MCAT-Behavioral Science Unit 5
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is a motivation?
The purpose, or the driving force, behind one’s actions.
Extrinsic motivation
Motivation for external rewards or avoid punishment.
Intrinsic motivation
Motivation for internal satisfaction, enjoyment.
Instinct theory of motivation
Certain behaviors are based on evolutionarily programmed instincts.
Arousal Theory
People perform actions to maintain a maximum level of arousal; raising it when it is below the optimal level, and reducing it when it is above.
What is “Arousal”?
The psychological and physiological state of being awake and reactive to stimuli.
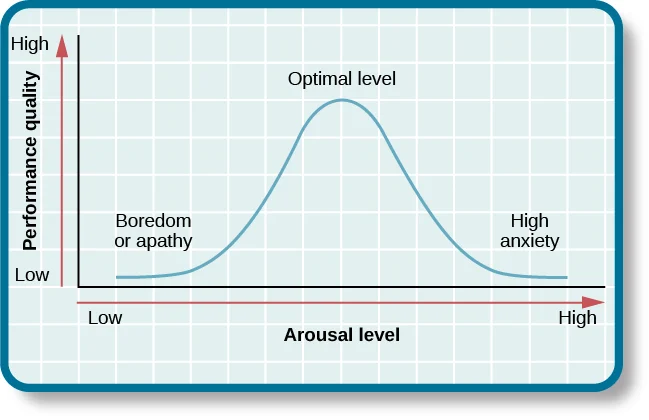
Yerkes-Dodson Law
Drive Reduction Theory
Drives create discomfort within an individual to provide motivation for the individual to reduce these drives.
What are some examples of “Primary Drives”?
The need for food, water, and warmth.
Negative Feedback Loops
Self-regulating systems that work to reduce or counteract a change
What are “Secondary Drives”?
Learned motivations, not tied to survival, that become powerful because they are associated with satisfying primary drives (like hunger, thirst) through classical conditioning.
Need-Based Theory
People are motivated to allocate energy and resources to best satisfy their needs.
What are the Primary Needs in the Need-Based Theory?
The need for food, water, sleep, and shelter.
What are the Secondary Needs in the Need-Based Theory?
Mental desires, such as the desire for power, achievement, or social belonging.
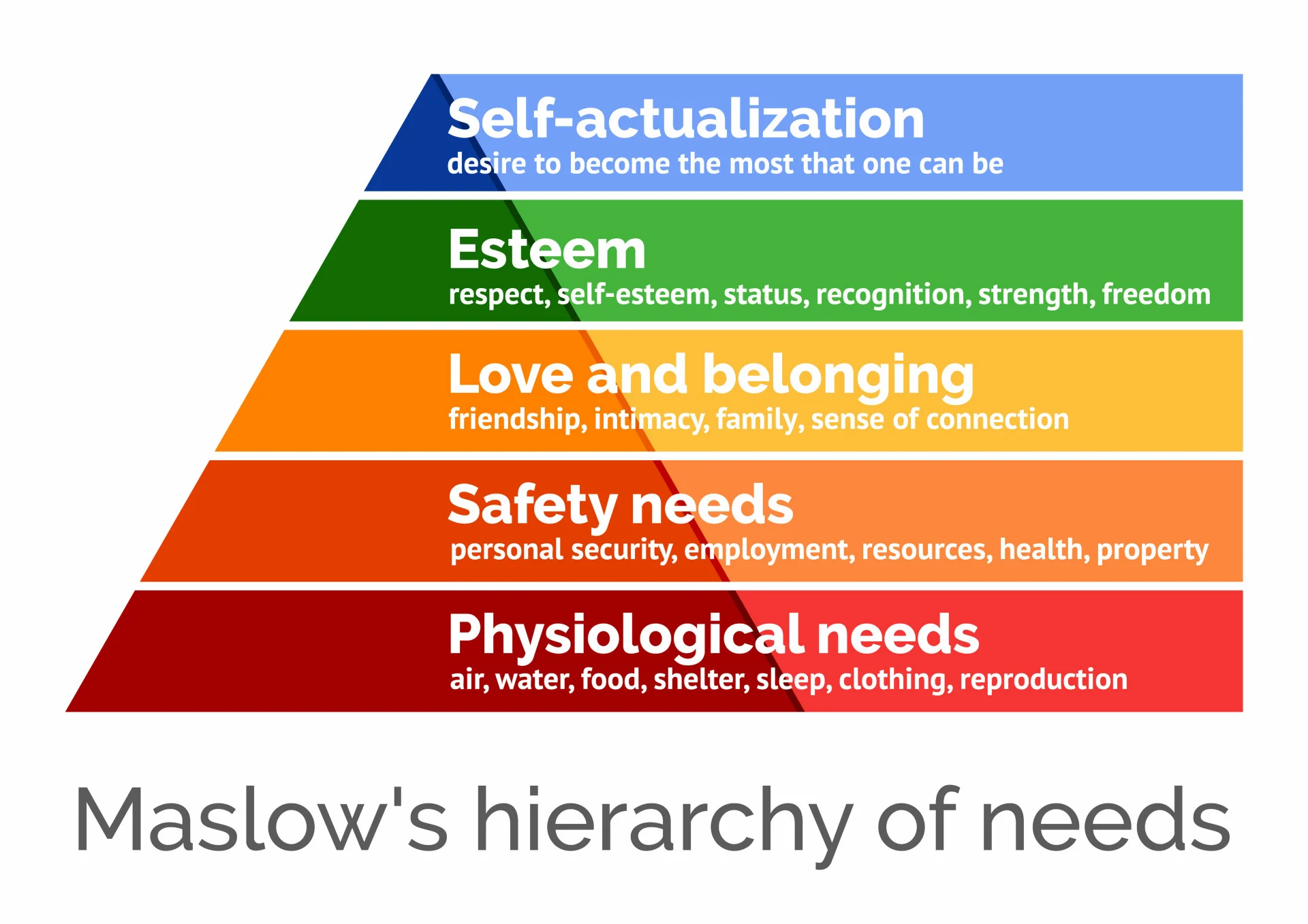
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
What are the three universal needs according to Self-determination theory (SDT)?
1) Autonomy: The need to be in control of one’s actions and ideas.
2) Competence: The need to complete and excel at difficult tasks.
3) Relatedness: The need to feel accepted and loved in a relationship.
Incentive Theory of Motivation
Behavior is motivated not by need or arousal, but by the desire pursue rewards and to avoid punishment.
Expectancy Theory of Motivation
The amount of motivation needed to reach a goal is the result of both the individual’s expectation of success in reaching the goal and the degree to which the individual values succeeding at the goal.
What does the “Opponent-process Theory” explain about continuous drug use?
When a drug is taken repeatedly, the body will counteract the effects of the drug by changing its physiology.
List Maslow’s hierarchy of needs in descending order
1) Self-actualization
2) Esteem
3) Love/belonging
4) Safety
5) Physiological
What are the three elements of emotion?
1) The physiological response
2) The behavioral response
3) The cognitive response
What are 7 universal emotions?
1) Happiness
2) Sadness
3) Contempt
4) Surprise
5) Fear
6) Disgust
7) Anger
Facial-Feedback Effect/Hypothesis
Certain facial expressions can affect emotions
James-Lange Theory of Emotions
A stimulus results in a physiological arousal, which leads to a corresponding emotion. (physiological change → emotion expression)
Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotions
Conscious experience of emotion and physiological arousal occur simultaneously.
Schachter-Singer Theory
Both physiological arousal and a cognitive label are required to produce an emotion.
Cognitive Appraisal of Stress
The subjective evaluation of a situation that induces stress.
Primary appraisal
The initial examination which identify the stress as irrelevant, benign-positive, or stressful. (Positive or Negative)
Secondary appraisal
If the primary appraisal identifies the stress as a threat, then the secondary appraisal is the evaluation of whether the organism’s capability of coping with that stress. (Intensity or risk)
What is a Stressor?
A stressor is a biological element, external condition, or event that leads to a stress response.
What is the difference between a distress and an eustress?
A distress is perceived as negative, or unpleasant (a threat), whereas an eustress is the result of a positively perceived stressor.
Social readjustment rating scale
A measuring system of stress level in “life change units”.
What are the three stages in the “general adaptation syndrome”?
1) Alarm
2) Resistance
3) Exhaustion
What is the difference between Acute Stress and Chronic Stress?
Acute stress is a short-term reaction to immediate demands (like a deadline) with quick onset and resolution, causing a racing heart, tension
Chronic stress is prolonged, ongoing stress (job pressure, finances) leading to fatigue, anxiety, and serious health issues like heart disease.
Diathesis-stress model
Psychological disorders results from an interaction between a pre-existing vulnerability (diathesis, often genetic or biological) and environmental stressors (stressful life events)
Approach-approach conflict
A dilemma where you must choose between two equally desirable options
Approach-avoidance conflict
A psychological struggle where a single goal has both positive (approach) and negative (avoidance) aspects, creating internal tension, indecision, and wavering behavior as you're drawn to the reward but repelled by the potential downsides.
Avoidance-avoidance conflict
A dilemma where you must choose between two equally undesirable or negative options