Physics - Electric Current
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
define electric current
rate of flow of charge
define voltage
work done per unit charge
define electromotive force
the amount of energy transferred by a source to each unit of charge that passes through it
define resistance
R = V/I
define internal resistance
the resistance to the flow of charge within a source. internal resistance results in energy being dissipated within the source
state ohm's law
for an ohmic conductor, current is directly proportional to the potential difference across it, given that the physical conditions such as temperature are kept constant
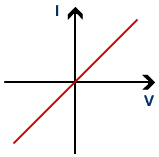
what does a current voltage graph of an ohmic conductor look like
straight line through the origin, directly proportional
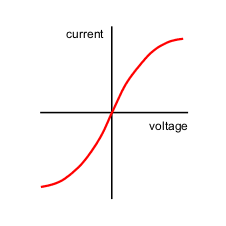
what does a current voltage graph of a filament lamp look like
as V increases I increases, but not at the same rate as V, as I increases R increases
what does a current voltage graph of a semiconductor diode look like
when looking at the current-voltage graph of this component you must consider its forward and reverse bias. the forward bias of a diode is the direction in which it will allow current to flow easily past the threshold voltage, which is the smallest voltage needed to allow current to flow. in the direction of the reverse bias, the resistance of the diode is extremely high meaning that only a very small current can flow.
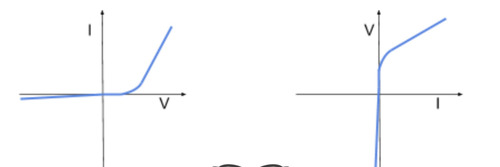
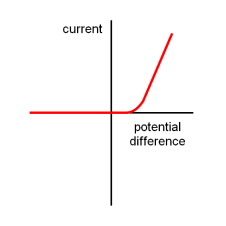
what does a current voltage graph of a diode look like
I = 0 up to forward operating voltage
what does an ideal ammeter mean
assumed to have zero resistance
what does an ideal volmeter mean
assumed to have infinite resistance, no current flows through it
define resistivity
a measure of how easily a material conducts electricity
give the equation for resistivity
ρ = RA/L
explain the qualitative effect of temperature on the resistance of metal conductors (5)
- when temperature of a metal conductor increases, its resistance will increase
- this is because the atoms of the metal gain kinetic energy and move more
- which causes the charge carriers (electrons) to collide with the atoms more frequently
- causing them to slow down
- therefore current decreases and so resistance increases
explain the qualitative effect of temperature on the resistance of thermistors (4)
-as temperature of a thermistor increases, its resistance decreases
- this is because increasing the temperature of a thermistor causes electrons to be emitted from atoms
- therefore the number of charge carriers increases
- so current increases causing resistance to decrease
give an application of thermistors
a temperature sensor, which can trigger an event to occur once the temperature drops or reaches a certain value
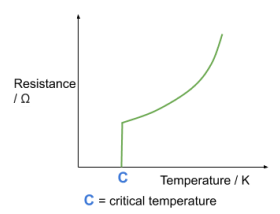
what is a superconductor
a material which below a certain temperature, known as the critical temperature, has zero resistivity and resistance
give two applications of a superconductor
- power cables, which would reduce energy loss through heating to zero during transmission.
- strong magnetic fields, which would not require a constant power source