AP Art History Unit 10 Renaissance Art - Chapter 14 Renaissance in Northern Europe
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
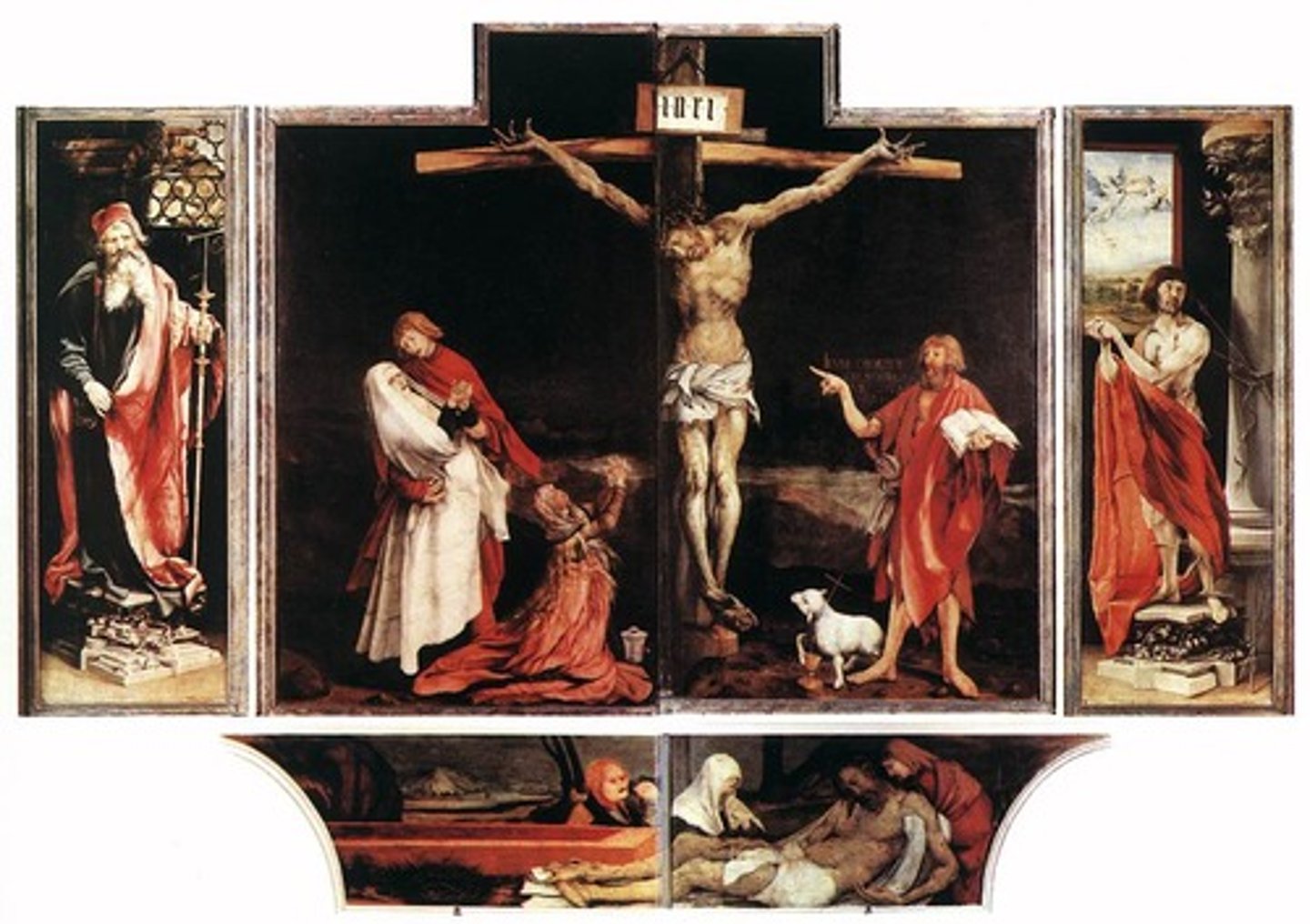
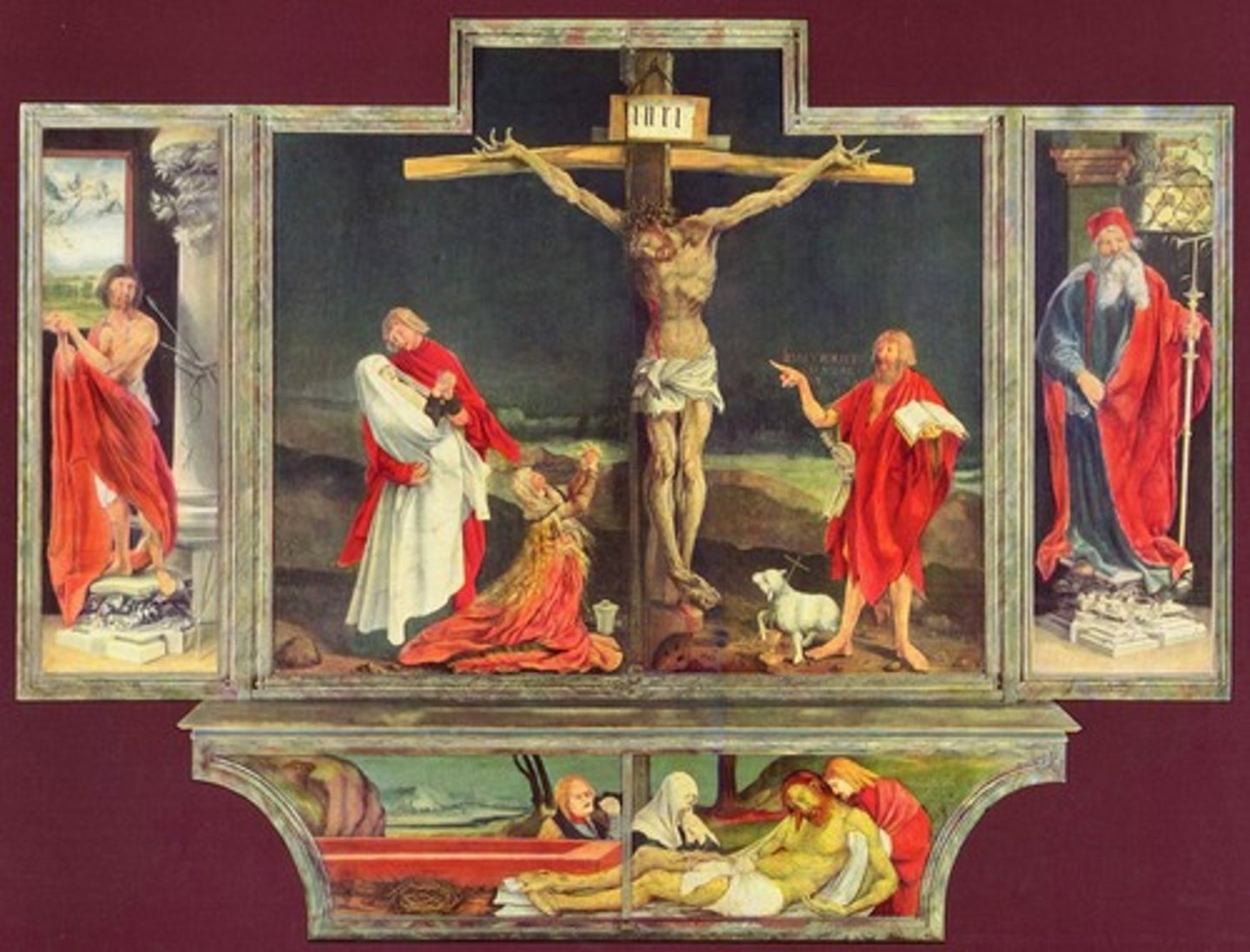
Altarpiece
a painted or sculpted panel set on an altar of a church
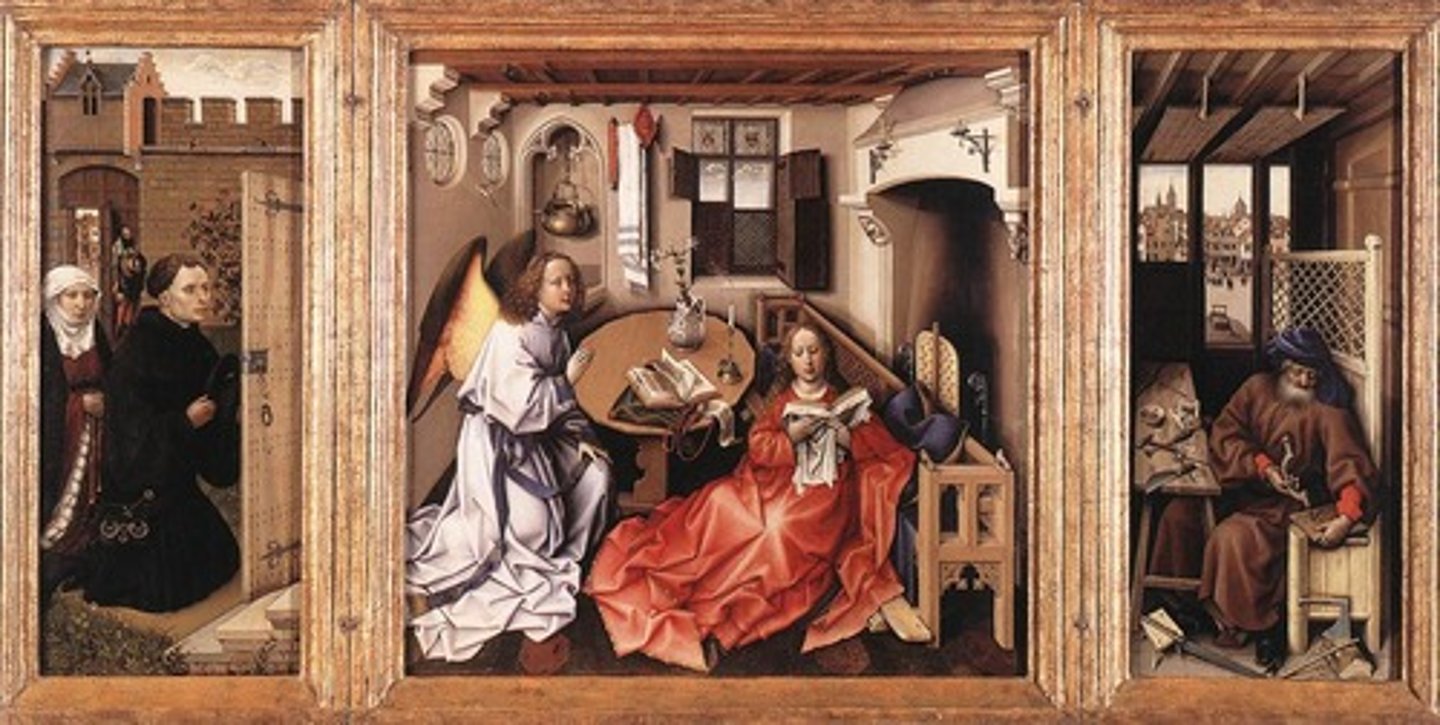
Annunciation
in Christianity, an episode in the Book of Luke 1:26-38 in which Angel Gabriel announces to Mary that she would be the Virgin Mother of Jesus

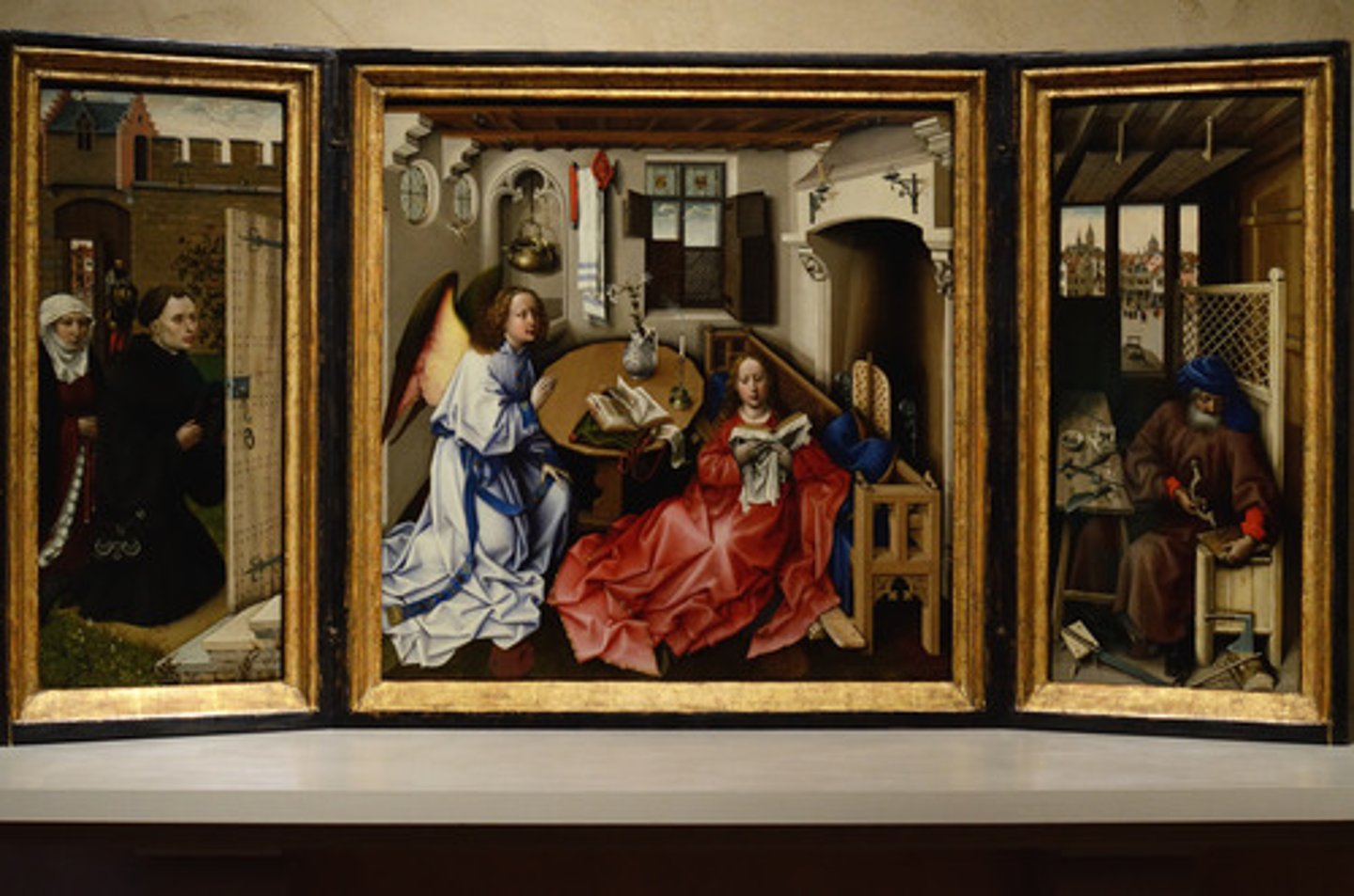
Donor
a patron of a work of art, who is often seen in that work

Engraving
a printmaking process in which a tool called a burin is used to carve into a metal plate, causing impressions to be made in the surface. Ink is passed into the crevices of the plate and paper is applied. The result is a print with remarkable details and finely shaded contours
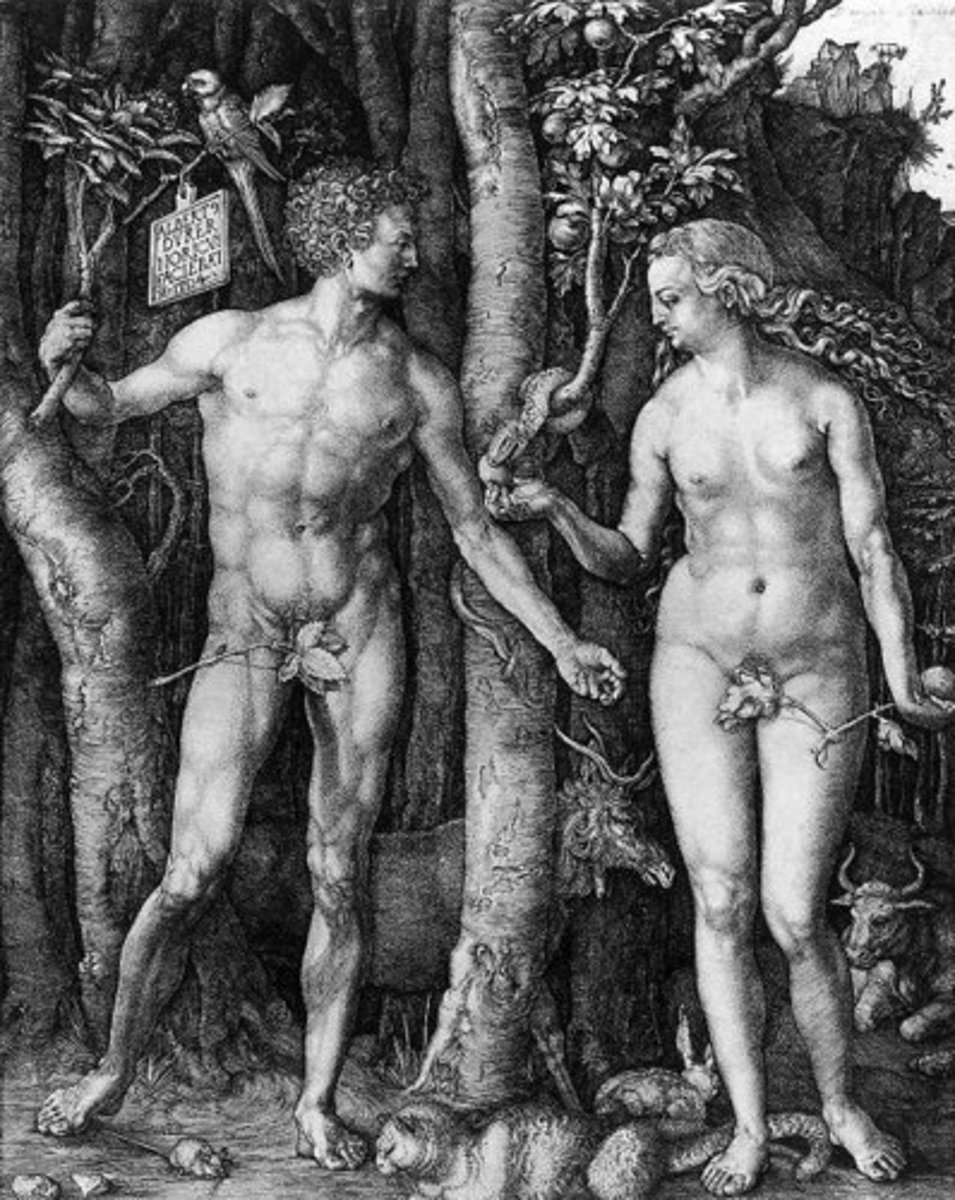

Etching
A printmaking process in which a metal plate is covered with a ground made of wax. The artist uses a tool to cut into the wax to leave the plate exposed. The plate is then submerged into an acid bath, which eats away at the exposed portions of the plate. The plate is removed from the acid, cleaned, and ink is filled into the crevices caused by the acid. Paper is applied and an impression is made. Etching produces the finest detail of the three types of early prints.
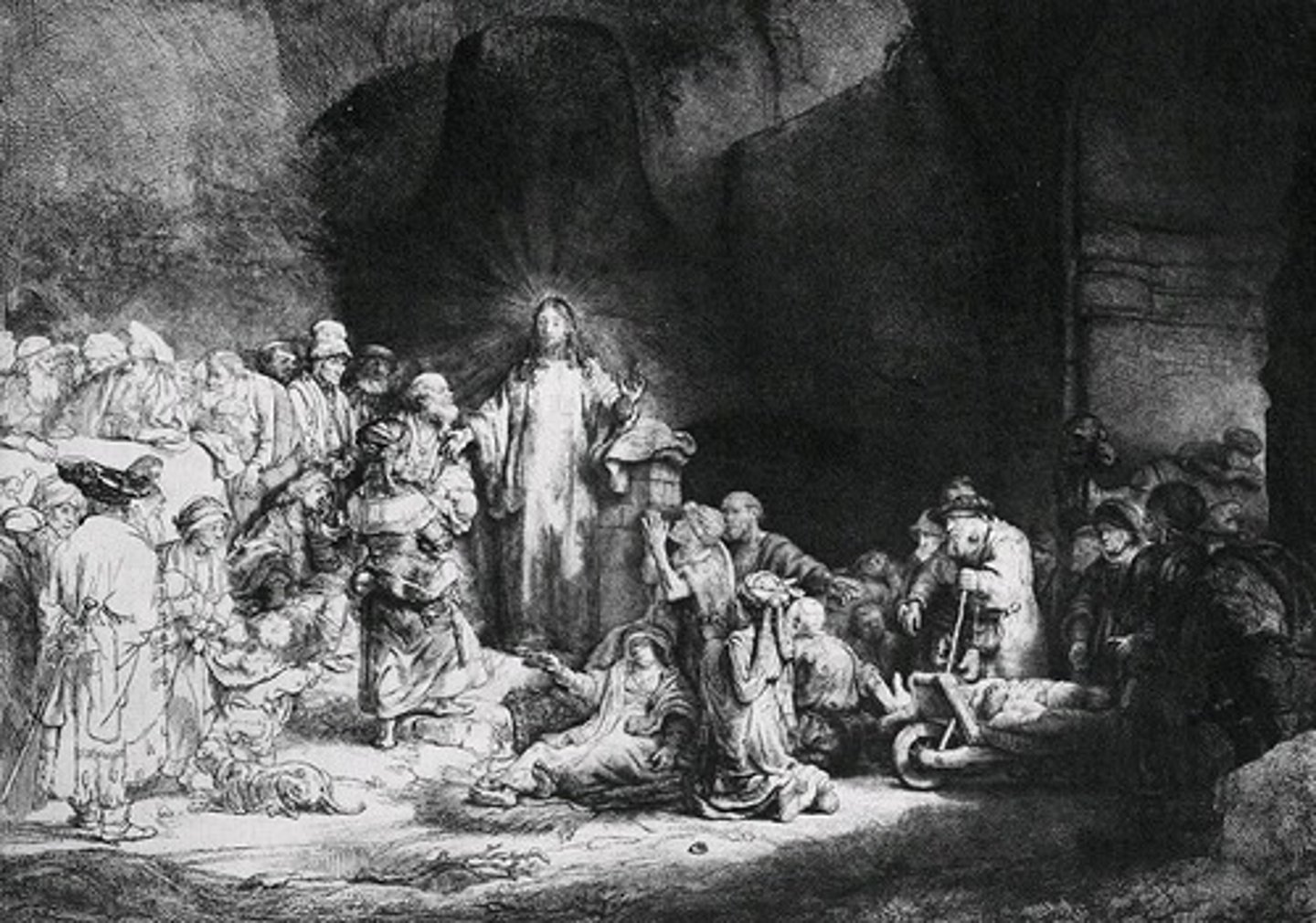

Oil paint
a paint in which pigments are suspended in an oil-based medium. Oil dries slowly allowing for corrections or additions; also allows for a great range of luster and minute details

Predella
the base of an altarpiece that is filled with small paintings, often narrative scenes
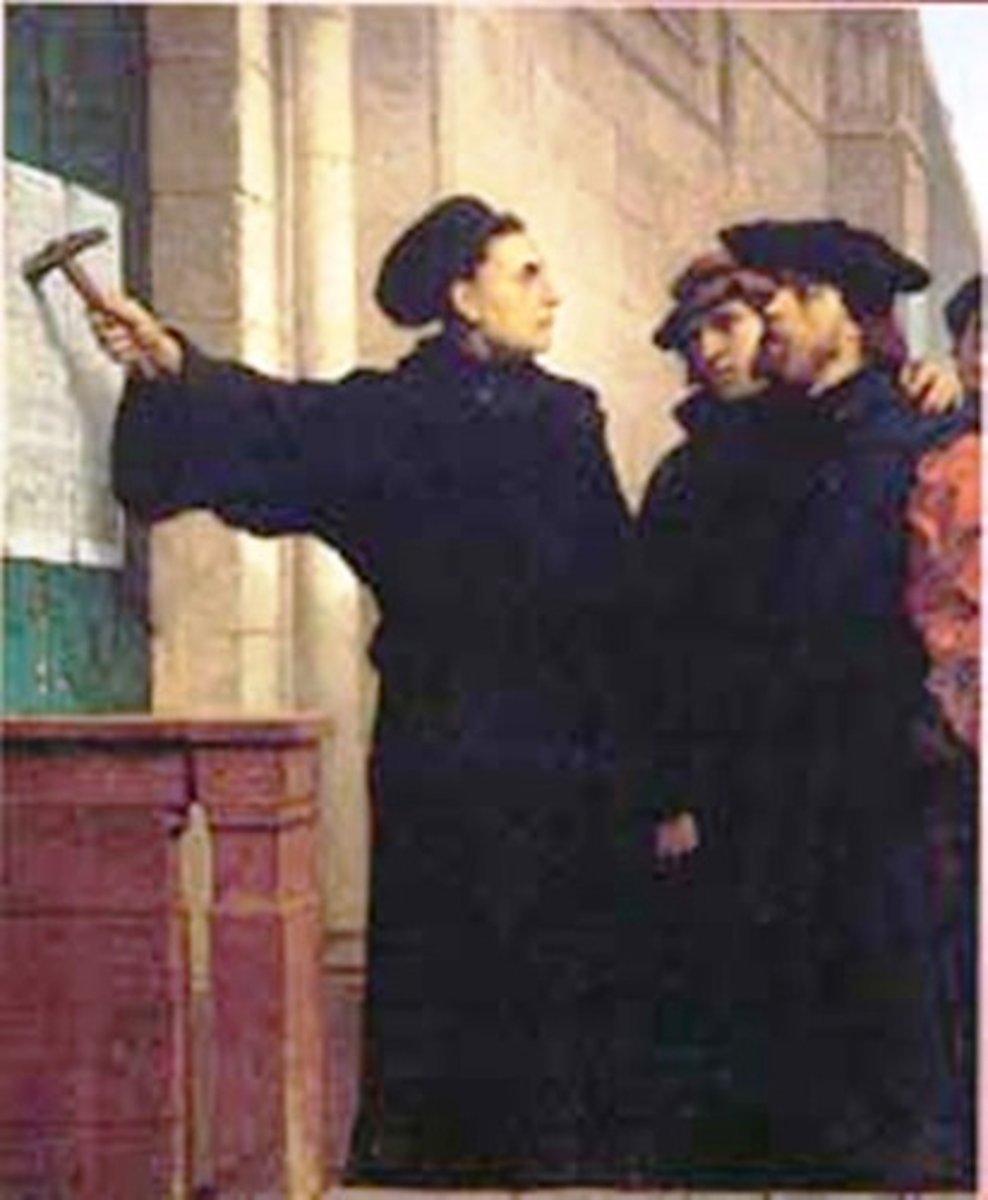
Reformation
a division in western Christianity in which reformers broke away from the Catholic Church and formed a series of Protestant movements. It is considered to have started with the publication of the Ninety-five Theses by Martin Luther in 1517

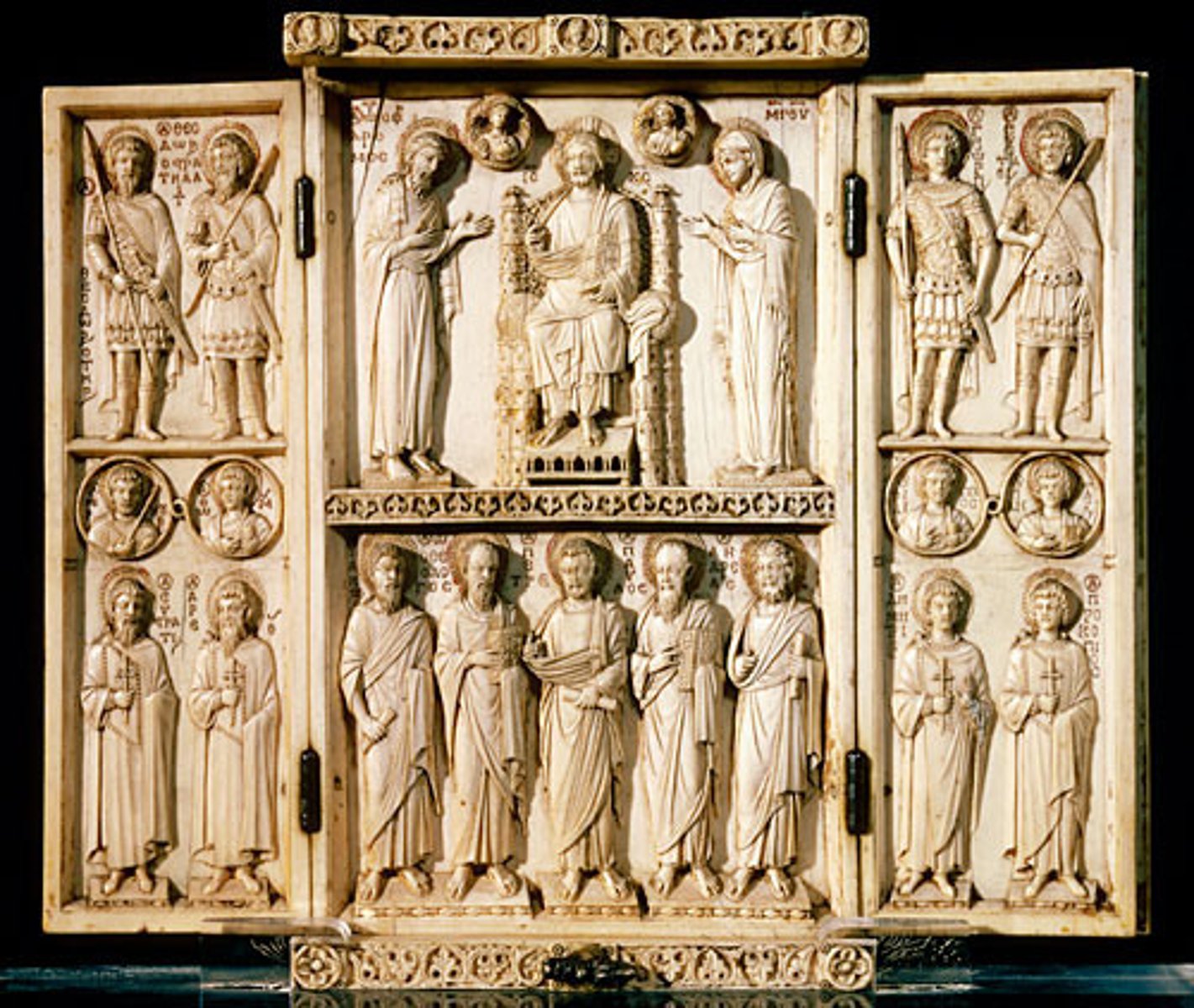
Triptych
A three-paneled painting or sculpture.

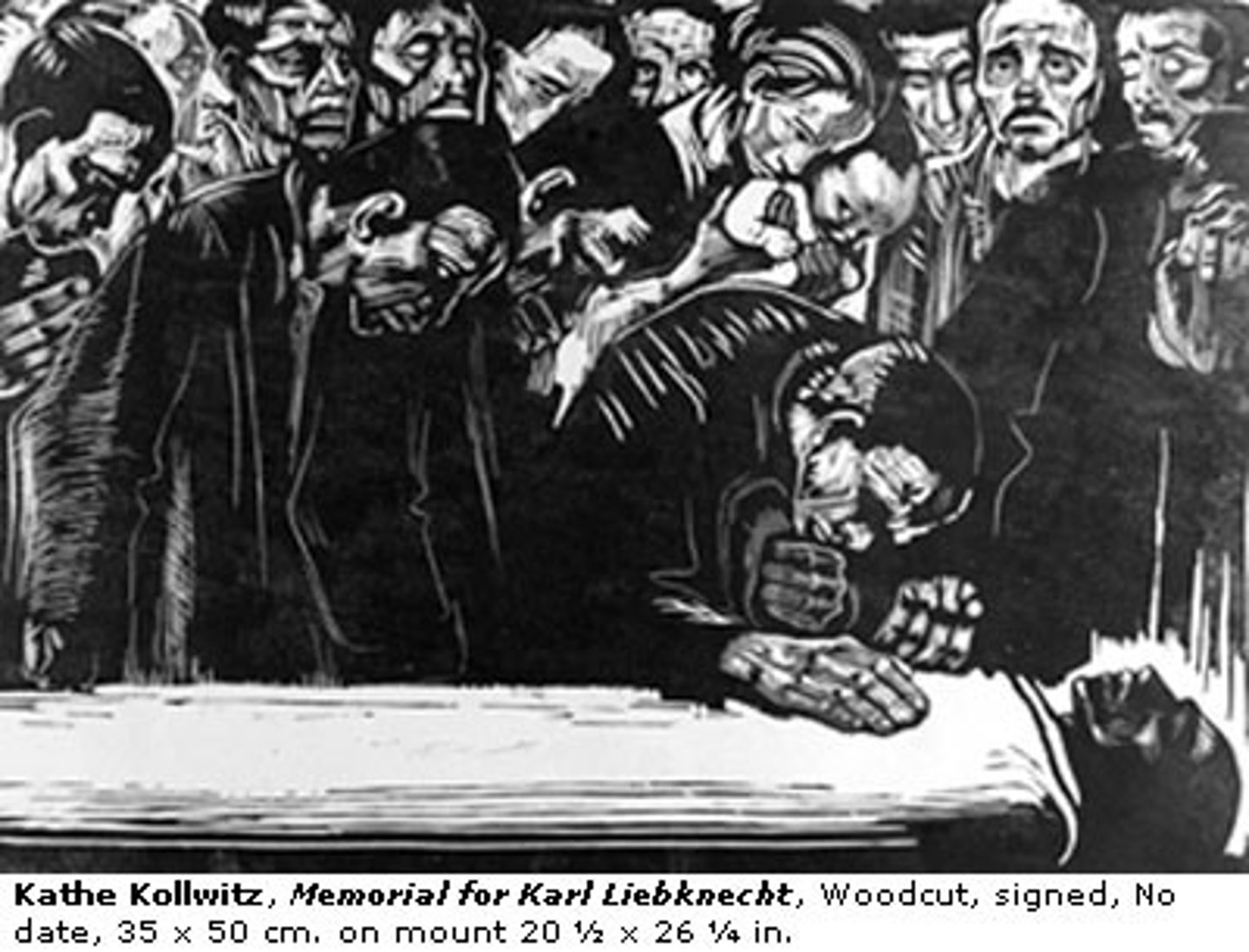
Woodcut
A printmaking process by which a wooden tablet is carved into with a tool, leaving the design raised and the background cut away (very much as how a rubber stamp looks); ink is rolled onto the raised portions and an impression is made when paper is applied to the surface; woodcuts have strong angular surfaces with sharply delineated lines
