It is when the birth rate is below the death rate
What continent has the highest natural increase
Africa
What is birth rate
It is the number of live babies born per 1,000 per year
What is demographic momentum
The tendency for a population to continue growing even after fertility rates have declined, due to a larger proportion of people in their reproductive years.
What is death rate
It is the number of people who have die per 1,000 per year
What is the infant mortality rate
It is the number of babies who die within their first year of life per 1,000 per year
What is the carrying capacity
It is the largest number of people that the resources of the planet or a give area can support
What is over population
Too many people in an area that can be supported by its resources and technology.
What are the causes of overpopulation
Low levels of education causing larger families
Natural disasters, political unrest or war elsewhere causing in-migration to an area
Lack of development & high levels of natural increase, maybe because of strict religious views so contraception isn’t used
What are the consequences of overpopulation
Out-migration
Starvation/famine or civil unrest
Unemployment and poverty
Overcrowding
What is underpopulation
Too few people in an area to utilize its resources available efficiently using current technology levels
What are the causes of underpopulation
Difficult climate and weather
Remoteness
What are the consequences of underpopulation
High employment rates and high wages (to maintain workers but doesn’t always happen)
In-migration (people see opportunity)
What is optimum population
The right amount of people to utilize the resources available in a given area.
What is the case study for overpopulation
Bangaldesh
What is the case study for underpopulation
Australia
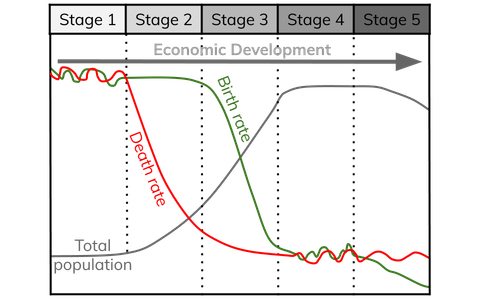
What is the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
It shows how the population of a country changes throughout economic development as birth and death rates change.
How many stages are in the demographic transition model
5
What happens to economies in stage 1 of DTM
Birth rates are very high because there is high infant mortality rate and no access to contraception like condoms because they are very poor.
The death rates are also high because there are not many doctors, hospitals and no schools to educate people on diseases and how they spread.
What happens to economies in stage 2 of DTM
The death rate begins to fall because people’s understanding of diseases have improved and they are educated on how to improve their health systems.
Birth rates are still high because people do not know yet their children are likely to live longer. This also occurs because these nations usually have lots of jobs in agriculture and having lots of children is beneficial.
What happens to economies in stage 3 of DTM
The birth rates begin to fall to the level of death rates
Improved access to contraception, belief that children will survive to adulthood and increased female education
Healthcare systems continue to improve
Most stage 3 economies like Vietnam and India focus on manufacturing, so having lots of children to work on farm reduces
What happens to economies in stage 4 & 5 of DTM
Birth rates are low because of low infant mortality, good access to contraception and equality of access to education
Death rates are low because of good healthcare systems, high levels of education and high incomes
What is an example of a HIC economy that is in stage 5 of the DTM and is declining in population
Japan
What are examples of countries in stage 5 of the DTM
Germany and Japan
At which stage of the DTM is the economy most dominated by agriculture
Stage 2
What is the most developed stages of the DTM and why
Stages 4 & 5 because most HIC are in these stages
What are the 3 types of factors influencing birth rate of a country
Economic, political and social
List economic factors influencing birth rate
Poorer countries have higher fertility rates as children are considered good labour because they work in fields .
In the LEDCs, there are no pensions available for older people so children are expected to provide for their parents.
In HICs birth rates are lower as couples decide that children are expensive.
List political factors influencing birth rate
Government policies can affect birth rate
Countries with ageing populations have pro-natalist policies to encourage women to have children
Countries with huge populations that are increasing rapidly may limit the number of children allowed
List social factors influencing birth rate
Tradition demands high birth rate as a measure of social status so birth rate remains high
Education for women reduces the birth rate as they have a greater knowledge of birth control and more chances of work or a career
Strict Muslim and Catholic societies do not permit the use of contraception so the birth rate is generally higher
In HICs, couples marry later so start families later, this limits the number of children produced
Examples of countries with pro-natalist policies
France made a policy called “Code de la famille”
When did the France pro-natalist policy start
1939
What were the gifts given to families in France for having a third child
Paid up to £1064 for having a third child.
Three-child families were given family allowances to increase their buying power.
Mothers were given maternity pay (at nearly full pay) for 20 weeks for their first child and for 40 weeks or more for a third child.
Preferential treatment when bidding for council flats with three bedrooms.
Three-child families got a 30% fare reduction on all public transport.
Mothers and housewives received a full pension scheme.
Examples of countries with increasing huge population that may limit the number of children allowed
China have a One Child policy of 1979-2015
What were the gifts given to families in China for having one child
Parents of one child received larger pensions.
Families with only 1 kid received the best education for free.
The legal age of marriage was raised to 22 for men and to 20 for women, and they had to have state permission.
What were the penalties for having more than one child in China
Parents had their benefits taken away.
The family’s income was fined by up to 15%.
Abortions became compulsory for a second pregnancy, and there was a lot of worry that many of these were forced abortions.
What were the impacts of the one child policy in China
300 million births were prevented and China's population has stabilized at 1.4 billion people.
Accusations that China violated human rights with forced abortions and causing female infanticide because people would rather have a male child.
The current ratio of men to women is 118:100.
The current fertility rate (1.6) is below the replacement rate of 2.1, leading to an ageing population.
By 2040, the ratio of worker to retiree will be 2:1.
What are the 2 main factors influencing death rate of a country
Education and health-related factors
List ways education influence death rate
The best-educated people generally live in the most developed nations and they have the highest life expectancies
The UK has a society which educates women whereas Nigeria does not
The key to developing a country is educating girls as this encourages fewer babies
Fewer children improves the standard of living for all as there is more food for all
List ways health influence death rate
After WW2, vaccines and cures for tropical diseases decreased death rates significantly around the world
Richer nations benefited first so their life expectancy increased significantly but most of the developing world has caught up
In LICs, people are more likely to die from poverty and lack of effective treatments from water-borne illness e.g. cholera, typhoid
What is migration
The movement of people from one place to another for a short period of time or permanently.
What is internal or national migration
The movement of people to a city within the same country
What is international migration
he movement of people to a city in a different country
What is labour or economic migration
The movement of people for economic gain
What is forced migration
The movement of people because of events such as a war which pose a sudden threat to people.
List push factors (factors that encourage people to leave an area)
People can't afford to repair damage caused by natural disasters.
Mechanisation of farming equipment means fewer jobs are available.
Desertification can make it hard for people to support themselves as the land becomes less productive.
People might be forced to flee their homes because of conflict.
List pull factors (factors that attract people to an area)
Urban areas provide more jobs, and jobs which are often better paid.
Health care and education are more easily accessible in urban areas.
The thought of joining other family members that have already moved.
There is a perception that urban areas provide a better quality of life.
What are the positive impacts on countries of origin
Unemployment may decrease.
If the migrants return after a few years, they may bring money and skills back with them.
There may be better life chances for young migrants
What are the negative impacts on countries of origin
Economic hardship may come about because of the loss of young workers.
Losing highly trained or skilled people, in particular health workers, can create problems for the countries of origin (brain drain).
There may not be enough people left to farm the land (food shortage).
Migration may cause social problems for children who are raised without parents.
What are the positive impacts on countries of destination
Migration leads to greater cultural diversity (more cultures sharing a home).
Economic growth (better standard of living) keeps going, even if the population is ageing.
There is the advantage of “brain gain” (increase in highly trained foreign-born professionals).
Job vacancies and skill gaps are removed.
The pension gap can be solved by new workers paying taxes.
What are the negative impacts of countries of destination
Lower wages may be offered.
Migrants may be forced to do the DDD jobs (dirty, dangerous and degrading) to make a living.
Public services like schools and hospitals may not be able to cope with the increase in population size.
If migration cannot be controlled, unemployment may increase.
There may be integration (mixing in), language or racism problems between the local people and the migrants.
What are the positive impacts of migration on migrants
There may be the opportunity of better pay for migrants.
There may be a better choice of jobs.
There may be better opportunities to improve skills, training or education.
Migrants may be able to make sure that family members still living in the country of origin are looked after financially.
Migrants may be able to learn new languages.
What are the negative impacts of migration on migrants
Migrants may suffer from loneliness or racist abuse.
The journey for migrants is sometimes very expensive and very dangerous.
Migrants may be forced to do the DDD jobs (dirty, dangerous and degrading) to make a living.
What is population density
It is the number of people per square km
List physical factors that causes low population density
Mountainous land is too cold and difficult to build on
The area may have little resources e.g. infertile soil, limited water supply
Extreme weather conditions
They area may be remote and far away from communities
List physical factors that causes high population density
The area may be flat
The area may have lots of resources e.g. water, fertile soil
Pleasant weather conditions
The area may be easy to access
List economic factors that causes low population density
Lack of jobs in rural areas
Locations with little or no infrastructure, transport, energy and sanitation
List economic factors that causes high population density
Lots of jobs available in cities
There may be lots of suitably priced housing for people
List political factors that causes low population density
There may be wars that force people to move away
There may be oppressions that forces people to move away
List political factors that causes high population density
There may be a democratic society
There may be a stable government
List social factors that causes low population density
Some cultures prefer isolation to preserve cultural heritage
There may be farming over very large areas
List social factors that causes low population density
There is easy access to entertainment shopping and education in cities
There may be shared values, a common language and security provided
What are settlements
Places where people live and sometimes work
What are the 3 types of settlement pattern
Dispersed, nucleated and linear
Describe a dispersed settlement
When homes are spread out with large areas of land between them
They are normally located in rural areas (countryside), large areas of farmland and remote areas
They usually occur in times of peace because people do not need to defend themselves
Describe a linear settlement
Where homes are spread out in a line
They are usually located around high or steep valleys because building takes place along the low lying areas
People usually set up their settlement along a route or a coastline
Describe a nucleated settlement
Where homes are built together around a specific point
They normally started out villages or market towns
The focal point is normally a road intersection, market square or village green
They can be found in lowland areas (easy to build there) or by springs (easy access to water).
They can expand quickly along routeways or rivers.
What are the 4 types of land use in the city
Industrial areas
Rural-urban fringe
Residential area
Central Business District (CBD)
Describe an Industrial area
It is an area where manufacturing plants, factories, transport links and other businesses are located.
These areas sometimes include science parks and universities.
Old industrial areas are now being turned into housing, leisure and modern cultural sites.
Describe a rural-urban fringe
It is the edge of the city where it meets the countryside
It is not an obvious area unless there is a planned greenbelt area around the city
Describe a residential area
It is an area where people live
There are different types of residential buildings from tall high-rise flats to detached housing
In HICs, lots of people begin to move out to the suburbs once the city becomes too busy
In LICs, very poor people live in slums
Describe a CBD
It is a city centre where lots of offices in skyscrapers and not much residential housing is located because the land is expensive
The CBD usually have the best transport connections
In European and colonial countries, it is the oldest part of the city with a town hall, old churches and transport hubs
Contains shops, offices and entertainment as it is the core of the city
What is a burgess concentric circle model
It is a model of urban land use that works for some HIC cities

What is the name of this model
The burgess concentric circle model
Describe a transition zone/inner city
Mixed land use of small industries
Small houses and offices
Developed in the 19th century
Redevelopment occurring
High density terraced housing
Describe an inner suburb/lower class zone
Housing dates 80-100 yrs
Terraced houses with backyards
It is generally where new immigrants settle
Tree lined streets
Describe an outer suburb/middle class zone
Semi-detached houses
Council houses
Shopping parades
Out-of-town shops
On the rural-urban fringe
Describe a commuter/middle class/countryside zone
Green belt around urban areas
Beyond it small towns and villages
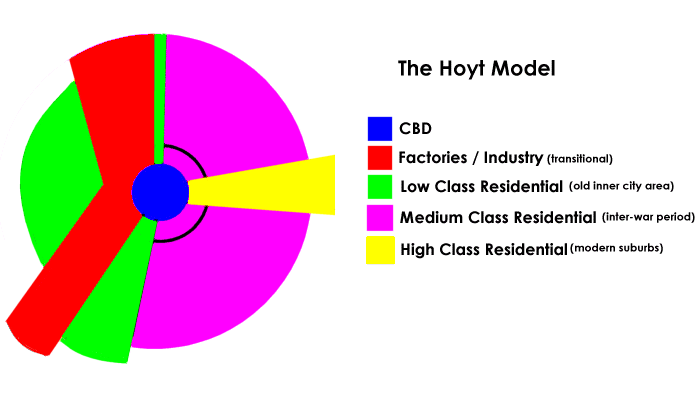
What model is this
The Hoyt model
What is the Hoyt model
It is an improvement on the Burgess model
How is the zones arranged in the Hoyt model
The zones are arranged in the sectors radiating from the CBD
List effects of redeveloping a land (change in urban areas)
Redeveloped areas forces people out of houses as it becomes to expensive
This also causes people to move to a run-down part of the city therefore not solving the problem
List effects of urban sprawl (change in urban areas)
Middle-class people have been moving to the outskirts of cities to avoid the noise pollution
The city spreads out with shopping centres and business parks locating here
Airports and motorways are built on the edges of cities
List effects of rapid urban growth (change in urban areas)
When housing can’t keep up with the demand there is overpopulation
Shanty towns (slums) develop which are illegal
Standards of living and quality of life decrease because people are stuck in poverty and unemployed due to lack of jobs
List effects of conflict over urban sprawl (change in urban areas)
Farmers lose land or have to have houses all around their farm
Big shopping parks cause pollution
Transport routes and airports cause noise and light pollution
Areas previously protected for environmental reasons are used as recreational areas and become degraded
Solutions to reduce pollution in urban areas
Reducing vehicle use by using electric vehicles, public transport and emission laws
Include laws stopping industries that dump in rivers and building proper sewage systems
Include laws to limit hours of noise and fines for people that break the rules
Recycling, reusing and reducing waste are solutions to land pollution as well as using waste as a fuel in power stations
Localised clean-up days and government schemes like community service
Solution to reduce housing and traffic problems
Building on brownfield sites
Subsidising housing costs to reduce commuting
Building more social houses
Improving public transport
Increasing safe cycle paths
Creating toll roads
Having high parking costs
How is traffic congestion reduced in London
London's tube system has 11 lines.
Santander or 'Boris' bikes can be rented to get from A to B.
Consumers can 'tap in' and 'tap out' of the tube or buses using an Oyster card, a bank card or their mobile phones.
Lagos is constructing 2 new train lines to try to improve their public transport system.
Buses often have priority lanes, making them faster than driving yourself.
London introduced a congestion charge of £11.50 per day to use their car in central London.
Taxi services offer on-demand, cheap taxis
Pedestrianized zones reduce congestion.
Businesses allowing employees to work remotely, work from home, or work flexible hours can reduce congestion at peak travel times.
Schools close early before midweek football matches
What is urbanisation
It is the rise in the proportion of people living in towns and cities known as urban areas
Push factors
People's homes and jobs destroyed by a natural disaster.
Automation in farming cause people to lose their jobs in rural agriculture.
Land becomes uninhabitable because of processes like desertification.
Civil wars can force people to leave a place
Countries like Singapore force people to move from their farms to cities by a government mandate
Pull factors
More higher paid jobs in cities
Cities usually have more doctors, nurses, teachers, and other wellbeing infrastructure.
If the trend is that more people are moving to cities, people may just move to live closer to their family and friends.
Cities usually provide more entertainment like cinemas, shops, parks, clubs etc.
Better quality of life
Disadvantages of urbanization of urban areas
Suburbs are usually developed near greenbelt areas. This can harm local wildlife and reduce biodiversity.
Lots of people commute to work using cars which is environmentally-unfriendly
The risk of flooding goes up as housing is built on floodplains and impermeable concrete covers a larger area of land.
A rural village's culture can be eroded by the urbanisation of rural areas.
Ways that make urban life sustainable
Waste recycling
Water conservation
Energy conservation
Creating green spaces
What are squatter settlements
Informal illegal housing caused by overpopulation and housing shortages
Features of the populations in squatter settlements (shanty towns)
People living in squatter settlements don’t have high incomes.
Literacy levels are low.
The populations are mostly migrants, from rural places or from other countries
Healthcare and education levels are low.
There are high levels of disease from dirty water and overcrowding.
There are high crime rates, and settlements are sometimes run by gangs
What are the 2 main causes of urbanisation
Rural-urban migration and natural increase