AbP final exam - semester 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
1
New cards
animal selection
breeding procedures in which the breeders chooses the parents for the futur generation
2
New cards
4 types of selection
* natural : free in nature, wild animals
* artificial : man - breeder
* mass : group of animal, eliminating undesirable genes
* individual: every animal is assessed ( appearance, pedigree, production)
* artificial : man - breeder
* mass : group of animal, eliminating undesirable genes
* individual: every animal is assessed ( appearance, pedigree, production)
3
New cards
breeding and selection goal
choose and breed animals with desirable traits
eleminate undesirable genes
eleminate undesirable genes
4
New cards
degeneration + classification
higher in related individuals
outcome of domestication
\
lethal genes -- death during gravidity
semi lethal genes -- death of young animals
subvital genes-- lower vitality
\
morphological
physiological
psychological
outcome of domestication
\
lethal genes -- death during gravidity
semi lethal genes -- death of young animals
subvital genes-- lower vitality
\
morphological
physiological
psychological
5
New cards
variability of quantitative traits
* continuous variables : birth weight, amount of milk production
* discontinous variables : number of eggs, piglets per litter
* discontinous variables : number of eggs, piglets per litter
6
New cards
quantitative inheritance
involve individual less and population more
7
New cards
quantitative traits characterisitic
* influenced by many pair of genes
* P=G+E --- G = Additive gene action + Dominance gene action + Epistasis gene action
* P=G+E --- G = Additive gene action + Dominance gene action + Epistasis gene action
8
New cards
population genetic
* study of genetic variation among a population
\
\
9
New cards
polygenic trait
group of genes that when expressed together gives a particular phenotype
== controlled by two or more genes
== controlled by two or more genes
10
New cards
arithmetic mean importance -- calculation
* phenotypic value of the traits
* number of individual in population
* number of individual in population
11
New cards
Aim of selection
improve average value in the population ( selection of parents above average)
12
New cards
why do we use statistical evaluation of quantitative trait
* offspring who carries desirable properties
* with which certainty some traits will be transferred( heredity)
* with which certainty some traits will be transferred( heredity)
13
New cards
Heritability (h²)
* strength of inheritance of a character ( likely or not to be transferred)
* based on how much relatives resemble each others
* concerned with differences between inidivuals or group of individuals == not absolute values
* value between 0 and 1 ( 0= no genetic variability)
\
* can be used in a
* narrow sense : includes only A ( additive types of gene action) or average effect of each gene in population
* broad sense : all of the effect of the heredity for each individual + addition of variation due to additive gene ( dominance…)
\
* based on how much relatives resemble each others
* concerned with differences between inidivuals or group of individuals == not absolute values
* value between 0 and 1 ( 0= no genetic variability)
\
* can be used in a
* narrow sense : includes only A ( additive types of gene action) or average effect of each gene in population
* broad sense : all of the effect of the heredity for each individual + addition of variation due to additive gene ( dominance…)
\
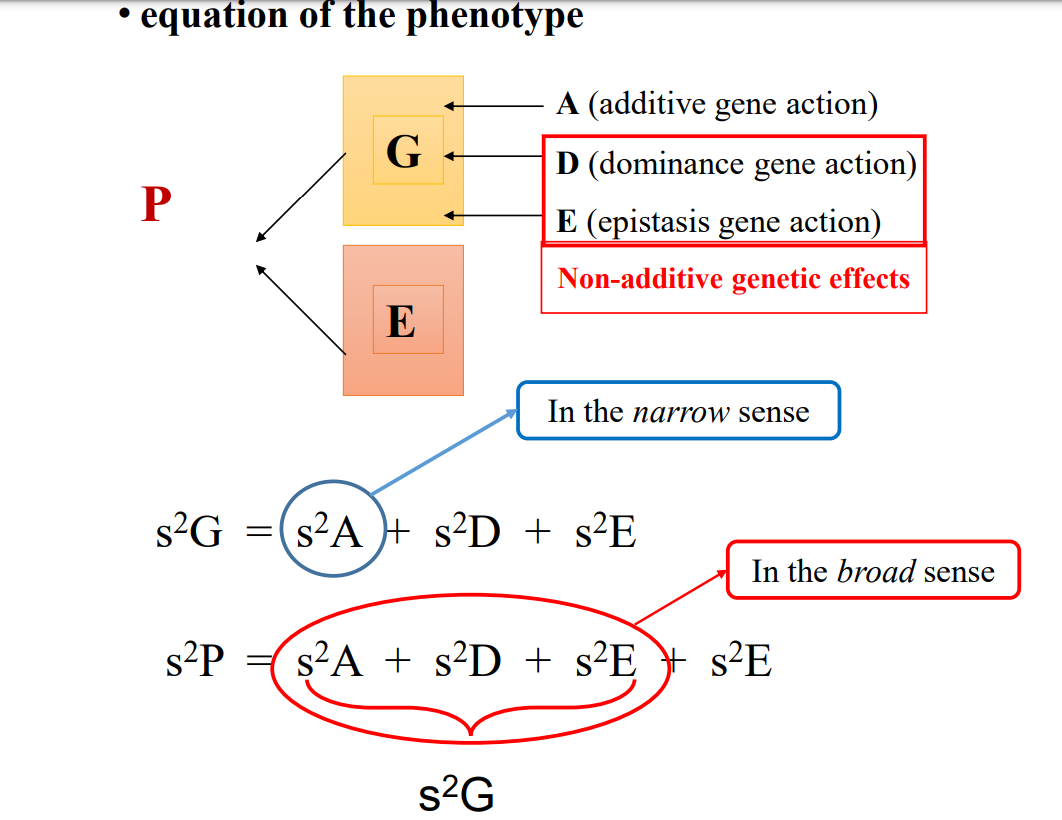
14
New cards
Additive gene action
* **phenotypic of one gene add to another**
* traits of economic importance
* when traits are **highly heritable** + little to no heterosis or inbreeding
* important to standardize the environment to avoid P variations
* select the best and mate it with the best
* traits of economic importance
* when traits are **highly heritable** + little to no heterosis or inbreeding
* important to standardize the environment to avoid P variations
* select the best and mate it with the best
15
New cards
Dominance gene action
* usually desirable traits
* heterozygous = superior to homozygous ( superior in vigor of performance)
* --- important to identify heterozygous individuals to eliminate recessive gene
* heterozygous = superior to homozygous ( superior in vigor of performance)
* --- important to identify heterozygous individuals to eliminate recessive gene
16
New cards
Epistatic gene action
* interaction between genes that are not alleles
\
\
17
New cards
high h² estimates
large portion of phenotype is connected with genotype
18
New cards
low h² estimates
* often
* selection procedures according to phenotype is not reccomended
* -- low correlation btwn phenotype and genotype
* -- low variation due to Additive gene action
* -- high importance of dominance and epistasis genes
* == important to look at the performance of the relatives and progeny
* not a static value ( varies)
* selection procedures according to phenotype is not reccomended
* -- low correlation btwn phenotype and genotype
* -- low variation due to Additive gene action
* -- high importance of dominance and epistasis genes
* == important to look at the performance of the relatives and progeny
* not a static value ( varies)
19
New cards
H² estimates is determined
ressemblre btwn
1- siblings
2- half sibling
3- parents and offspring
\
* useful in gain tests
1- siblings
2- half sibling
3- parents and offspring
\
* useful in gain tests
20
New cards
repeatability estimates
* expression of the same trait at a different time in the life -- likelyhood of repeatability
* fraction of differences between single records
* heritability and repeatibility are related to superiority and inferiority of animals
* fraction of differences between single records
* heritability and repeatibility are related to superiority and inferiority of animals
21
New cards
Criteria for selection
* mean = starting point ( and then + or - depending on trait)
* number of individual necessary to get replaced
\
* number of individual necessary to get replaced
\
22
New cards
selection differential
* how good the parents chosen will be == superiority of selected parents in comparison to the mean
* SD = Xs- X (mean of the parents- overall mean)
* indicator of efficiency in selection
* the more the number of selected trait, the smaller the selection differential for each individuals traits
* SD = Xs- X (mean of the parents- overall mean)
* indicator of efficiency in selection
* the more the number of selected trait, the smaller the selection differential for each individuals traits
23
New cards
selection intensity
is= SD/ Phenotypic standard deviation
\
Phenotypic standard deviation = if the variation is normally find in the trait of a population
\
Phenotypic standard deviation = if the variation is normally find in the trait of a population
24
New cards
generation interval
* time interval between generations ( average age of parents when offspring is born)
* limited by puberty
* \
* limited by puberty
* \
25
New cards
reasons for replacement
* renewal rate-- number per year
* replacement rate = Renewal rate / **average** number of **offsrping** of the same **sex** per animal per **year**
* replacement rate = Renewal rate / **average** number of **offsrping** of the same **sex** per animal per **year**
26
New cards
Positive effect of crosses
* hybrid ( heterozygote)
* heterosis ( positive hybrid vigor)-- better than the mean of the parents
* heterosis=(Mean F1 offspring -mean of parents)/ Mean of parental breeds x100
* heterosis ( positive hybrid vigor)-- better than the mean of the parents
* heterosis=(Mean F1 offspring -mean of parents)/ Mean of parental breeds x100
27
New cards
prediction amount of progress through selection
* Gain per generation= heritability x selection differential
28
New cards
Polymorphic genes
many genes are polymorphic - different forms
29
New cards
degree of which selection affect a trait depends on (4)
* heritability
* variability
* intensity of selection
* generation interval
* variability
* intensity of selection
* generation interval
30
New cards
factors to consider when selecting a breeding stock
* age -- younger animals ( longer productive life)
* lvl of performance -- highest prdction level ( high milk, woo,egg prdction)
* physical fitness -- free from any physical defect, not sick
* body conformation -- according to production type
* temperature and behaviour -- bad behaviour-- culled
* quality of product -- high quality ( meat, milk, egg…°
* Mothering ability --
* adaptability (climatic condition)
* prolificacy -- highly prolific
* lvl of performance -- highest prdction level ( high milk, woo,egg prdction)
* physical fitness -- free from any physical defect, not sick
* body conformation -- according to production type
* temperature and behaviour -- bad behaviour-- culled
* quality of product -- high quality ( meat, milk, egg…°
* Mothering ability --
* adaptability (climatic condition)
* prolificacy -- highly prolific
31
New cards
breeding value
* **economic worth of an animal genotype**
\-- judged by ability of offspring
* for qualitative and quantitative traits
== genetic merit
* measured with Estimate breeding value
* performance of animal is compared to the other individual in the group
* advantages : makes it possible to avoid extreme values for particular traits
\-- judged by ability of offspring
* for qualitative and quantitative traits
== genetic merit
* measured with Estimate breeding value
* performance of animal is compared to the other individual in the group
* advantages : makes it possible to avoid extreme values for particular traits
32
New cards
Method of estimation for BV
* pedigree -- **performance of ancestor**
* performance test ( individual or mass selection) -- **animal phenotype**
* performance of relatives -- **relatives phenotype**
* progeny testin -- **phenotype of progeny**
* BLUP method ( combination of data)
* **genetic test**
* performance test ( individual or mass selection) -- **animal phenotype**
* performance of relatives -- **relatives phenotype**
* progeny testin -- **phenotype of progeny**
* BLUP method ( combination of data)
* **genetic test**
33
New cards
estimation according to ancestors
* if ancestor also have traits of quality it is more likely that they will transfer it to their offspring
* pedigree ( 3 generations)
* depends on h²
\
* pedigree ( 3 generations)
* depends on h²
\
34
New cards
Estimation according to production records
* exterior ( breed strandards)
* primary and secondary sexual characterisitics
* health
\
* linear scoring
* measuring and grading
* body score
* performance test (field test)
* depends on type and sex
* measured on animal ( fattening charac…)
* BV= h²\*(Px-A)
* A= population average
* Px= phenotype of the individual
* reapitability ( accuracy)
\
* primary and secondary sexual characterisitics
* health
\
* linear scoring
* measuring and grading
* body score
* performance test (field test)
* depends on type and sex
* measured on animal ( fattening charac…)
* BV= h²\*(Px-A)
* A= population average
* Px= phenotype of the individual
* reapitability ( accuracy)
\
35
New cards
Estimation according to performance of relatives
* for low h²
* **Sib test**
* often for pigs breeding
* **Sib test**
* often for pigs breeding
36
New cards
Estimation according to the progeny
* progeny testing
* when low h² or only in one sex
* the greater the number of offspring the more accurate it will be
\
* factors for successful progeny testing: - random selection
* offspring are in production the same year and same season
* environmental factors should be as equal as possible
\
* when low h² or only in one sex
* the greater the number of offspring the more accurate it will be
\
* factors for successful progeny testing: - random selection
* offspring are in production the same year and same season
* environmental factors should be as equal as possible
\
37
New cards
BLUP ( best linear unbiased prediction) method
* most accurate
* goal : to improve a higher number of properties simultaneously
* advatanges : - BV assessment btwn farms
* performance form pedigrees
* large amount of information = accurate
* goal : to improve a higher number of properties simultaneously
* advatanges : - BV assessment btwn farms
* performance form pedigrees
* large amount of information = accurate
38
New cards
Genetic selection
* genomic selection
39
New cards
pig breeding program
* pyramid organization
* nucleus herd
* multiplying herd
* production ( commercial herd)
* market pigs
* nucleus herd
* multiplying herd
* production ( commercial herd)
* market pigs
40
New cards
Field test
* **Animal testing in production condition**
* implementation of testing
* measurement of properties
* data records
== improvement of pig production by BLUP method
\
* selection procedure :
* litter selection
* selection after weighing
* data entry
* data calculation
* implementation of testing
* measurement of properties
* data records
== improvement of pig production by BLUP method
\
* selection procedure :
* litter selection
* selection after weighing
* data entry
* data calculation
41
New cards
Cattle breeding
* milk production :
* milk control : measuring and sampling
* results are including in breedin program
* meat production :
* BV are calculated for the net daily gain
* fitness
* natural mating
* pregnancy
* prenatal death
* exterior
* description and evaluation
\
* milk control : measuring and sampling
* results are including in breedin program
* meat production :
* BV are calculated for the net daily gain
* fitness
* natural mating
* pregnancy
* prenatal death
* exterior
* description and evaluation
\
42
New cards
genetic BV estimation cattle
* MMM= mixed model methodology
* BLUP results
* MM= sires and cows are simultaneously evaluated using genetic linkage
* data included :
* ease of calving
* fertility charac
* quality of meat
* exterior
* milk production testing
* Total merit index
* BLUP results
* MM= sires and cows are simultaneously evaluated using genetic linkage
* data included :
* ease of calving
* fertility charac
* quality of meat
* exterior
* milk production testing
* Total merit index
43
New cards
Targeted mating
* selection of top bull’s sire and bull’s dam
\
* top dams :
* elite cow
* production properties surpasse population for 2 SD
* inlcuded in MOET
* top sire :
* positive test values
\
* top dams :
* elite cow
* production properties surpasse population for 2 SD
* inlcuded in MOET
* top sire :
* positive test values
44
New cards
sheep breeding improvment
* control of milk production
* performance test in fields condition
* performance test in fields condition
45
New cards
sheep estimation of breeding value ( what’s taken into account)
* lambing season
* lactation stage
* lamb weight
* litter size
* Additive genetic action on lamb
* lactation stage
* lamb weight
* litter size
* Additive genetic action on lamb
46
New cards
improvment of goat breeding and selection
* reproductive traits
* milk production
* performance test (field conditions)
* milk production
* performance test (field conditions)
47
New cards
Horse breeding selection criteria
* pedigree
* external appearance
* health
* performance test
* colour
* progeny performance
* external appearance
* health
* performance test
* colour
* progeny performance
48
New cards
Poultry breeding
* age
* fertility
* eggs charac ( size, number, colour…)
* feather colour
* fertility
* eggs charac ( size, number, colour…)
* feather colour
49
New cards
dog and cats breeding important traits
* appearance
* behvaiour
* behvaiour
50
New cards
biotechnology definition
technological application that uses biological system, living organism to make or modify products
51
New cards
biotech i livestock production
* biological
* chemical
* physical techniques that influence animal health, nutrition, breeding and reproduction
* chemical
* physical techniques that influence animal health, nutrition, breeding and reproduction
52
New cards
biotech animal health
* vaccine production === primary
* vector control
* quarantine
* === secondary
* advances: - detection of nucleic a, proteins and specific antibodies
* futur : genome sequencing data ( for vaccins)-- heat stable vaccins ( no need for refrigiration)
* important area in developping countries -- high disease challenge
* vector control
* quarantine
* === secondary
* advances: - detection of nucleic a, proteins and specific antibodies
* futur : genome sequencing data ( for vaccins)-- heat stable vaccins ( no need for refrigiration)
* important area in developping countries -- high disease challenge
53
New cards
biotech in ABP
* maintaining **genetic biodiversity**
* increasing **breeding efficiency** and livestock
* within organized breeding scheme
* conservation of animal genetic
* criterias taken account: - growth rate and litter size
* genetic gain -- thanks to **Artificial insemination** and embryo transfer -- new : cloning, transgenic animal
* increasing **breeding efficiency** and livestock
* within organized breeding scheme
* conservation of animal genetic
* criterias taken account: - growth rate and litter size
* genetic gain -- thanks to **Artificial insemination** and embryo transfer -- new : cloning, transgenic animal
54
New cards
Artificial insemination -- biotech reproduction
* genetic progress 4 times better than natural mating
* use of superior sires = most effective tool
* mainly for dairy cattle
* use of superior sires = most effective tool
* mainly for dairy cattle
55
New cards
Embryo transfer
* function : increase reproductivity rate of valuable females
* in cattle
* in highly commercialized livestock production
* MOET ( multiple ovulation and embryo transfer technique) -- increase the utilization of superior dam ( increase intensity of selection) -- use of PMSG and FSH
* recepient cow must be in estrus within 1.5 days of the donor’s result
* in cattle
* in highly commercialized livestock production
* MOET ( multiple ovulation and embryo transfer technique) -- increase the utilization of superior dam ( increase intensity of selection) -- use of PMSG and FSH
* recepient cow must be in estrus within 1.5 days of the donor’s result
56
New cards
Genetic markers
genes or DNA that have a known location and are easily identifable
ex: causative mutation
ex: causative mutation
57
New cards
MAS -- marker assisted selection
phenotype selection method
use of genetic map
difficult in developing countries
use of genetic map
difficult in developing countries
58
New cards
breeding scheme
* offer opportunity for use of biotech
*
*
59
New cards
transgenic animal def
* animal which carry foreign dna in genome
* why ? :
* to improve milk production
* increase disease resistance
* improve feed efficiency
* increase growth rate
* high cost limited success
* why ? :
* to improve milk production
* increase disease resistance
* improve feed efficiency
* increase growth rate
* high cost limited success
60
New cards
farm animal cloning
* might be useful for : - preservation of elite male and female
* modify genes
* modify genes