Topic 1 - Cell biology
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Eukaryotic cells
-have genetic material that forms chromosomes and is contained in the nucleus
-much bigger than prokaryotic cells
-plant and animal cells
Subcellular structures
-cell membrane which controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
-nucleus which contains DNA
-mitochondria which is where energy is released through respiration
-cytoplasm which is where chemical reactions take place
-permanent vacuole which stores cell sap
-chloroplasts which contain chloroplasts that absorb light energy for photosynthesis
-cell wall which is made of glucose to strengthen the cell wall
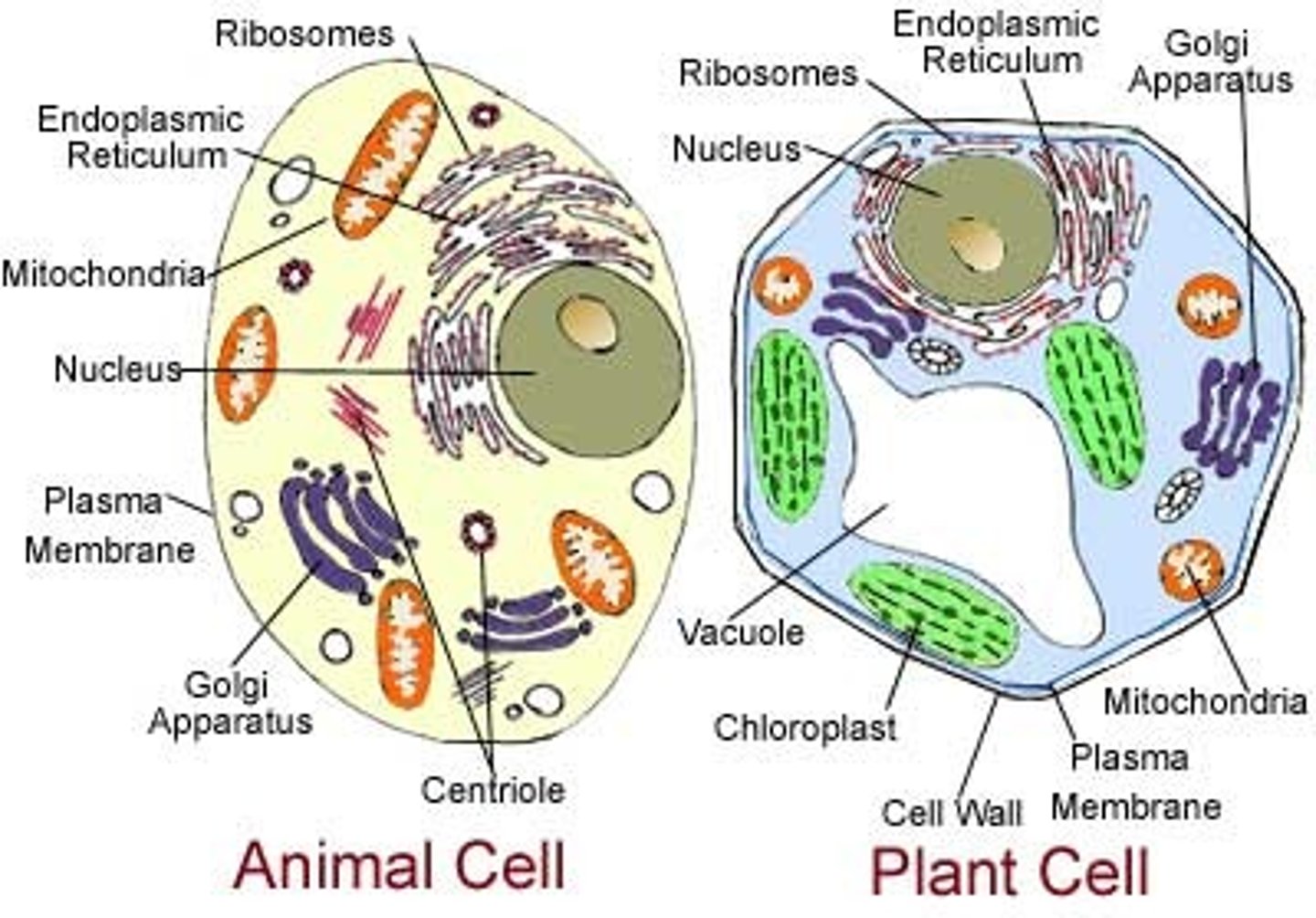
Animal cell subcellular substructures
-cell membrane
-nucleus
-mitochondria
-ribosomes
-cytoplasm
Plant cell subcellular structure
-cell membrane
-nucleus
-mitochondria
-ribosomes
-cytoplasm
-permanent vacuole
-chloroplasts
-cell wall
Prokaryotic cells
-single celled
-no nucleus and have a single loop of DNA
-have small rings of DNA called plasmids
-smaller than eukaryotic cells
-bacteria
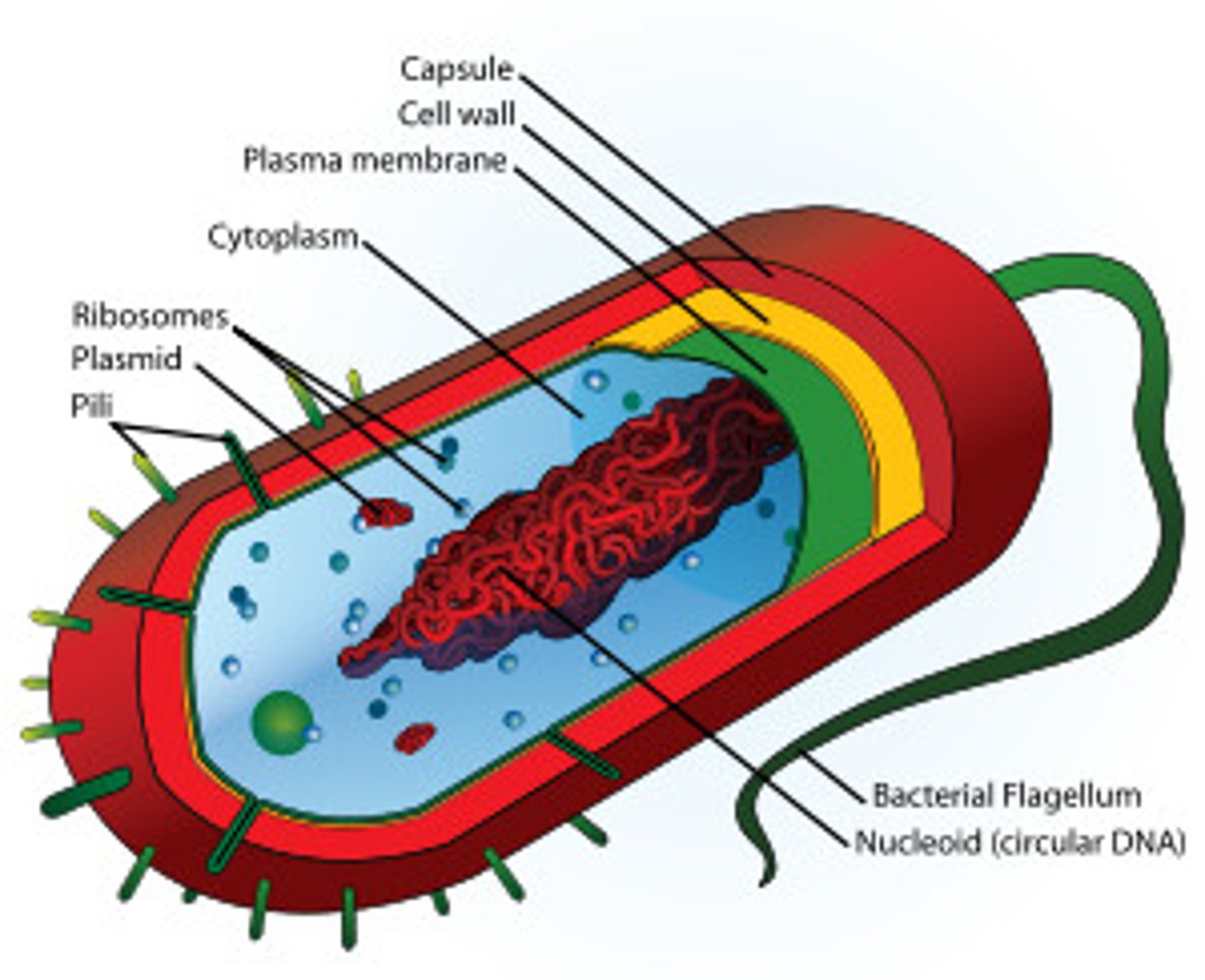
Subcellular structures in prokaryotic cells
-cell wall
-cytoplasm
-cell membrane
-flagellum
-bacterial DNA loop
-plasmid DNA rings
Light microscopes
-use light to form images
-living samples can be viewed
-relatively cheap
-low magnification
-low resolution
-can't see sub cellular structures

Electron microscopes
-uses beams of electrons to form images
-sample cannot be living
-expensive
-high magnification
-high resolution
-allow you to view sub cellular structures
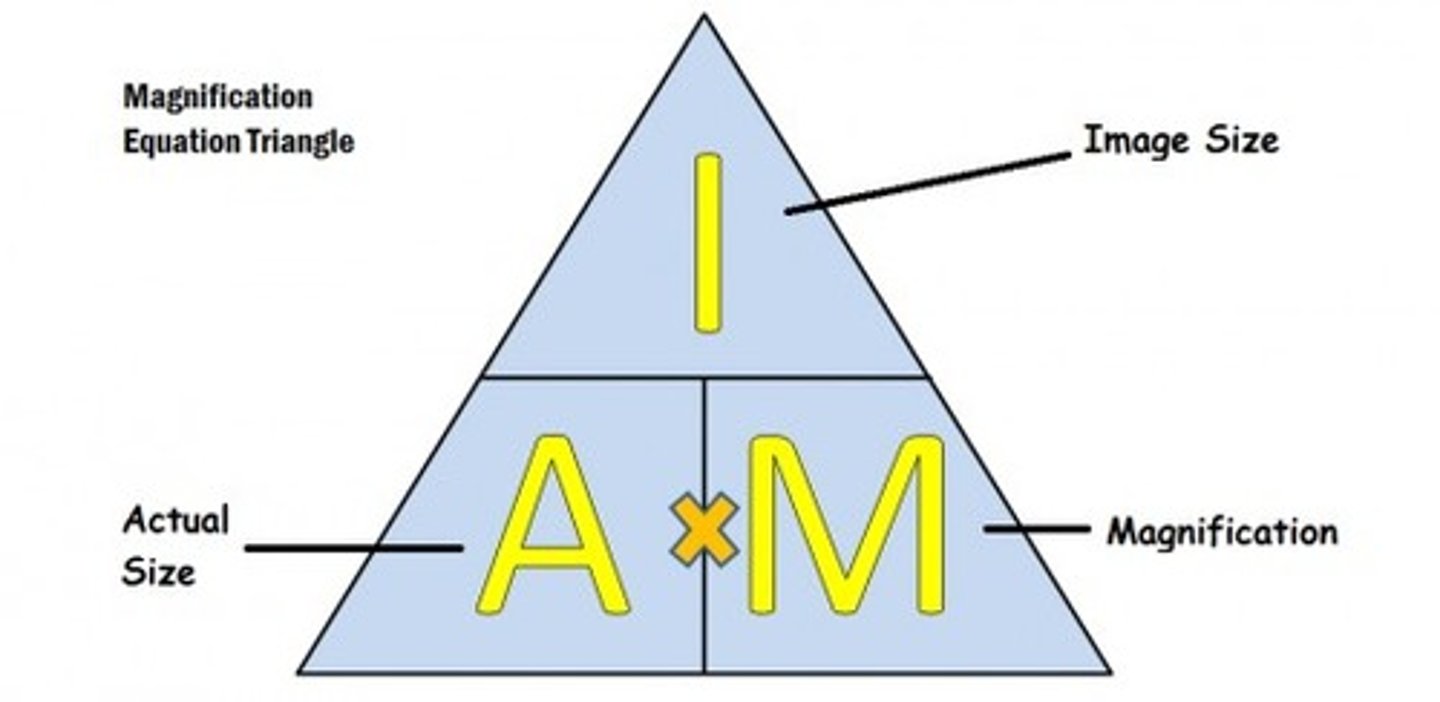
Magnification equation
-image size/object size
Specialised cells
-cells in plants in animals and plants that differentiate to form types of cells that are adapted to perform a particular function
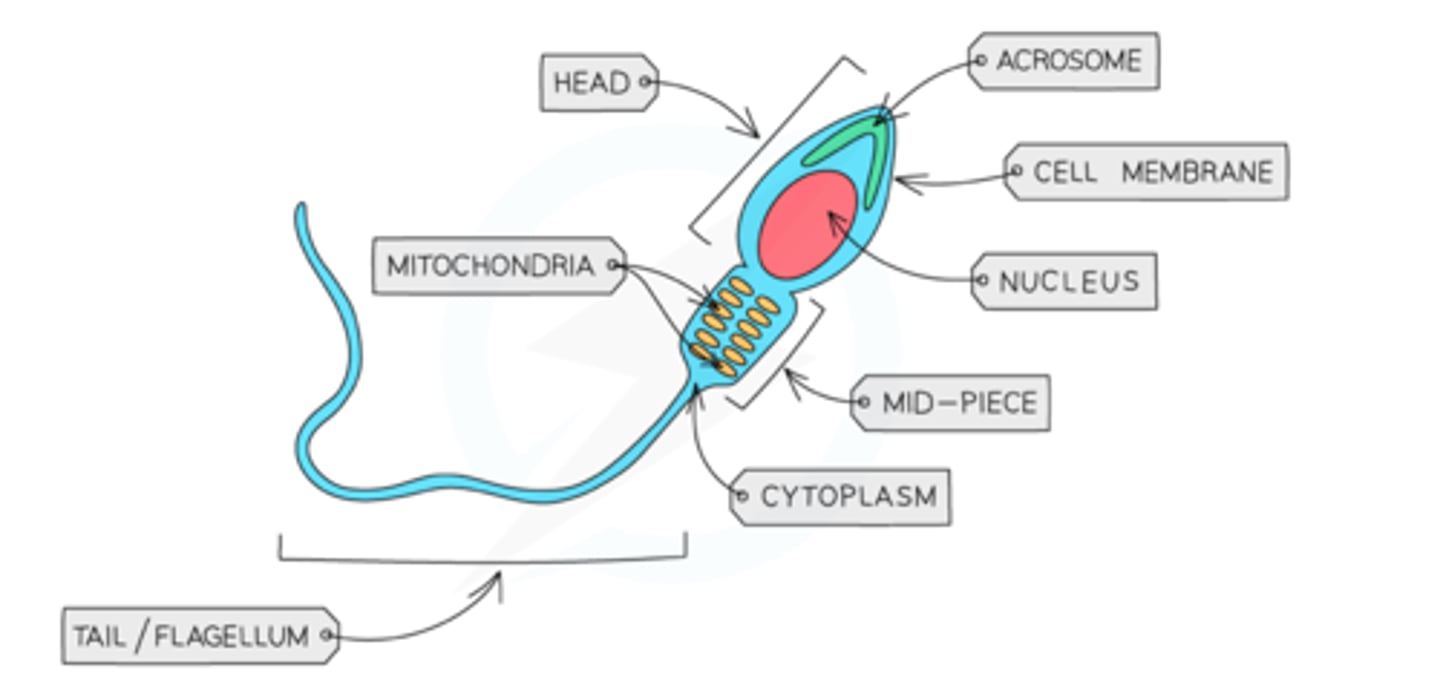
Sperm cell adaptation
-tail to swim to the ovum and fertilise it
-lots of mitochondria to release energy from respiration which enables the sperm to swim to the ovum
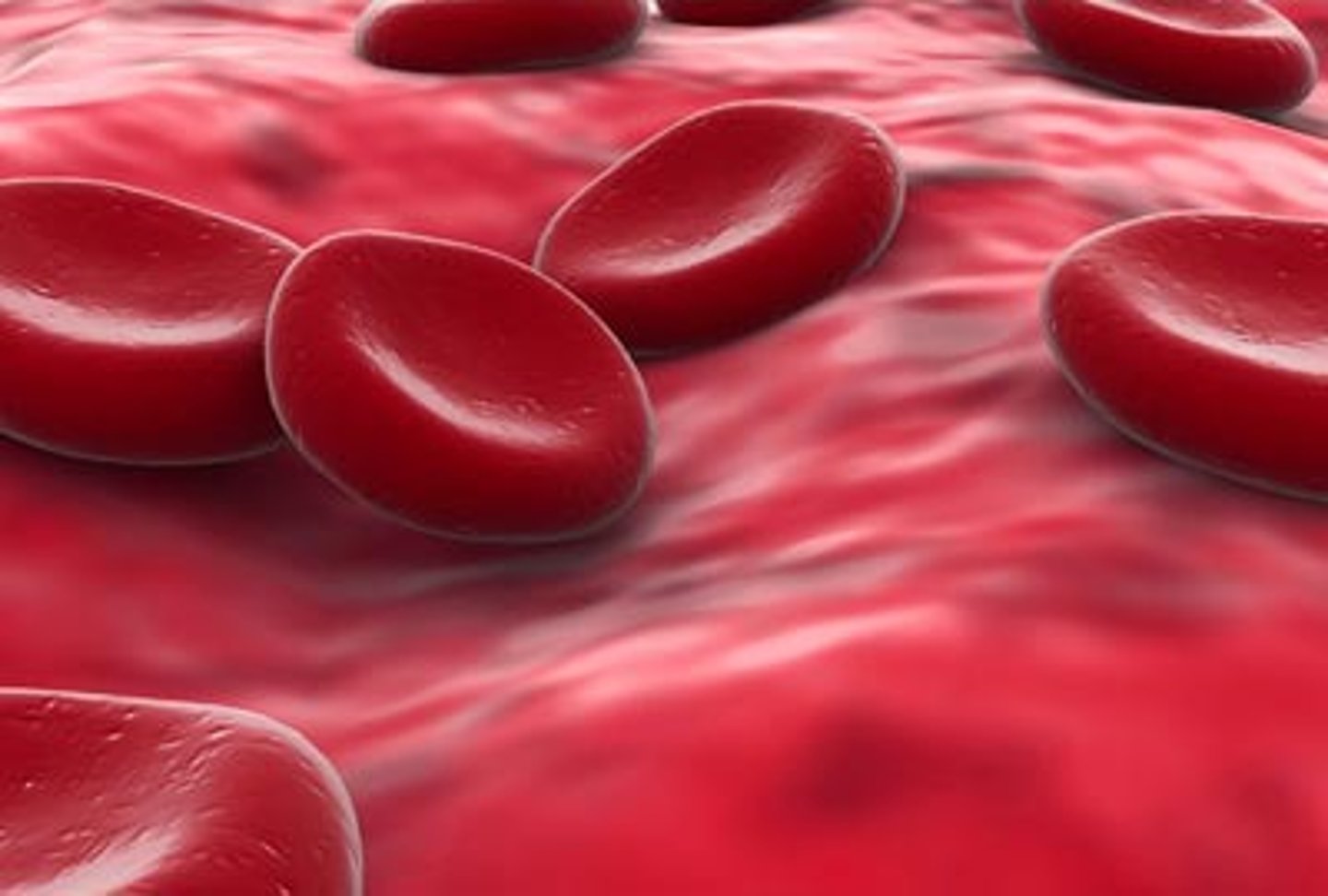
Red blood cell adaptation
-no nucleus so more room to carry oxygen
-contains a red pigment called haemoglobin to bind to oxygen molecules
-flt biconcave shape to increase surface area to volume ratio
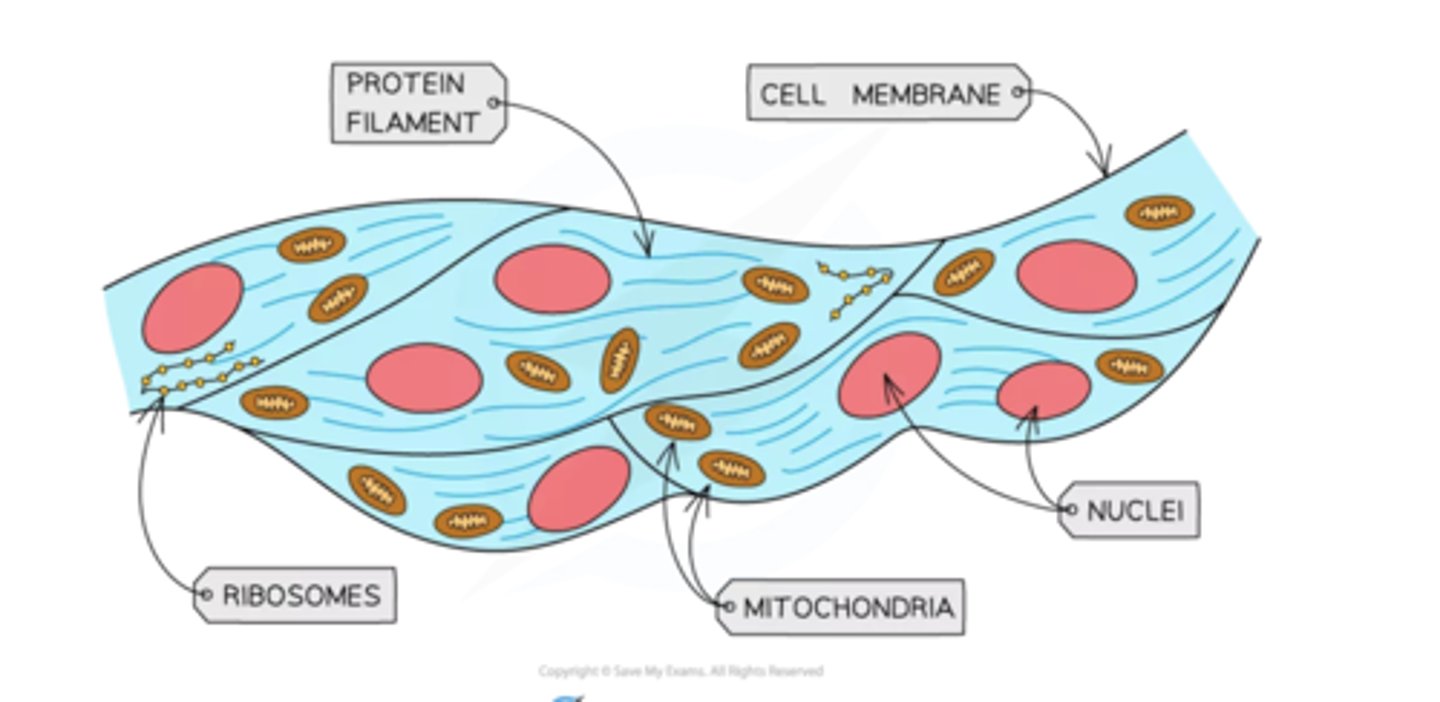
Muscle cell adaptation
-contains protein fibres which can contract to make the cell shorter
-contains lots of mitochondria to release energy from respiration allowing the muscle to contract
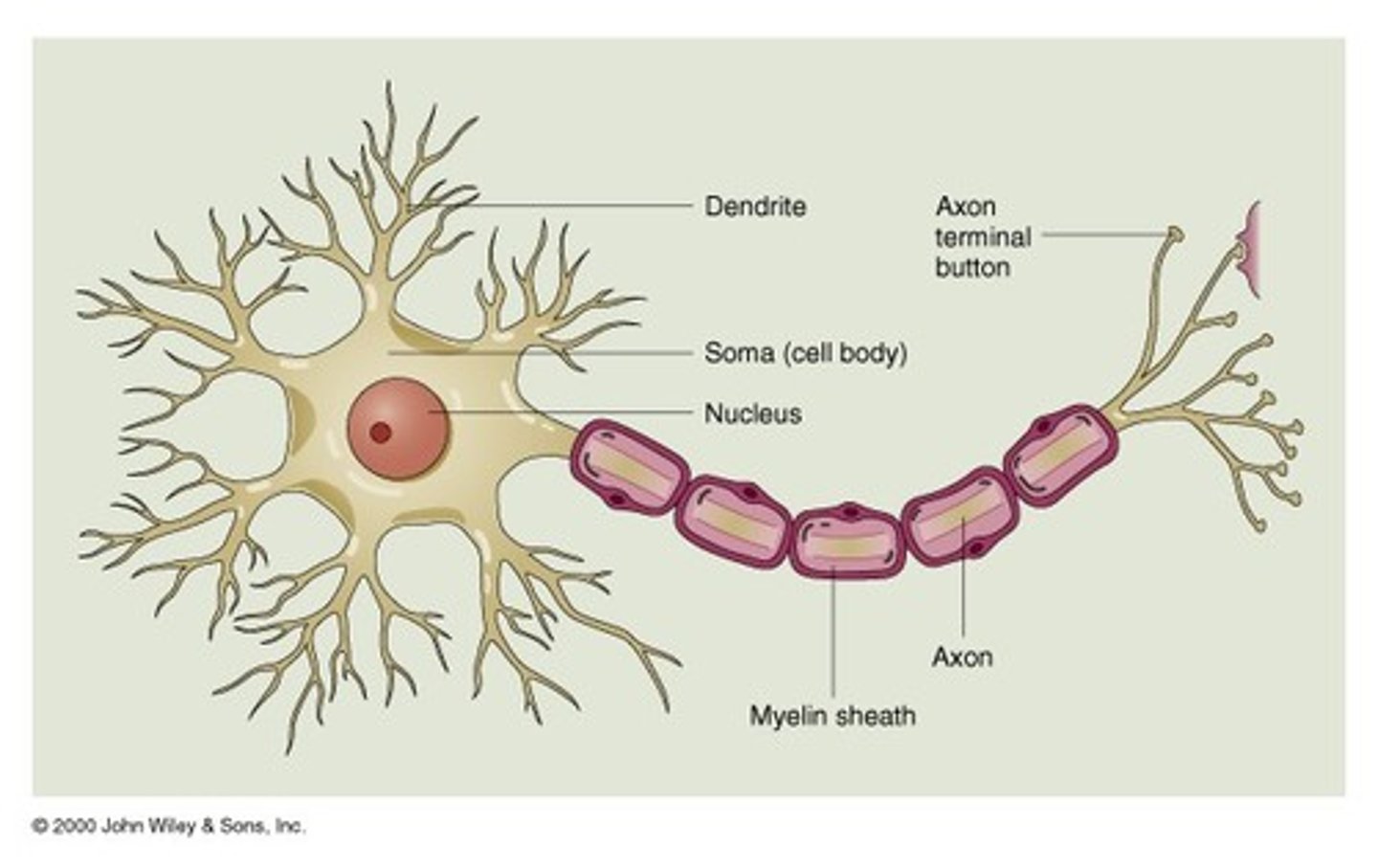
Nerve cell adaptation
-branched endings called dendrites to make connections with other neurones and effectors
-myelin sheath which insulates the axon in order to increase the transmission speed of electrical impulses
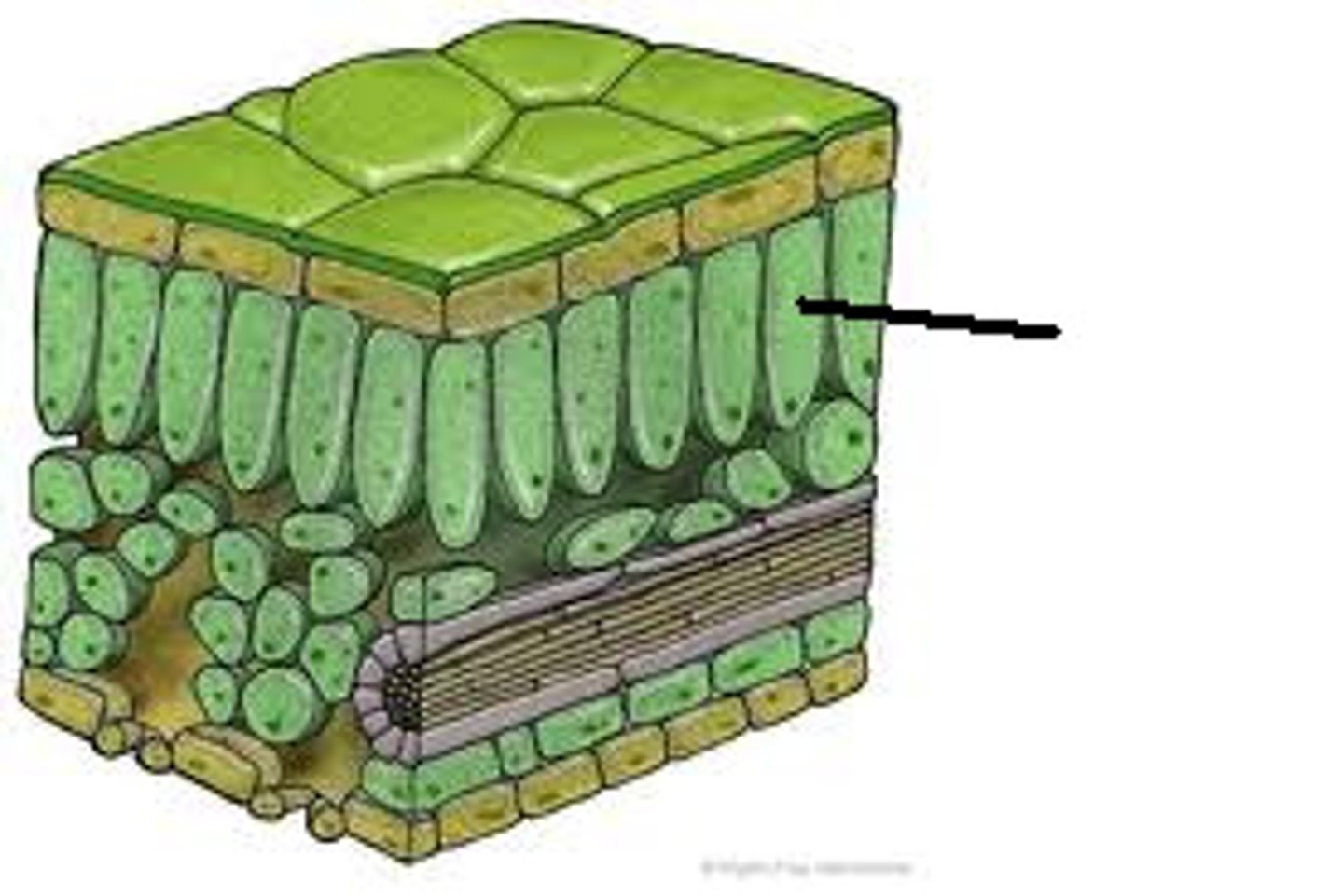
Palisade cell adaptations
-lots of chloroplasts containing chlorophyll to absorb light energy for photosynthesis
-located at the top surface of the leaf where it can absorb the most light energy
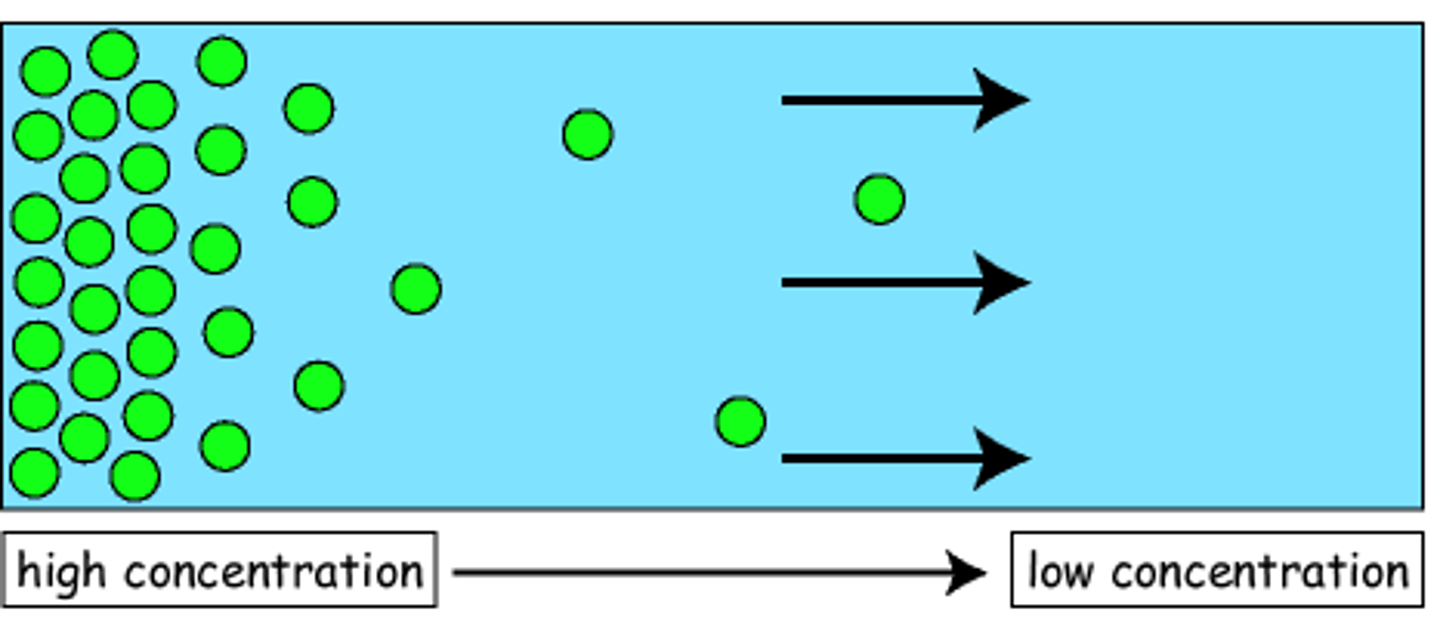
Diffusion
-the spreading out of particles resulting in a net movement from an area of high concentration to a low concentration
-particles move down the concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to a low concentration
-passive process meaning no energy is required
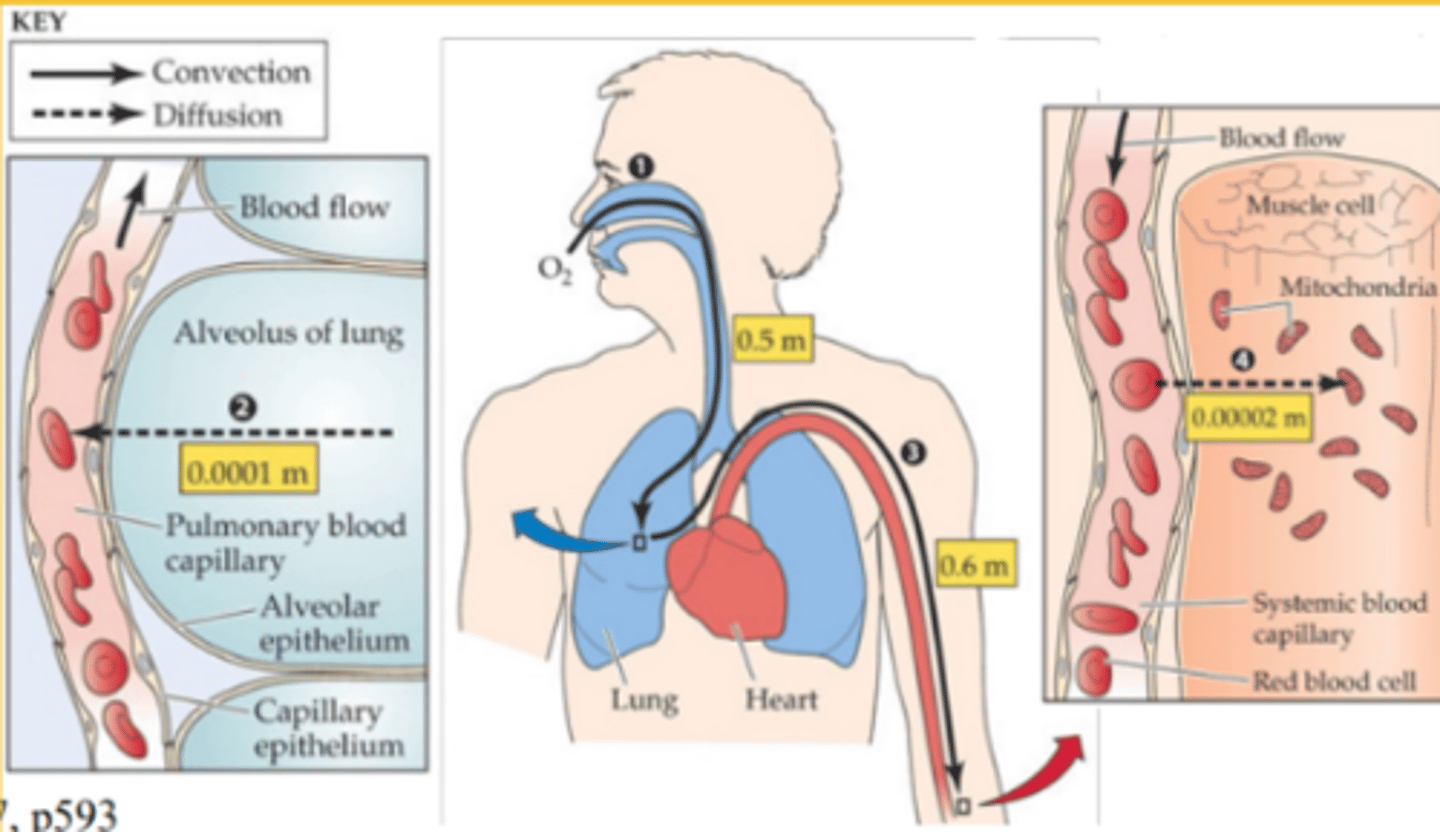
Diffusion in humans
-nutrients in the small intestine diffuse into the capillaries through the villi
-oxygen diffuses from the air in the alveoli into the blood in the capillaries and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood in the capillaries into the air in the alveoli
-urea diffuses from cells into the blood or excretion in the kidney
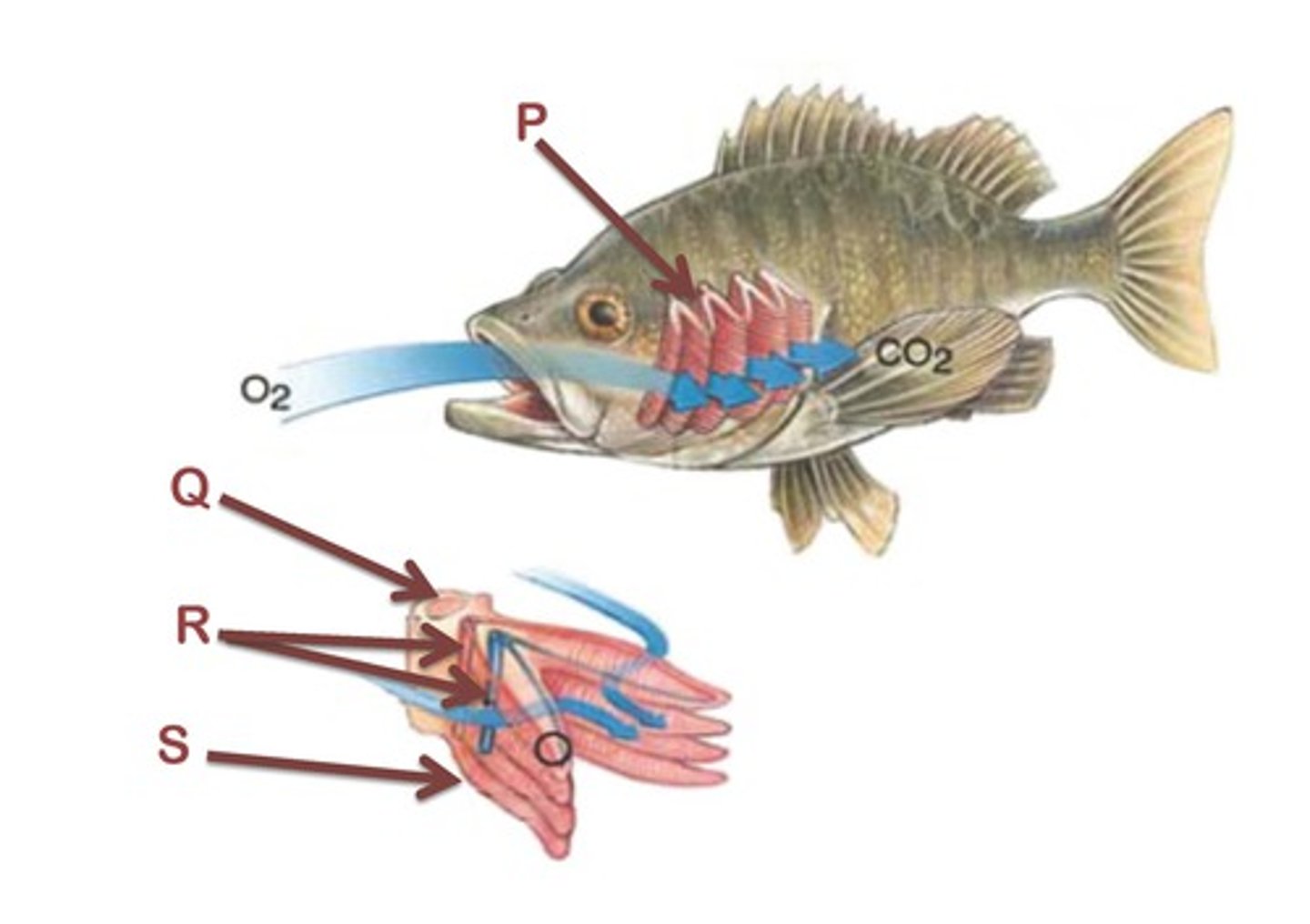
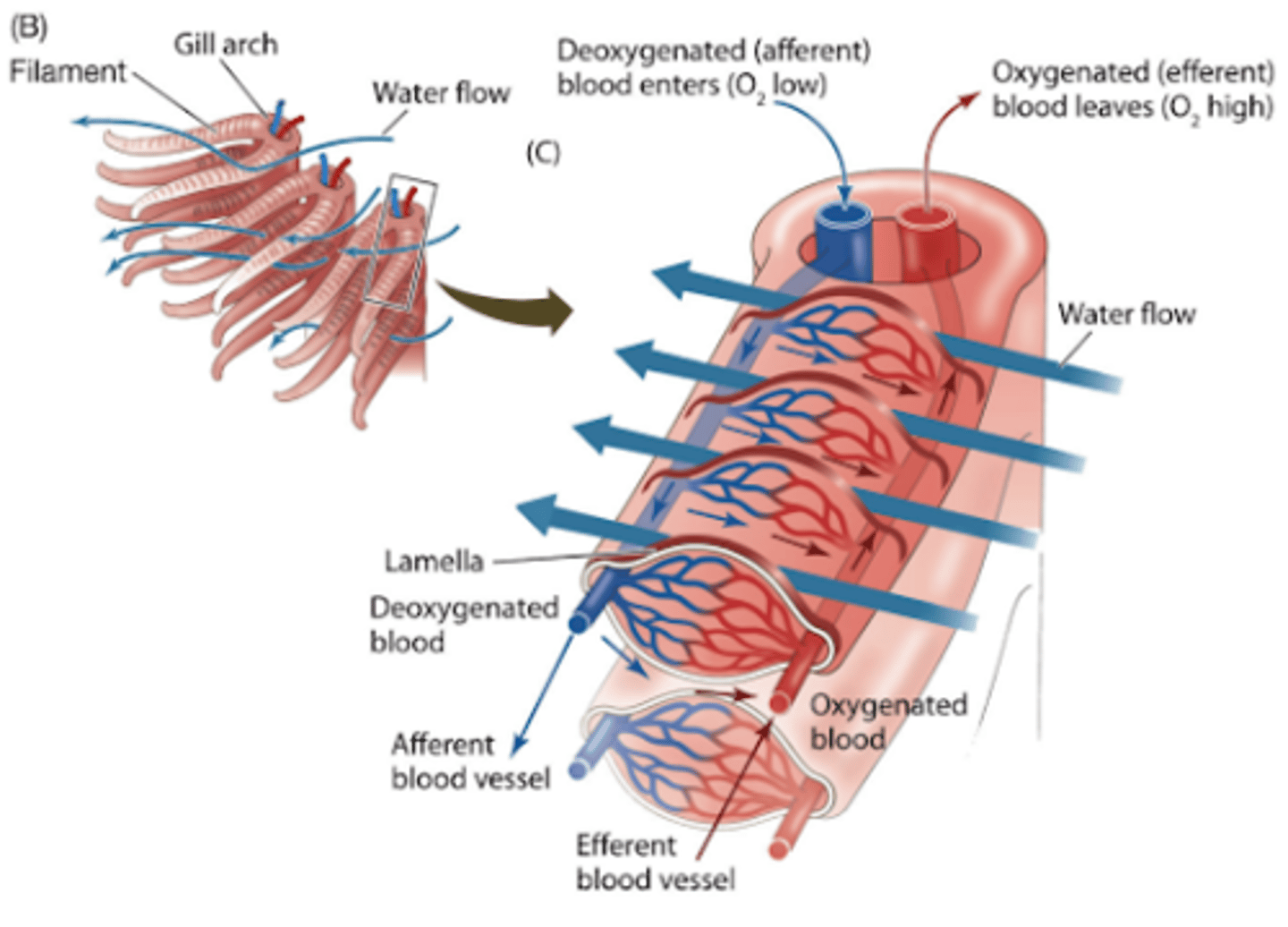
Diffusion in fish
-oxygen from water passing over the gills diffuse into the blood in the gill filaments
-carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood in the gill filaments into the water
Diffusion in plants
-carbon dioxide used for photosynthesis diffuses into leaves through the stomata
-oxygen produced during photosynthesis diffuses out of the leaves through the stomata
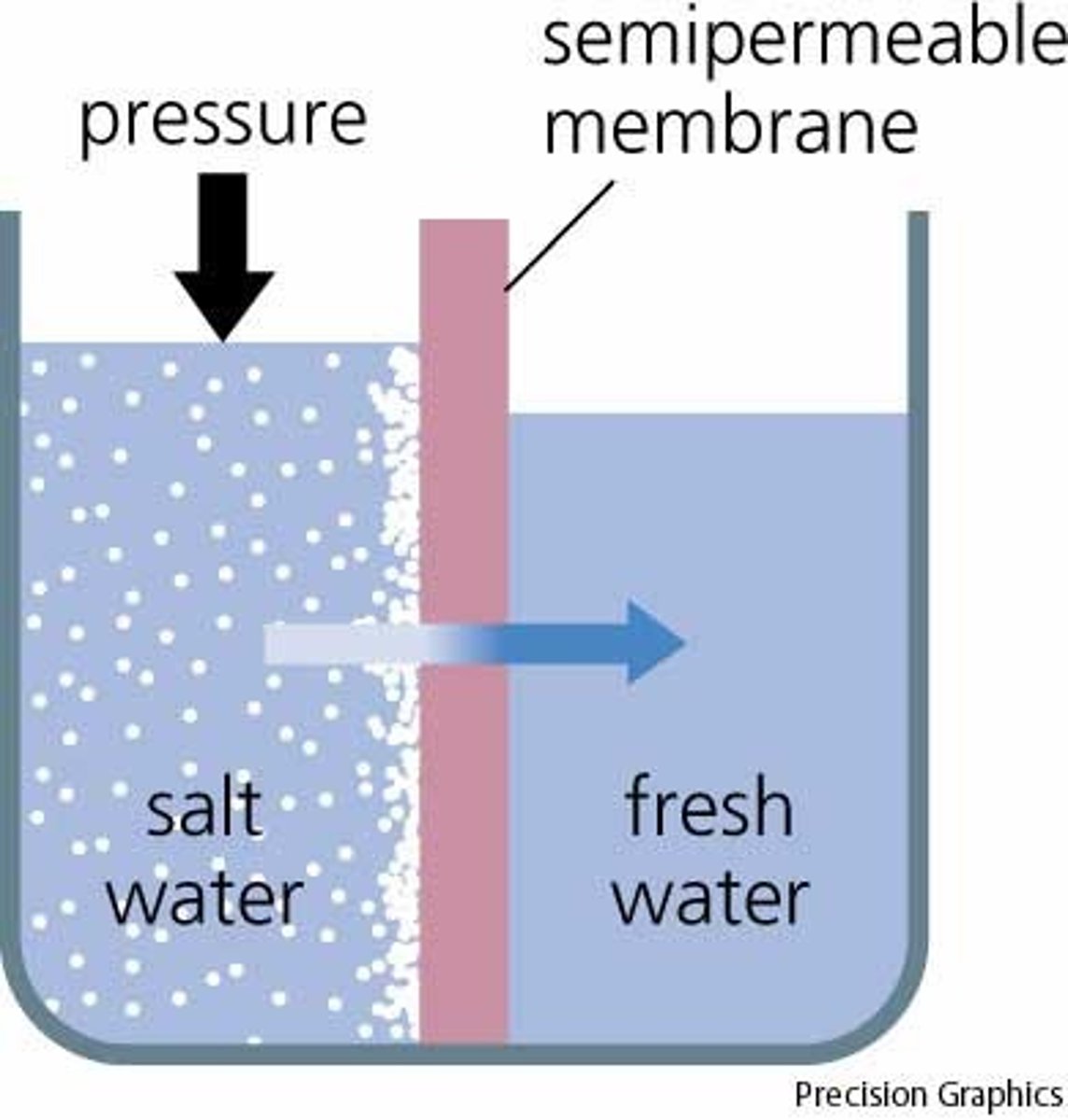
Osmosis
-the diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane
-water moves from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
-passive process meaning no energy is requited
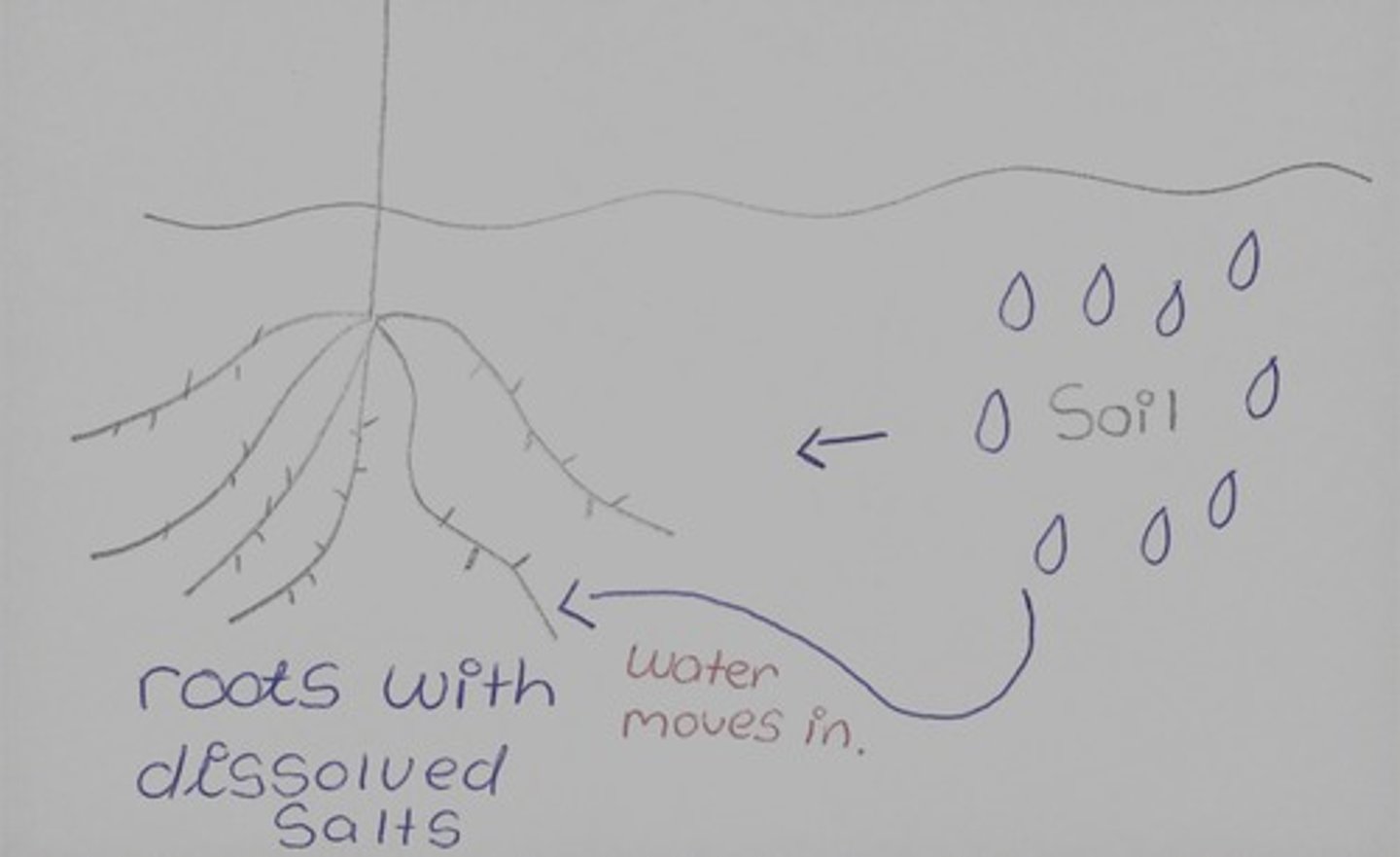
Osmosis in plants
-water moves by osmosis from a dilute solution in the soil to a concentrated solution in the root hair cell
Active transport
-particles move against the concentration gradient meaning they move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration
-not a passive process meaning energy is required
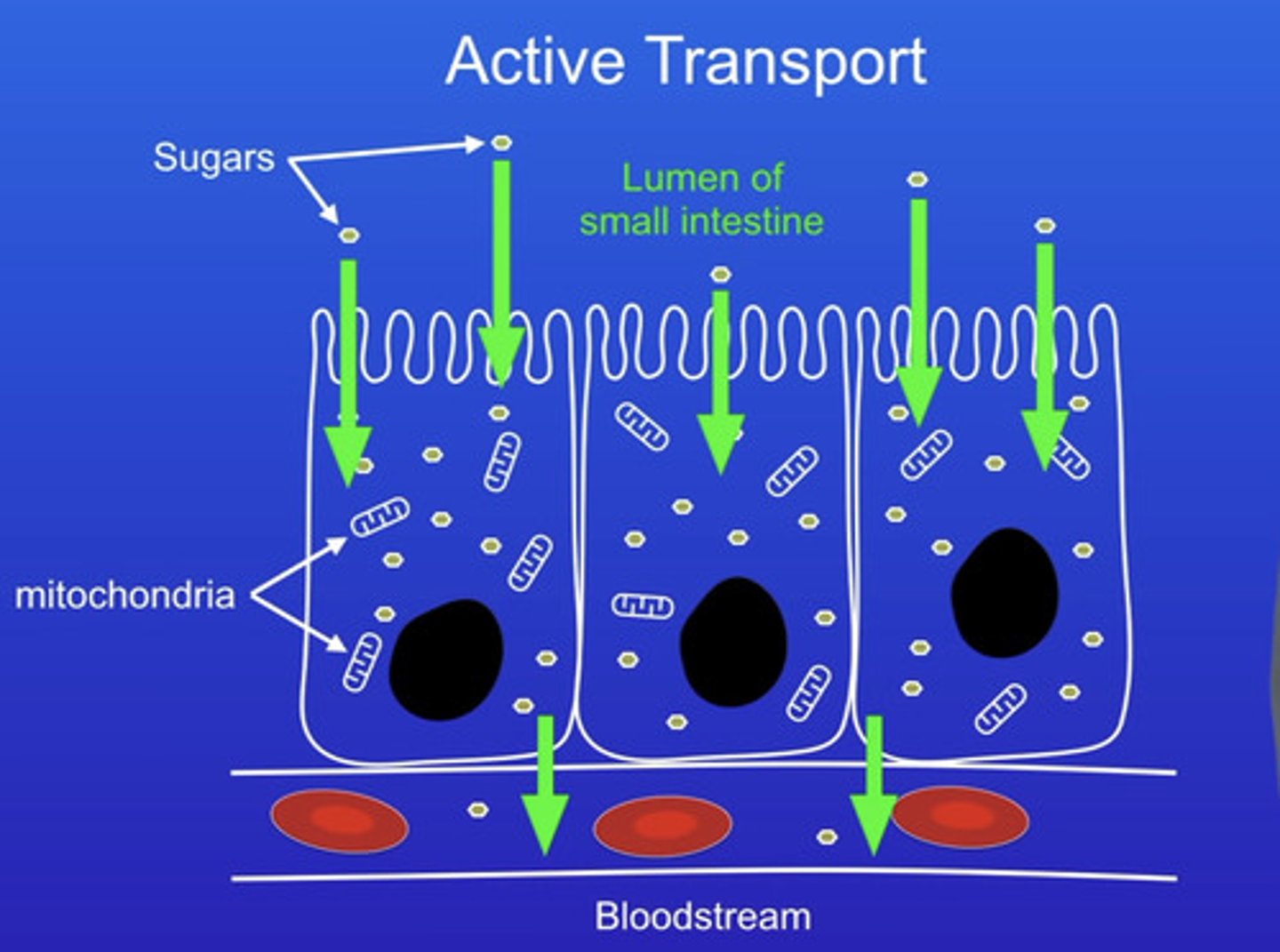
Active transport in humans
-active transport allows sugar molecules to be absorbed from the small intestine when the sugar concentration is higher in the blood than in the small intestine
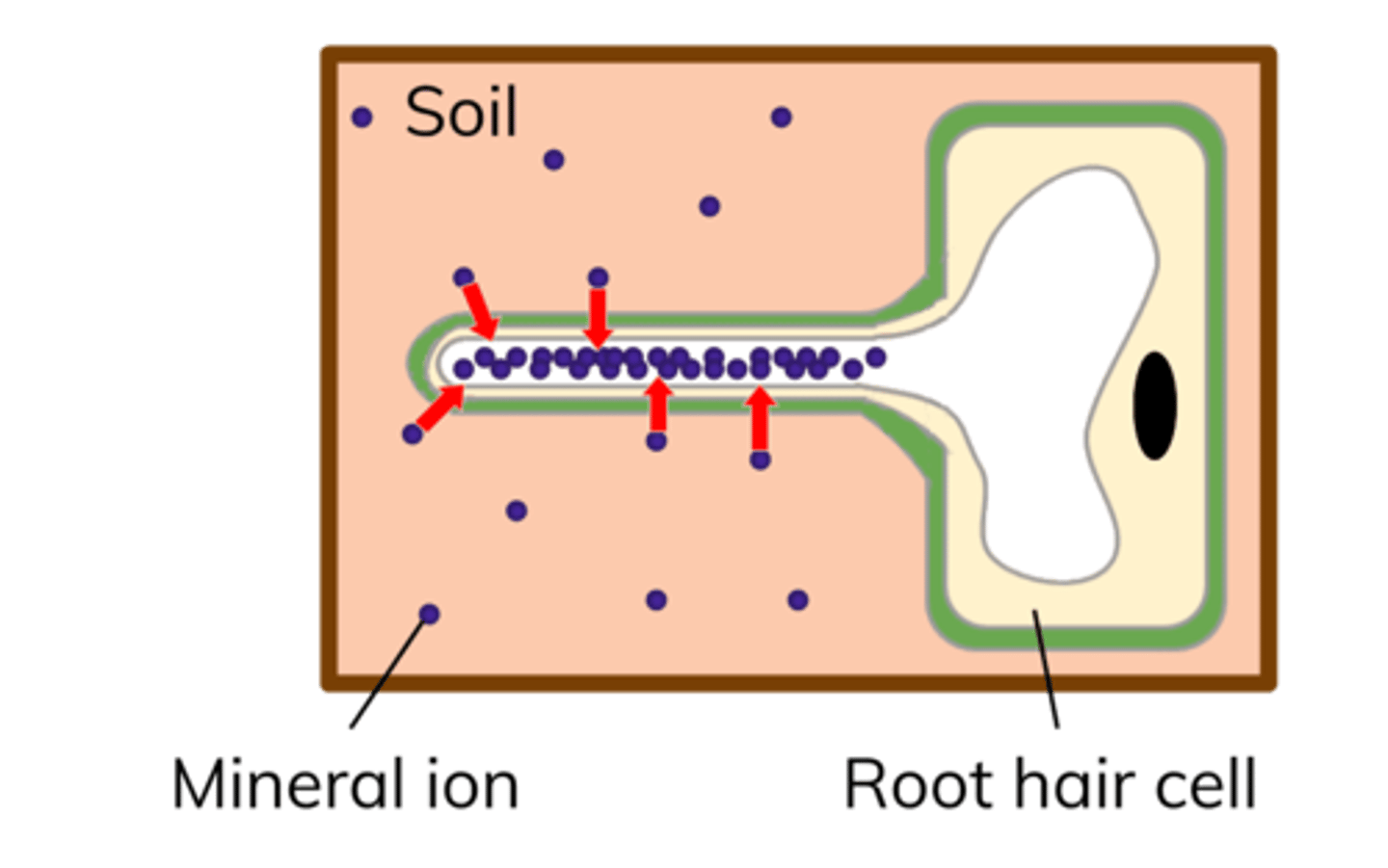
Active transport in plants
-used to absorb mineral ions into the root hair cells from more dilute solutions in the soil
Factors that affect the rate of diffusion
-the steeper the concentration gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion
-the higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion
-the larger the membrane surface area, the faster the rate of diffusion
Adaptation of villi in the small intestine for absorbing nutrients
-network of capillaries
-large surface area to volume ratio to ensure enough molecules can be transported across the cell membranes to meet the needs
-thin wall which is only cell thick allowing a short diffusion path
-good blood supply
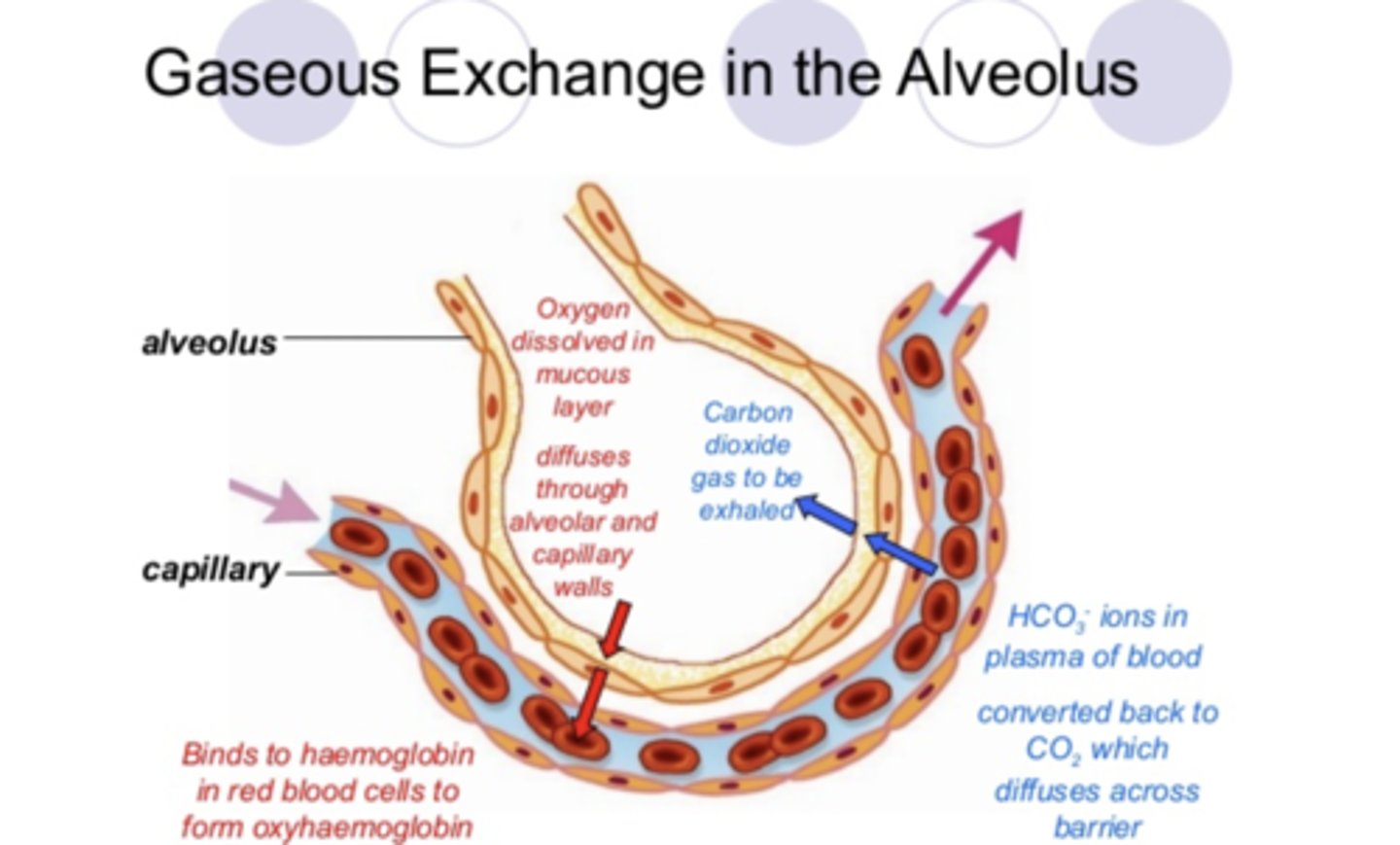
Adaptations of the alveoli in the lungs for gas exchange
-network of capillaries which provide a good blood supply
-the membrane in the alveoli has a large surface area and is one cell thick increasing the rate of diffusion and proving a short pathway for diffusion
Adaptations of fish gills for gas exchange
-made with stacks of thin filaments which have a large surface area and a network of capillaries providing a good blood supply that help increase the rate of diffusion
Adaptations of root hair cells for uptake of water and minerals
-lots of mitochondria for lots of energy to be released from respiration for active transport of mineral ions
-large surface area providing efficient absorption of water and minerals
The cell cycle
-body cells divide to form two identical daughter cells by going through a series of stages
-cell division by mitosis is important for growth and repair of cells
-mitosis is also used for asexual production
Stage 1 of the cell cycle
-cells grow bigger
-DNA replicates meaning chromosomes are duplicated
-increased number of subcellular structures such as ribosomes and mitochondria
Stage 2 of the cell cycle
-a complete set of chromosomes is pulled to each end of the cell
-the nucleus divides to form two nuclei
Stage 3 of the cell cycle
-cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to form two identical daughter cells
Stem cells in medicine
-a stem cell is an undifferentiated cell that can develop into one or more types of specialised cell
-the two types of stem cells in animals are adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells
-the stem cells in plants are plant meristem
-stem cells can be cloned to produce large numbers of identical cells
Adult stem cells
-found in specific parts of the body in adults and children such as bone marrow
-can only differentiate to form certain types of cells for example stem cells in bone marrow can only differentiate to form blood cells

Advantages of adult stem cells
-fewer ethical issues as adults can consent to have their stem cells removed and used
-established technique for treating diseases such as leukaemia
-relatively safe to use as treatment and donors recover quickly
Disadvantages of adult stem cells
-requires a donor potentially causing a long waiting time to find someone suitable
-can only differentiate into certain types of specialised cells so fewer disease can be treated
Embryonic stem cells
-found in early human embryos
-can differentiate into any type of specialised cell in the body
Advantages of embryonic stem cells
-can treat a wide range of diseases as they can differentiate into any type of specialised cell
-may be possible to grow whole replacement organs
-usually no donor is needed as they are obtained from spare embryos from fertility clinics
Disadvantages of embryonic stem cells
-ethical issues as the embryo is destroyed and each embryo is a potential human life
-risk of transferring viral infections to the patient
-newer treatment so it is relatively under researched meaning it is not yet clear if they can cure as many diseases as thought
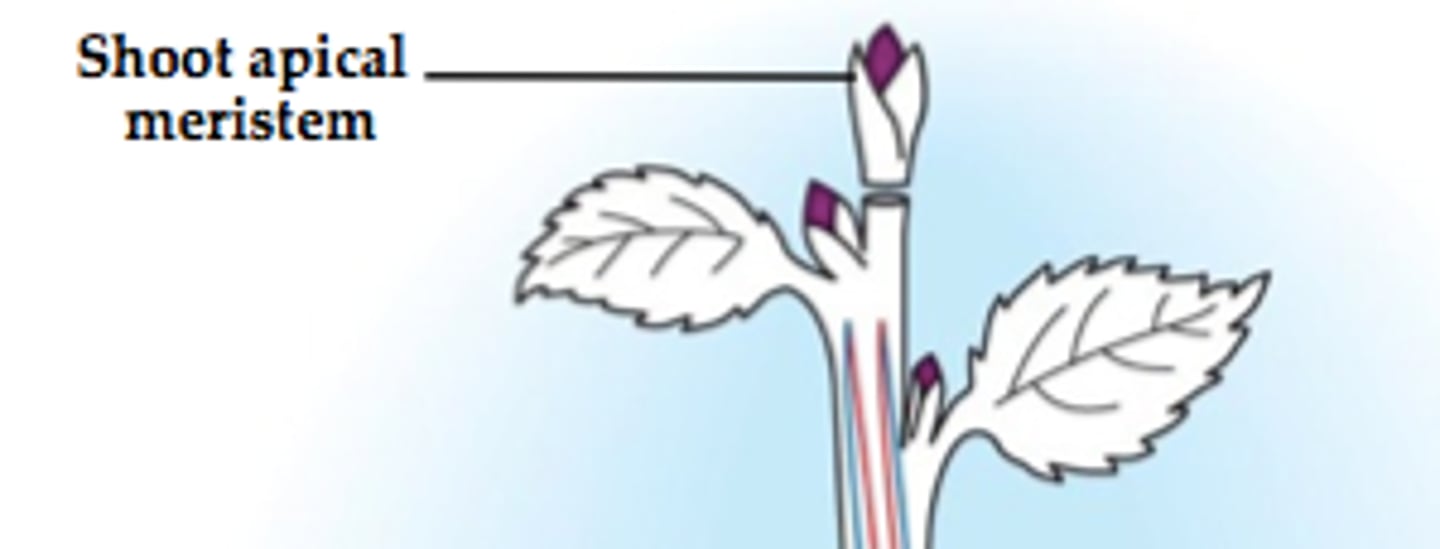
Plant meristem
-found in meristem regions in the roots and shoots of plants
-can differentiate into any type of cell and can be used to create whole clones of plants
Advantages of plant meristem
-rare species of plants can be cloned to prevent extinction
-plants with desirable characteristics such as disease resistance can be cloned t produce large numbers of identical plants
-fast and low cost production of a large number of plants
Disadvantages of plant meristem
-cloned plants are genetically identical so a whole crop is at risk of being destroyed by a single disease or genetic defect
Therapeutic cloning
-cells from a patient's body are used to create a cloned early embryo of themselves
-stem cells from this embryo can be used for medical treatments and growing new organs
-these stem cells have the same genes as the patient so they are less likely to be rejected when transplanted