[1.1] Combined Gas Law
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Namnamin
How do the macroscopic properties of gases relate to each other?
The macroscopic properties of gases, such as pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), and number of moles (n), are interrelated by three fundamental gas laws: Boyle's Law, Charles's Law, and Gay-Lussac's Law. These relationships can be summarized in the ideal gas law equation: PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is temperature. These laws describe how changes in one property affect the others when the other properties are held constant. Additionally, Avogadro's Law states that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules, further relating volume and the number of moles. These laws collectively explain how changes in pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles affect each other in gases.
Temperature
is the measure of the average kinetic energy of the gas particles.
Volume
is the space occupied by the gas molecules. The volume of a gas depends on the container.
Pressure
is the force applied per unit area as the gas molecules collide with the walls of the container.
Boyle’s Law
Charles’s Law
Gay-Lussac’s Law
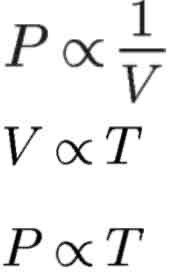
directly proportional
inversely proportional
volume of a gas is ___ to its temperature and ____ to its pressure.
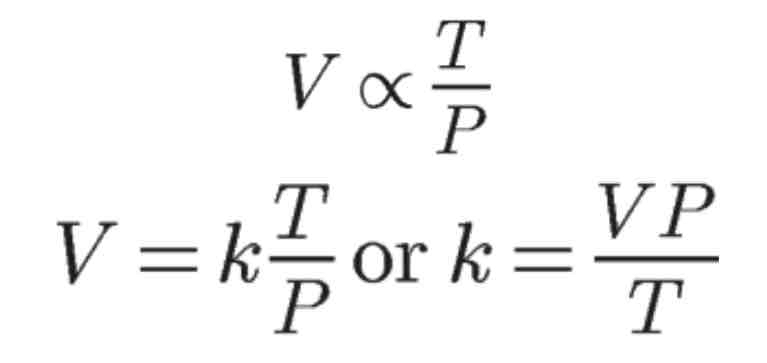
Combined Gas Law
The combined gas law can be used regardless if one of the macroscopic properties of gases were to be kept constant. The constant property will cancel out in the combined gas law equation.
Use this formula to solve any of the six variables when the other three are given.
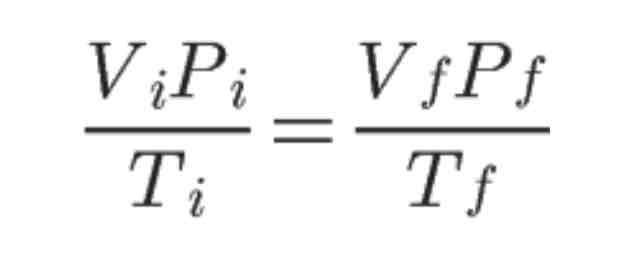
Combined Gas Law
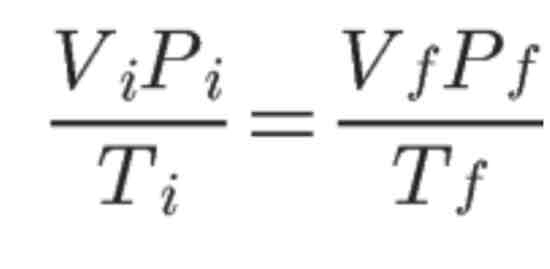
The gas behaves ideally
The conditions remain within the range where the gas laws are valid
The system is closed
What are the conditions for the combined gas law to hold?
1. This means that the gas particles have negligible volume and do not interact with each other. In reality, this is true for gases at low pressures and high temperatures.
The combined gas law is derived from Boyle’s Law, Charles’s Law, and Gay-Lussac’s Law, which are valid under certain conditions. These conditions include low pressures and high temperatures where gas molecules are far apart and have high kinetic energy.
The system containing the gas is sealed, so there is no exchange of matter with the surroundings.